News
Tesla’s emergency braking issue recall is already done, and it was addressed in one day
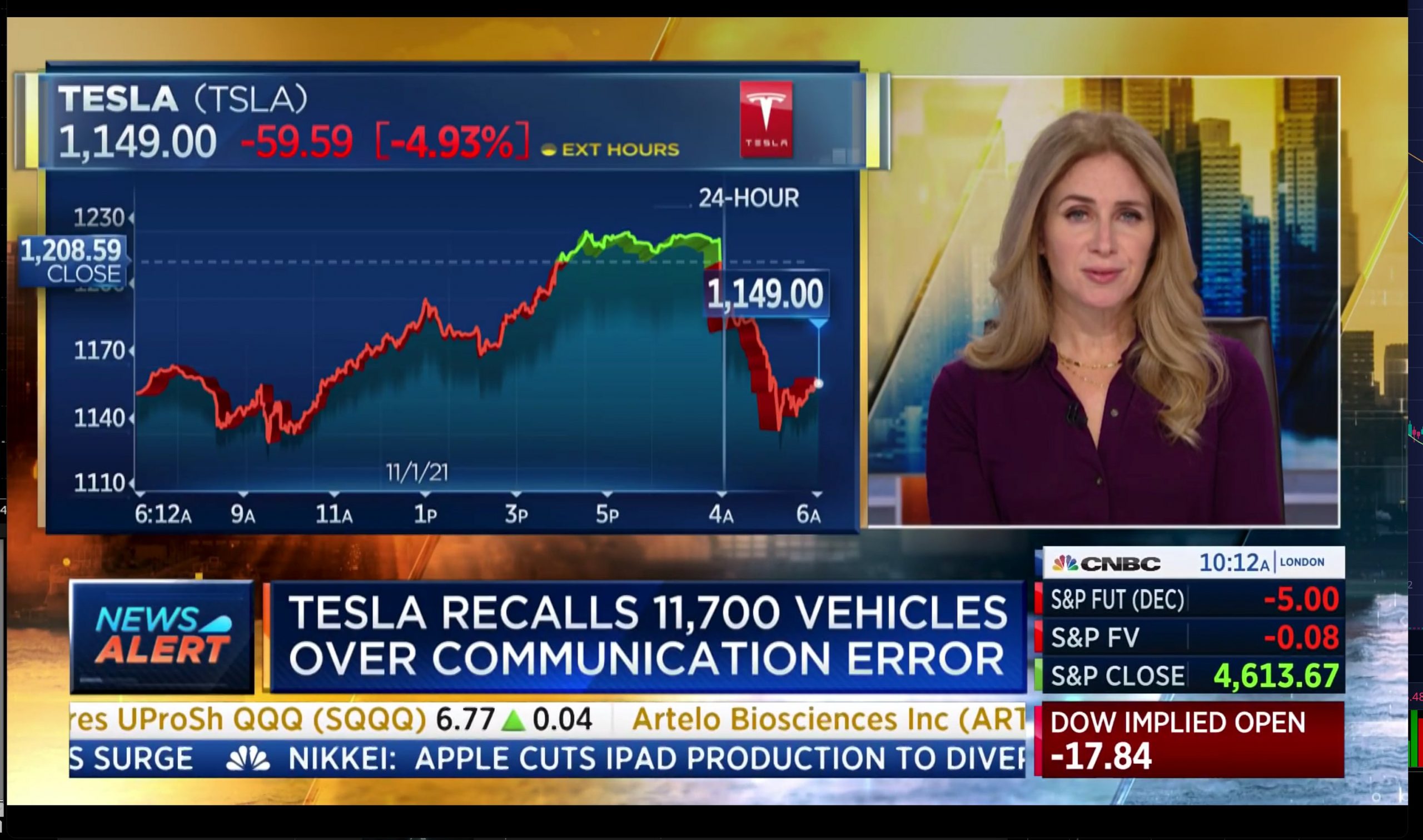
Just recently, reports emerged stating that Tesla is recalling about 11,700 Model S, Model 3, and Model X vehicles from 2020 to 2021. This was because software version 2021.36.5.2 may have a communication error that may cause an unexpected activation of the vehicles’ Automatic Emergency Braking (ABS) or Forward Collision Warning (FCW) systems. The reports cited a notice filed with the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration as a source for the recall information.
The recall made the rounds on mainstream media, but while the NHTSA’s notice was frequently referenced, what was generally ignored was that the safety agency also indicated that the issue had already been addressed by the EV maker through a software update. This is not surprising at all, considering that the recall was caused by software and Tesla, being a tech-centric automaker, was able to address the potential communication error in its vehicles through a simple over-the-air update.
“Tesla quickly remedied the condition OTA with firmware release 2021.36.5.3, which was released to the subject population on October 25, 2021. The OTA remedy will carry forward in firmware release 2021.36.5.3 and later. As of this filing, more than 99.8% of the subject population (i.e., all vehicles but for 17) installed firmware release 2021.36.5.3 or a later release. No further action is necessary from owners whose vehicles are equipped with firmware release 2021.36.5.3 or a later release,” the NHTSA noted.
This particular detail was generally left out in mainstream media’s reporting of the recall.
Looking further into the NHTSA’s notice, it is difficult not to be quite impressed with the speed upon which the software fix was implemented by Tesla. According to the chronology of events outlined by the safety agency, Tesla received reports of false FCW and AEB events from customers on the morning of October 24, 2021. By the evening of the same day, Tesla had already developed a fix for the issue. Software update 2021.36.5.3, which contained the fix, was released the next day, October 25, 2021.
“By the evening on the same day, we deterministically reproduced the condition, identified the root cause, and developed software release 2021.36.5.3 as a correction solution. Global engineering and quality assurance teams performed testing and validation on the new release throughout the night and into the next morning, and were successfully unable to produce the condition. On Monday morning, October 25, 2021, after completing validation, we began deploying 2021.36.5.3 OTA to the subject population and re-enabled FCW and AEB features on vehicles with 2021.36.5.3 installed,” the NHTSA’s document noted.
Read the NHTSA’s full Safety Recall Report notice below.
RCLRPT-21V846-7836 by Simon Alvarez on Scribd
Don’t hesitate to contact us with news tips. Just send a message to tips@teslarati.com to give us a heads up.

News
Tesla adds awesome new driving feature to Model Y
Tesla is rolling out a new “Comfort Braking” feature with Software Update 2026.8. The feature is exclusive to the new Model Y, and is currently unavailable for any other vehicle in the Tesla lineup.

Tesla is adding an awesome new driving feature to Model Y vehicles, effective on Juniper-updated models considered model year 2026 or newer.
Tesla is rolling out a new “Comfort Braking” feature with Software Update 2026.8. The feature is exclusive to the new Model Y, and is currently unavailable for any other vehicle in the Tesla lineup.
Tesla writes in the release notes for the feature:
“Your Tesla now provides a smoother feel as you come to a complete stop during routine braking.”
🚨 Tesla has added a new “Comfort Braking” update with 2026.8
“Your Tesla provides a smoother feel as you come to a complete stop during routine braking.” https://t.co/afqCpBSVeA pic.twitter.com/C6MRmzfzls
— TESLARATI (@Teslarati) March 13, 2026
Interestingly, we’re not too sure what catalyzed Tesla to try to improve braking smoothness, because it hasn’t seemed overly abrupt or rough from my perspective. Although the brake pedal in my Model Y is rarely used due to Regenerative Braking, it seems Tesla wanted to try to make the ride comfort even smoother for owners.
There is always room for improvement, though, and it seems that there is a way to make braking smoother for passengers while the vehicle is coming to a stop.
This is far from the first time Tesla has attempted to improve its ride comfort through Over-the-Air updates, as it has rolled out updates to improve regenerative braking performance, handling while using Full Self-Driving, improvements to Steer-by-Wire to Cybertruck, and even recent releases that have combatted Active Road Noise.
Tesla holds a unique ability to change the functionality of its vehicles through software updates, which have come in handy for many things, including remedying certain recalls and shipping new features to the Full Self-Driving suite.
Tesla seems to have the most seamless OTA processes, as many automakers have the ability to ship improvements through a simple software update.
We’re really excited to test the update, so when we get an opportunity to try out Comfort Braking when it makes it to our Model Y.
News
Tesla finally brings a Robotaxi update that Android users will love
The breakdown of the software version shows that Tesla is actively developing an Android-compatible version of the Robotaxi app, and the company is developing Live Activities for Android.

Tesla is finally bringing an update of its Robotaxi platform that Android users will love — mostly because it seems like they will finally be able to use the ride-hailing platform that the company has had active since last June.
Based on a decompile of software version 26.2.0 of the Robotaxi app, Tesla looks to be ready to roll out access to Android users.
According to the breakdown, performed by Tesla App Updates, the company is preparing to roll out an Android version of the app as it is developing several features for that operating system.
🚨 It looks like Tesla is preparing to launch the Robotaxi app for Android users at last!
A decompile of v26.2.0 of the Robotaxi app shows some progress on the Android side for Robotaxi 🤖 🚗 https://t.co/mThmoYuVLy
— TESLARATI (@Teslarati) March 13, 2026
The breakdown of the software version shows that Tesla is actively developing an Android-compatible version of the Robotaxi app, and the company is developing Live Activities for Android:
“Strings like notification_channel_robotaxid_trip_name and android_native_alicorn_eta_text show exactly how Tesla plans to replicate the iOS Live Activities experience. Instead of standard push alerts, Android users are getting a persistent, dynamically updating notification channel.”
This is a big step forward for several reasons. From a face-value perspective, Tesla is finally ready to offer Robotaxi to Android users.
The company has routinely prioritized Apple releases because there is a higher concentration of iPhone users in its ownership base. Additionally, the development process for Apple is simply less laborious.
Tesla is working to increase Android capabilities in its vehicles
Secondly, the Robotaxi rollout has been a typical example of “slowly then all at once.”
Tesla initially released Robotaxi access to a handful of media members and influencers. Eventually, it was expanded to more users, so that anyone using an iOS device could download the app and hail a semi-autonomous ride in Austin or the Bay Area.
Opening up the user base to Android users may show that Tesla is preparing to allow even more users to utilize its Robotaxi platform, and although it seems to be a few months away from only offering fully autonomous rides to anyone with app access, the expansion of the user base to an entirely different user base definitely seems like its a step in the right direction.
News
Lucid unveils Lunar Robotaxi in bid to challenge Tesla’s Cybercab in the autonomous ride hailing race
Lucid’s Lunar robotaxi is gunning for Tesla’s Cybercab in the autonomous ride hailing race
![Lucid Lunar robotaxi concept [Credit: Rendering by TESLARATI]](https://www.teslarati.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/03/lucid-lunar-robotaxi-concept-teslarati-rendering.jpg)
Lucid Group pulled back the curtain on its purpose-built autonomous robotaxi platform dubbed the Lunar Concept. Announced at its New York investor day event, Lunar is arguably the company’s most ambitious concept yet, and a direct line of sight toward the autonomous ride haling market that Tesla looks to control.
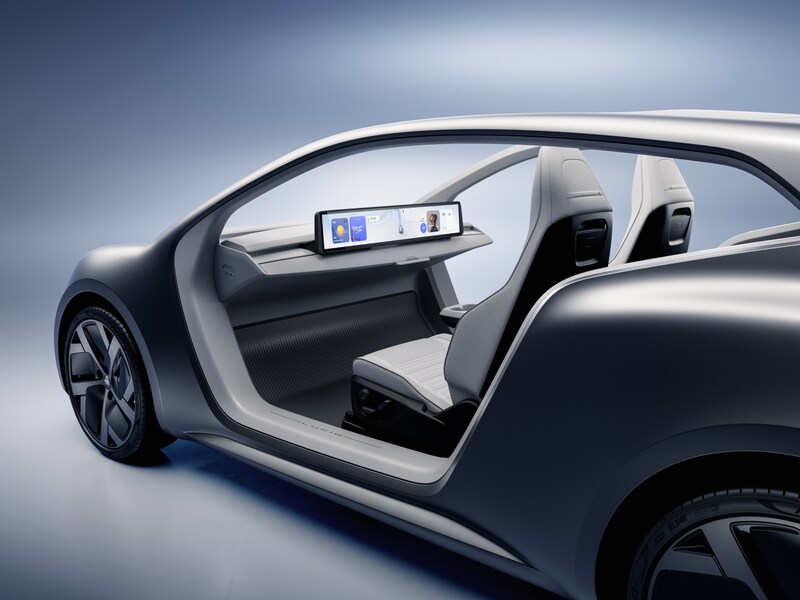

At Lucid Investor Day 2026, the company introduced Lunar, a purpose-built robotaxi concept based on the Midsize platform.
A comparison to Tesla’s Cybercab is unavoidable. The concept of a Tesla robotaxi was first introduced by Elon Musk back in April 2019 during an event dubbed “Autonomy Day,” where he envisioned a network of self-driving Tesla vehicles transporting passengers while not in use by their owners. That vision took another major step in October 2024 when, Musk unveiled the Cybercab at the Tesla “We, Robot” event held at Warner Bros. Studios in Burbank, California, where 20 concept Cybercabs autonomously drove around the studio lot giving rides to attendees.
Fast forward to today, and Tesla’s ambitions are finally materializing, but not without friction. As we recently reported, the Cybercab is being spotted with increasing frequency on public roads and across the grounds of Gigafactory Texas, suggesting that the company’s road testing and validation program is ramping meaningfully ahead of mass production. Tesla already operates a small scale robotaxi service in Austin using supervised Model Ys, but the Cybercab is designed from the ground up for high-volume, low-cost production, with Musk stating an eventual goal of producing one vehicle every 10 seconds.
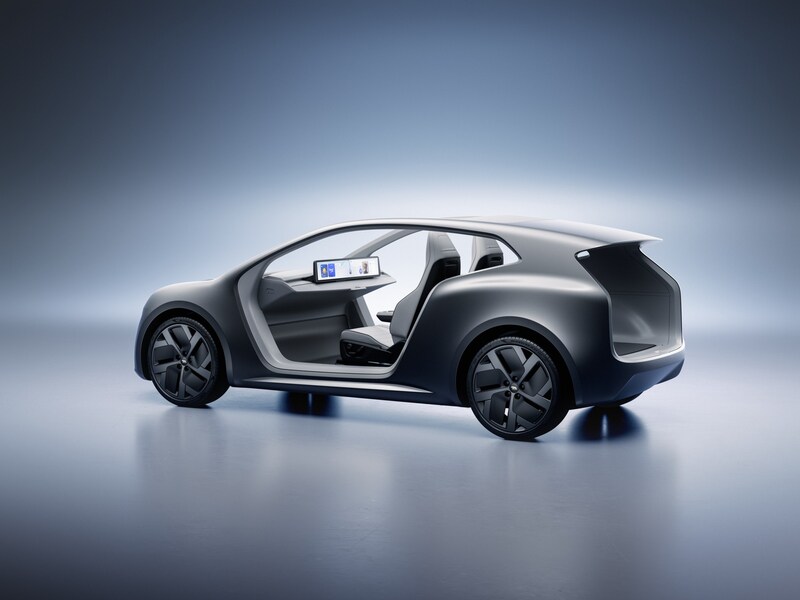

At Lucid Investor Day 2026, the company introduced Lunar, a purpose-built robotaxi concept based on the Midsize platform.
Into this landscape steps Lucid’s Lunar. Built on the company’s all-new Midsize EV platform, which will also underpin consumer SUVs starting below $50,000. The Lunar mirrors the Cybercab’s core philosophy of having two seats, no driver controls, and a focus on fleet economics. The platform introduces Lucid’s redesigned Atlas electric drive unit, engineered to be smaller, lighter, and cheaper to manufacture at scale.
Unlike Tesla’s strategy of building its own ride hailing network from scratch, Lucid is partnering with Uber. The companies are said to be in advanced discussions to deploy Midsize platform vehicles at large scale, with Uber CEO Dara Khosrowshahi publicly backing Lucid’s engineering credentials and autonomous-ready architecture.
In the investor day event, Lucid also outlined a recurring software revenue model, with an in-vehicle AI assistant and monthly autonomous driving subscriptions priced between $69 and $199. This can be seen as a nod to the software revenue stream that Tesla has long championed with its Full Self-Driving subscription.
Tesla’s Cybercab is targeting a price point below $30k and with operating costs as low as 20 cents per mile. But with regulatory hurdles still ahead, the window for competition is open. Lucid’s Lunar may not have a launch date yet, but it arrives at a pivotal moment, and when the robotaxi race is no longer viewed as hypothetical. Rather, every serious EV player needs to come to bat on the same plate that Tesla has had countless practice swings on over the last seven years.


![Lucid Lunar robotaxi concept [Credit: Rendering by TESLARATI]](https://www.teslarati.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/03/lucid-lunar-robotaxi-concept-teslarati-rendering-80x80.jpg)





