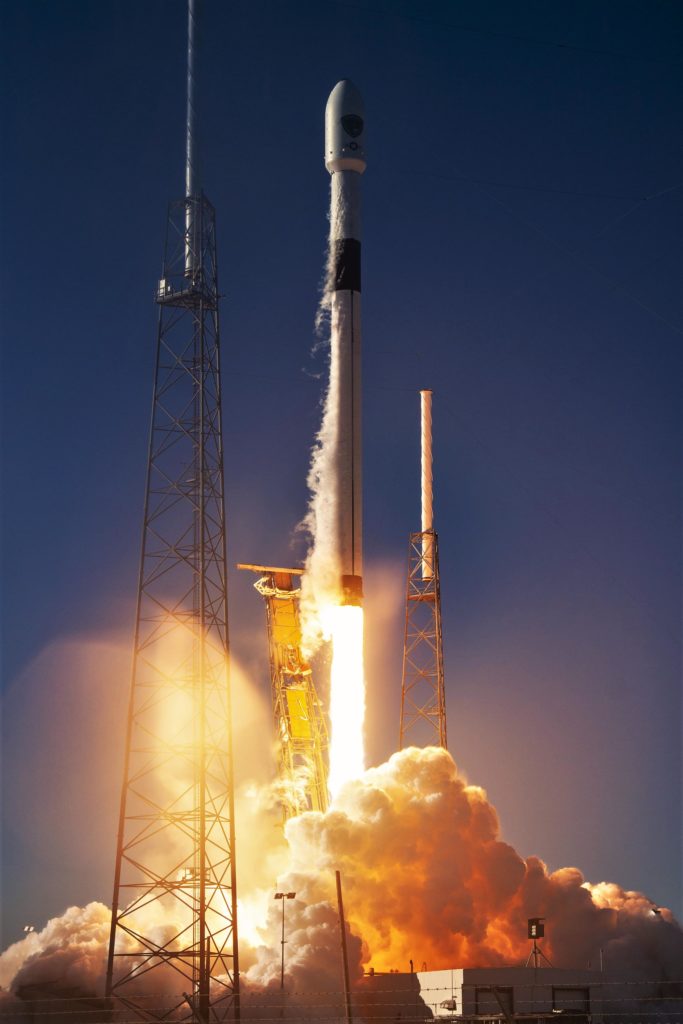
SpaceX
SpaceX CEO Elon Musk says that BFR could cost less to build than Falcon 9
SpaceX CEO Elon Musk believes that there may be a path for the company to ultimately build the massive Starship spacecraft and Super Heavy booster (formerly BFR) for less than Falcon 9/Falcon Heavy, a rocket 3-9 times smaller than BFR.
While it certainly ranks high on the list of wild and wacky things the CEO has said over the years, there may be a few ways – albeit with healthy qualifications – that Starship/Super Heavy production costs could ultimately compare favorably with SpaceX’s Falcon family of launch vehicles. Nevertheless, there are at least as many ways in which the next-gen rocket can (or should) never be able to beat the production cost of what is effectively a far simpler rocket.
This will sound implausible, but I think there’s a path to build Starship / Super Heavy for less than Falcon 9
— Elon Musk (@elonmusk) February 11, 2019
Dirty boosters done dirt cheap
On the one hand, Musk might not necessarily be wrong, especially if one throws the CEO several bones in the interpretation of his brief tweet. BFR at its simplest is going to require a full 38 main rocket engines to achieve its nominal performance goals, 7 on Starship and 31 on Super Heavy. As a dramatically more advanced, larger, and far more complex engine, Raptor will (with very little doubt) cost far more per engine than the relatively simple Merlin 1D. BFR avionics (flight computers, electronics, wiring, harnesses) are likely to be more of a known quantity, meaning that costs will probably be comparable or even lower than Falcon 9’s when measured as a proportion of overall vehicle cost. Assuming that BFR can use the exact same cold gas thruster assemblies currently flying on Falcon 9, that cost should only grow proportionally with vehicle size. Finally, Starship will not require a deployable payload fairing (~10% of Falcon 9’s production cost).
All of those things mean that Starship/Super Heavy will probably be starting off with far better cost efficiency than Falcon 9 was able to, thanks to almost a decade of interim experience both building, flying, and refurbishing the rocket since its 2010 debut. Still, BFR will have to account for entirely new structures like six large tripod fins/wings and their actuators, wholly new thrust structures (akin to Falcon 9’s octaweb) for both stages, and more. Considering Starship on its own, the production of a human-rated spacecraft capable of safely housing dozens of people in space for weeks or months will almost without a doubt rival the cost of airliner production, where a 737 – with almost half a century of production and flight heritage – still holds a price tag of $100-130+ million.
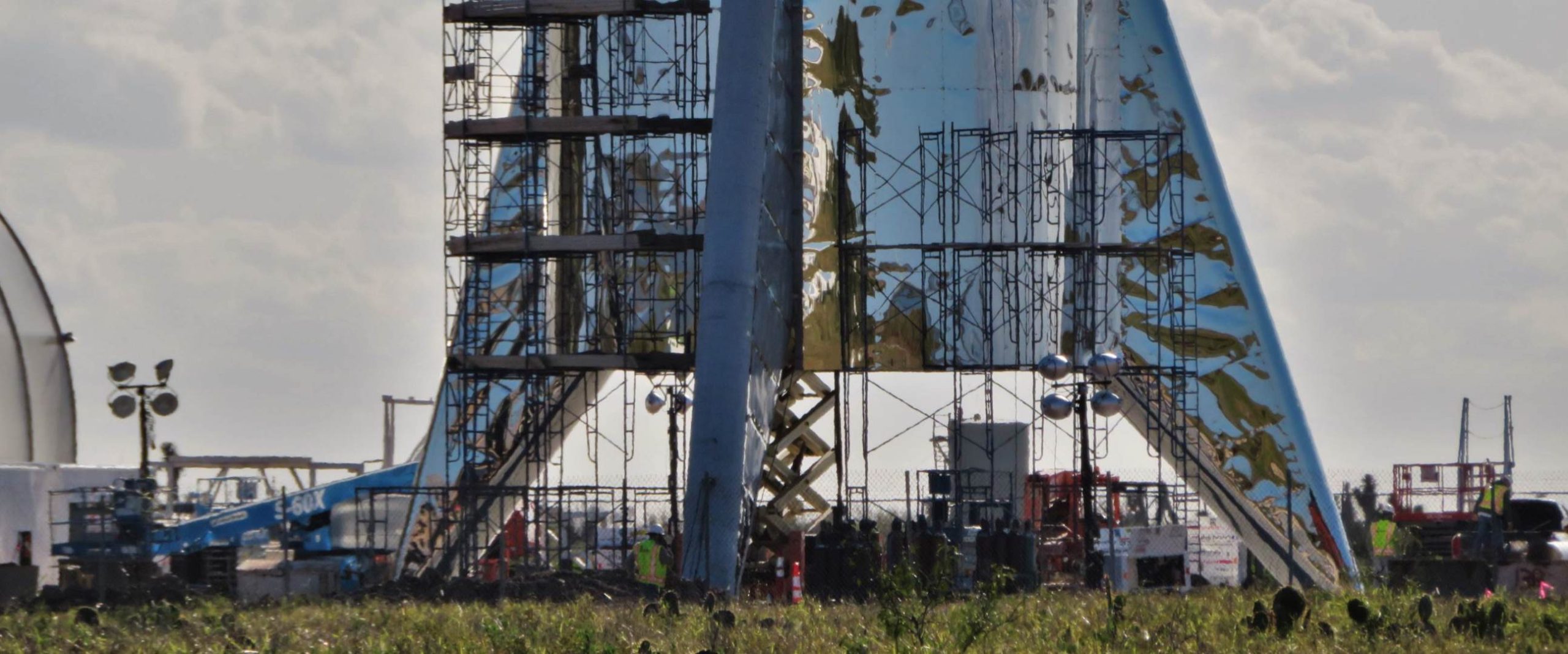
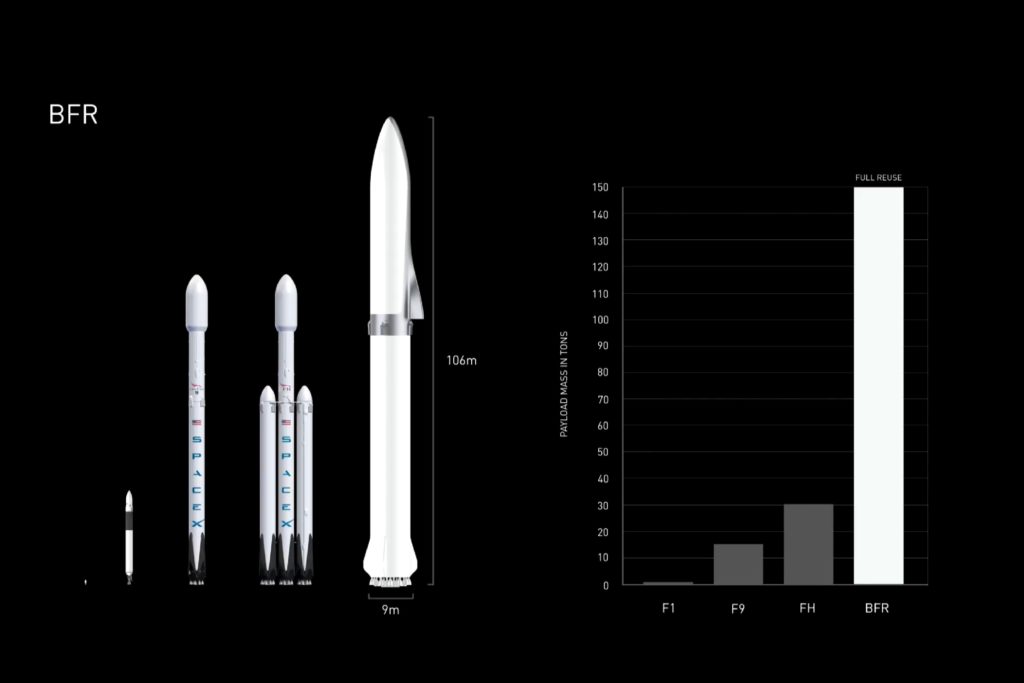
- BFR shown to scale with Falcon 1, 9, and Heavy. (SpaceX)
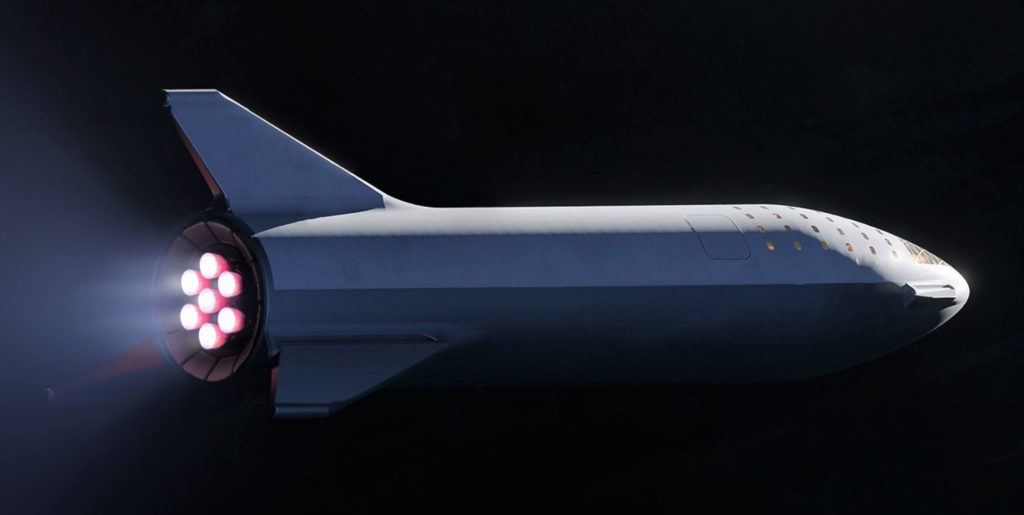
- A September 2018 render of Starship (then BFS) shows one of the vehicle’s two hinged wings/fins/legs. (SpaceX)
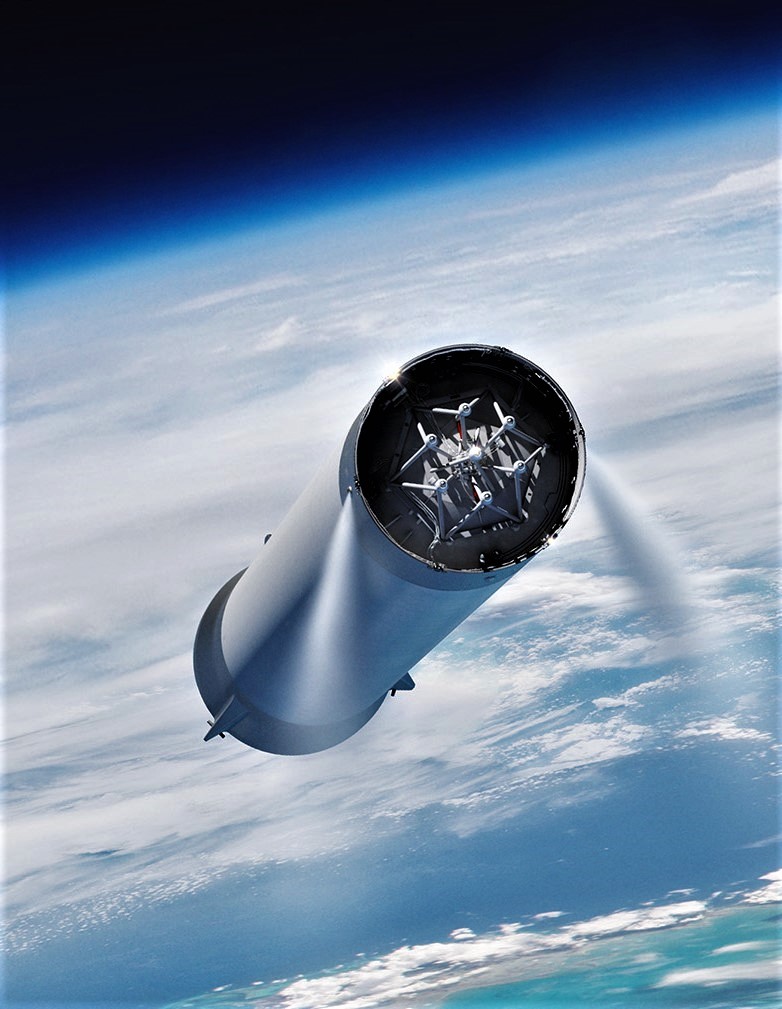
- BFR’s booster, now known as Super Heavy. (SpaceX)
- Sadly, this is a not a sight that will greet Falcon 9 booster B1046’s fourth launch – Crew Dragon’s critical In-Flight Abort test. (SpaceX)
Adding one more assumption, the most lenient interpretation of Musk’s tweet assumes that he is really only subjecting the overall structure (sans engines and any crew-relevant hardware) of BFR relative to Falcon 9. In other words, could a ~300-ton stainless steel rocket structure (BFR) cost the same amount or less to fabricate than a ~30-ton aluminum-lithium alloy rocket structure (Falcon 9/Heavy)? From the very roughest of numerical comparisons, Musk estimated the cost of the stainless steel alloys (300-series) to be used for BFR at around $3 per pound ($6.60/kg), while aluminum-lithium alloys used in aerospace (and on Falcon 9) are sold for around $20/lb ($44/kg)*. As such, simply buying the materials to build the basic structures of BFR and Falcon 9 would cost around and $7.5M and $5M, respectively.
Assuming that the process of assembling, welding, and integrating Starship and Super Heavy structures is somehow 5-10 times cheaper, easier, and less labor-intensive, it’s actually not inconceivable that the cost of building BFR’s structure could ultimately compete with Falcon 9 after production has stabilized after the new rocket’s prototyping phase is over and manufacturing processes are mature.
*Very rough estimate, difficult to find a public cost per unit mass from modern Al-Li suppliers

Costs vs. benefits
On the opposite hand, stainless steel rockets do not have a history of being uniquely cost-effective relative to vehicles using alternative materials. The only orbital-class launch vehicles to use stainless steel (and balloon) tanks are the Atlas booster and the Centaur upper stage, with Atlas dating back to the late 1950s and Centaur beginning launches in the early ’60s. Stainless steel Atlas launches ended in 2005 with the final Atlas III mission, while multiple forms of Centaur continue to fly regularly on ULA’s Atlas V and Delta IV.
Based on a 1966 contract between NASA and General Dynamics placed shortly after Centaur’s tortured development had largely been completed, Centaur upper stages were priced around $25M apiece (2018 USD). In 1980, the hardware for a dedicated Atlas-Centaur launch of a ~1500 kg Comstar I satellite to GTO cost the US the 2018 equivalent of a bit less than $40M ($71M including miscellaneous administrative costs) – $22.4M for Centaur and $17.6M for Atlas. For Atlas, the rocket’s airframe (tanks and general structure) was purchased for around $8.5M. That version of Atlas-Centaur (Atlas-SLV3D Centaur-D1A) was capable of lifting around 5100 kg (11,250 lb) into Low Earth Orbit (LEO) and 1800 kg (~4000 lb) to geostationary transfer orbit (GTO), while it stood around 40m (130 ft) tall, had a tank diameter of 3.05m (10 ft), and weighed ~150t (330,000 lb) fully fueled.
- Atlas shows off its shiny steel balloon tanks. (SDASM)
- The original space-faring Atlas, known as SM-65, seen here with a Mercury space capsule. (NASA)
- A Centaur upper stage is pictured here in 1964. (NASA)
- Atlas SLV3D is pictured here launching a Comstar I satellite.
- A Falcon 9 booster is seen here near the end of its tank welding, just prior to painting. (SpaceX)
- An overview of SpaceX’s Hawthorne factory floor in early 2018. (SpaceX)
In a very loose sense, that particular stainless steel Atlas variant was about half as large and half as capable as the first flight-worthy version of Falcon 9 at roughly the same price at launch ($60-70M). What does this jaunt through the history books tell us about the prospects of a stainless steel Starship and Super Heavy? Well, not much. The problem with trying to understand and pick apart official claims about SpaceX’s next-generation launch architecture is quite simple: only one family of rockets in the history of the industry (Atlas) regularly flew with stainless steel propellant tanks, a half-century lineage that completed its final launch in 2005.
Generally speaking, an industrial sample size of more or less one makes it far from easy to come to any particular conclusions about a given technology or practice, and SpaceX – according to CEO Elon Musk – fully intends to push past the state of the art of stainless steel rocket tankage with BFR. Ultimately, American Marietta/Martin Marietta/Lockheed Martin was never able to produce launch vehicle variants of the stainless steel Atlas family at a cost more than marginally competitive with Falcon 9, despite the latter rocket’s use of a far more expensive metal alloy throughout its primary tanks and structure.
At least 10X cheaper
— Elon Musk (@elonmusk) February 11, 2019
At some point, it’s even worth asking whether the per-unit cost of Starship and Super Heavy should be relevant at all to their design and construction, at least within reason. If the goal of BFR is to drastically lower the cost of launch by radically improving the ease of reuse, it would be truly bizarre (and utterly unintuitive) if those goals could somehow be achieved without dramatically raising the cost of initial hardware procurement. Perhaps the best close comparison to BFR’s goals, modern airliners are eyewateringly expensive ($100-500M apiece) as a consequence of the extraordinary reliability, performance, efficiency, and longevity customers and regulatory agencies demand from them, although those costs are admittedly not the absolute lowest they could be in a perfect manufacturing scenario.
At the end of the day, it appears that Musk is increasingly of the opinion that the pivot to stainless steel could ultimately make BFR simultaneously “better, faster, [&] cheaper”. However improbable that may be, if it does turn out to be the case, Starship and Super Heavy could be an unfathomable leap ahead for reliable and affordable access to space. It could also be another case of Musk’s excitement and optimism getting the better of him and hyping a given product well beyond what it ultimately is able to achieve. Time will tell!
Check out Teslarati’s newsletters for prompt updates, on-the-ground perspectives, and unique glimpses of SpaceX’s rocket launch and recovery processes!

Elon Musk
SpaceX secures win as US labor board drops oversight case
The NLRB confirmed that it no longer has jurisdiction over SpaceX.

SpaceX scored a legal victory after the National Labor Relations Board (NLRB) decided to dismiss a case which accused the company of terminating engineers who were involved in an open letter against founder Elon Musk.
The NLRB confirmed that it no longer has jurisdiction over SpaceX. The update was initially shared by Bloomberg News, which cited a letter about the matter it reportedly reviewed.
In a letter to the former employees’ lawyers, the labor board stated that the affected employees were under the jurisdiction of the National Mediation Board (NMB), not the NLRB. As a result, the labor board stated that it was dismissing the case.
As per Danielle Pierce, a regional director of the agency, “the National Labor Relations Board lacks jurisdiction over the Employer and, therefore, I am dismissing your charge.”
The NMB typically oversees airlines and railroads. The NLRB, on the other hand, covers most private-sector employers, as well as manufacturers such as Boeing.
The former SpaceX engineers have argued that the private space company did not belong under the NMB’s jurisdiction because SpaceX only offers services to “hand-picked customers.”
In an opinion, however, the NMB stated that SpaceX was under its jurisdiction because “space transport includes air travel” to get to outer space. The mediation board also noted that anyone can contact SpaceX to secure its services.
SpaceX had previously challenged the NLRB’s authority in court, arguing that the agency’s structure was unconstitutional. Jennifer Abruzzo, the NLRB general counsel under former United States President Joe Biden, rejected SpaceX’s claims. Following Abruzzo’s termination under the Trump administration, however, SpaceX asked the labor board to reconsider its arguments.
SpaceX is not the only company that has challenged the constitutionality of the NLRB. Since SpaceX filed its legal challenge against the agency in 2024, other high-profile companies have followed suit. These include Amazon, which has filed similar cases that are now pending.
Elon Musk
SpaceX blocks unauthorized Starlink terminals used by Russian troops
Ukrainian officials confirmed that Starlink terminals believed to be used by Russian troops were disabled after coordination with SpaceX.

SpaceX has taken steps to block unauthorized use of its Starlink satellite internet network, a move Ukrainian officials stated is already disrupting Russian military communications.
Russian units lose a key communications tool
As per a report from The Guardian, Ukrainian defense officials have confirmed that Starlink terminals believed to be used by Russian troops were recently disabled after coordination with SpaceX. The move reportedly affected frontline communications and drone operations, especially in areas where traditional military radios are unreliable or easily jammed.
For months, Russian units had relied on large numbers of illicitly obtained Starlink terminals to stay connected along the front. The satellite internet service allowed faster coordination and more precise drone use for Russian forces.
Several Russian military bloggers close to frontline units have acknowledged the impact of the Starlink shutdown, with some describing sudden connectivity problems in the satellite internet service.
Russia lacks comparable replacement
Russia does not have a satellite internet system that matches Starlink’s speed, coverage, and ease of deployment. Alternatives such as fiber-optic lines, short-range wireless links, and digital radio systems take longer to install and work inadequately for fast-moving units.
Russia does operate limited satellite communications through state-linked providers, but those systems rely mainly on geostationary satellites, which are notably slower. Coverage is uneven, and data capacity is far lower than Starlink’s low-Earth-orbit network.
For now, Ukraine has stated that it has introduced a verification system that allows only approved Starlink terminals to connect. Devices believed to be linked to Russian forces are blocked from the network. That being said, Ukrainian officials have also claimed Russian units are trying to work around the restrictions by asking civilians to register Starlink terminals in their names.
Elon Musk
Elon Musk pivots SpaceX plans to Moon base before Mars
The shift, Musk explained, is driven by launch cadence and the urgency of securing humanity’s long-term survival beyond Earth, among others.

Elon Musk has clarified that SpaceX is prioritizing the Moon over Mars as the fastest path to establishing a self-growing off-world civilization.
The shift, Musk explained, is driven by launch cadence and the urgency of securing humanity’s long-term survival beyond Earth, among others.
Why the Moon is now SpaceX’s priority
In a series of posts on X, Elon Musk stated that SpaceX is focusing on building a self-growing city on the Moon because it can be achieved significantly faster than a comparable settlement on Mars. As per Musk, a Moon city could possibly be completed in under 10 years, while a similar settlement on Mars would likely require more than 20.
“For those unaware, SpaceX has already shifted focus to building a self-growing city on the Moon, as we can potentially achieve that in less than 10 years, whereas Mars would take 20+ years. The mission of SpaceX remains the same: extend consciousness and life as we know it to the stars,” Musk wrote in a post on X.
Musk highlighted that launch windows to Mars only open roughly every 26 months, with a six-month transit time, whereas missions to the Moon can launch approximately every 10 days and arrive in about two days. That difference, Musk stated, allows SpaceX to iterate far more rapidly on infrastructure, logistics, and survival systems.
“The critical path to a self-growing Moon city is faster,” Musk noted in a follow-up post.
Mars still matters, but runs in parallel
Despite the pivot to the Moon, Musk stressed that SpaceX has not abandoned Mars. Instead, Mars development is expected to begin in about five to seven years and proceed alongside the company’s lunar efforts.
Musk explained that SpaceX would continue launching directly from Earth to Mars when possible, rather than routing missions through the Moon, citing limited fuel availability on the lunar surface. The Moon’s role, he stated, is not as a staging point for Mars, but as the fastest achievable location for a self-sustaining off-world civilization.
“The Moon would establish a foothold beyond Earth quickly, to protect life against risk of a natural or manmade disaster on Earth,” Musk wrote.