

SpaceX
SpaceX’s Crew Dragon to launch astronauts in July, says Russian source
A source familiar with Russia’s aerospace industry recently informed state newspaper RIA Novosti that NASA has provided Russian space agency Roscosmos with an updated planning schedule for International Space Station (ISS) operations, including a preliminary target for SpaceX’s first Crew Dragon launch with astronauts aboard.
According to RIA’s source, NASA informed Roscosmos that the agency was tentatively planning for the launch of SpaceX’s Demonstration Mission 2 (DM-2) as early as July 25th, with the spacecraft departing the ISS, reentering the atmosphere, and safely returning astronauts Bob Behnken and Doug Hurley to Earth on August 5th. In a bizarre turn of events, Russian news agency TASS published a separate article barely 12 hours later, in which – once again – an anonymous space agency source told the outlet that “the [DM-2] launch of Crew Dragon is likely to be postponed to November”. For the time being, the reality likely stands somewhere in the middle.
While it’s hard not to jump to conclusions about the oddity of two wholly contradictory reports arising from similar sources in similar articles just half a day apart, it’s just as likely that the near-simultaneous publishing of both TASS and RIA stories is mainly a coincidence. At the same time, truth can be found in both comments made by the anonymous source(s), while they also offer a sort of best-case and worst-case scenario for the first crewed launch of SpaceX’s Crew Dragon spacecraft.
RIA began the series on March 22nd with a brief news blurb featuring one substantive quote from the aforementioned space industry source.
“The American side informed the Russian side that the launch of the [first crewed launch of] Dragon-2…to the ISS…is scheduled for July 25. The docking with the station is scheduled [to occur around one day later]. The separation from the ISS and return to Earth is expected on August 5,” the agency’s source said.
Put in a slightly different way, NASA informed Roscosmos that it had begun to loosely plan for the launch of SpaceX’s DM-2 no earlier than (NET) late July, much like NASA and SpaceX publicly announced that Crew Dragon’s DM-1 launch debut was scheduled NET January 17th as of early December 2018. DM-1’s actual debut wound up occurring on March 2nd, a delay of approximately six weeks. The cause(s) behind the discrepancy between NASA’s first serious planning date and the actual launch remains unknown but it’s safe to say that things took quite a bit longer than expected even after Crew Dragon and Falcon 9 were technically “go” for launch.
Although NASA and SpaceX now have the luxury of a vast cache of flight data and the practical experience derived from conducting Crew Dragon’s first – and nearly flawless – orbital launch and ISS rendezvous, Crew Dragon’s DM-2 mission remains an entirely different animal. Aside from requiring a number of significant hardware changes and introducing the visceral pressure of real human lives hanging in the balance, DM-2 will be a major first for the NASA after having spent the better part of eight years unable to launch its own astronauts into orbit.
A ‘race’ no more
Meanwhile, Boeing’s Starliner spacecraft – a companion to Crew Dragon under NASA’s Commercial Crew Program – has suffered multiple setbacks in 2019, reportedly pushing the vehicle’s uncrewed launch debut from April to NET August, a delay of at least four months. As a result, nothing short of severe anomalies during Crew Dragon hardware preparation and/or NASA’s reviews of DM-1 performance and DM-2 flight-readiness could prevent SpaceX from becoming the first commercial entity to build, launch, and operate a crewed spacecraft in the history of spaceflight.
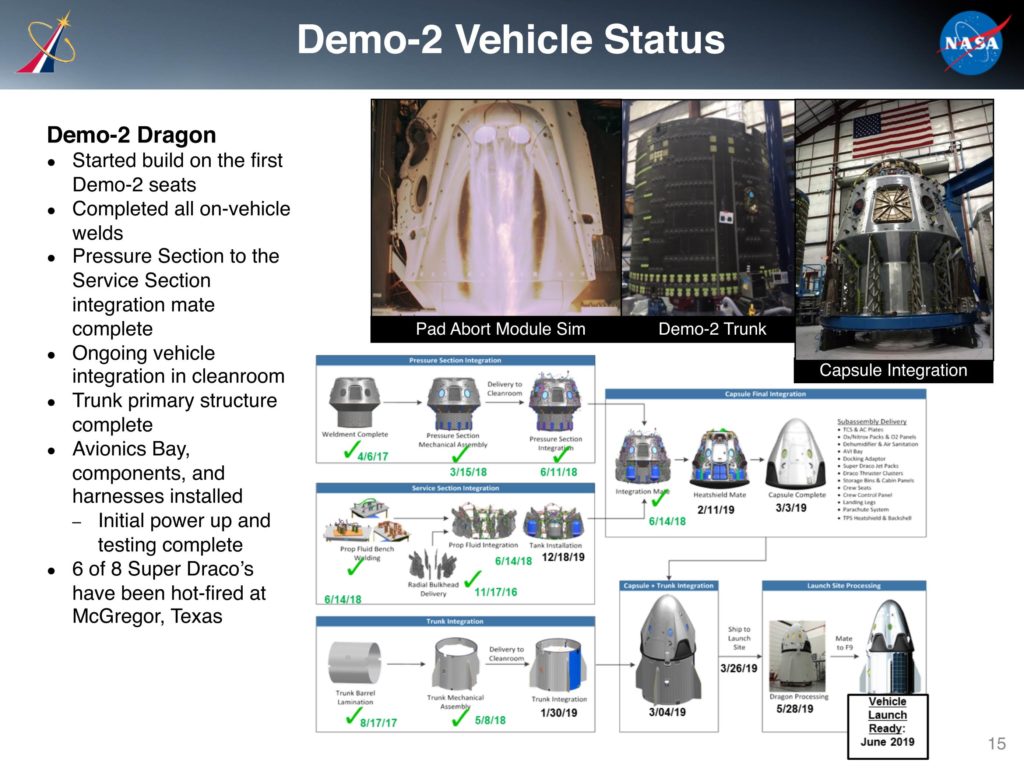

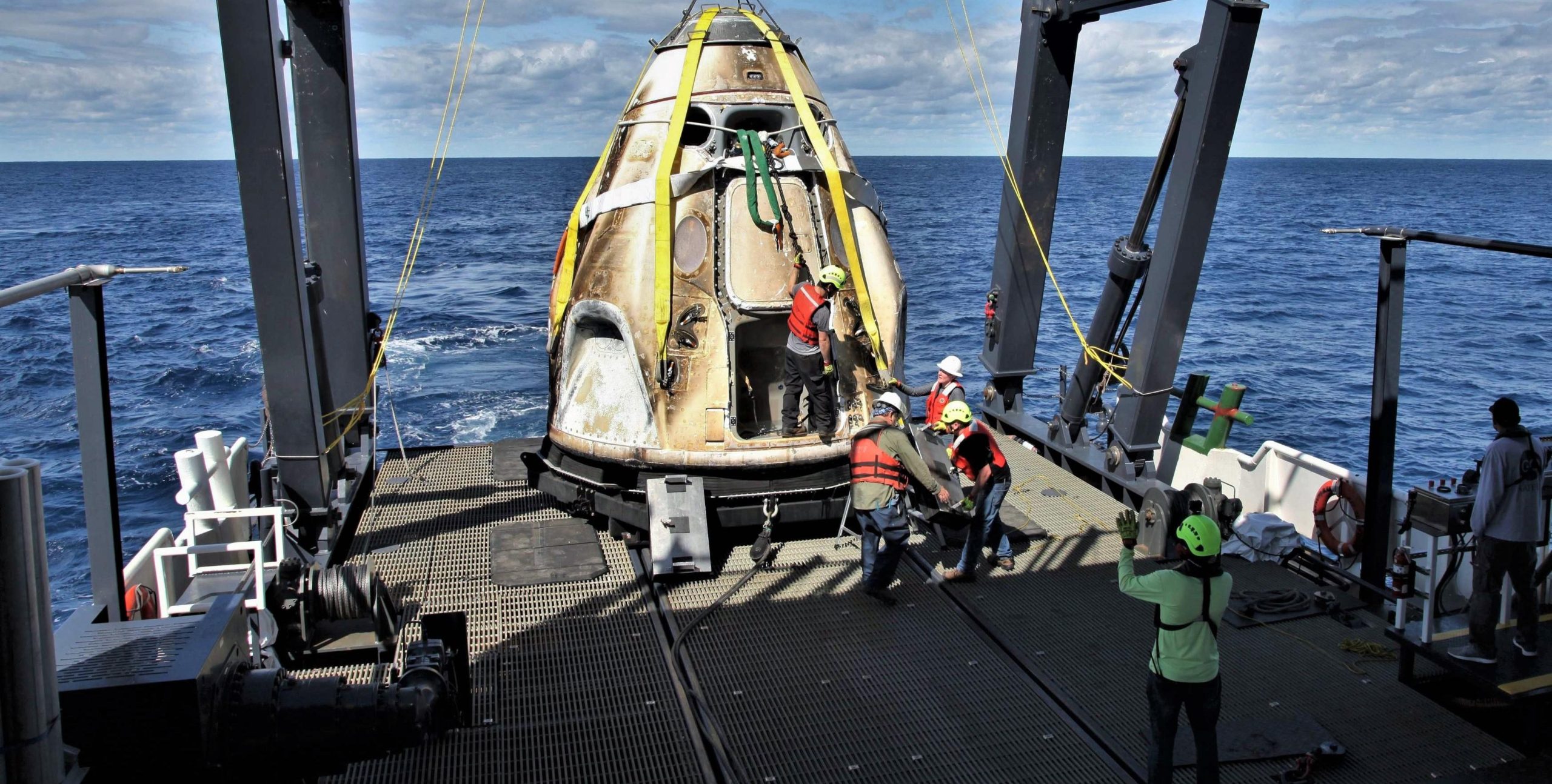
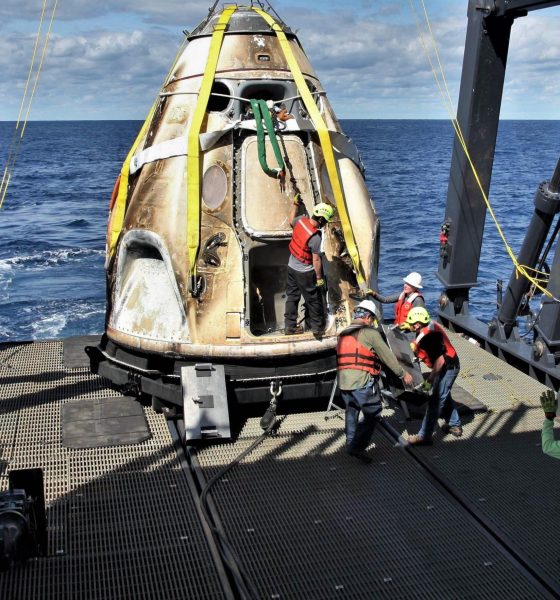
According to a December 2018 update provided during NASA’s quarterly Advisory Council meetings, the entirety of Crew Dragon DM-2’s manufacturing and integration may already be complete, with the capsule potentially heading to SpaceX’s Florida payload processing facilities later this week. NAC’s December 2018 dates did not, however, account for the DM-1 launch delays that shortly followed, plausibly impacting the completion of DM-2 integration and pad delivery to ensure that any potential anomalies experienced during Crew Dragon’s test flight could be resolved in Hawthorne, CA.
According to NASA and SpaceX, DM-2’s Crew Dragon will need to be retrofitted with thermal regulation hardware to prevent Draco thruster plumbing from freezing under a handful of specific conditions on orbit, as well as potential modifications to the craft’s parachute system and the installation of four windows instead of two. SpaceX will also need to install Crew Dragon’s first orbit-ready display and control hardware. Finally, SpaceX has opted to conduct an in-flight abort (IFA) test of Crew Dragon to verify that the spacecraft can safely carry astronauts to safety from the moment of launch to orbital insertion, a test that will have to be completed successfully and reviewed by NASA before the agency allows SpaceX to proceed with DM-2.

All of the above tasks – including major agency-wide reviews of Crew Dragon’s performance during its DM-1 debut – must be completed before SpaceX will be permitted to launch astronauts to the ISS, all of which inherently add some level of uncertainty to DM-2’s practical launch schedule. If all reviews and modifications proceed flawlessly, including a perfect in-flight abort test as early as late June, it’s possible that SpaceX and NASA could be prepared to launch Crew Dragon once more by the end of July.
In reality, it’s extremely unlikely that everything will proceed perfectly, as evidenced by the drawn-out process required for NASA and SpaceX to eventually reach flight-readiness prior to DM-1. If a significant number of challenges arise over the next few months of reviews and work, it’s not out of the question for DM-2’s launch to slip to Q4 2019 or Q1 2020. Splitting the difference, it would be safest to bet that Crew Dragon will lift off with astronauts aboard no earlier than August or September. Regardless, a great many exciting milestones are soon to come for SpaceX’s first human spaceflight program. Stay tuned as SpaceX prepares to ship the second flightworthy Crew Dragon to Florida.
Check out Teslarati’s Marketplace! We offer Tesla accessories, including for the Tesla Cybertruck and Tesla Model 3.

Elon Musk
Musk bankers looking to trim xAI debt after SpaceX merger: report
xAI has built up $18 billion in debt over the past few years, with some of this being attributed to the purchase of social media platform Twitter (now X) and the creation of the AI development company. A new financing deal would help trim some of the financial burden that is currently present ahead of the plan to take SpaceX public sometime this year.

Elon Musk’s bankers are looking to trim the debt that xAI has taken on over the past few years, following the company’s merger with SpaceX, a new report from Bloomberg says.
xAI has built up $18 billion in debt over the past few years, with some of this being attributed to the purchase of social media platform Twitter (now X) and the creation of the AI development company. Bankers are trying to create some kind of financing plan that would trim “some of the heavy interest costs” that come with the debt.
The financing deal would help trim some of the financial burden that is currently present ahead of the plan to take SpaceX public sometime this year. Musk has essentially confirmed that SpaceX would be heading toward an IPO last month.
The report indicates that Morgan Stanley is expected to take the leading role in any financing plan, citing people familiar with the matter. Morgan Stanley, along with Goldman Sachs, Bank of America, and JPMorgan Chase & Co., are all expected to be in the lineup of banks leading SpaceX’s potential IPO.
Since Musk acquired X, he has also had what Bloomberg says is a “mixed track record with debt markets.” Since purchasing X a few years ago with a $12.5 billion financing package, X pays “tens of millions in interest payments every month.”
That debt is held by Bank of America, Barclays, Mitsubishi, UFJ Financial, BNP Paribas SA, Mizuho, and Société Générale SA.
X merged with xAI last March, which brought the valuation to $45 billion, including the debt.
SpaceX announced the merger with xAI earlier this month, a major move in Musk’s plan to alleviate Earth of necessary data centers and replace them with orbital options that will be lower cost:
“In the long term, space-based AI is obviously the only way to scale. To harness even a millionth of our Sun’s energy would require over a million times more energy than our civilization currently uses! The only logical solution, therefore, is to transport these resource-intensive efforts to a location with vast power and space. I mean, space is called “space” for a reason.”
The merger has many advantages, but one of the most crucial is that it positions the now-merged companies to fund broader goals, fueled by revenue from the Starlink expansion, potential IPO, and AI-driven applications that could accelerate the development of lunar bases.
Elon Musk
SpaceX launches Crew-12 on Falcon 9, lands first booster at new LZ-40 pad
Beyond the crew launch, the mission also delivered a first for SpaceX’s Florida recovery operations.
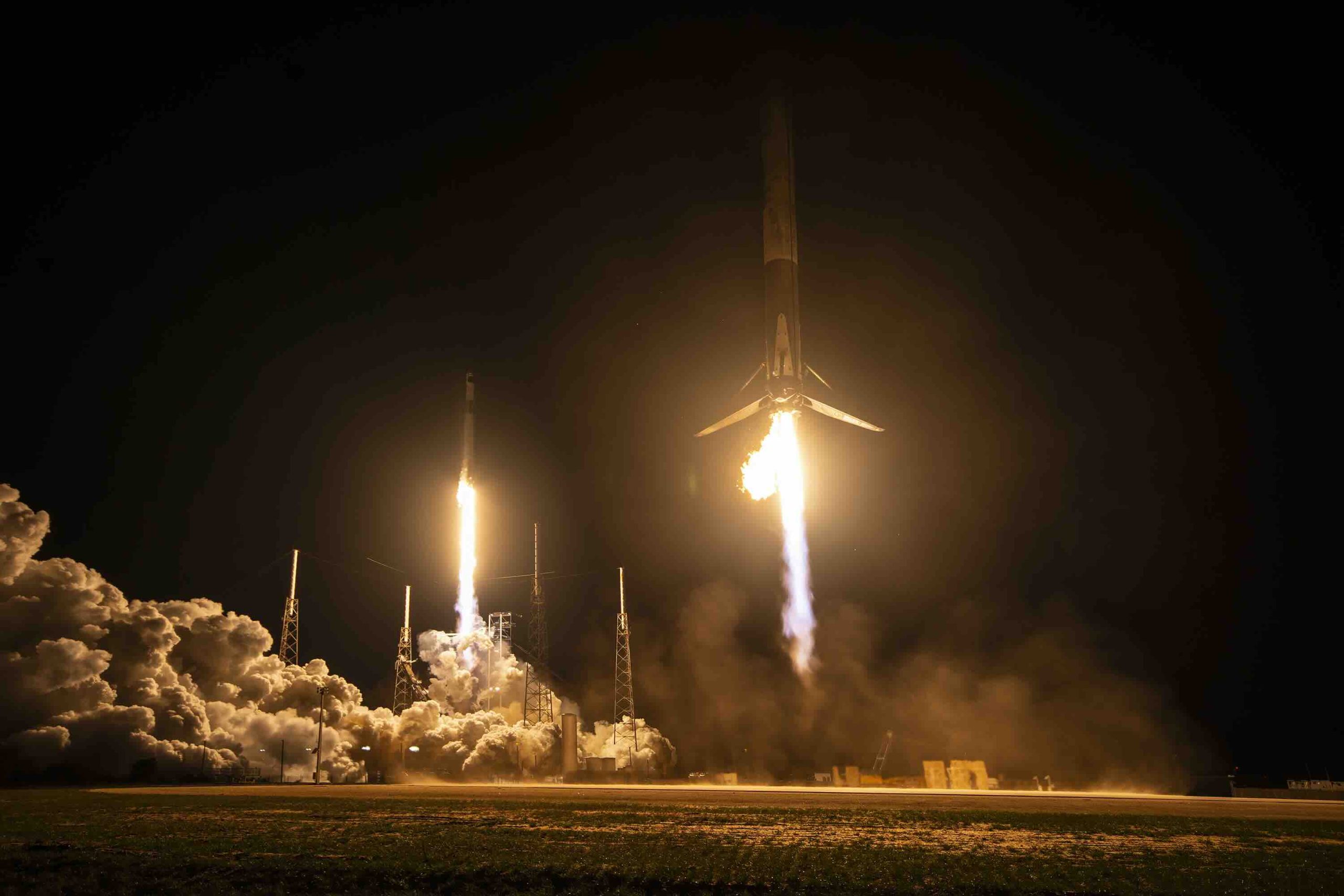

SpaceX opened February 13 with a dual milestone at Cape Canaveral, featuring a successful Crew-12 astronaut launch to the International Space Station (ISS) and the first Falcon 9 booster landing at the company’s newly designated Landing Zone 40 (LZ-40).
A SpaceX Falcon 9 lifted off at 5:15 a.m. Eastern from Space Launch Complex 40 (SLC-40) at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station, placing the Crew Dragon Freedom into orbit on the Crew-12 mission.
The spacecraft is carrying NASA astronauts Jessica Meir and Jack Hathaway, ESA astronaut Sophie Adenot, and Roscosmos cosmonaut Andrey Fedyaev, as noted in a report from Space News.
The flight marked NASA’s continued shift of Dragon crew operations to SLC-40. Historically, astronaut missions launched from Launch Complex 39A at Kennedy Space Center. NASA is moving Falcon 9 crew and cargo launches at SLC-40 to reserve 39A for Falcon Heavy missions and future Starship flights.
Crew-12 is scheduled to dock with the ISS on Feb. 14 and will remain in orbit for approximately eight months.
Beyond the crew launch, the mission also delivered a first for SpaceX’s Florida recovery operations. The Falcon 9 first stage returned to Earth and touched down at Landing Zone 40, a new pad built adjacent to SLC-40.
The site replaces Landing Zone 1, located several kilometers away, which has been reassigned by the U.S. Space Force to other launch providers. By bringing the landing area next to the launch complex, SpaceX is expected to reduce transport time and simplify processing between flights.
Bill Gerstenmaier, SpaceX’s vice president of build and flight reliability, stated that landing close to the pad keeps “launch and landing in the same general area,” improving efficiency. The company operates a similar side-by-side launch and landing configuration at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California.
Elon Musk
Starlink terminals smuggled into Iran amid protest crackdown: report
Roughly 6,000 units were delivered following January’s unrest.

The United States quietly moved thousands of Starlink terminals into Iran after authorities imposed internet shutdowns as part of its crackdown on protests, as per information shared by U.S. officials to The Wall Street Journal.
Roughly 6,000 units were delivered following January’s unrest, marking the first known instance of Washington directly supplying the satellite systems inside the country.
Iran’s government significantly restricted online access as demonstrations spread across the country earlier this year. In response, the U.S. purchased nearly 7,000 Starlink terminals in recent months, with most acquisitions occurring in January. Officials stated that funding was reallocated from other internet access initiatives to support the satellite deployment.
President Donald Trump was aware of the effort, though it remains unclear whether he personally authorized it. The White House has not issued a comment about the matter publicly.
Possession of a Starlink terminal is illegal under Iranian law and can result in significant prison time. Despite this, the WSJ estimated that tens of thousands of residents still rely on the satellite service to bypass state controls. Authorities have reportedly conducted inspections of private homes and rooftops to locate unauthorized equipment.
Earlier this year, Trump and Elon Musk discussed maintaining Starlink access for Iranians during the unrest. Tehran has repeatedly accused Washington of encouraging dissent, though U.S. officials have mostly denied the allegations.
The decision to prioritize Starlink sparked internal debate within U.S. agencies. Some officials argued that shifting resources away from Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) could weaken broader internet access efforts. VPNs had previously played a major role in keeping Iranians connected during earlier protest waves, though VPNs are not effective when the actual internet gets cut.
According to State Department figures, about 30 million Iranians used U.S.-funded VPN services during demonstrations in 2022. During a near-total blackout in June 2025, roughly one-fifth of users were still able to access limited connectivity through VPN tools.
Critics have argued that satellite access without VPN protection may expose users to geolocation risks. After funds were redirected to acquire Starlink equipment, support reportedly lapsed for two of five VPN providers operating in Iran.
A State Department official has stated that the U.S. continues to back multiple technologies, including VPNs alongside Starlink, to sustain people’s internet access amidst the government’s shutdowns.








