

News
SpaceX’s first orbital Starship rocket engine is almost ready for testing
CEO Elon Musk says that SpaceX is “about a month away” from testing a rocket engine that will be essential for Starship and its Super Heavy booster to reach their full potential.
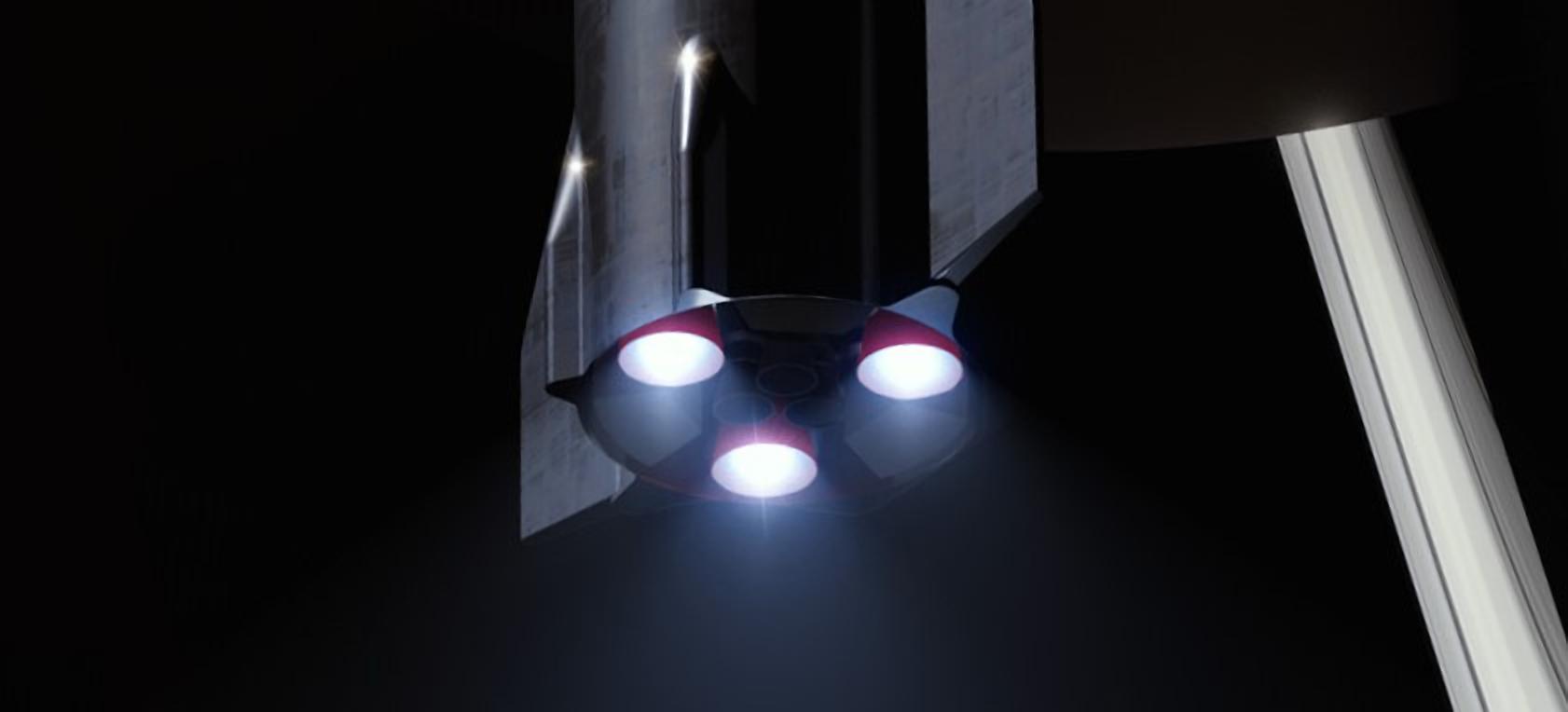
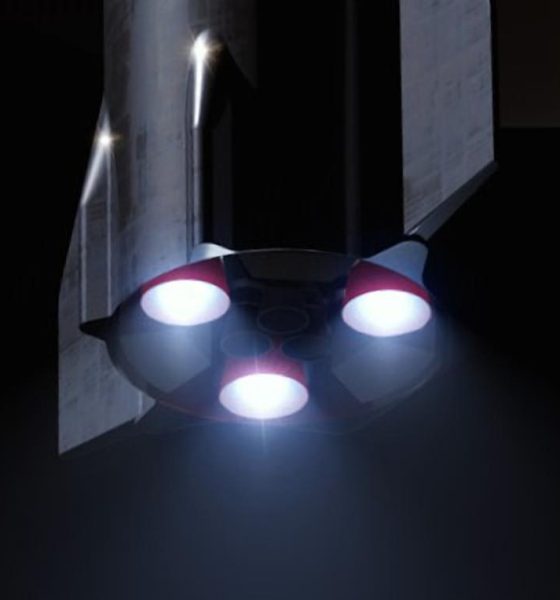
Known as Raptor Vacuum, the engine – as its name suggests – is a variant of the base Raptor engine optimized for maximum performance and efficiency in the vacuum of space. Although Starship could technically still function and likely reach orbit with only sea level-optimized Raptors installed, it would likely significantly limit the amount of payload it could carry into Earth orbit and would especially harm the ship’s performance to higher orbits and other planets.
Back in May 2019, Musk revealed that SpaceX had shifted gears again, forgoing a plan to begin orbital Starship flight operations with only sea level Raptors, gradually designing and phasing in RaptorVac engines much further down the road. Instead, SpaceX restarted (relatively) urgent work on the vacuum variant and Musk hinted that it would “aspirationally” be ready to support launches in the near term. A few weeks shy of a year later, Musk says that Raptor Vacuum testing could begin as early as June 2020.
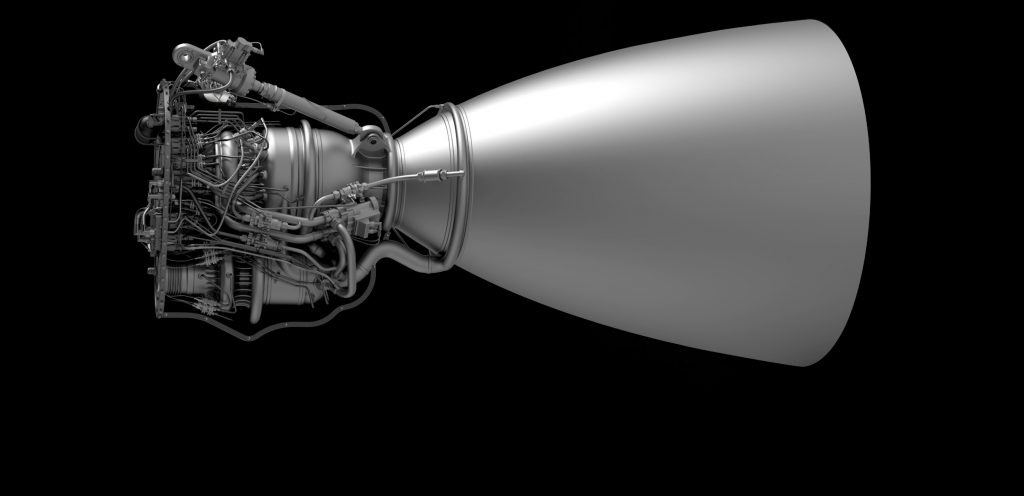
For a variety of reasons, even if based directly off of an existing design, vacuum-optimized engines are typically much more complex than a comparable sea level variant. While efficiency is always relatively important for rocket engine design, it becomes even more paramount when dealing with vacuum rocketry, as the entire point of a dedicated vacuum-optimized engine is to eke as much efficiency as possible out of a launch vehicle’s orbital stage(s).
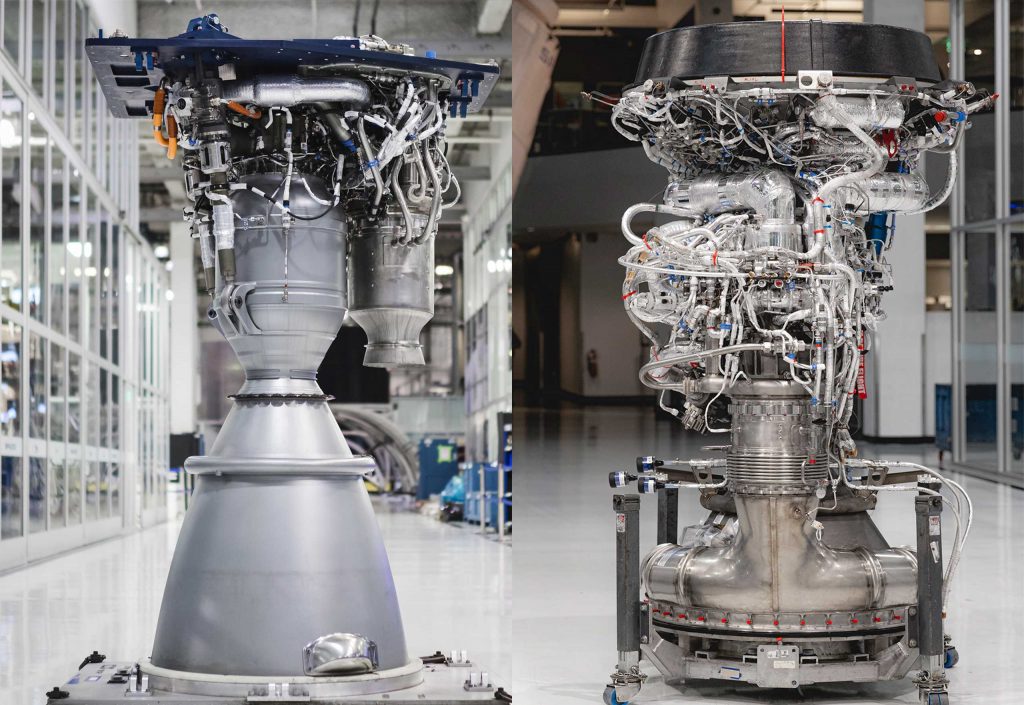
For example, even from a purely visual perspective, Merlin Vacuum (MVac) is substantially different when compared to the Merlin 1D engine it’s based on. Due to a number of major and largely unknown differences, the engines’ shared components are largely invisible. It’s unclear how similar they are but it’s safe to say that they share at least ~50% commonality. Obviously, the most apparent part of the difference between a vacuum-optimized engine and an atmosphere-optimized engine is the bell nozzle: MVac has a nozzle that is dramatically larger than M1D.
Raptor will be no different, with the sea-level variant featuring a nozzle about 1m (3.2 ft) in diameter, whereas RaptorVac’s bell will have a diameter closer to 2.5m (~8 ft). With SpaceX’s apparent May 2019 pivot back to working on RaptorVac now, the company has been working on a dedicated vacuum variant of the high-performance methane-oxygen engine for at least a full year. Now, perhaps beginning as early as June or July, Musk suggests that the first RaptorVac engine (SN0? SN1?) is almost ready to commence static fire testing.
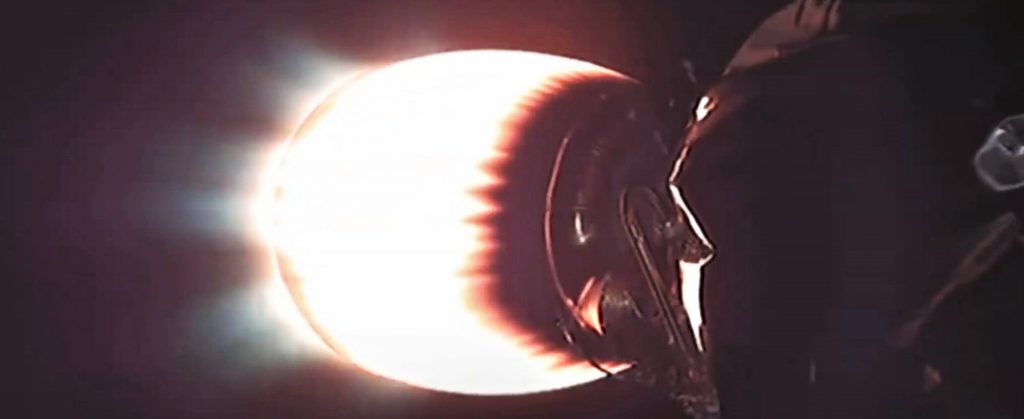
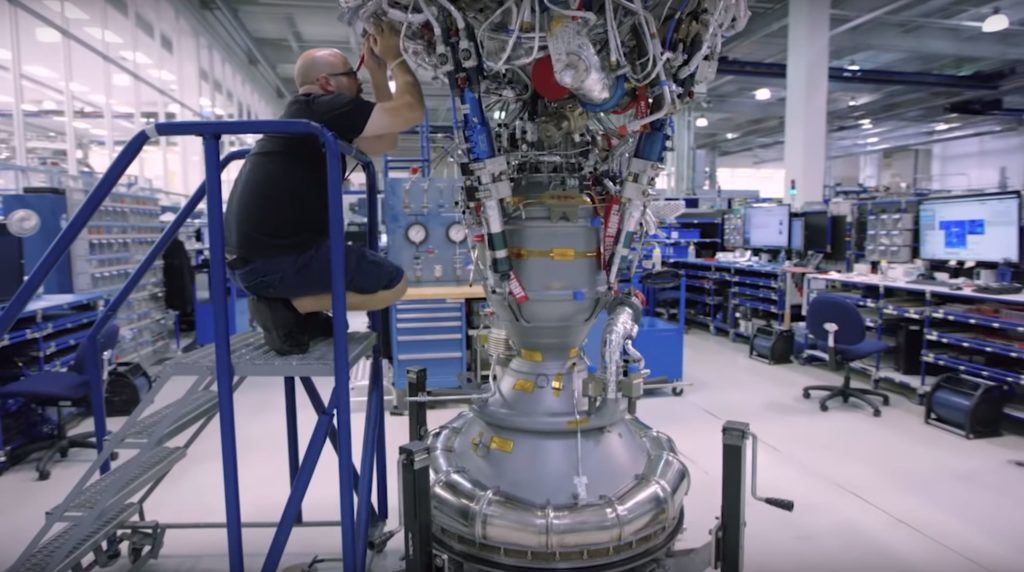
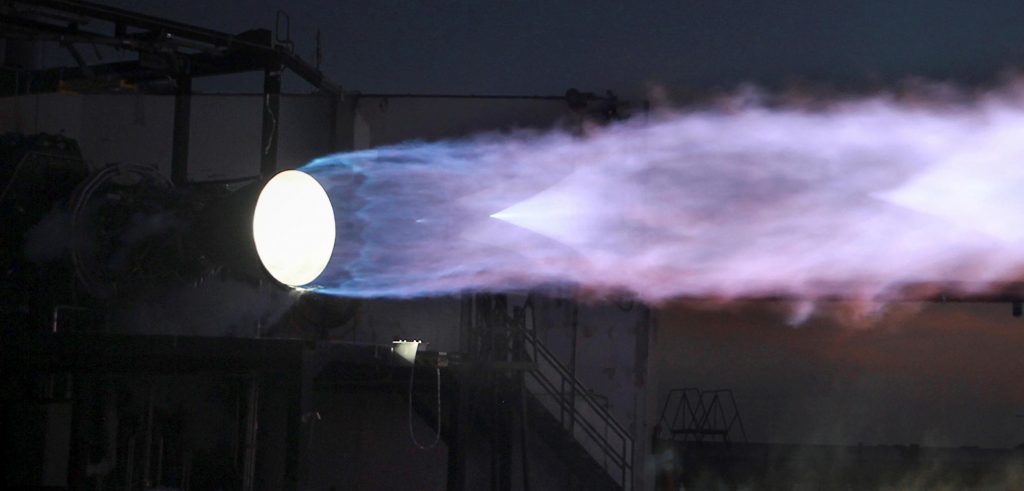



The nature of that testing is a bit of a mystery. While it will almost certainly occur at SpaceX’s McGregor, Texas test and development facilities, it’s unclear if Raptor Vacuum’s first static fire test campaign will be attempted with the engine’s extended nozzle installed. Back in October 2019, Musk suggested that yes, Raptor Vacuum version 1.0 would have a nozzle small enough to operate at sea level without destroying itself or its test facilities. With Merlin Vacuum engines, SpaceX performs acceptance tests in Texas but only without their nozzle extensions installed. If Musk’s October 2019 comments remain true, that may not be the case for RaptorVac.
Either way, it will be thoroughly interesting to note the differences between RaptorVac and its sea level-optimized predecessor if or when Elon Musk or SpaceX releases photos of their newest engine as it nears its first major tests. Simultaneously, SpaceX is also readying a sea-level Raptor for its inaugural static fire test while attached to a full-scale Starship prototype, while the first test with three Raptor engines installed could be attempted just a few weeks from now.

Cybertruck
Tesla Cybertruck’s newest trim will undergo massive change in ten days, Musk says
It appears as if the new All-Wheel-Drive trim of Cybertruck won’t be around for too long, however. Elon Musk revealed this morning that it will be around “only for the next 10 days.”
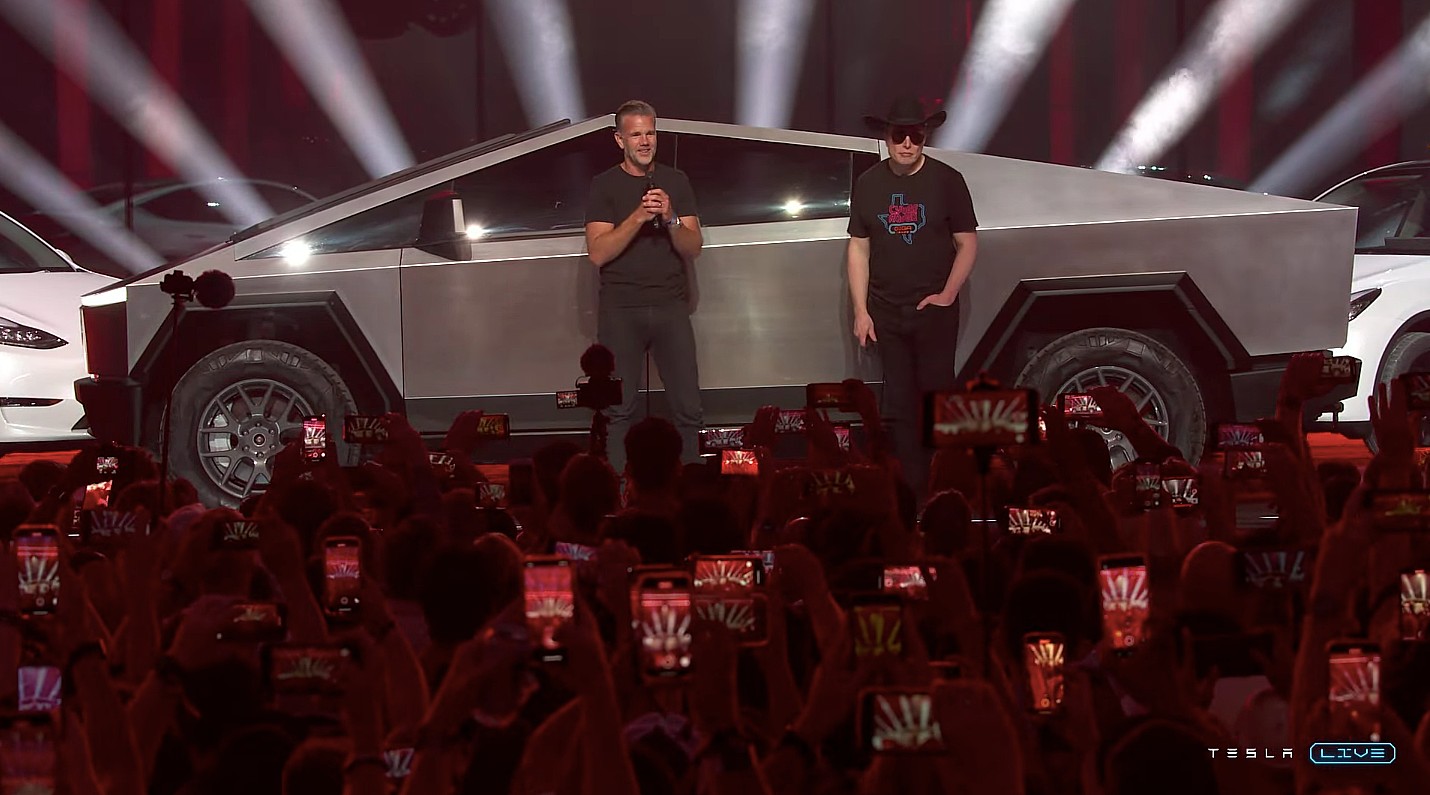

Tesla’s new Cybertruck trim has already gotten the axe from CEO Elon Musk, who said the All-Wheel-Drive configuration of the all-electric pickup will only be available “for the next ten days.”
Musk could mean the price, which is $59,990, or the availability of the trim altogether.
Last night, Tesla launched the All-Wheel-Drive configuration of the Cybertruck, a pickup that comes in at less than $60,000 and features a competitive range and features that are not far off from the offerings of the premium trim.
Tesla launches new Cybertruck trim with more features than ever for a low price
It was a nice surprise from Tesla, considering that last year, it offered a Rear-Wheel-Drive trim of the Cybertruck that only lasted a few months. It had extremely underwhelming demand because it was only $10,000 cheaper than the next trim level up, and it was missing a significant number of premium features.
Simply put, it was not worth the money. Tesla killed the RWD Cybertruck just a few months after offering it.
With the news that Tesla was offering this All-Wheel-Drive configuration of the Cybertruck, many fans and consumers were encouraged. The Cybertruck has been an underwhelming seller, and this seemed to be a lot of truck for the price when looking at its features:
- Dual Motor AWD w/ est. 325 mi of range
- Powered tonneau cover
- Bed outlets (2x 120V + 1x 240V) & Powershare capability
- Coil springs w/ adaptive damping
- Heated first-row seats w/ textile material that is easy to clean
- Steer-by-wire & Four Wheel Steering
- 6’ x 4’ composite bed
- Towing capacity of up to 7,500 lbs
- Powered frunk
It appears as if this trim of Cybertruck won’t be around for too long, however. Musk revealed this morning that it will be around “only for the next 10 days.”
Only for the next 10 days https://t.co/82JnvZQGh2
— Elon Musk (@elonmusk) February 20, 2026
Musk could mean the price of the truck and not necessarily the ability to order it. However, most are taking it as a cancellation.
If it is, in fact, a short-term availability decision, it is baffling, especially as Tesla fans and analysts claim that metrics like quarterly deliveries are no longer important. This seems like a way to boost sales short-term, and if so many people are encouraged about this offering, why would it be kept around for such a short period of time?
Some are even considering the potential that Tesla axes the Cybertruck program as a whole. Although Musk said during the recent Q4 Earnings Call that Cybertruck would still be produced, the end of the Model S and Model X programs indicates Tesla might be prepared to do away with any low-volume vehicles that do not contribute to the company’s future visions of autonomy.
The decision to axe the car just ten days after making it available seems like a true head-scratcher.
Elon Musk
Elon Musk’s Neuralink sparks BCI race in China
One of the most prominent is NeuroXess, which launched in 2021 and is already testing implants in patients.

Neuralink, founded by Elon Musk, is helping spark a surge of brain-computer interface (BCI) development in China, where startups are moving quickly into human trials with strong state backing.
One of the most prominent is NeuroXess, which launched in 2021 and is already testing implants in patients.
Neuralink’s clinical work and public demonstrations have drawn worldwide attention to invasive brain implants that allow patients to control digital devices using their minds. The company is currently running a global clinical trial and is also busy preparing for its next product, Blindsight, which would restore vision to people with visual impairments.
Neuralink’s visibility has helped accelerate similar efforts in China. Beijing last year classified brain-computer interfaces as a strategic sector and issued a roadmap calling for two or three globally competitive companies by 2030, as per the Financial Times. Since February last year, at least 10 clinical trials for invasive brain chips have launched in the country.
NeuroXess recently reported that a paralyzed patient was able to control a computer cursor within five days of implantation. Founder Tiger Tao credited government support for helping shorten the path from research to trials.
Investment activity has followed the policy push. Industry data show dozens of financing rounds for Chinese BCI startups over the past year, reflecting rising capital interest in the field. Ultimately, while Neuralink remains one of the most closely watched players globally, its momentum has clearly energized competitors abroad.
News
Tesla Supercharger vandalized with frozen cables and anti-Musk imagery amid Sweden union dispute
The incident comes amid Tesla’s ongoing labor dispute with IF Metall.
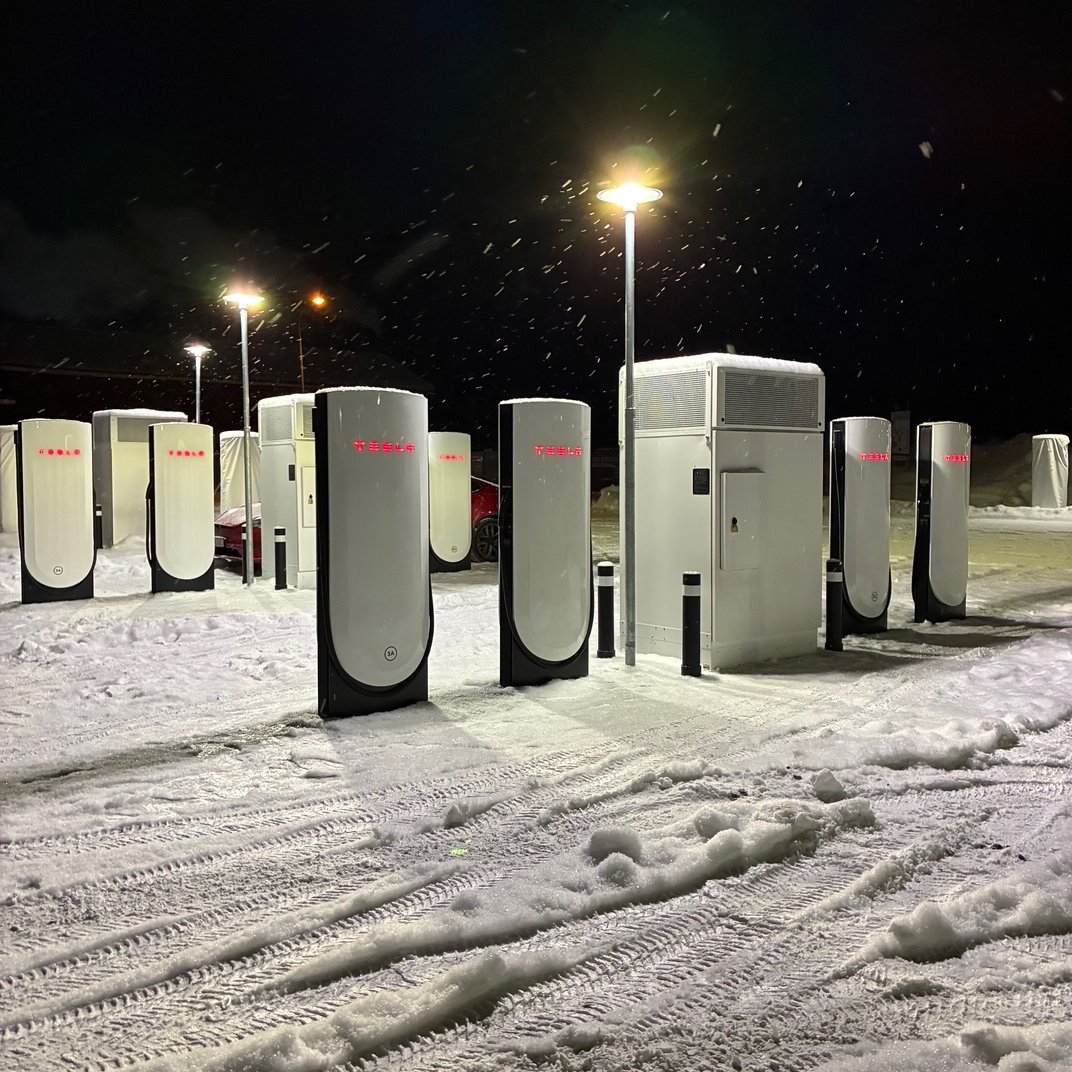

Tesla’s Supercharger site in Vansbro, Sweden, was vandalized during peak winter travel weeks. Images shared to local media showed frozen charging cables and a banner reading “Go home Elon,” which was complete with a graphic of Musk’s controversial gesture.
The incident comes amid Tesla’s ongoing labor dispute with IF Metall, which has been striking against the company for more than two years over collective bargaining agreements, as noted in a report from Expressen.
Local resident Stefan Jakobsson said he arrived at the Vansbro charging station to find a board criticizing Elon Musk and accusing Tesla of strikebreaking. He also found the charging cables frozen after someone seemingly poured water over them.
“I laughed a little and it was pretty nicely drawn. But it was a bit unnecessary,” Jakobsson said. “They don’t have to do vandalism because they’re angry at Elon Musk.”
The site has seen heavy traffic during Sweden’s winter sports holidays, with travelers heading toward Sälen and other mountain destinations. Jakobsson said long lines formed last weekend, with roughly 50 Teslas and other EVs waiting to charge.
Tesla Superchargers in Sweden are typically open to other electric vehicle brands, making them a reliable option for all EV owners.
Tesla installed a generator at the location after sympathy strikes from other unions disrupted power supply to some stations. The generator itself was reportedly not working on the morning of the incident, though it is unclear whether that was connected to the protest.
The dispute between Tesla and IF Metall centers on the company’s refusal to sign a collective agreement covering Swedish workers. The strike has drawn support from other unions, including Seko, which has taken steps affecting electricity supply to certain Tesla facilities. Tesla Sweden, for its part, has insisted that its workers are already fairly compensated and it does not need a collective agreement,
Jesper Pettersson, press spokesperson for IF Metall, criticized Tesla’s use of generators to keep charging stations running. Still, IF Metall emphasized that it strongly distances itself from the vandalism incident at the Vansbro Supercharger.
“We think it is remarkable that instead of taking the easy route and signing a collective agreement for our members, they are choosing to use every possible means to get around the strike,” Pettersson said.








