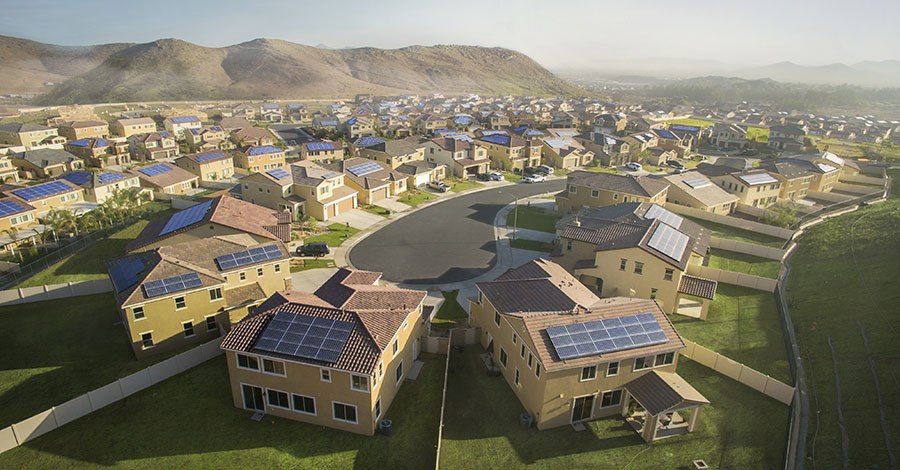
The recent merger of Tesla and SolarCity introduces a new era in residential solar energy generation. With the demand for solar energy in the U.S. rising each year, benefits to both our environment and the nation’s economy increase. The trend toward residential solar installations does require efficient planning and execution of public policies. It also calls for analysis of the status of residential solar in order to move toward an enhanced solar integration across the U.S.
What does residential solar look like today in the U.S.?
Residential solar today is primarily a coastal phenomenon, although more than half of the states have enough residential solar to power at least a few thousand homes. Yet, in the third quarter of 2016, the U.S. surpassed all previous quarterly solar photovoltaic (PV) installation records: 4,143 megawatts (MW), or a rate of one megawatt (MW) every 32 minutes. That pace is even faster today, as the fourth quarter will surpass this past quarter’s historic total, according to the Solar Energies Industry Association (SEIA).
“The solar market now enjoys an economically-winning hand that pays off both financially and environmentally, and American taxpayers have noticed,” Tom Kimbis, SEIA’s interim president, said of the recent rise in residential solar. “With a 90 percent favorability rating and 209,000 plus jobs, the U.S. solar industry has proven that when you combine smart policies with smart 21st century technology, consumers and businesses both benefit.”
Here are the top five U.S. states with residential solar rooftops in September, 2016:
- California: 3,258 MW
- Arizona: 539 MW
- New York: 444 MW
- New Jersey: 386 MW
- Massachusetts: 361 MW
These levels are considered ample to power a significant number of homes in their regions.
What’s the potential for other states to increase residential solar in the near future?
In order to power more than a few thousand homes and to become a major energy source across America, solar saturation must become deeper across existing states and more widespread among states that currently provide limited residential solar. Rooftops provide a large expanse of untapped area for solar energy generation, according to the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL). What’s needed to reduce costs and losses often associated with transmission and distribution of electricity? Onsite distributed generation, such as that which is available from SolarCity and others. Yet, to create a paradigm in which onsite distributed generation can become a reality, different and sometimes dissonant potentials must be addressed.
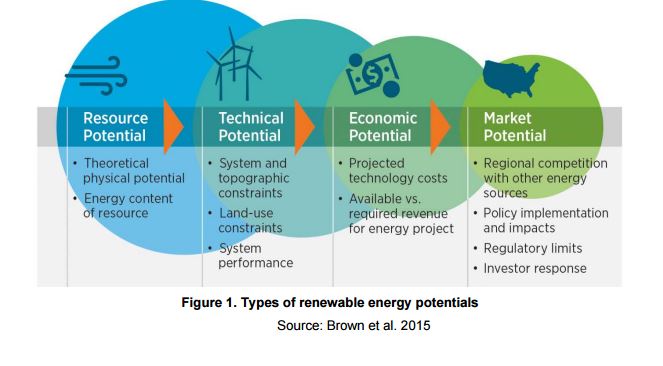 Technical potential considers multiple factors in a given region, such as resource availability and quality, technical system performance, and the physical availability of a suitable area for development. In other words, it measures how much of the total resource can actually be captured. It is often the only area of focus when residential solar is discussed.
Technical potential considers multiple factors in a given region, such as resource availability and quality, technical system performance, and the physical availability of a suitable area for development. In other words, it measures how much of the total resource can actually be captured. It is often the only area of focus when residential solar is discussed.
However, in order for solar to reduce pollution, help homeowners to lower utility bills and gain more energy independence, technical aspects of the larger solar equation must work in sync with resource, economic and market potential.
- Resource potential is the entire amount of energy in a particular form for the region;
- Economic potential is possible generation quantity that results as a positive return on the
investment of constructing the systems; and, - Market potential estimates the quantity of energy expected to be generated from the deployment of a technology into the market. It considers factors such as policies, competition with other technologies, and rate of adoption.
A study from the NREL indicates that, taking into account these four types of potential, there are broad regional trends in both the suitability and electric-generation possibilities of rooftops. Although only 26% of the total rooftop area on small buildings is suitable for PV deployment, the sheer number of buildings in this class gives small buildings the greatest technical potential.
What factors contribute to successful onsite distributed solar generation?
Small building rooftops could accommodate 731 GW of PV capacity and generate 926 TWh of PV energy annually, according to NREL, which represents approximately 65% of the total technical potential of rooftop PV. Think about how much energy could be generated by rooftop solar panels in each state if they were installed on all suitable roofs. Of course, the amount of suitable roof area, which takes into account factors such as shading, roof tilt, roof position, and roof size, must be included in any potential residential solar project planning.
The folks at SolarCity truly believe that, in every state, home rooftop solar could be a major energy resource. With research data backing their conclusions, they feel that U.S. total home solar capacity could increase 100 times over, and each state could meet 10-45% of its electricity needs from residential solar alone.
Add in roofs of medium and large buildings, and the solar integration number rises to 40 percent of all the electric demand in the continental U.S. By comparison, all rooftop solar today combined provides less than 0.5 percent of the nation’s electricity.
The potential for home rooftop solar to become a major energy source is enormous — in every state. And SolarCity argues that, the sooner that homes across the country become a part of that future, the more years they’ll have to enjoy its benefits.
Sources: Solar Energy Industries Association, National Renewable Energy Laboratory, SolarCity