

News
SpaceX Falcon 9 booster becomes fourth to launch and land ten times
For the fourth time, a SpaceX Falcon 9 booster has successfully completed ten orbital-class launches and landings.
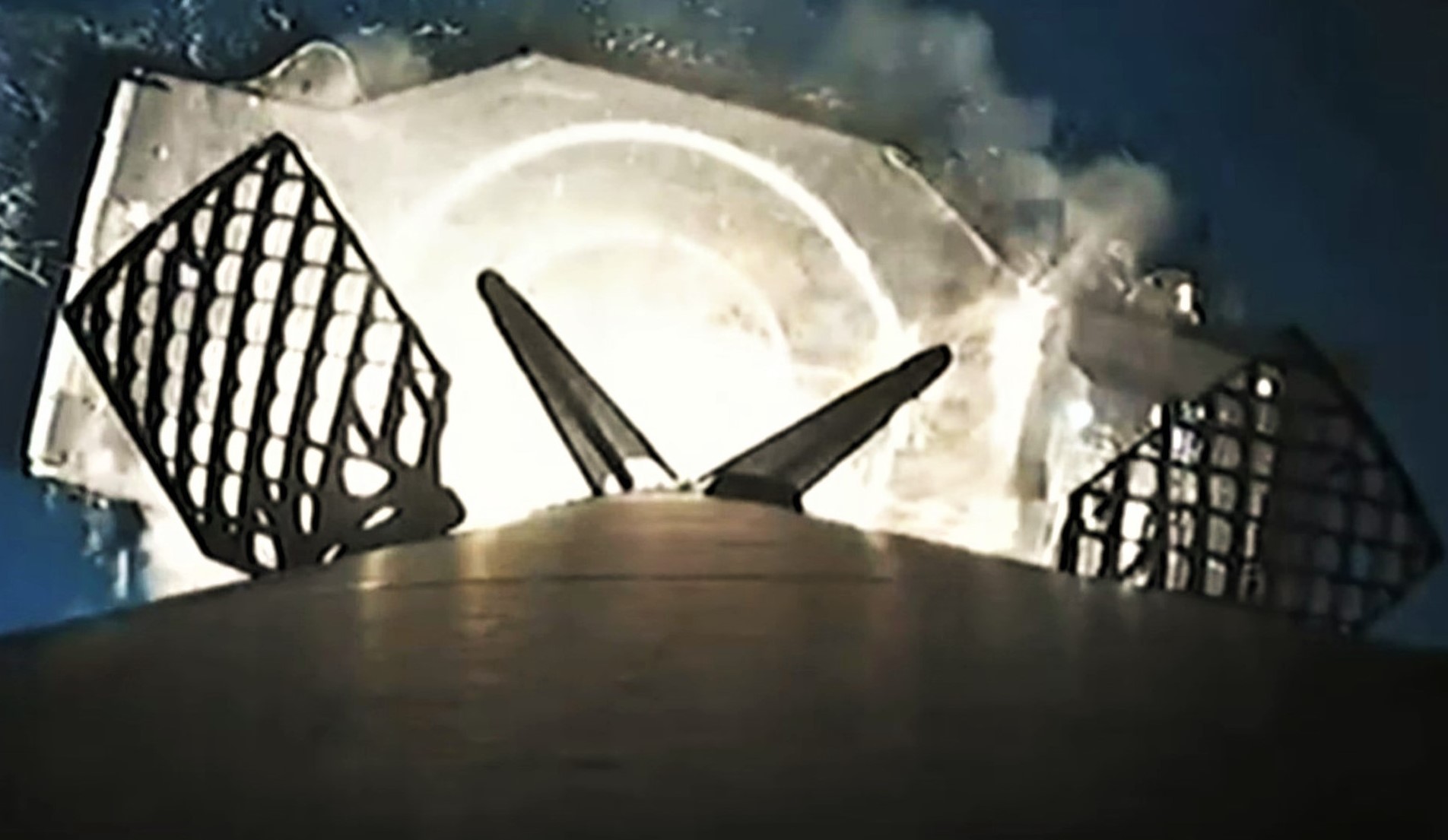
A day later than planned, Falcon 9 booster B1060 lifted off from Kennedy Space Center’s Pad 39A at 9:02 pm EST (02:02 UTC) on Tuesday, January 18th. Carrying an expendable Falcon upper stage and 49 Starlink V1.5 satellites, the booster performed its job without issue, boosting the payload and second stage mostly free of Earth’s atmosphere and about a quarter of the way to orbital velocity (2.2 km/s or Mach 6.5). As is now routine, B1060 then separated from the upper stage, flipped around, coasted to an apogee of ~130 km (80 mi), reentered Earth’s atmosphere, and touched down on one of SpaceX’s drone ships.
Unlike most other SpaceX launches, that drone ship – named A Shortfall Of Gravitas (ASOG) – was stationed southeast of Kennedy Space Center and off the coast of the Bahamas, where the weather and warmer seas are calmer and more optimal for safe booster and fairing recovery. Starlink 4-6 is the second time SpaceX has significantly customized a Starlink launch trajectory to optimize for booster recovery after Starlink 4-5, a virtually identical mission that launched on January 6th.

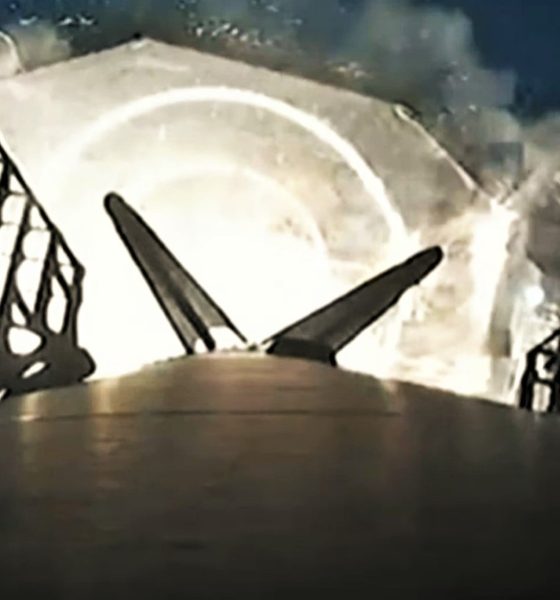
While the rare trajectory again prevented SpaceX from broadcasting Starlink satellite deployment live, CEO Elon Musk confirmed that the mission was a full success – the most important aspect of any operational rocket launch. Nonetheless, five years into Falcon reuse, booster recovery is now a crucial objective of virtually every Falcon launch – likely second only to payload deployment. Starlink 4-6 was no different and carried its own Falcon recovery and reuse milestones along with it.
For B1060, it was the booster’s tenth successful spaceflight and orbital-class launch and landing, making it the fourth Falcon 9 first stage to cross that milestone since May 2021 – and the third in the last four months. B1060 accomplished the feat faster than any of the three boosters before it, supporting ten orbital-class launches in a little over 18 months just five days after Falcon 9 B1058 crossed its own ten-flight milestone in 19 months.
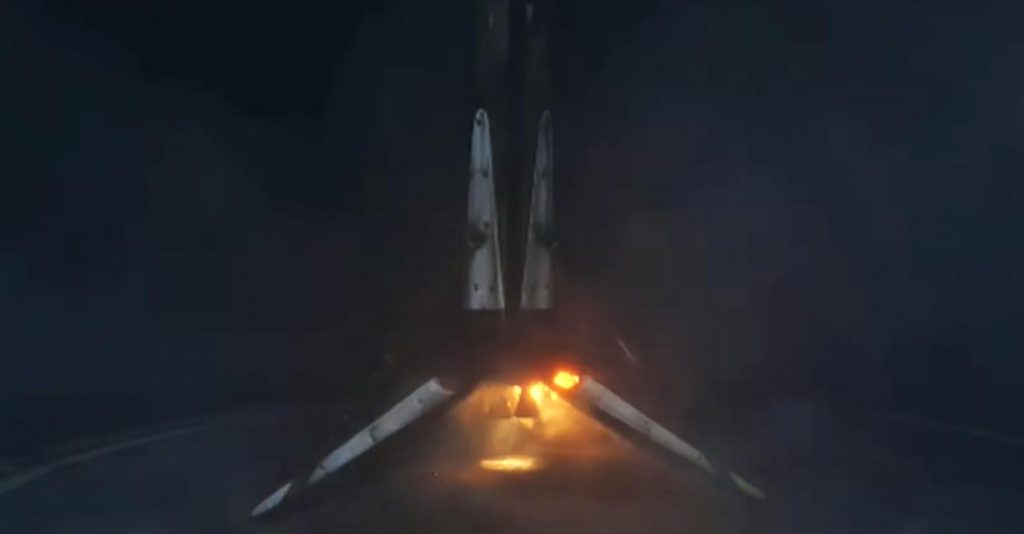
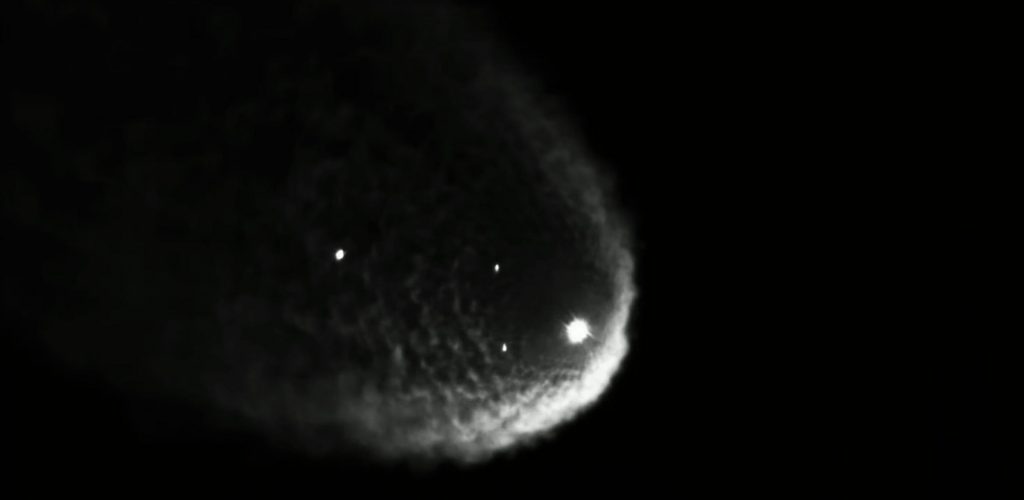

More significantly, B1060’s success means that four boosters have now launched 41 times total and supported 40 of 73 Falcon launches completed by SpaceX in the last three years. While responsible for ~55% of all Falcon launches in that timeframe, those 4 boosters represent just 20% of the 20 boosters SpaceX launched at least once in the same period. That extraordinary accomplishment helps make it clearer than ever what a fleet of rockets capable of reliable recovery and reuse are truly capable of.
Starlink 4-6 included the 2000th Starlink satellite launched by SpaceX since May 2019 and, if all those spacecraft are in good health, raised the tally of operational Starlink satellites launched by Falcon 9 to 1967.
SpaceX has another two launches scheduled this month for five total: Italy’s CSG-2 Earth observation satellite no earlier than (NET) January 27th and Starlink 4-7 NET January 29th.

Elon Musk
Tesla’s Elon Musk: 10 billion miles needed for safe Unsupervised FSD
As per the CEO, roughly 10 billion miles of training data are required due to reality’s “super long tail of complexity.”

Tesla CEO Elon Musk has provided an updated estimate for the training data needed to achieve truly safe unsupervised Full Self-Driving (FSD).
As per the CEO, roughly 10 billion miles of training data are required due to reality’s “super long tail of complexity.”
10 billion miles of training data
Musk comment came as a reply to Apple and Rivian alum Paul Beisel, who posted an analysis on X about the gap between tech demonstrations and real-world products. In his post, Beisel highlighted Tesla’s data-driven lead in autonomy, and he also argued that it would not be easy for rivals to become a legitimate competitor to FSD quickly.
“The notion that someone can ‘catch up’ to this problem primarily through simulation and limited on-road exposure strikes me as deeply naive. This is not a demo problem. It is a scale, data, and iteration problem— and Tesla is already far, far down that road while others are just getting started,” Beisel wrote.
Musk responded to Beisel’s post, stating that “Roughly 10 billion miles of training data is needed to achieve safe unsupervised self-driving. Reality has a super long tail of complexity.” This is quite interesting considering that in his Master Plan Part Deux, Elon Musk estimated that worldwide regulatory approval for autonomous driving would require around 6 billion miles.
FSD’s total training miles
As 2025 came to a close, Tesla community members observed that FSD was already nearing 7 billion miles driven, with over 2.5 billion miles being from inner city roads. The 7-billion-mile mark was passed just a few days later. This suggests that Tesla is likely the company today with the most training data for its autonomous driving program.
The difficulties of achieving autonomy were referenced by Elon Musk recently, when he commented on Nvidia’s Alpamayo program. As per Musk, “they will find that it’s easy to get to 99% and then super hard to solve the long tail of the distribution.” These sentiments were echoed by Tesla VP for AI software Ashok Elluswamy, who also noted on X that “the long tail is sooo long, that most people can’t grasp it.”
News
Tesla earns top honors at MotorTrend’s SDV Innovator Awards
MotorTrend’s SDV Awards were presented during CES 2026 in Las Vegas.

Tesla emerged as one of the most recognized automakers at MotorTrend’s 2026 Software-Defined Vehicle (SDV) Innovator Awards.
As could be seen in a press release from the publication, two key Tesla employees were honored for their work on AI, autonomy, and vehicle software. MotorTrend’s SDV Awards were presented during CES 2026 in Las Vegas.
Tesla leaders and engineers recognized
The fourth annual SDV Innovator Awards celebrate pioneers and experts who are pushing the automotive industry deeper into software-driven development. Among the most notable honorees for this year was Ashok Elluswamy, Tesla’s Vice President of AI Software, who received a Pioneer Award for his role in advancing artificial intelligence and autonomy across the company’s vehicle lineup.
Tesla also secured recognition in the Expert category, with Lawson Fulton, a staff Autopilot machine learning engineer, honored for his contributions to Tesla’s driver-assistance and autonomous systems.
Tesla’s software-first strategy
While automakers like General Motors, Ford, and Rivian also received recognition, Tesla’s multiple awards stood out given the company’s outsized role in popularizing software-defined vehicles over the past decade. From frequent OTA updates to its data-driven approach to autonomy, Tesla has consistently treated vehicles as evolving software platforms rather than static products.
This has made Tesla’s vehicles very unique in their respective sectors, as they are arguably the only cars that objectively get better over time. This is especially true for vehicles that are loaded with the company’s Full Self-Driving system, which are getting progressively more intelligent and autonomous over time. The majority of Tesla’s updates to its vehicles are free as well, which is very much appreciated by customers worldwide.
Elon Musk
Judge clears path for Elon Musk’s OpenAI lawsuit to go before a jury
The decision maintains Musk’s claims that OpenAI’s shift toward a for-profit structure violated early assurances made to him as a co-founder.

A U.S. judge has ruled that Elon Musk’s lawsuit accusing OpenAI of abandoning its founding nonprofit mission can proceed to a jury trial.
The decision maintains Musk’s claims that OpenAI’s shift toward a for-profit structure violated early assurances made to him as a co-founder. These claims are directly opposed by OpenAI.
Judge says disputed facts warrant a trial
At a hearing in Oakland, U.S. District Judge Yvonne Gonzalez Rogers stated that there was “plenty of evidence” suggesting that OpenAI leaders had promised that the organization’s original nonprofit structure would be maintained. She ruled that those disputed facts should be evaluated by a jury at a trial in March rather than decided by the court at this stage, as noted in a Reuters report.
Musk helped co-found OpenAI in 2015 but left the organization in 2018. In his lawsuit, he argued that he contributed roughly $38 million, or about 60% of OpenAI’s early funding, based on assurances that the company would remain a nonprofit dedicated to the public benefit. He is seeking unspecified monetary damages tied to what he describes as “ill-gotten gains.”
OpenAI, however, has repeatedly rejected Musk’s allegations. The company has stated that Musk’s claims were baseless and part of a pattern of harassment.
Rivalries and Microsoft ties
The case unfolds against the backdrop of intensifying competition in generative artificial intelligence. Musk now runs xAI, whose Grok chatbot competes directly with OpenAI’s flagship ChatGPT. OpenAI has argued that Musk is a frustrated commercial rival who is simply attempting to slow down a market leader.
The lawsuit also names Microsoft as a defendant, citing its multibillion-dollar partnerships with OpenAI. Microsoft has urged the court to dismiss the claims against it, arguing there is no evidence it aided or abetted any alleged misconduct. Lawyers for OpenAI have also pushed for the case to be thrown out, claiming that Musk failed to show sufficient factual basis for claims such as fraud and breach of contract.
Judge Gonzalez Rogers, however, declined to end the case at this stage, noting that a jury would also need to consider whether Musk filed the lawsuit within the applicable statute of limitations. Still, the dispute between Elon Musk and OpenAI is now headed for a high-profile jury trial in the coming months.








