SpaceX
SpaceX shows off Crew Dragon atop Falcon 9 as govt shutdown kills momentum
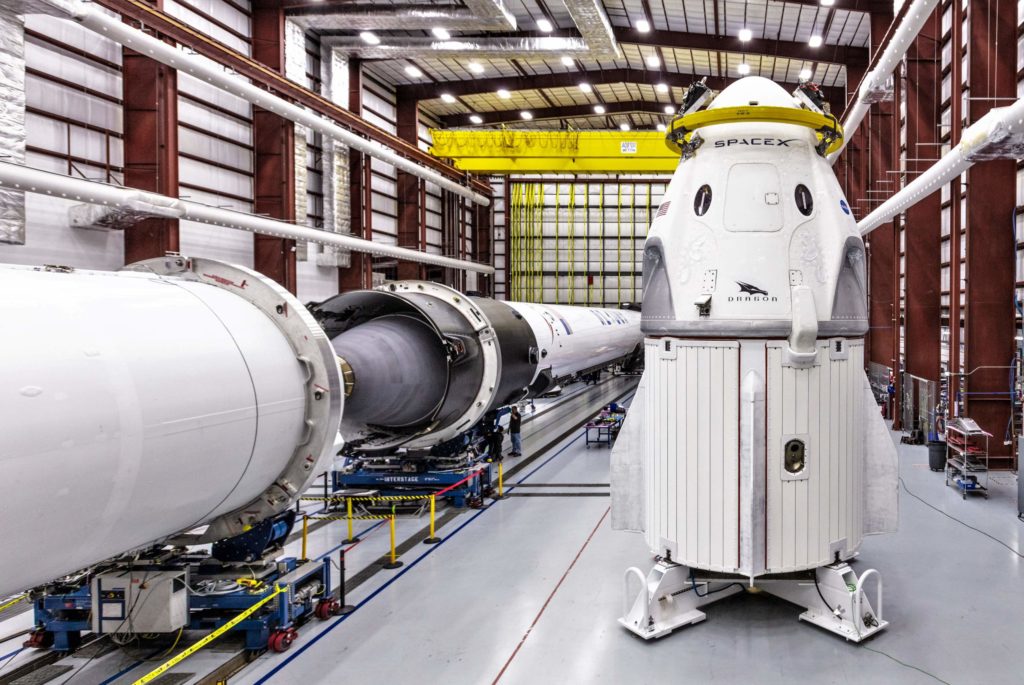
Late last week, SpaceX published official photos of Crew Dragon’s first trip out to Launch Complex 39A (Pad 39A) atop its specially-certified Falcon 9 Block 5 rocket, showing off what looks to have been a successful integrated fit check and an important precursor to the debut launch of the company’s first human-rated spacecraft.
Despite the obvious readiness of SpaceX’s hardware and facilities for this historic mission, the company has been met with a brick wall that has almost indefinitely killed almost all forward momentum towards Crew Dragon’s first trip to orbit, appearing in the form of elected leaders so inept that they have failed to properly fund the bureaucracies underpinning the vast majority of the federal government for more than three weeks, NASA included.
About a month away from the first orbital test flight of crew Dragon https://t.co/U01Oxu3M7E
— Elon Musk (@elonmusk) January 5, 2019
NASA has been severely impacted by the shutdown since it began on Dec 21 and has been operating at barely 5% capacity since then, just shy of the equivalent of throwing a bucket of wrenches into an intricately complex machine. Put simply, the entire agency is more or less at a standstill, aside from the most basic of operations and the support of spacecraft and facilities that cannot pause for the convenience of childish games of political brinksmanship. Among the parts of the agency harmed are those involved with the late-stage Commercial Crew Program (CCP) certification work and general program support, directly translating into an almost indefinite pause on Crew Dragon’s autonomous launch debut, known as DM-1.
Science-funding agencies that are open: DOE, DOD, and NIH.
The big ones that are affected: NSF, NIST, NOAA, NASA, EPA, USGS, FDA, Smithsonian, USDA@sciencemagazine has a rundown of the impact of the shutdown for agencies with a science focus https://t.co/uAPz7AWoVT
— Maryam Zaringhalam, PhD (@webmz_) January 5, 2019
Despite the ironic fact that their operations would likely be considered critical and thus be free of the brunt of a government shutdown’s impact once SpaceX’s Crew Dragon and Boeing’s Starliner are demonstrated and declared operational, almost all conceivable programmatic aspects of Commercial Crew Program currently fall into non-critical categories as both providers prepare for their first uncrewed demonstration missions to orbit. These autonomous demo missions will be immediately followed by crewed demonstration missions in which real NASA astronauts will fly to the International Space Station before NASA can finally complete the operational certification of Crew Dragon and Starliner.
Simultaneous ironic and gratingly painful, the first operational crewed launches are explicitly dependent on certifications to immediately follow crewed demonstration launches, which themselves are no less dependent upon the receipt of NASA certifications after each spacecraft’s first uncrewed demonstration launch. As such, every delay to CCPs uncrewed demo launches will likely translate into a near 1:1 delay (if not worse) for the operational debut of both spacecraft, already operating dangerously close to the edge of assured access to the ISS thanks to a range of delays caused by technical challenges and NASA sluggishness.
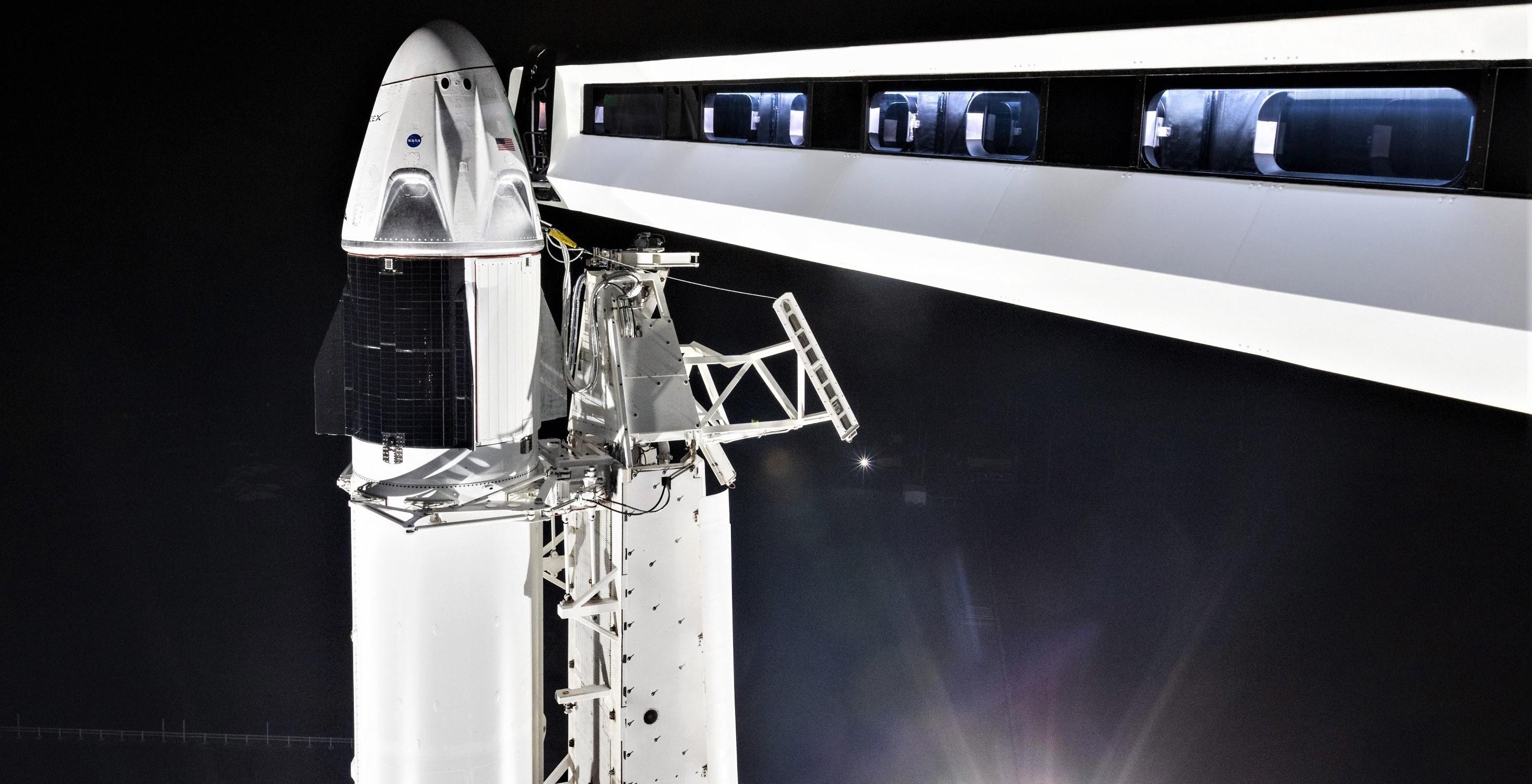
- An impressive view of Crew Dragon (DM-1), Falcon 9 B1051, and its upper stage. (SpaceX)
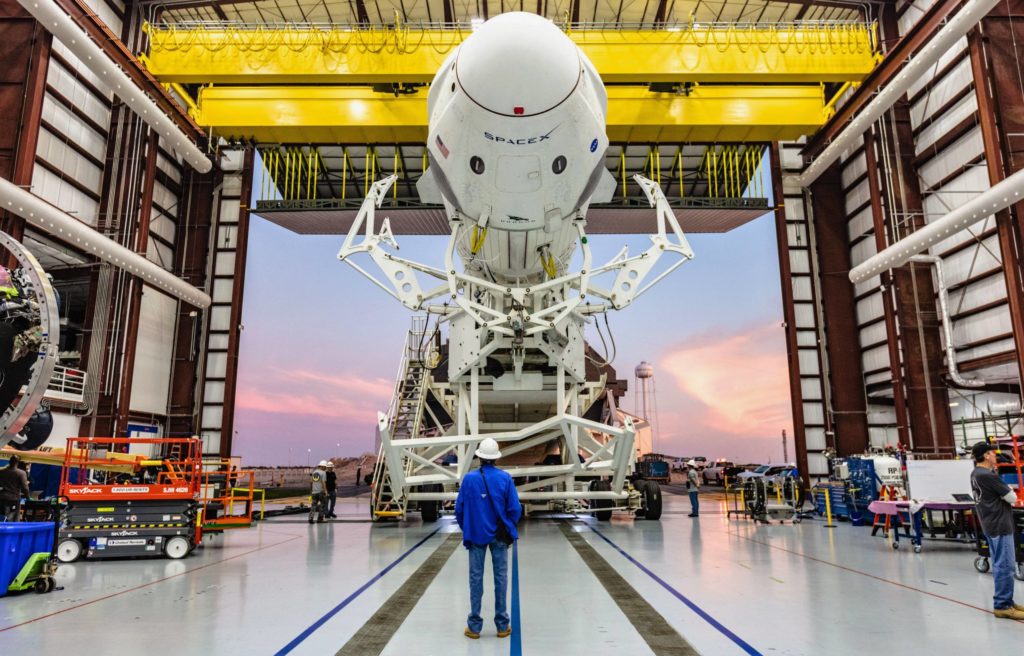
- The integrated DM-1 Crew Dragon ‘stack’ rolled out to Pad 39A for the first time in the first few days of 2019. (SpaceX)
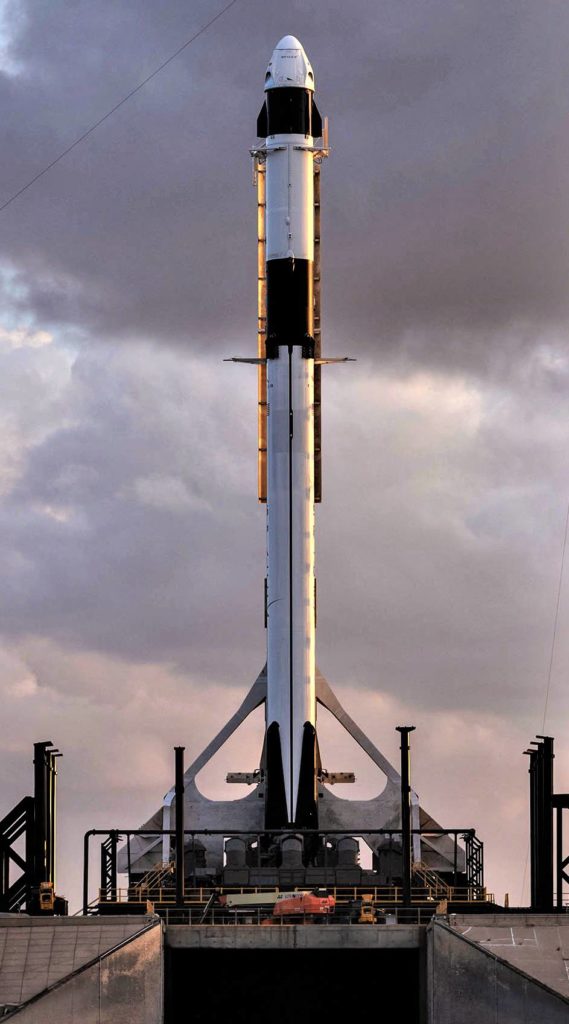
- Falcon 9 B1051 and Crew Dragon vertical at Pad 39A. (SpaceX)
- The view of Crew Dragon from SpaceX’s freshly-installed Crew Access Arm at Pad 39A. (SpaceX)
NASA currently relies entirely on launch contracts on Russian space agency Roscosmos’ Soyuz rocket and spacecraft to deliver NASA astronauts to the ISS, and those contracts are set to end in a fairly permanent manner as early as November 2019, although the end of NASA’s Soyuz access could potentially be pushed back as far as Q1 2020. Ultimately, a single month of delays at this phase of SpaceX’s Crew Dragon launch debut preparations could snowball into even worse delays for the crewed DM-2 and PCM-1 (Post-Certification Mission) missions and beyond, all of which are heavily dependent on NASA completing a vast sea of paperwork that would likely be ongoing at this very moment if 95% of the agencies staff wasn’t furloughed.

Thankfully, SpaceX at least was able to still perform a dry Falcon 9 and Crew Dragon rollout at Pad 39A, likely serving as an integrated fit-test for the rocket, spacecraft, and fresh pad infrastructure, which includes a brand-new Crew Access Arm (CAA) installed near the end of 2018. While spectacular and apparently successful, it’s undeniably hard to ignore the marring of the government shutdown and inevitable schedule delays it will cause.
SpaceX and its hardware is clearly ready for business – how much longer will we have to wait for the elected representatives of the US demonstrate a similar interest in doing their jobs?
For prompt updates, on-the-ground perspectives, and unique glimpses of SpaceX’s rocket recovery fleet check out our brand new LaunchPad and LandingZone newsletters!
Elon Musk
Elon Musk reveals SpaceX’s target for Starship’s 10th launch
Elon Musk has revealed SpaceX’s target timeline for the next Starship launch, which will be the tenth in program history.
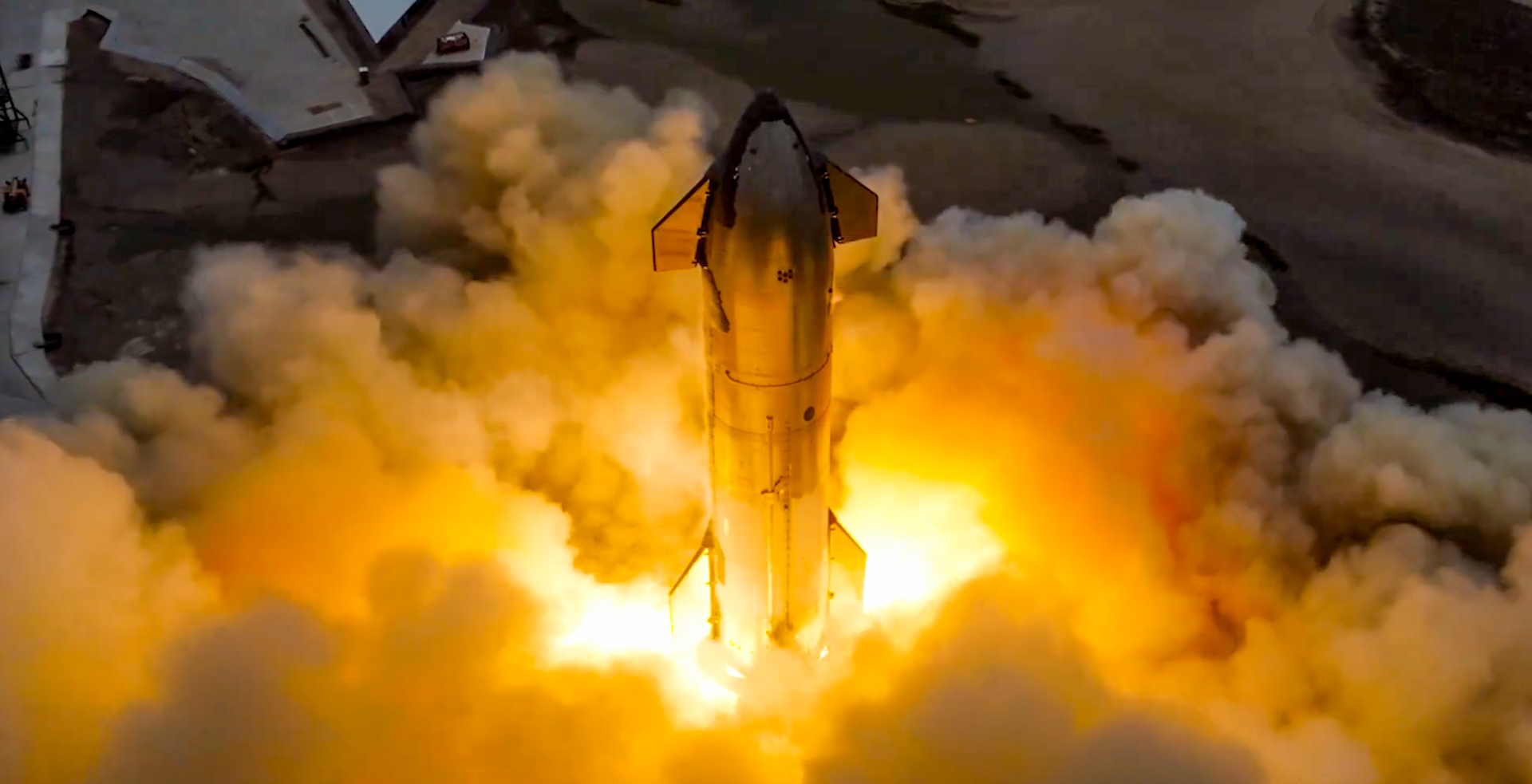

Elon Musk has revealed SpaceX’s target timeline for the next Starship launch, which will be the tenth in program history.
Musk says SpaceX is aiming for a timeline of roughly three weeks from now, which would come about ten weeks after the previous launch.
Coincidentally, it would bring the two launches 69 days apart, and if you know anything about Elon Musk, that would be an ideal timeline between two launches.
🚨 Just wanted you to know, Starship 10’s projected test flight date, according to Grok, is August 4.
Starship’s ninth test flight took place on May 27.
August 4 is 69 days after May 27.
Do with that what you will. 🚀 https://t.co/IISpT08rIy
— TESLARATI (@Teslarati) July 16, 2025
SpaceX is coming off a test flight in which it lost both the Super Heavy Booster and the Upper Stage in the previous launch. The Super Heavy Booster was lost six minutes and sixteen seconds into the flight, while SpaceX lost communication with the Ship at 46 minutes and 48 seconds.
Musk is aiming for the tenth test flight to take place in early August, he revealed on X:
Launching again in ~3 weeks
— Elon Musk (@elonmusk) July 14, 2025
This will be SpaceX’s fourth test flight of the Starship program in 2025, with each of the previous three flights bringing varying results.
IFT-7 in January brought SpaceX its second successful catch of the Super Heavy Booster in the chopstick arms of the launch tower. The ship was lost after exploding during its ascent over the Turks and Caicos Islands.
IFT-8 was on March 6, and SpaceX caught the booster once again, but the Upper Stage was once again lost.
The most recent flight, IFT-9, took place on May 27 and featured the first reused Super Heavy Booster. However, both the Booster and Upper Stage were lost.
The Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) hit SpaceX with a mishap investigation for Flight 9 on May 30.
News
SpaceX’s Crew-11 mission targets July 31 launch amid tight ISS schedule
The flight will lift off from Launch Complex 39A at Kennedy Space Center in Florida.
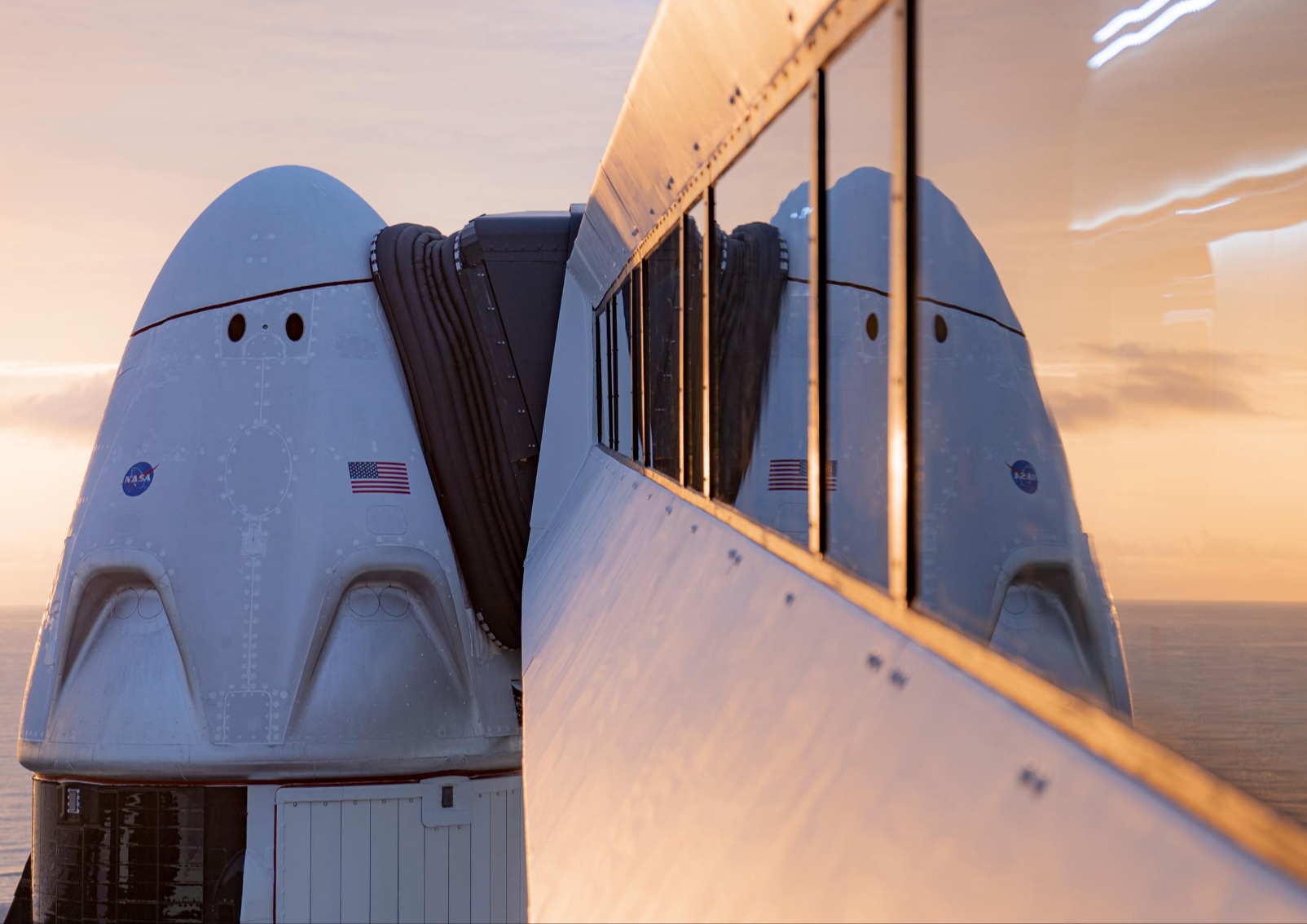

NASA and SpaceX are targeting July 31 for the launch of Crew-11, the next crewed mission to the International Space Station (ISS). The flight will lift off from Launch Complex 39A at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, using the Crew Dragon Endeavour and a Falcon 9 booster.
Crew Dragon Endeavour returns
Crew-11 will be the sixth flight for Endeavour, making it SpaceX’s most experienced crew vehicle to date. According to SpaceX’s director of Dragon mission management, Sarah Walker, Endeavour has already carried 18 astronauts representing eight countries since its first mission with NASA’s Bob Behnken and Doug Hurley in 2020, as noted in an MSN report.
“This Dragon spacecraft has successfully flown 18 crew members representing eight countries to space already, starting with (NASA astronauts) Bob (Behnken) and Doug (Hurley) in 2020, when it returned human spaceflight capabilities to the United States for the first time since the shuttle retired in July of 2011,” Walker said.
For this mission, Endeavour will debut SpaceX’s upgraded drogue 3.1 parachutes, designed to further enhance reentry safety. The parachutes are part of SpaceX’s ongoing improvements to its human-rated spacecraft, and Crew-11 will serve as their first operational test.
The Falcon 9 booster supporting this launch is core B1094, which has launched in two previous Starlink missions, as well as the private Ax-4 mission on June 25, as noted in a Space.com report.
The four-members of Crew-11 are NASA astronauts Zena Cardman and Mike Fincke, as well as Japan’s Kimiya Yui and Russia’s Oleg Platonov.
Tight launch timing
Crew-11 is slated to arrive at the ISS just as NASA coordinates a sequence of missions, including the departure of Crew-10 and the arrival of SpaceX’s CRS-33 mission. NASA’s Bill Spetch emphasized the need for careful planning amid limited launch resources, noting the importance of maintaining station altitude and resupply cadence.
“Providing multiple methods for us to maintain the station altitude is critically important as we continue to operate and get the most use out of our limited launch resources that we do have. We’re really looking forward to demonstrating that capability with (CRS-33) showing up after we get through the Crew-11 and Crew-10 handover,” Spetch stated.
News
SpaceX launches Ax-4 mission to the ISS with international crew
The SpaceX Falcon 9 launched Axiom’s Ax-4 mission to ISS. Ax-4 crew will conduct 60+ science experiments during a 14-day stay on the ISS.
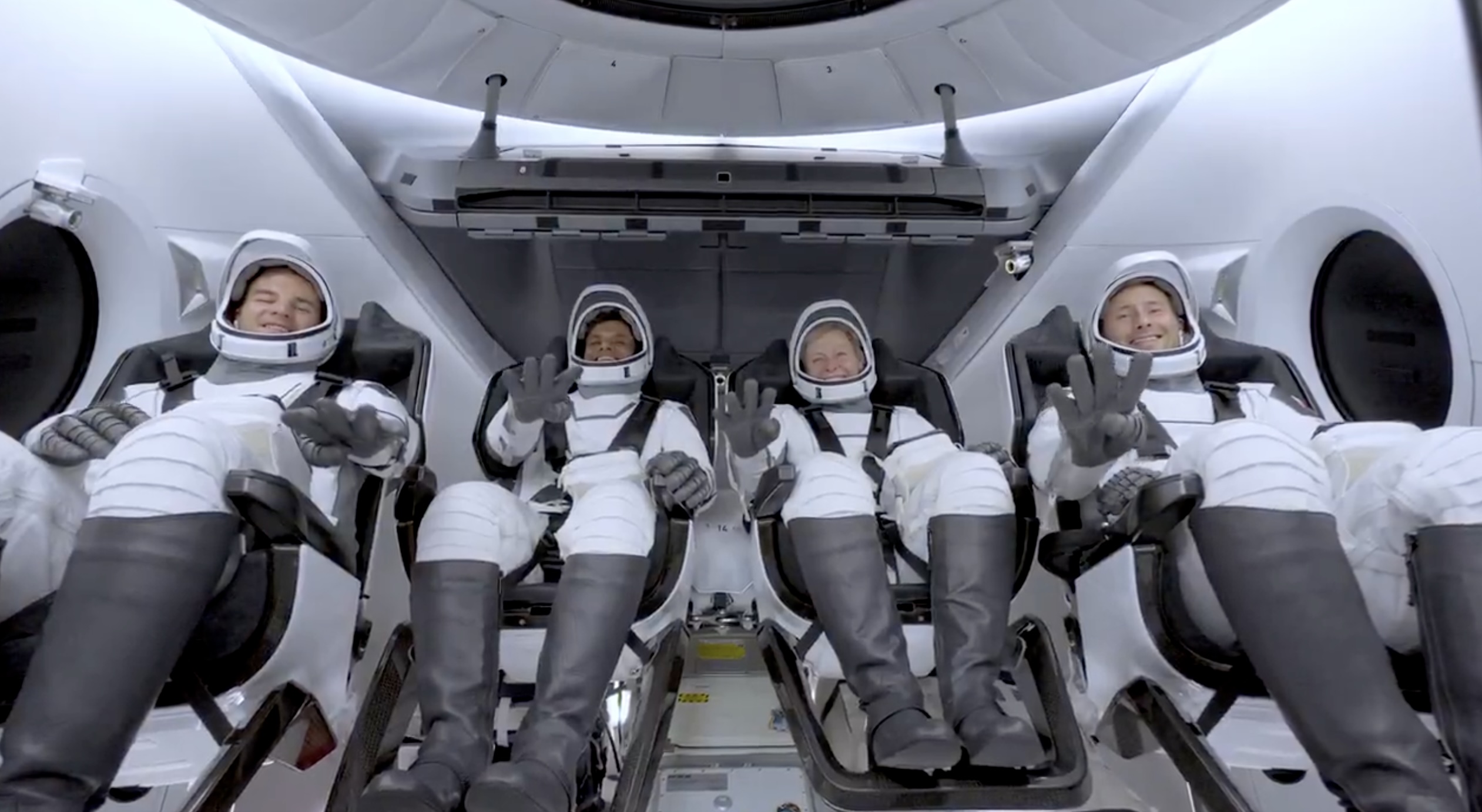

SpaceX launched the Falcon 9 rocket kickstarting Axiom Space’s Ax-4 mission to the International Space Station (ISS). Axiom’s Ax-4 mission is led by a historic international crew and lifted off from Kennedy Space Center’s Launch Complex 39A at 2:31 a.m. ET on June 25, 2025.
The Ax-4 crew is set to dock with the ISS around 7 a.m. ET on Thursday, June 26, 2025. Axiom Space, a Houston-based commercial space company, coordinated the mission with SpaceX for transportation and NASA for ISS access, with support from the European Space Agency and the astronauts’ governments.
The Ax-4 mission marks a milestone in global space collaboration. The Ax-4 crew, commanded by U.S. astronaut Peggy Whitson, includes Shubhanshu Shukla from India as the pilot, alongside mission specialists Sławosz Uznański-Wiśniewski from Poland and Tibor Kapu from Hungary.
“The trip marks the return to human spaceflight for those countries — their first government-sponsored flights in more than 40 years,” Axiom noted.
Shukla’s participation aligns with India’s Gaganyaan program planned for 2027. He is the first Indian astronaut to visit the ISS since Rakesh Sharma in 1984.
Axiom’s Ax-4 mission marks SpaceX’s 18th human spaceflight. The mission employs a Crew Dragon capsule atop a Falcon 9 rocket, designed with a launch escape system and “two-fault tolerant” for enhanced safety. The Axiom mission faced a few delays due to weather, a Falcon 9 leak, and an ISS Zvezda module leak investigation by NASA and Roscosmos before the recent successful launch.
As the crew prepares to execute its scientific objectives, SpaceX’s Ax-4 mission paves the way for a new era of inclusive space research, inspiring future generations and solidifying collaborative ties in the cosmos. During the Ax-4 crew’s 14-day stay in the ISS, the astronauts will conduct nearly 60 experiments.
“We’ll be conducting research that spans biology, material, and physical sciences as well as technology demonstrations,” said Whitson. “We’ll also be engaging with students around the world, sharing our experience and inspiring the next generation of explorers.”
SpaceX’s Ax-4 mission highlights Axiom’s role in advancing commercial spaceflight and fostering international partnerships. The mission strengthens global space exploration efforts by enabling historic spaceflight returns for India, Poland, and Hungary.
-

 Elon Musk1 day ago
Elon Musk1 day agoWaymo responds to Tesla’s Robotaxi expansion in Austin with bold statement
-

 News1 day ago
News1 day agoTesla exec hints at useful and potentially killer Model Y L feature
-

 Elon Musk2 days ago
Elon Musk2 days agoElon Musk reveals SpaceX’s target for Starship’s 10th launch
-

 Elon Musk3 days ago
Elon Musk3 days agoTesla ups Robotaxi fare price to another comical figure with service area expansion
-

 News1 day ago
News1 day agoTesla’s longer Model Y did not scale back requests for this vehicle type from fans
-

 News1 day ago
News1 day ago“Worthy of respect:” Six-seat Model Y L acknowledged by Tesla China’s biggest rivals
-

 News2 days ago
News2 days agoFirst glimpse of Tesla Model Y with six seats and extended wheelbase
-
 Elon Musk2 days ago
Elon Musk2 days agoElon Musk confirms Tesla is already rolling out a new feature for in-car Grok