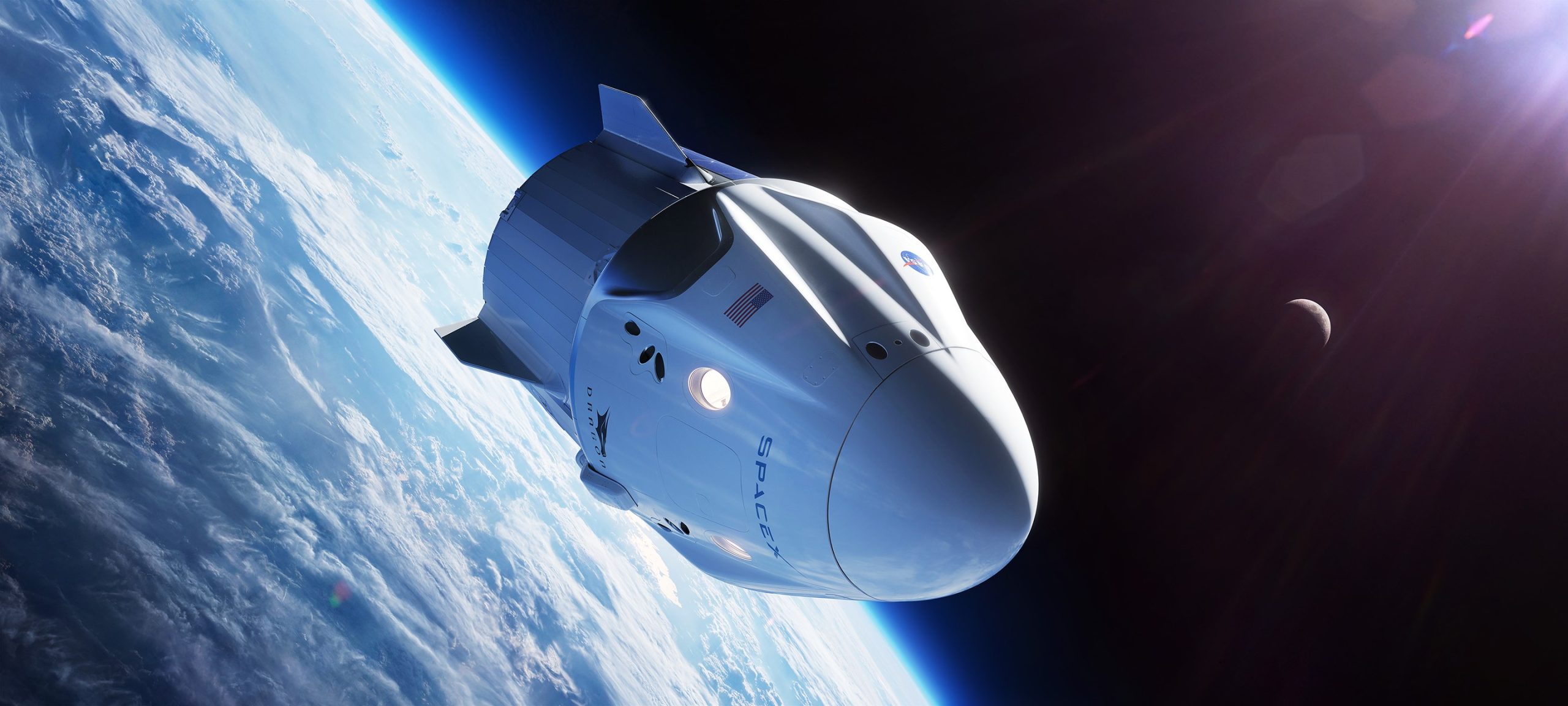


SpaceX
SpaceX’s Crew Dragon and Falcon 9 Block 5 rocket are almost ready for astronauts
In a Commercial Crew update presented by Program Manager Kathy Lueders to the NASA Advisory Council (NAC), the agency has confirmed that SpaceX is deep into the final stages of hardware preparation and testing ahead of their first uncrewed and crewed demonstrations launches of Crew Dragon.
Barring a miracle for Commercial Crew Program partner Boeing’s Starliner spacecraft program or serious faults leading up to SpaceX’s own debuts, SpaceX is all but guaranteed to become the first private company in history to design, build, and launch a spacecraft into Earth orbit with real astronauts onboard.
PICTURE OF B1051!!! It will ship to the Cape from McGregor soon.
Solar panel array on the trunk for the DM-1 capsule will take place in Hawthorne. pic.twitter.com/K82GANn5zr
— Michael Baylor (@MichaelBaylor_) August 27, 2018
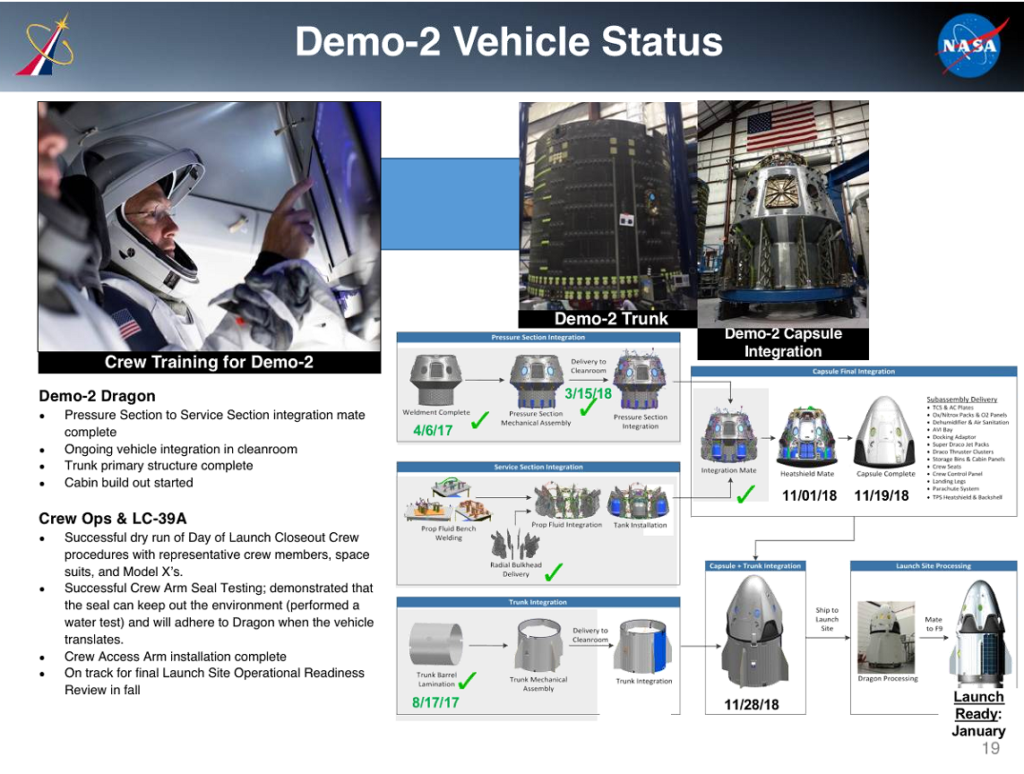
SpaceX’s DM-1 Crew Dragon (serial number C201; “C” for capsule, “2” for Dragon 2, and “01” for capsule #1) capsule is already in Florida at one of the company’s spacecraft processing facilities, while that vehicle’s trunk segment – a module mounted below the capsule responsible for providing power (solar arrays), thermal regulation (radiator panels), and external cargo lift capacity – is scheduled to ship from Hawthorne, CA to Florida by the end of September. Demonstration Mission-1 (DM-1) is currently targeting a launch debut no earlier than November 2018.
DM-1’s Falcon 9 launch vehicle, booster B1051 and an expendable second stage, are also making significant progress towards the Crew Dragon’s uncrewed debut launch. NASA’s report noted that B1051 was on track for shipment (presumably to the Cape) sometime in the fall (technically anytime after August 31st) and that the upper stage would likely find its way to Florida soon after, sometime in September. Due to the fact that Merlin Vacuum engine qualification has not yet been completed, that milestone is likely the only thing standing between S2 shipment to FL, as SpaceX typically builds and tests both Falcon 9 segments near-simultaneously.
- One of the aforementioned balloon-drop parachute tests. (SpaceX)
- The DM-1 Crew Dragon capsule soon after completion. (SpaceX)
- DM-1 seen conducting acoustic testing in Ohio. (SpaceX)
- Falcon 9 B1051, DM-1’s rocket of choice, seen during construction in SpaceX’s Hawthorne factory. (SpaceX)
- B1051’s octaweb, the structure that Merlin engines attach to and thrust against. (SpaceX)
- The DM-2 Crew Dragon’s trunk module seen during production. (SpaceX)
- Crew Dragon astronauts test the capsule’s display controls. (SpaceX)
- SpaceX Crew Dragon capsule C203 – then assigned DM-2 – is seen here in August 2018. (Pauline Acalin)
Meanwhile, SpaceX has successfully completed a duo of unique and critical tests of Crew Dragon’s parachute systems, carrying a Crew Dragon mass simulator (i.e. boilerplate) up to 45,000 feet (13,700 m) under a huge balloon before dropping the mockup, a test series designed to prove out the ability of the parachute system to successfully deploy and function in the exact flight regimes the real hardware will experience while safely returning astronauts to Earth. As NASA Commercial Crew Program Manager Kathy Lueders herself noted, that type of testing is extremely difficult to pull off, but SpaceX has thus far completed two.
On the launch pad side of things, SpaceX will be exclusively conducting Crew Dragon missions from Pad 39A. The company completed installation of a strikingly modern-looking crew access arm (CAA) just days ago, marking a crucial milestone for the historic launch complex to be truly ready to support human spaceflight once more, a heritage represented physically by the tower the arm is installed on (Shuttle-era) and the pad’s foundation and thrust diverter (constructed to support Saturn V’s Apollo moon missions).
That’s right provided the two Crew Dragon test flights go well. Hardware will def be ready. https://t.co/KcAFArYn1x
— Elon Musk (@elonmusk) August 6, 2018
Further down the road, SpaceX has already entered into the late stages of hardware integration and preparation for the second Crew Dragon demonstration mission (DM-2), which will almost without a doubt see SpaceX become the first private entity in history to build, launch, and operate a crewed spacecraft in Earth orbit.
According to NASA’s SpaceX-derived schedule, that particularly historic spacecraft is expected to be ready for launch as early as January, a full three months prior to its current April 2018 launch date. CEO Elon Musk did note recently on Twitter that the hardware for both crewed and uncrewed demonstration missions would “def[initely] be ready” for the launch dates of November 2018 and April 2019.
Catch all the technical SpaceX-related slides below.
- August 27, 2018. (NASA)
- August 27, 2018. (NASA)
- August 27, 2018. (NASA)
- August 27, 2018. (NASA)
- August 27, 2018. (NASA)
For prompt updates, on-the-ground perspectives, and unique glimpses of SpaceX’s rocket recovery fleet check out our brand new LaunchPad and LandingZone newsletters!

Elon Musk
FCC chair criticizes Amazon over opposition to SpaceX satellite plan
Carr made the remarks in a post on social media platform X.

U.S. Federal Communications Commission (FCC) Chairman Brendan Carr criticized Amazon after the company opposed SpaceX’s proposal to launch a large satellite constellation that could function as an orbital data center network.
Carr made the remarks in a post on social media platform X.
Amazon recently urged the FCC to reject SpaceX’s application to deploy a constellation of up to 1 million low Earth orbit satellites that could serve as artificial intelligence data centers in space.
The company described the proposal as a “lofty ambition rather than a real plan,” arguing that SpaceX had not provided sufficient details about how the system would operate.
Carr responded by pointing to Amazon’s own satellite deployment progress.
“Amazon should focus on the fact that it will fall roughly 1,000 satellites short of meeting its upcoming deployment milestone, rather than spending their time and resources filing petitions against companies that are putting thousands of satellites in orbit,” Carr wrote on X.
Amazon has declined to comment on the statement.
Amazon has been working to deploy its Project Kuiper satellite network, which is intended to compete with SpaceX’s Starlink service. The company has invested more than $10 billion in the program and has launched more than 200 satellites since April of last year.
Amazon has also asked the FCC for a 24-month extension, until July 2028, to meet a requirement to deploy roughly 1,600 satellites by July 2026, as noted in a CNBC report.
SpaceX’s Starlink network currently has nearly 10,000 satellites in orbit and serves roughly 10 million customers. The FCC has also authorized SpaceX to deploy 7,500 additional satellites as the company continues expanding its global satellite internet network.
Elon Musk
NASA watchdog says Starship development delays could affect Artemis timeline
The report noted that several technical milestones still need to be completed before Starship can serve as a crewed lunar lander.

A NASA watchdog report stated that continued development work on SpaceX’s Starship could affect the timeline for the agency’s planned Artemis moon missions. The report noted that several technical milestones still need to be completed before the spacecraft can serve as a crewed lunar lander.
The findings were detailed in a report from NASA’s Office of Inspector General, as noted in a report from Reuters.
NASA selected SpaceX’s Starship in 2021 to serve as the Human Landing System (HLS) for its Artemis lunar program. The vehicle is intended to transport astronauts from lunar orbit to the surface of the Moon and back as part of future Artemis missions.
According to the watchdog report, Starship’s development has experienced roughly two years of schedule delays compared to earlier expectations. Still, NASA is targeting 2028 for the first crewed lunar landing using the Starship lander.
One of the most significant technical milestones for Starship’s lunar missions is in-space refueling.
To support a crewed lunar landing, multiple Starship launches will be required to deliver propellant to orbit. Tanker versions of Starship will transfer fuel to a storage depot spacecraft, which will then refuel the lunar lander.
The report noted that this approach could require more than 10 Starship launches to fully refuel the spacecraft needed for a single lunar landing mission.
NASA officials indicated that demonstrating cryogenic propellant transfer in orbit remains one of the most important technical steps before Starship can be certified for lunar missions.
SpaceX has conducted 11 Starship test flights since 2023 as the company continues developing the fully reusable launch system. A 12th test flight, this time featuring Starship V3, is expected to be held in early April.
Elon Musk
SpaceX weighs Nasdaq listing as company explores early index entry: report
The company is reportedly seeking early inclusion in the Nasdaq-100 index.

Elon Musk’s SpaceX is reportedly leaning toward listing its shares on the Nasdaq for a potential initial public offering (IPO) that could become the largest in history.
As per a recent report, the company is reportedly seeking early inclusion in the Nasdaq-100 index. The update was reported by Reuters, citing people familiar with the matter.
According to the publication, SpaceX is considering Nasdaq as the venue for its eventual IPO, though the New York Stock Exchange is also competing for the listing. Neither exchange has reportedly been informed of a final decision.
Reuters has previously reported that SpaceX could pursue an IPO as early as June, though the company’s plans could still change.
One of the publication’s sources also suggested that SpaceX is targeting a valuation of about $1.75 trillion for its IPO. At that level, the company would rank among the largest publicly traded firms in the United States by market capitalization.
Nasdaq has proposed a rule change that could accelerate the inclusion of newly listed megacap companies into the Nasdaq-100 index.
Under the proposed “Fast Entry” rule, a newly listed company could qualify for the index in less than a month if its market capitalization ranks among the top 40 companies already included in the Nasdaq-100.
If SpaceX is successful in achieving its target valuation of $1.75 trillion, it would become the sixth-largest company by market value in the United States, at least based on recent share prices.
Newly listed companies typically have to wait up to a year before becoming eligible for major indexes such as the Nasdaq-100 or S&P 500.
Inclusion in a major index can significantly broaden a company’s shareholder base because many institutional investors purchase shares through index-tracking funds.
According to Reuters, Nasdaq’s proposed fast-track rule is partly intended to attract highly valued private companies such as SpaceX, OpenAI, and Anthropic to list on the exchange.















![Lucid Lunar robotaxi concept [Credit: Rendering by TESLARATI]](https://www.teslarati.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/03/lucid-lunar-robotaxi-concept-teslarati-rendering-80x80.jpg)





