

News
Scientists use AI neural network to translate speech from brain activity
Three recently published studies focused on using artificial intelligence (AI) neural networks to generate audio output from brain signals have shown promising results, namely by producing identifiable sounds up to 80% of the time. Participants in the studies first had their brain signals measured while they were either reading aloud or listening to specific words. All the data was then given to a neural network to “learn” how to interpret brain signals after which the final sounds were reconstructed for listeners to identify. These results represent hopeful prospects for the field of brain-computer interfaces (BCIs), where thought-based communication is quickly moving from the realm of science fiction to reality.
The idea of connecting human brains to computers is far from new. In fact, several relevant milestones have been made in recent years including enabling paralyzed individuals to operate tablet computers with their brain waves. Elon Musk has also famously brought attention to the field with Neuralink, his BCI company that essentially hopes to merge human consciousness with the power of the Internet. As brain-computer interface technology expands and develops new ways to foster communication between brains and machines, studies like these, originally highlighted by Science Magazine, will continue demonstrating the steady march of progress.
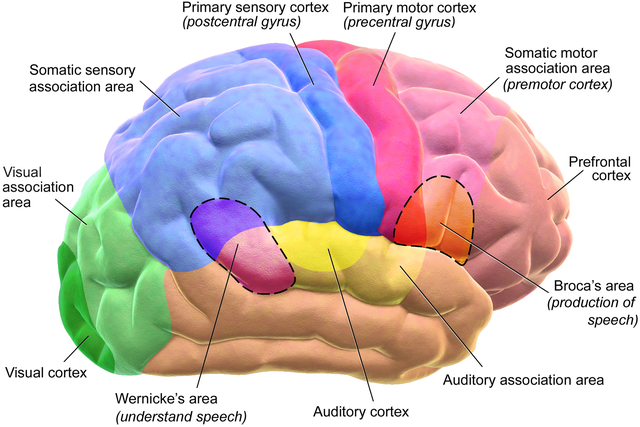
In the first study conducted by researchers from Columbia University and Hofstra Northwell School of Medicine, both in New York, five epileptic participants had the brain signals from their auditory cortexes recorded as they listened to stories and numbers being read to them. The signal data was provided to a neural network for analysis which then reconstructed audio files that were accurately identified by participating listeners 75% of the time.
In the second study conducted by a team from the University of Bremen (Germany), Maastricht University (Netherlands), Northwestern University (Illinois), and Virginia Commonwealth University (Virginia), brain signal data was gathered from six patients’ speech planning and motor areas while undergoing tumor surgeries. Each patient read specific words aloud to target the data collected. After the brain data and audio data were given to their neural network for training, the program was given brain signals not included in the training set to recreate audio, the result producing words that were recognizable 40% of the time.
Finally, in a third study by a team at the University of California, San Francisco, three participants with epilepsy read text aloud while brain activity was captured from the speech and motor areas of their brains. The audio generated from their neural network’s analysis of the signal readings was presented to a group of 166 people who were asked to identify the sentences from a multiple choice test – some sentences were identified with 80% accuracy.
While the research presented in these studies shows serious progress towards connecting human brains to computers, there are still a few significant hurdles. For one, the way neuron signal patterns in the brain translate into sounds varies from person to person, so neural networks must be trained on each individual person. The best results require the best data possible, i.e., the most precise neuron signals possible, meaning this is something that can only be obtained by placing electrodes in the brain itself. The opportunities to collect data at this invasive level for research are limited, relying on voluntary participation and approval of experiments.
All three of the studies highlighted demonstrated an ability to reconstruct speech based on neural data in some significant capacity; however, also in all cases, the study participants were able to create audible sounds to use with the computer training set. In the case of patients unable to speak, the level of difficultly in interpreting the brain’s speech signals from other signals will be the biggest challenge. Also, the differences between brain signals during actual speech vs. thinking about speech will complicate matters further.

Cybertruck
Tesla drops latest hint that new Cybertruck trim is selling like hotcakes
According to Tesla’s Online Design Studio, the new All-Wheel-Drive Cybertruck will now be delivered in April 2027. Earlier orders are still slated for early this Summer, but orders from here on forward are now officially pushed into next year:

Tesla’s new Cybertruck offering has had its delivery date pushed back once again. This is now the second time, and deliveries for the newest orders are now pushed well into 2027.
According to Tesla’s Online Design Studio, the new All-Wheel-Drive Cybertruck will now be delivered in April 2027. Earlier orders are still slated for early this Summer, but orders from here on forward are now officially pushed into next year:
🚨 Tesla has updated the $59,990 Cybertruck Dual Motor AWD’s estimated delivery date to April 2027.
First deliveries are still slated for June, but if you order it now, you’ll be waiting over a year.
Demand appears to be off the charts for the new Cybertruck and consumers are… pic.twitter.com/raDCCeC0zP
— TESLARATI (@Teslarati) February 26, 2026
Just three days ago, the initial delivery date of June 2026 was pushed back to early Fall, and now, that date has officially moved to April 2027.
The fact that Tesla has had to push back deliveries once again proves one of two things: either Tesla has slow production plans for the new Cybertruck trim, or demand is off the charts.
Judging by how Tesla is already planning to raise the price based on demand in just a few days, it seems like the company knows it is giving a tremendous deal on this spec of Cybertruck, and units are moving quickly.
That points more toward demand and not necessarily to slower production plans, but it is not confirmed.
Tesla Cybertruck’s newest trim will undergo massive change in ten days, Musk says
Tesla is set to hike the price on March 1, so tomorrow will be the final day to grab the new Cybertruck trim for just $59,990.
It features:
- Dual Motor AWD w/ est. 325 mi of range
- Powered tonneau cover
- Bed outlets (2x 120V + 1x 240V) & Powershare capability
- Coil springs w/ adaptive damping
- Heated first-row seats w/ textile material that is easy to clean
- Steer-by-wire & Four Wheel Steering
- 6’ x 4’ composite bed
- Towing capacity of up to 7,500 lbs
- Powered frunk
Interestingly, the price offering is fairly close to what Tesla unveiled back in late 2019.
Elon Musk
Elon Musk outlines plan for first Starship tower catch attempt
Musk confirmed that Starship V3 Ship 1 (SN1) is headed for ground tests and expressed strong confidence in the updated vehicle design.

Elon Musk has clarified when SpaceX will first attempt to catch Starship’s upper stage with its launch tower. The CEO’s update provides the clearest teaser yet for the spacecraft’s recovery roadmap.
Musk shared the details in recent posts on X. In his initial post, Musk confirmed that Starship V3 Ship 1 (SN1) is headed for ground tests and expressed strong confidence in the updated vehicle design.
“Starship V3 SN1 headed for ground tests. I am highly confident that the V3 design will achieve full reusability,” Musk wrote.
In a follow-up post, Musk addressed when SpaceX would attempt to catch the upper stage using the launch tower’s robotic arms.
“Should note that SpaceX will only try to catch the ship with the tower after two perfect soft landings in the ocean. The risk of the ship breaking up over land needs to be very low,” Musk clarified.
His remarks suggest that SpaceX is deliberately reducing risk before attempting a tower catch of Starship’s upper stage. Such a milestone would mark a major step towards the full reuse of the Starship system.
SpaceX is currently targeting the first Starship V3 flight of 2026 this coming March. The spacecraft’s V3 iteration is widely viewed as a key milestone in SpaceX’s long-term strategy to make Starship fully reusable.
Starship V3 features a number of key upgrades over its previous iterations. The vehicle is equipped with SpaceX’s Raptor V3 engines, which are designed to deliver significantly higher thrust than earlier versions while reducing cost and weight.
The V3 design is also expected to be optimized for manufacturability, a critical step if SpaceX intends to scale the spacecraft’s production toward frequent launches for Starlink, lunar missions, and eventually Mars.
News
Tesla FSD (Supervised) could be approved in the Netherlands next month: Musk
Musk shared the update during a recent interview at Giga Berlin.

Tesla CEO Elon Musk shared that Full Self-Driving (FSD) could receive regulatory approval in the Netherlands as soon as March 20, potentially marking a major step forward for Tesla’s advanced driver-assistance rollout in Europe.
Musk shared the update during a recent interview at Giga Berlin, noting that the date was provided by local authorities.
“Tesla has the most advanced real-world AI, and hopefully, it will be approved soon in Europe. We’re told by the authorities that March 20th, it’ll be approved in the Netherlands,’ what I was told,” Musk stated.
“Hopefully, that date remains the same. But I think people in Europe are going to be pretty blown away by how good the Tesla car AI is in being able to drive.”
Tesla’s FSD system relies on vision-based neural networks trained on real-world driving data, allowing vehicles to navigate using cameras and AI rather than traditional sensor-heavy solutions.
The performance of FSD Supervised has so far been impressive. As per Tesla’s safety report, Full Self-Driving Supervised has already traveled 8.3 billion miles. So far, vehicles operating with FSD Supervised engaged recorded one major collision every 5,300,676 miles.
In comparison, Teslas driven manually with Active Safety systems recorded one major collision every 2,175,763 miles, while Teslas driven manually without Active Safety recorded one major collision every 855,132 miles. The U.S. average during the same period was one major collision every 660,164 miles.
If approval is granted on March 20, the Netherlands could become the first European market to greenlight Tesla’s latest supervised FSD (Supervised) software under updated regulatory frameworks. Tesla has been working to secure expanded FSD access across Europe, where regulatory standards differ significantly from those in the United States. Approval in the Netherlands would likely serve as a foundation for broader EU adoption, though additional country-level clearances may still be required.








