SpaceX
SpaceX reveals details on Falcon Heavy landing pad and Dragon facility, in new report
A draft environmental impact report by SpaceX and the 45th Space Wing at Patrick Air Force Base, Florida has been recently released for public review on the environmental section of the Patrick AFB website. The report contains details on proposed new rocket landing pads, the expected sonic boom activity from the planned rocket landings, and information about a proposed Dragon capsule processing facility. The report was originally completed in December 2016.
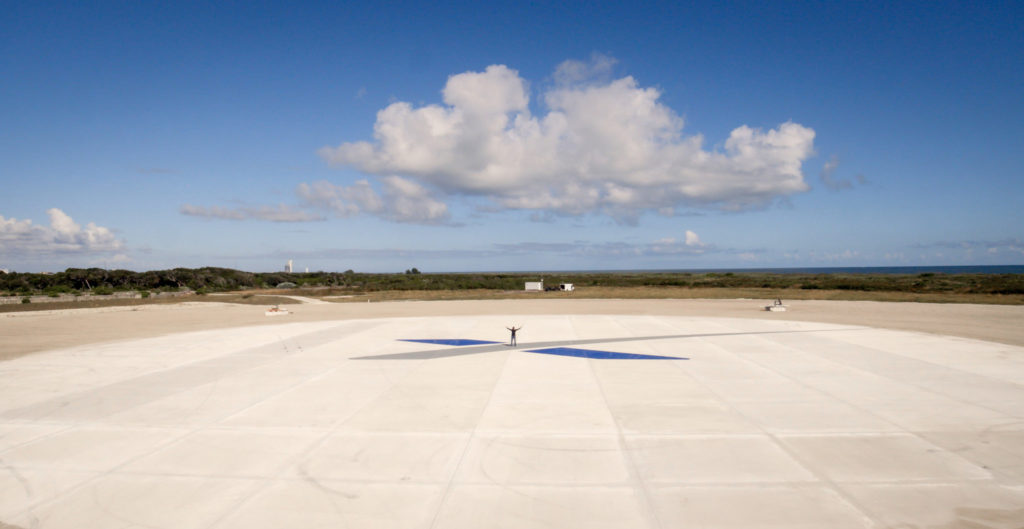
One of the most ambitious goals of SpaceX’s Falcon Heavy rocket is the triple landing of two first stage boosters and center core onto ground. All three parts together comprise twenty-seven Merlin rocket engines and generate 5.13 million pounds of thrust at liftoff. Each of the first stage boosters is equivalent to the first stage of a Falcon 9 rocket, the landings for which have been successful four times out of the give most recent attempts.

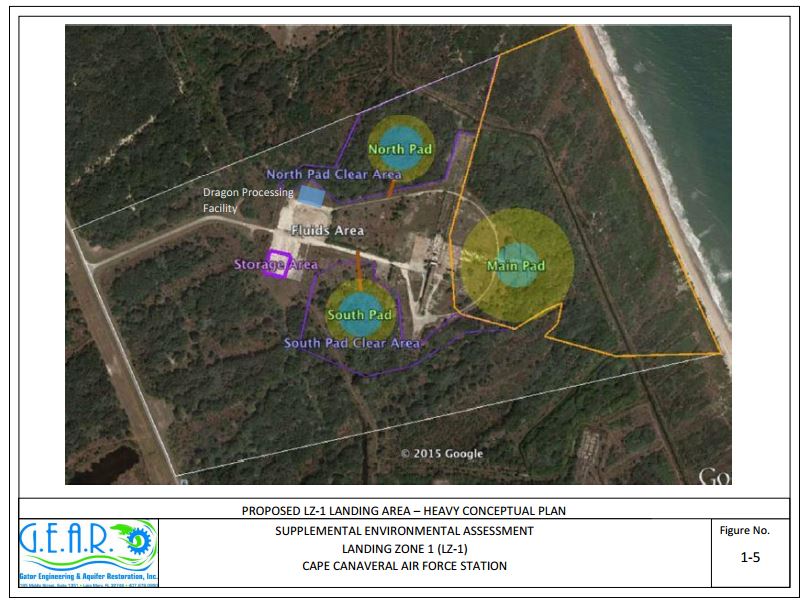
In order to achieve a triple landing with Falcon Heavy from the east coast, SpaceX requires the construction of two new landing pads nearby the existing main pad at Cape Canaveral Air Force Base (CCAFB). According to the environmental report, each new pad will need to be 282 feet in diameter with an additional hard-packed, 50-foot soil “apron” surrounding the pad. The pads will further require a depth of 18 inches in order to withstand the weight and thrust energy of Falcon 9-type landings. All construction activity would take place in the area of CCAFB known as Landing Zone 1/Launch Complex 13.
In the report, SpaceX estimates six possible Falcon Heavy launches per year once development and construction are complete in addition to the previously estimated twelve Falcon 9 launches. A proposal to additionally utilize the landing zone area for a Dragon capsule processing facility is also part of the report which would measure approximately 100 x 130 x 30 feet in size.
The addition of the new landing pads would expand SpaceX’s booster recovery options; however, the company may still utilize autonomous droneships for landing purposes subsequently with the new pads. Even with the droneship option, the report further asserts that without the additional landing pads, reusability of the boosters would suffer due to recovery options only including an ocean splashdown for at least one stage of a Falcon Heavy assembly.
The full report includes complete investigation summaries of the construction and landing impacts on land use, noise, biological resources, historical resources, hazardous materials & waste, climate, and water resources along with other environmental factors.
Of particular interest is the assessment of the sound impacts on local residents. Up to 2 sonic boom events per landing stage could occur over residential areas, totaling 6 sonic booms per Falcon Heavy launch. While the sound levels would fall within mandatory range limitations, the report suggests public awareness efforts in order to “reduce surprise” upon hearing the boom events. The public comments attached as an appendix to the report were highly supportive of SpaceX’s construction proposal and overall mission.
News of the report’s release was originally reported by NASA Spaceflight after it was submitted to a forum following notification by a Patrick AFB official of its publication.

Elon Musk
FCC chair criticizes Amazon over opposition to SpaceX satellite plan
Carr made the remarks in a post on social media platform X.

U.S. Federal Communications Commission (FCC) Chairman Brendan Carr criticized Amazon after the company opposed SpaceX’s proposal to launch a large satellite constellation that could function as an orbital data center network.
Carr made the remarks in a post on social media platform X.
Amazon recently urged the FCC to reject SpaceX’s application to deploy a constellation of up to 1 million low Earth orbit satellites that could serve as artificial intelligence data centers in space.
The company described the proposal as a “lofty ambition rather than a real plan,” arguing that SpaceX had not provided sufficient details about how the system would operate.
Carr responded by pointing to Amazon’s own satellite deployment progress.
“Amazon should focus on the fact that it will fall roughly 1,000 satellites short of meeting its upcoming deployment milestone, rather than spending their time and resources filing petitions against companies that are putting thousands of satellites in orbit,” Carr wrote on X.
Amazon has declined to comment on the statement.
Amazon has been working to deploy its Project Kuiper satellite network, which is intended to compete with SpaceX’s Starlink service. The company has invested more than $10 billion in the program and has launched more than 200 satellites since April of last year.
Amazon has also asked the FCC for a 24-month extension, until July 2028, to meet a requirement to deploy roughly 1,600 satellites by July 2026, as noted in a CNBC report.
SpaceX’s Starlink network currently has nearly 10,000 satellites in orbit and serves roughly 10 million customers. The FCC has also authorized SpaceX to deploy 7,500 additional satellites as the company continues expanding its global satellite internet network.
Elon Musk
NASA watchdog says Starship development delays could affect Artemis timeline
The report noted that several technical milestones still need to be completed before Starship can serve as a crewed lunar lander.

A NASA watchdog report stated that continued development work on SpaceX’s Starship could affect the timeline for the agency’s planned Artemis moon missions. The report noted that several technical milestones still need to be completed before the spacecraft can serve as a crewed lunar lander.
The findings were detailed in a report from NASA’s Office of Inspector General, as noted in a report from Reuters.
NASA selected SpaceX’s Starship in 2021 to serve as the Human Landing System (HLS) for its Artemis lunar program. The vehicle is intended to transport astronauts from lunar orbit to the surface of the Moon and back as part of future Artemis missions.
According to the watchdog report, Starship’s development has experienced roughly two years of schedule delays compared to earlier expectations. Still, NASA is targeting 2028 for the first crewed lunar landing using the Starship lander.
One of the most significant technical milestones for Starship’s lunar missions is in-space refueling.
To support a crewed lunar landing, multiple Starship launches will be required to deliver propellant to orbit. Tanker versions of Starship will transfer fuel to a storage depot spacecraft, which will then refuel the lunar lander.
The report noted that this approach could require more than 10 Starship launches to fully refuel the spacecraft needed for a single lunar landing mission.
NASA officials indicated that demonstrating cryogenic propellant transfer in orbit remains one of the most important technical steps before Starship can be certified for lunar missions.
SpaceX has conducted 11 Starship test flights since 2023 as the company continues developing the fully reusable launch system. A 12th test flight, this time featuring Starship V3, is expected to be held in early April.
Elon Musk
SpaceX weighs Nasdaq listing as company explores early index entry: report
The company is reportedly seeking early inclusion in the Nasdaq-100 index.

Elon Musk’s SpaceX is reportedly leaning toward listing its shares on the Nasdaq for a potential initial public offering (IPO) that could become the largest in history.
As per a recent report, the company is reportedly seeking early inclusion in the Nasdaq-100 index. The update was reported by Reuters, citing people familiar with the matter.
According to the publication, SpaceX is considering Nasdaq as the venue for its eventual IPO, though the New York Stock Exchange is also competing for the listing. Neither exchange has reportedly been informed of a final decision.
Reuters has previously reported that SpaceX could pursue an IPO as early as June, though the company’s plans could still change.
One of the publication’s sources also suggested that SpaceX is targeting a valuation of about $1.75 trillion for its IPO. At that level, the company would rank among the largest publicly traded firms in the United States by market capitalization.
Nasdaq has proposed a rule change that could accelerate the inclusion of newly listed megacap companies into the Nasdaq-100 index.
Under the proposed “Fast Entry” rule, a newly listed company could qualify for the index in less than a month if its market capitalization ranks among the top 40 companies already included in the Nasdaq-100.
If SpaceX is successful in achieving its target valuation of $1.75 trillion, it would become the sixth-largest company by market value in the United States, at least based on recent share prices.
Newly listed companies typically have to wait up to a year before becoming eligible for major indexes such as the Nasdaq-100 or S&P 500.
Inclusion in a major index can significantly broaden a company’s shareholder base because many institutional investors purchase shares through index-tracking funds.
According to Reuters, Nasdaq’s proposed fast-track rule is partly intended to attract highly valued private companies such as SpaceX, OpenAI, and Anthropic to list on the exchange.