News
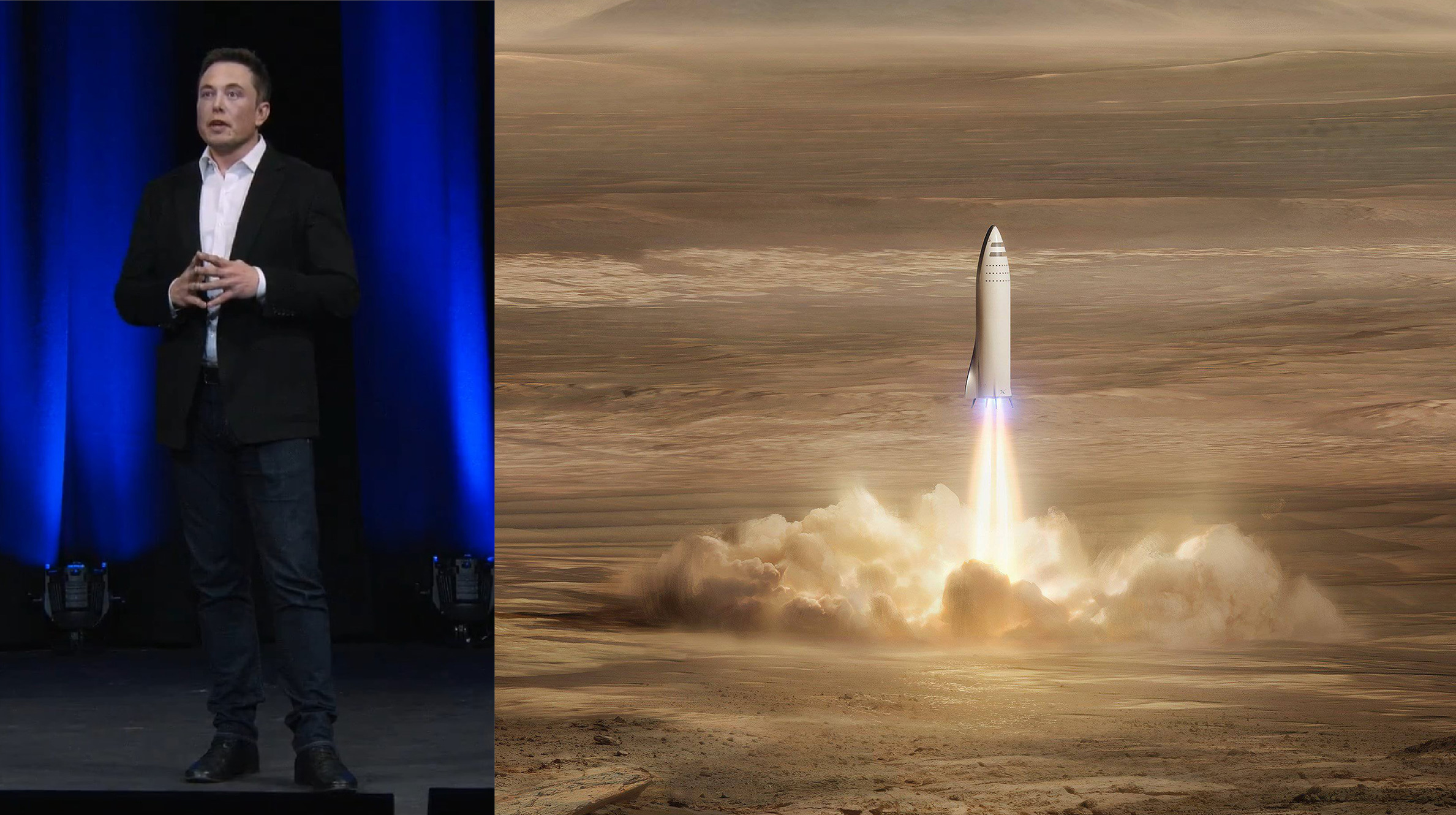
Elon Musk’s SpaceX AMA: Living on Mars, Spaceship Info, Timeline
SpaceX CEO Elon Musk hosted a Reddit AMA (Ask Me Anything) earlier this afternoon and spent several hours drinking whiskey, trolling the audience, answering some great questions, and generally having a blast. He revealed a vast array of fascinating new details about SpaceX’s giant new rocket (BFR), its upper stage spaceship (BFS), and much more.
All of Musk’s answers from the AMA have been collated and organized by category below. You’ll want to shy away from the AMA page itself, currently clocking in at more 10,000 comments.
When useful, particularly dense and technical responses have been summarized in italics for a broader audience.
Living on Mars
Q: Obviously there will be an extreme amount of care put into what is sent on the first missions, and the obvious answer of “Solar Panels” and “Fuel Production Equipment” is included, but what else?
A (Elon): Our goal is get you there and ensure the basic infrastructure for propellant production and survival is in place. A rough analogy is that we are trying to build the equivalent of the transcontinental railway. A vast amount of industry will need to be built on Mars by many other companies and millions of people.
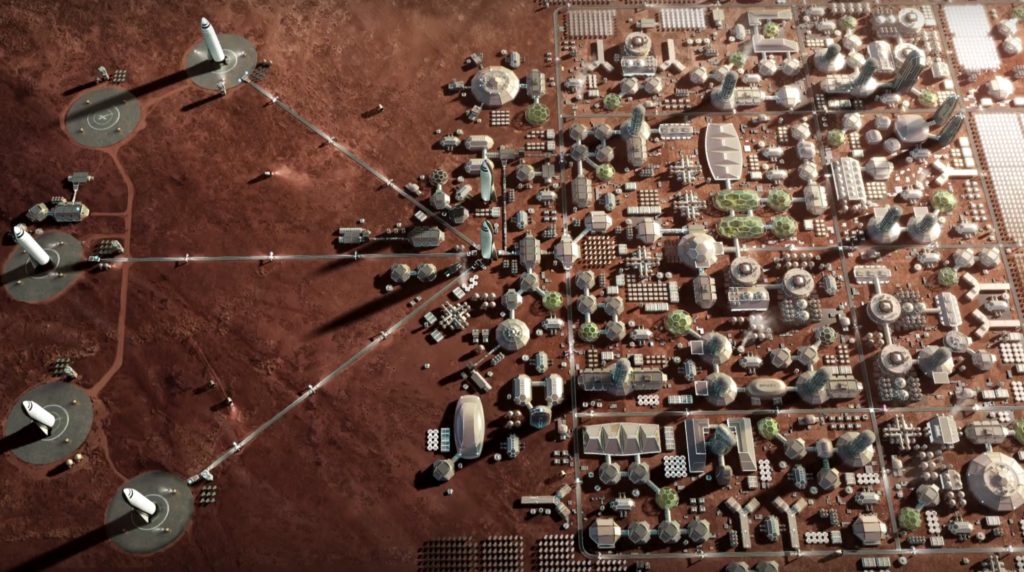
Q: Does your Mars city feature permanently anchored BFS spaceships?
A (Elon): Wouldn’t read too much into that illustration
Q: Have any candidate landing sites for the Mars base been identified?
A (Elon): Landing site needs to be low altitude to maximize aero braking, be close to ice for propellant production and not have giant boulders. Closer to the equator is better too for solar power production and not freezing your ass off.
Q: Who will design and build the ISRU system for the propellant depot, and how far along is it?
A (Elon): SpaceX. Design is pretty far along. It’s a key part of the whole system.
Without ISRU (In-Situ Resource Utilization), BFS is unlikely to ever be able to take humans to Mars affordably enough to enable large colonies. This news is thus of huge importance, and suggests that SpaceX will be able to focus on developing BFR and BFS near-term.
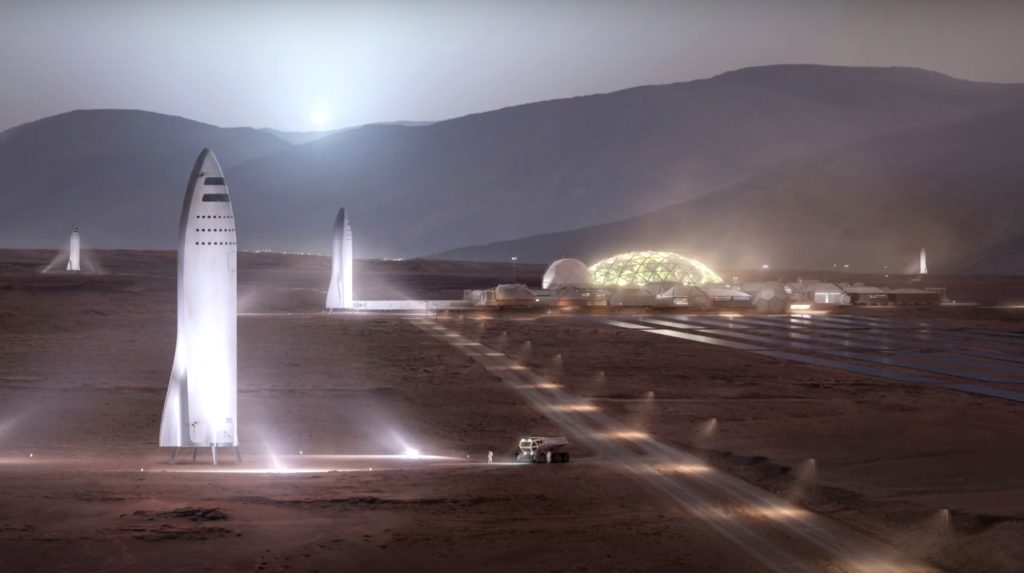

Another hypothetical SpaceX city on Mars. Bases will need to be located near water resources. (SpaceX)
SpaceX Big F** Spaceship (BFS)
Q: Will the BFS landing propellants have to be actively cooled on the long trip to Mars?
A (Elon): The main tanks will be vented to vacuum, the outside of the ship is well insulated (primarily for reentry heating) and the nose of the ship will be pointed mostly towards the sun, so very little heat is expected to reach the header tanks. That said, the propellant can be cooled either with a small amount of evaporation. Down the road, we might add a cryocooler.
A (Elon): exactly (while methane could be kept in its liquid form solely through high pressure storage, the pressures required are immense and would require tanks that would be far too heavy for a rocket’s second stage.
Cold liquid oxygen and methane will unavoidably warm up over time, eventually returning to their gaseous forms if allowed. SpaceX’s solution for BFS, which will spend several months between Earth and Mars, is to rely on the Ship’s already great insulation, as well as minimal evaporative cooling (similar to how swamp coolers work).
Q: Will the BFS heat shield be mounted on the skin, or embedded?
A (Elon): The heat shield plates will be mounted directly to the primary tank wall. That’s the most mass efficient way to go. Don’t want to build a box in box.

Dragon 2’s PICA-X heat shield can be seen on the right. BFS’s heat shield will be made of the same material, albeit on a much larger scale. (SpaceX)
Q: Can the BFS delta wings and heat shield be removed for deep space missions?
A (Elon): Wouldn’t call what BFS has a delta wing. It is quite small (and light) relative to the rest of the vehicle and is never actually used to generate lift in the way that an aircraft wing is used.
Its true purpose is to “balance out” the ship, ensuring that it doesn’t enter engines first from orbit (that would be really bad), and provide pitch and yaw control during reentry.
Q: Why is the 2017 BFS spaceship largely cylindrical?
A (Elon): Best mass ratio is achieved by not building a box in a box. The propellant tanks need to be cylindrical to be remotely mass efficient and they have to carry ascent load, so lowest mass solution is just to mount the heat shield plates directly to the tank wall.
For a rocket, mass ratio refers to its weight with a full load of propellant divided by its weight while completely empty. The lighter a rocket’s structure, the more mass it can lift into a given orbit.
- SpaceX’s conceptual Interplanetary Transport System from 2016 was considerably larger and more structurally complex than 2017’s BFR. (SpaceX)
- The relatively cylindrical BFS reduces complexity and lowers weight. (SpaceX)
Q: How does the BFS achieve vertical stabilization, without a tail?
A (Elon): Tails are lame
A (Elon): +1 (The space shuttle’s vertical stabilizer was completely useless for most of the reentry profile, as it was in complete aerodynamic shadow. I think it’s clear a craft doesn’t need one for reentry, only for subsonic gliding, which BFS doesn’t really do.)
BFS doesn’t need a tail because tails add weight, are of little use during orbital reentry, and BFS is not intended to glide.
Q: Why was the number of BFS landing legs increased from 3 to 4?
A (Elon): Because 4
A (Elon): Improves stability in rough terrain
Q: How is the radiation shielding in the ITS?
A (Elon): Ambient radiation damage is not significant for our transit times. Just need a solar storm shelter, which is a small part of the ship. Buzz Aldrin is 87.
While radiation fearmongers may balk at this statement, it is to some extent true. The risks from radiation (PDF) for a six month journey in deep space are approximately similar to several dozen CT scans, while two years spent on the surface of Mars with little to no shielding would result in about the same amount of exposure. Underground habitats could alleviate a considerable amount of the risk from living on Mars’ surface.
The issues and dangers posed by radiation ought not be trivialized but they can be dealt with, particularly if BFR can deliver massive payloads to the planet.
Q: Why was the location and shape of the BFS header/landing tanks changed?
A (Elon): The aspiration by the change was to avoid/minimize plumbing hell, but we don’t super love the current header tank/plumbing design. Further refinement is likely.
Header tanks refer to smaller tanks contained within the main propellant tanks that are used to ignite engines in microgravity. It’s easier to pressurize or simply fill the smaller tanks than it is to do so with the massive main tanks.
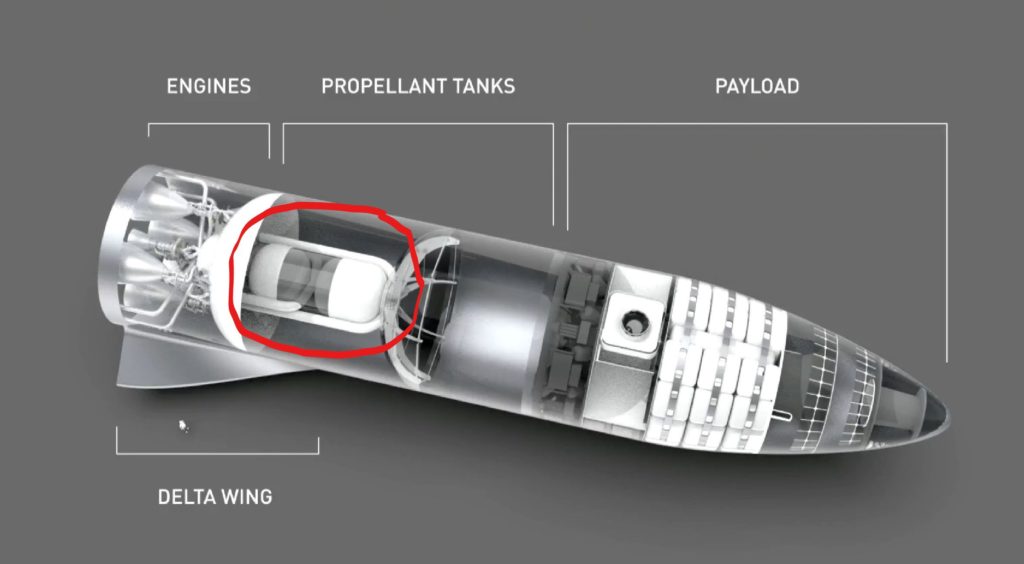
BFS’ header tanks circled in red. (SpaceX)
BFS Tanker
Q: Will the BFS tanker’s payload section be empty, or include extra propellant tanks?
A (Elon): At first, the tanker will just be a ship with no payload. Down the road, we will build a dedicated tanker that will have an extremely high full to empty mass ratio (warning: it will look kinda weird).
Using one version of the BFS as both a tanker and ship will streamline the initial development process for the rocket.
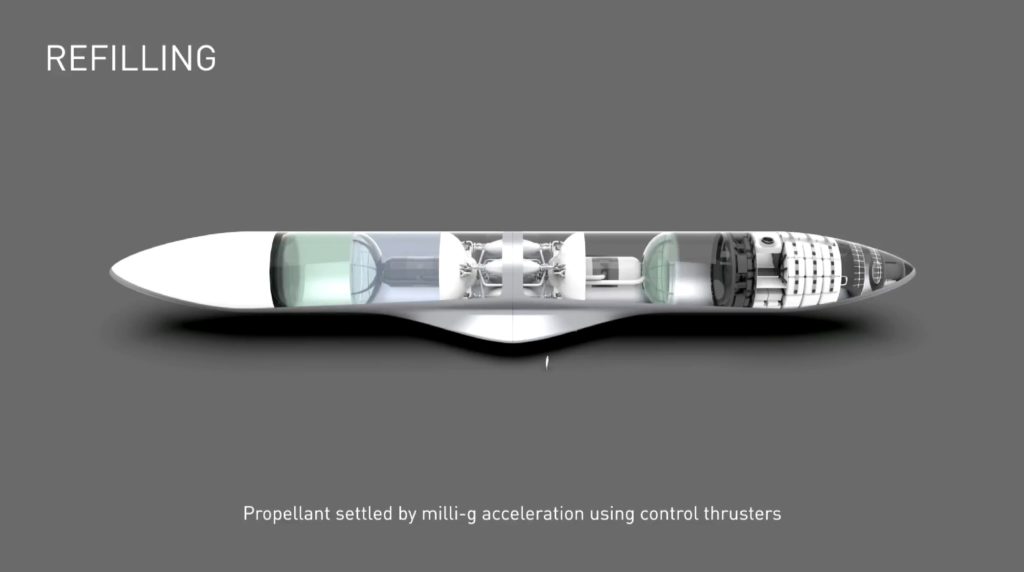

Two Spaceships docked for refuelling. (SpaceX)
Q: Will the BFS tanker ships (have to) do a hoverslam landing?
A (Elon): Landing will not be a hoverslam, depending on what you mean by the “slam” part. Thrust to weight of 1.3 will feel quite gentle. The tanker will only feel the 0.3 part, as gravity cancels out the 1. Launch is also around 1.3 T/W, so it will look pretty much like a launch in reverse….
BFS will land relatively gently, and BFR’s liftoff will also be gentle.
Development schedule
Q: With the first two cargo missions scheduled to land on Mars in 2022, what kind of development progress can we expect to see from SpaceX in the next 5 or so years leading up to the maiden flight?
Will we see BFS hops or smaller test vehicles similar to Grasshopper/F9R-Dev? Facilities being built? Propellant plant testing? etc. etc.
A (Elon): A lot. Yes, yes, and yes.
A (Elon): Will be starting with a full-scale Ship doing short hops of a few hundred kilometers altitude and lateral distance. Those are fairly easy on the vehicle, as no heat shield is needed, we can have a large amount of reserve propellant and don’t need the high area ratio, deep space Raptor engines.
Next step will be doing orbital velocity Ship flights, which will need all of the above. Worth noting that BFS is capable of reaching orbit by itself with low payload, but having the BF Booster increases payload by more than an order of magnitude. Earth is the wrong planet for single stage to orbit. No problemo on Mars.
The first real tests of the BFR will be done by hopping a full-scale BFS “several hundred kilometers”. BFS is capable of launching itself and a tiny payload into orbit, but the utility is limited on Earth. On Mars, BFS will be far more capable as a single stage to orbit (SSTO) launch vehicle.
- F9R-dev, used to test vertical take off and landing for Falcon 9. BFR will go through a similar program with its spaceship upper stage prior to orbital missions. (Steve Jurvetson)
- F9R sadly suffered a software bug and self-destructed in 2014, but SpaceX had already learned most of what it needed to begin Falcon 9 recoveries. (Steve Jurvetson)
Raptor and rocket propulsion
Q: Why was Raptor thrust reduced from ~300 tons-force to ~170 tons-force?
A (Elon): We chickened out. The engine thrust dropped roughly in proportion to the vehicle mass reduction from the first IAC talk. In order to be able to land the BF Ship with an engine failure at the worst possible moment, you have to have multiple engines. The difficulty of deep throttling an engine increases in a non-linear way, so 2:1 is fairly easy, but a deep 5:1 is very hard. Granularity is also a big factor. If you just have two engines that do everything, the engine complexity is much higher and, if one fails, you’ve lost half your power. Btw, we modified the BFS design since IAC to add a third medium area ratio Raptor engine partly for that reason (lose only 1/3 thrust in engine out) and allow landings with higher payload mass for the Earth to Earth transport function.
The Raptor engine’s maximum thrust has been decreased mainly because the size of the rocket decreased, from 12m to 9m in diameter. For redundancy’s sake, SpaceX has added a third central engine to the spaceship, versus the two engines mentioned at the 2017 IAC.
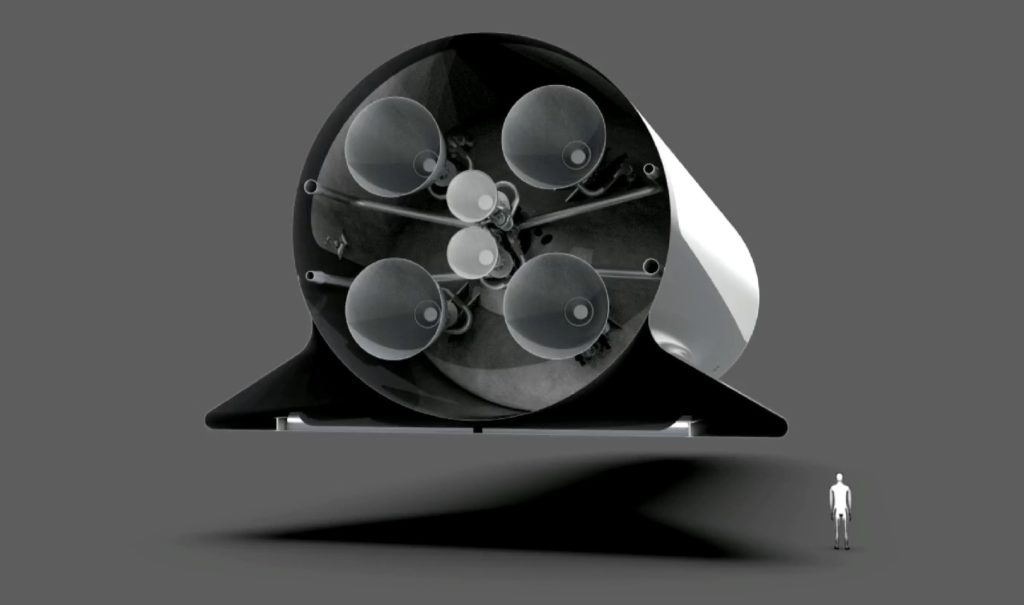

BFS’ delta “wings” from the rear of the ship. Also shown are the Raptors, with the two in the center now reportedly expanded to three engines. (SpaceX)
Q: Will the BFR autogenous pressurization system be heat exchanger based?
A (Elon): We plan to use the Incendio spell from Harry Potter
A (Elon): But, yes and probably
Autogenous pressurization refers to the method of propellant tank pressurization used. In microgravity conditions, tanks must be pressurized to keep fuel flowing to the engines and to improve the density of the fuel. While Falcon 9 currently uses high-pressure helium, ITS and now BFR have been designed to use the actual propellant in their tanks (methane and oxygen) for pressurization. This reduces the number of failure modes on BFR and improves the spaceship’s payload capabilities.
Q: Will the BFS methalox control thrusters be derived from Raptor or from SuperDraco engines?
A (Elon): The control thrusters will be closer in design to the Raptor main chamber than SuperDraco and will be pressure-fed to enable lowest possible impulse bit (no turbopump spin delay).
Like Falcon 9, BFR will need gas thrusters (RCS, reaction control system) to control its orientation (and refuel) while in microgravity conditions. While Falcon uses cold nitrogen gas thrusters, BFR will utilize the propellant it is already carrying for Raptor, methane and oxygen. Again, the goal of this is to reduce complexity.
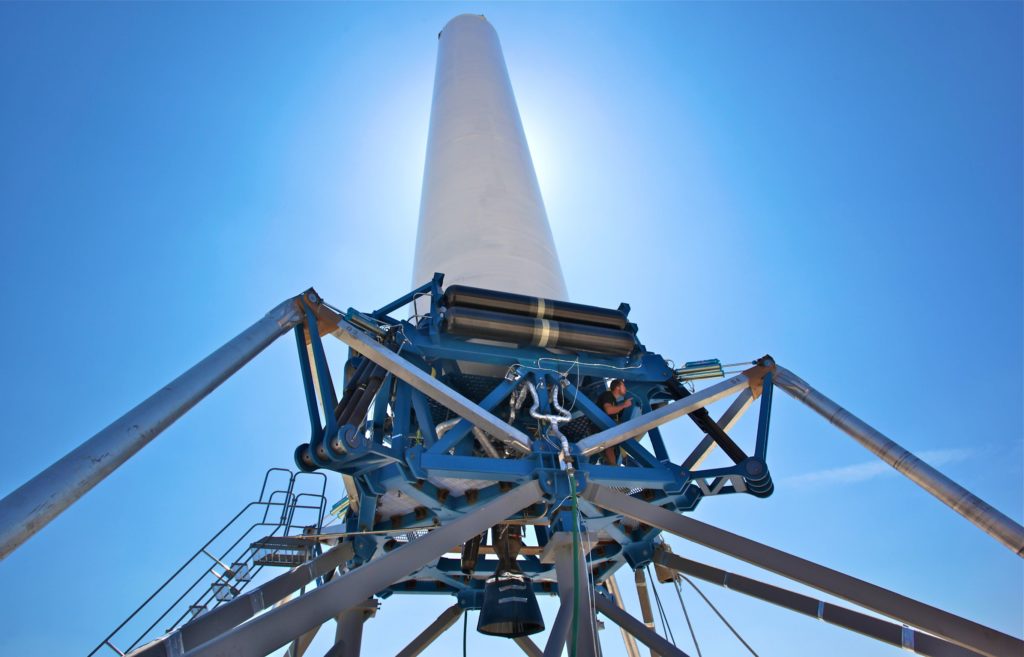
Q: Could you update us on the status of scaling up the Raptor prototype to the final size?
A (Elon): Thrust scaling is the easy part. Very simple to scale the dev Raptor to 170 tons.
The flight engine design is much lighter and tighter, and is extremely focused on reliability. The objective is to meet or exceed passenger airline levels of safety. If our engine is even close to a jet engine in reliability, has a flak shield to protect against a rapid unscheduled disassembly and we have more engines than the typical two of most airliners, then exceeding airline safety should be possible.
That will be especially important for point to point journeys on Earth. The advantage of getting somewhere in 30 mins by rocket instead of 15 hours by plane will be negatively affected if “but also, you might die” is on the ticket.
SpaceX’s subscale Raptor, the one seen in videos and photos of it firing, is understood to be a bit more than half the size of the operational engine described at IAC 2017. Increasing the scale of the engine is not the difficult aspect of development. Rather, optimization, weight reduction, and extreme reusability are the main sources of difficulty needed before Raptor is flight-ready. This reusability is central to the goal of reliable and rapid reuse of orbital-class rockets.
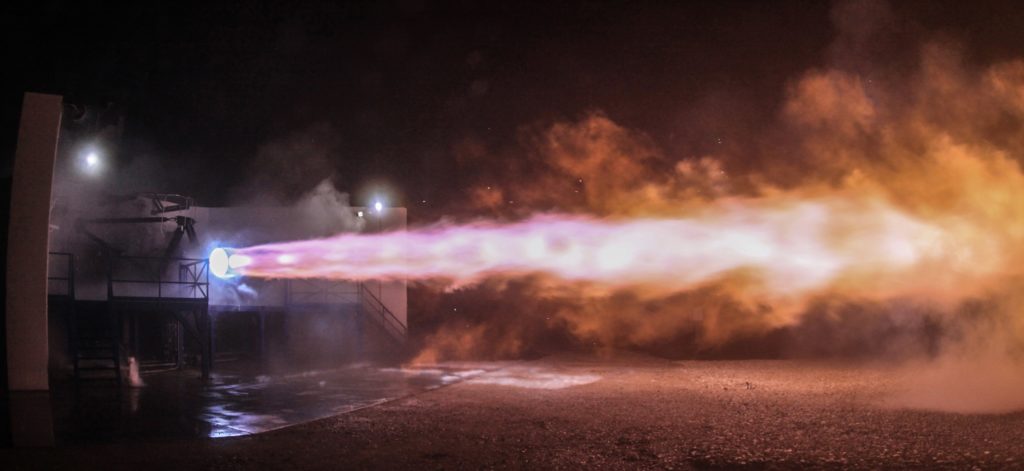
- SpaceX revealed this stunning photo of Raptor’s first (partial) hot-fire test the night before Musk’s talk at Guadalajara. (SpaceX)
- SpaceX’s subscale Raptor engine has completed more than 1200 seconds of testing in less than two years. (SpaceX)
Q: Can BFS vacuum-Raptors be fired at sea level pressure?
A: The “vacuum” or high area ratio Raptors can operate at full thrust at sea level. Not recommended.
Put simply, vacuum nozzles do not like to operate in an atmosphere.
Mars communications
Q: Does SpaceX have any interest in putting more satellites in orbit around Mars (or even rockets) for internet/communications before we get feet on the ground? Or are the current 5-6 active ones we have there sufficient?
A (Elon): Yes
Q: Also will there be some form of an internet or communications link with Earth? Is SpaceX going to be in charge of putting this in or are you contracting some other companies?
A (Elon): If anyone wants to build a high bandwidth comm link to Mars, please do.
Taken side by side, this likely indicates that SpaceX will develop a high-bandwidth Mars-Earth communications link if nobody else does, but that they would logical prefer that someone else builds that infrastructure beforehand.
Q: The concept of an internet connection on Mars is kinda awesome. You could theoretically make an internet protocol that would mirror a subset of the internet near Mars. A user would need to queue up the parts of the internet they wanted available and the servers would sync the relevant data.
A (Elon): Nerd
A (Elon): But, yes, it would make sense to strip the headers out and do a UDP-style feed with extreme compression and a CRC check to confirm the packet is good, then do a batch resend of the CRC-failed packets. Something like that. Earth to Mars is over 22 light-minutes at max distance.
A (Elon): 3 light-minutes at closest distance. So you could Snapchat, I suppose. If that’s a thing in the future.
The communication delay between Earth and Mars (at least several minutes one-way) will prevent any Martian habitats from simply integrating with Earth’s Internet. The delay will require some sort of mediation. As an example, a user on Mars could select the websites they want to browse or videos they want to watch beforehand, and they would be available between several minutes and an hour later.

SpaceX’s Starlink satellite constellation efforts could provide the company with valuable experience that can be applied around Mars. (unofficial logo by Eric Ralph)
Boring!
Q: Boring question about Mars:
A (Elon): More boring!
Miscellaneous silliness
Q: This is one bizarre AMA so far…
A (Elon): Just wait…
Q: i feel like thats a threat. “just wait. it will get way more bizarre than that. let me finish my whiskey”
A (Elon): How did you know? I am actually drinking whiskey right now. Really.
…No comment…
All things considered, this was a wildly successful AMA. Elon clearly had a whole lot of fun, the audience got lightheartedly trolled, and SpaceX fans will undoubtedly be chewing over the technical details he elucidated for weeks to come. Special thanks are owed to the subreddit /r/SpaceX and user /u/_Rocket_, who together managed to flood the AMA with an array of intelligent, pointed, and reasonable questions, at least ten of which were answered by Musk.

Elon Musk
What is Digital Optimus? The new Tesla and xAI project explained
At its core, Digital Optimus operates through a dual-process architecture inspired by human cognition.
Tesla and xAI announced their groundbreaking joint project, Digital Optimus, also nicknamed “Macrohard” in a humorous jab at Microsoft, earlier this week.
This software-based AI agent is designed to automate complex office workflows by observing and replicating human interactions with computers. As the first major outcome of Tesla’s $2 billion investment in xAI, it represents a powerful fusion of hardware efficiency and advanced reasoning.
At its core, Digital Optimus operates through a dual-process architecture inspired by human cognition.
Macrohard or Digital Optimus is a joint xAI-Tesla project, coming as part of Tesla’s investment agreement with xAI.
Grok is the master conductor/navigator with deep understanding of the world to direct digital Optimus, which is processing and actioning the past 5 secs of…
— Elon Musk (@elonmusk) March 11, 2026
Tesla’s specialized AI acts as “System 1”—the fast, instinctive executor—processing the past five seconds of real-time computer screen video along with keyboard and mouse actions to perform immediate tasks.
xAI’s Grok model serves as “System 2,” the strategic “master conductor” or navigator, providing high-level reasoning, world understanding, and directional oversight, much like an advanced turn-by-turn navigation system.
When combined, the two can create a powerful AI-based assistant that can complete everything from accounting work to HR tasks.
Will Tesla join the fold? Predicting a triple merger with SpaceX and xAI
The system runs primarily on Tesla’s low-cost AI4 inference chip, minimizing expensive Nvidia resources from xAI for competitive, real-time performance.
Elon Musk described it as “the only real-time smart AI system” capable, in principle, of emulating the functions of entire companies, handling everything from accounting and HR to repetitive digital operations.
Timelines point to swift deployment. Announced just days ago, Musk expects Digital Optimus to be ready for user experience within about six months, targeting rollout around September 2026.
It will integrate into all AI4-equipped Tesla vehicles, enabling parked cars to handle office work during downtime. Millions of dedicated units are also planned for deployment at Supercharger stations, tapping into roughly 7 gigawatts of available power.
Oh and it works in all AI4-equipped cars, so your car can do office work for you when not driving.
We’re also deploying millions of dedicated Digital Optimus units in the field at Superchargers where we have ~7 gigawatts of available power.
— Elon Musk (@elonmusk) March 12, 2026
Digital Optimus directly supports Tesla’s broader autonomy strategy. It leverages the same end-to-end neural networks, computer vision, and real-time decision-making tech that power Full Self-Driving (FSD) software and the physical Optimus humanoid robot.
By repurposing idle vehicle compute and extending AI4 hardware beyond driving, the project scales Tesla’s autonomy ecosystem from roads to digital workspaces.
As a virtual counterpart to physical Optimus, it divides labor: software agents manage screen-based tasks while humanoid robots tackle physical ones, accelerating Tesla’s vision of general-purpose AI for productivity, Robotaxi fleets, and beyond.
In essence, Digital Optimus bridges Tesla’s vehicle and robotics autonomy with enterprise-scale AI, promising massive efficiency gains. No other company currently matches its real-time capabilities on such accessible hardware.
It really could be one of the most crucial developments Tesla and xAI begin to integrate, as it could revolutionize how people work and travel.
News
Tesla adds awesome new driving feature to Model Y
Tesla is rolling out a new “Comfort Braking” feature with Software Update 2026.8. The feature is exclusive to the new Model Y, and is currently unavailable for any other vehicle in the Tesla lineup.

Tesla is adding an awesome new driving feature to Model Y vehicles, effective on Juniper-updated models considered model year 2026 or newer.
Tesla is rolling out a new “Comfort Braking” feature with Software Update 2026.8. The feature is exclusive to the new Model Y, and is currently unavailable for any other vehicle in the Tesla lineup.
Tesla writes in the release notes for the feature:
“Your Tesla now provides a smoother feel as you come to a complete stop during routine braking.”
🚨 Tesla has added a new “Comfort Braking” update with 2026.8
“Your Tesla provides a smoother feel as you come to a complete stop during routine braking.” https://t.co/afqCpBSVeA pic.twitter.com/C6MRmzfzls
— TESLARATI (@Teslarati) March 13, 2026
Interestingly, we’re not too sure what catalyzed Tesla to try to improve braking smoothness, because it hasn’t seemed overly abrupt or rough from my perspective. Although the brake pedal in my Model Y is rarely used due to Regenerative Braking, it seems Tesla wanted to try to make the ride comfort even smoother for owners.
There is always room for improvement, though, and it seems that there is a way to make braking smoother for passengers while the vehicle is coming to a stop.
This is far from the first time Tesla has attempted to improve its ride comfort through Over-the-Air updates, as it has rolled out updates to improve regenerative braking performance, handling while using Full Self-Driving, improvements to Steer-by-Wire to Cybertruck, and even recent releases that have combatted Active Road Noise.
Tesla holds a unique ability to change the functionality of its vehicles through software updates, which have come in handy for many things, including remedying certain recalls and shipping new features to the Full Self-Driving suite.
Tesla seems to have the most seamless OTA processes, as many automakers have the ability to ship improvements through a simple software update.
We’re really excited to test the update, so when we get an opportunity to try out Comfort Braking when it makes it to our Model Y.
News
Tesla finally brings a Robotaxi update that Android users will love
The breakdown of the software version shows that Tesla is actively developing an Android-compatible version of the Robotaxi app, and the company is developing Live Activities for Android.

Tesla is finally bringing an update of its Robotaxi platform that Android users will love — mostly because it seems like they will finally be able to use the ride-hailing platform that the company has had active since last June.
Based on a decompile of software version 26.2.0 of the Robotaxi app, Tesla looks to be ready to roll out access to Android users.
According to the breakdown, performed by Tesla App Updates, the company is preparing to roll out an Android version of the app as it is developing several features for that operating system.
🚨 It looks like Tesla is preparing to launch the Robotaxi app for Android users at last!
A decompile of v26.2.0 of the Robotaxi app shows some progress on the Android side for Robotaxi 🤖 🚗 https://t.co/mThmoYuVLy
— TESLARATI (@Teslarati) March 13, 2026
The breakdown of the software version shows that Tesla is actively developing an Android-compatible version of the Robotaxi app, and the company is developing Live Activities for Android:
“Strings like notification_channel_robotaxid_trip_name and android_native_alicorn_eta_text show exactly how Tesla plans to replicate the iOS Live Activities experience. Instead of standard push alerts, Android users are getting a persistent, dynamically updating notification channel.”
This is a big step forward for several reasons. From a face-value perspective, Tesla is finally ready to offer Robotaxi to Android users.
The company has routinely prioritized Apple releases because there is a higher concentration of iPhone users in its ownership base. Additionally, the development process for Apple is simply less laborious.
Tesla is working to increase Android capabilities in its vehicles
Secondly, the Robotaxi rollout has been a typical example of “slowly then all at once.”
Tesla initially released Robotaxi access to a handful of media members and influencers. Eventually, it was expanded to more users, so that anyone using an iOS device could download the app and hail a semi-autonomous ride in Austin or the Bay Area.
Opening up the user base to Android users may show that Tesla is preparing to allow even more users to utilize its Robotaxi platform, and although it seems to be a few months away from only offering fully autonomous rides to anyone with app access, the expansion of the user base to an entirely different user base definitely seems like its a step in the right direction.