

News
SpaceX’s Crew Dragon just became America’s longest-lived astronaut spaceship
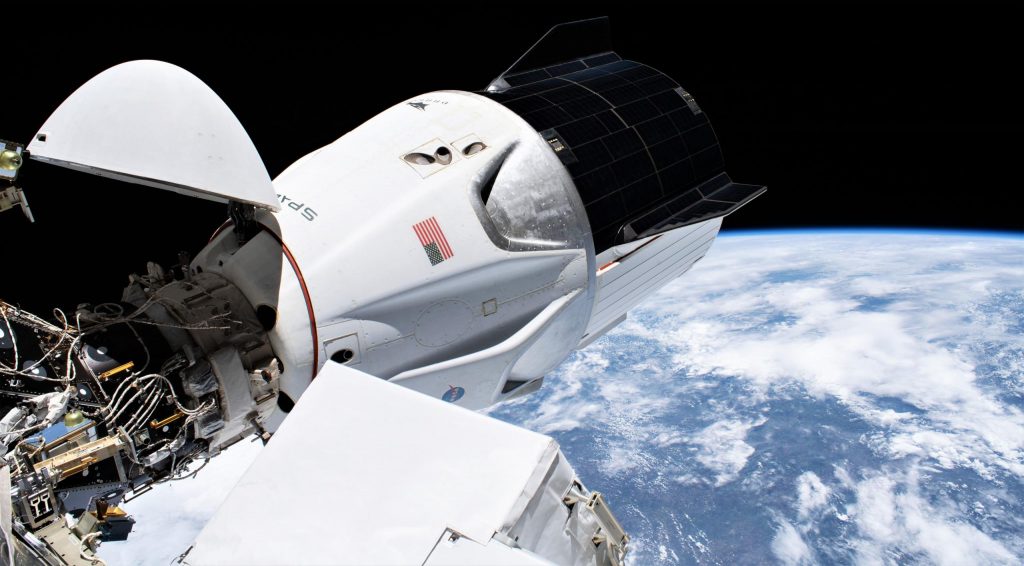
SpaceX’s Crew Dragon has officially become the longest-lived American astronaut spacecraft ever built, beating an 84-day record set by the Apollo-era Skylab-4 mission almost half a century ago.
Crew Dragon was able to beat that record so quickly because NASA ultimately chose to cannibalize its existing Saturn rocket and Apollo CSM spacecraft expertise, production capabilities, and budget to go all-in on the Space Shuttle program. Meant to be quickly and cheaply reusable, a wide range of compromises, budget shortfalls, and design-by-committee missteps ultimately produced a Shuttle that was horrifically complex, unsafe, only partially reusable, suboptimal for most tasks, and more expensive to launch than Saturn V.
The Space Shuttle was ultimately a beast to refurbish and “reuse”, often requiring an almost complete disassembly and reassembly and extensive rework on most propulsive components. Partially due to those extreme shortcomings and a catastrophically fatal launch failure just five years after its debut, the Shuttle was never able to get anywhere close to realizing its limited but still strong potential, including a maximum orbital longevity of just two or so weeks.
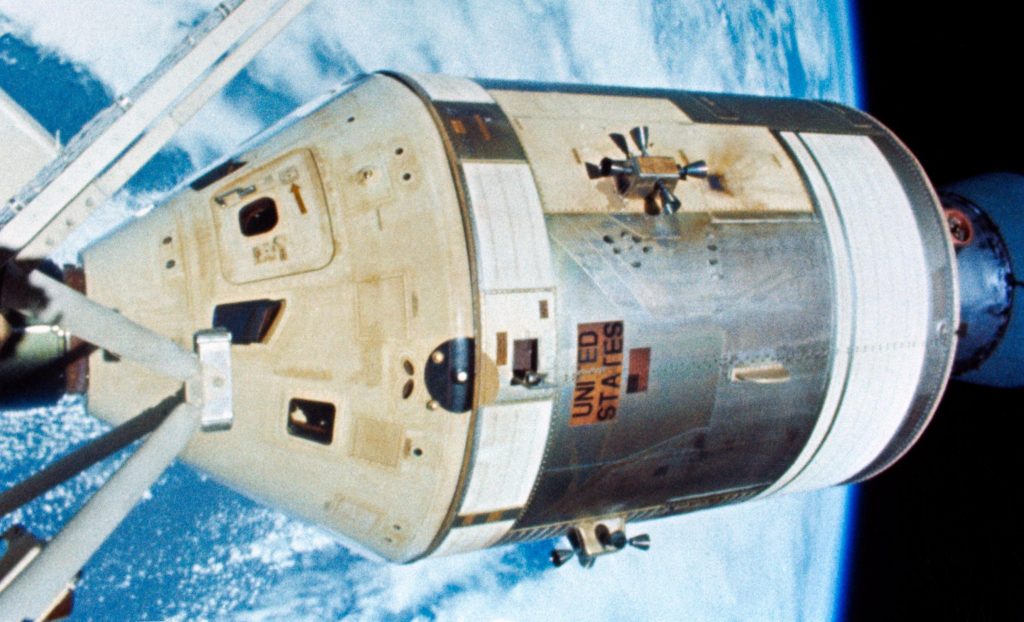

As a result, NASA went from Saturn I, Saturn V, and CSM – a combination that enabled single-launch space stations, multi-month crewed spaceflights, and the Apollo Program – to the Space Shuttle, an anchor that yanked the space agency’s human agency ambitions back to low Earth orbit (LEO). In the Space Shuttle’s defense, NASA did eventually join an international initiative to build the International Space Station (ISS), a program the Shuttle supported with several dozen launches of crucial modules, components, and supplies.
However, had NASA been able to continue the Skylab program with Saturn and CSM, a space station with a habitable volume similar to the 2021 ISS could have been completed in a mere three launches, compared to no less than 30 launches to build the ISS.
Regardless, after an unfortunate and unnecessary 47-year pause, SpaceX – with NASA funding – has returned the space agency and the US to its legacy of envelope-pushing. On the heels of 20 successful uncrewed Cargo Dragon missions to and from the ISS over the last 9 years, all of which spent around a month in orbit, SpaceX’s third Crew Dragon launch has already beat the US record for crewed spacecraft longevity on orbit and is ultimately poised to double it before the mission’s end.
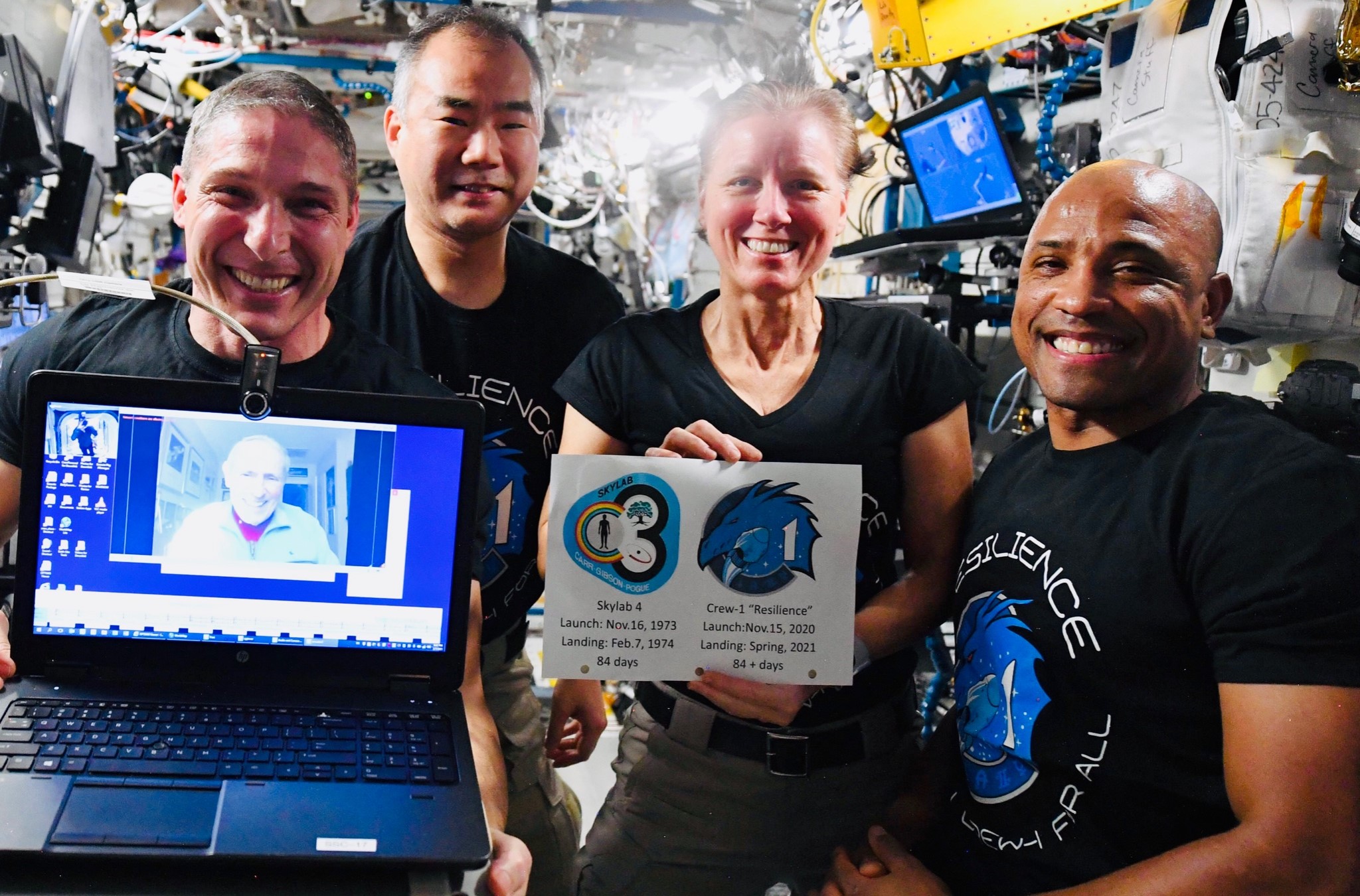
Crew Dragon’s Crew-1 astronauts even celebrated the milestone in orbit with (albeit virtually) Ed Gibson, one of the three astronauts that set Skylab-4’s record 47 years prior. Additionally, in a pleasing coincidence, Skylab-4 and SpaceX Crew-1 nearly launched on the same day, meaning that tomorrow (February 8th) is the true 47th anniversary of the Skylab-4 mission’s reentry and splashdown.
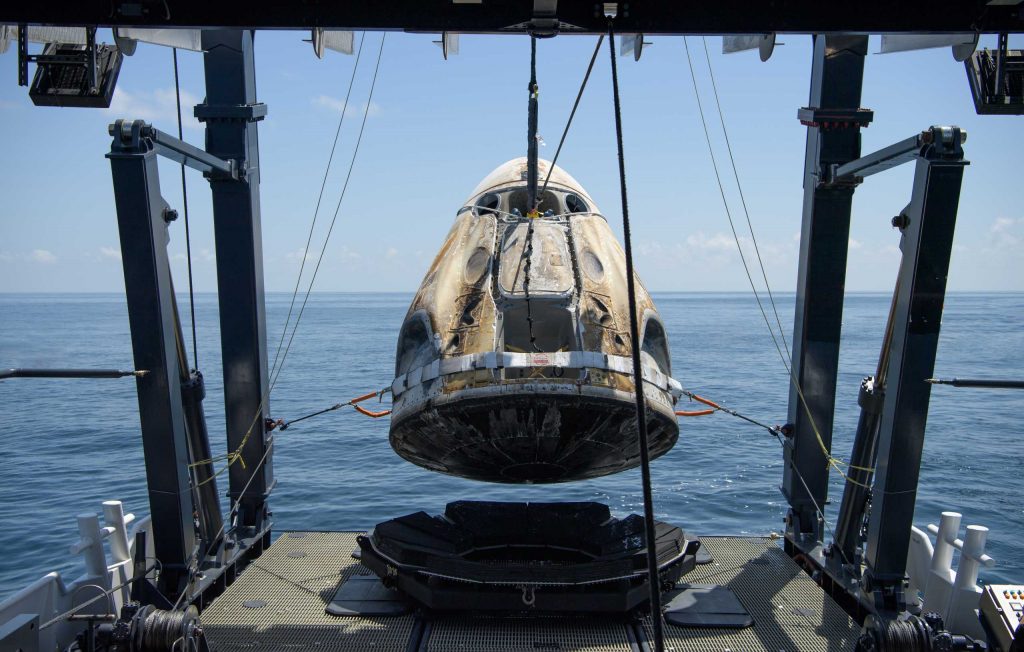

All told, all operational Crew Dragon missions – of which Crew-1 is the first – are scheduled to spend approximately 180 days in orbit between launch and reentry. As the first US spacecraft (and first private spacecraft) to attempt such a long spaceflight, there is obviously some uncertainty and no guarantee that this first try won’t be cut short, but odds are in SpaceX’s favor that Crew Dragon capsule C207 will depart the ISS without issue and safely return its four-astronaut crew back to Earth sometime in May 2021.


Elon Musk
Brazil Supreme Court orders Elon Musk and X investigation closed
The decision was issued by Supreme Court Justice Alexandre de Moraes following a recommendation from Brazil’s Prosecutor-General Paulo Gonet.

Brazil’s Supreme Federal Court has ordered the closure of an investigation involving Elon Musk and social media platform X. The inquiry had been pending for about two years and examined whether the platform was used to coordinate attacks against members of the judiciary.
The decision was issued by Supreme Court Justice Alexandre de Moraes following a recommendation from Brazil’s Prosecutor-General Paulo Gonet.
According to a report from Agencia Brasil, the investigation conducted by the Federal Police did not find evidence that X deliberately attempted to attack the judiciary or circumvent court orders.
Prosecutor-General Paulo Gonet concluded that the irregularities identified during the probe did not indicate fraudulent intent.
Justice Moraes accepted the prosecutor’s recommendation and ruled that the investigation should be closed. Under the ruling, the case will remain closed unless new evidence emerges.
The inquiry stemmed from concerns that content on X may have enabled online attacks against Supreme Court justices or violated rulings requiring the suspension of certain accounts under investigation.
Justice Moraes had previously taken several enforcement actions related to the platform during the broader dispute involving social media regulation in Brazil.
These included ordering a nationwide block of the platform, freezing Starlink accounts, and imposing fines on X totaling about $5.2 million. Authorities also froze financial assets linked to X and SpaceX through Starlink to collect unpaid penalties and seized roughly $3.3 million from the companies’ accounts.
Moraes also imposed daily fines of up to R$5 million, about $920,000, for alleged evasion of the X ban and established penalties of R$50,000 per day for VPN users who attempted to bypass the restriction.
Brazil remains an important market for X, with roughly 17 million users, making it one of the platform’s larger user bases globally.
The country is also a major market for Starlink, SpaceX’s satellite internet service, which has surpassed one million subscribers in Brazil.
Elon Musk
FCC chair criticizes Amazon over opposition to SpaceX satellite plan
Carr made the remarks in a post on social media platform X.

U.S. Federal Communications Commission (FCC) Chairman Brendan Carr criticized Amazon after the company opposed SpaceX’s proposal to launch a large satellite constellation that could function as an orbital data center network.
Carr made the remarks in a post on social media platform X.
Amazon recently urged the FCC to reject SpaceX’s application to deploy a constellation of up to 1 million low Earth orbit satellites that could serve as artificial intelligence data centers in space.
The company described the proposal as a “lofty ambition rather than a real plan,” arguing that SpaceX had not provided sufficient details about how the system would operate.
Carr responded by pointing to Amazon’s own satellite deployment progress.
“Amazon should focus on the fact that it will fall roughly 1,000 satellites short of meeting its upcoming deployment milestone, rather than spending their time and resources filing petitions against companies that are putting thousands of satellites in orbit,” Carr wrote on X.
Amazon has declined to comment on the statement.
Amazon has been working to deploy its Project Kuiper satellite network, which is intended to compete with SpaceX’s Starlink service. The company has invested more than $10 billion in the program and has launched more than 200 satellites since April of last year.
Amazon has also asked the FCC for a 24-month extension, until July 2028, to meet a requirement to deploy roughly 1,600 satellites by July 2026, as noted in a CNBC report.
SpaceX’s Starlink network currently has nearly 10,000 satellites in orbit and serves roughly 10 million customers. The FCC has also authorized SpaceX to deploy 7,500 additional satellites as the company continues expanding its global satellite internet network.
Energy
Tesla Energy gains UK license to sell electricity to homes and businesses
The license was granted to Tesla Energy Ventures Ltd. by UK energy regulator Ofgem after a seven-month review process.

Tesla Energy has received a license to supply electricity in the United Kingdom, opening the door for the company to serve homes and businesses in the country.
The license was granted to Tesla Energy Ventures Ltd. by UK energy regulator Ofgem after a seven-month review process.
According to Ofgem, the license took effect at 6 p.m. local time on Wednesday and applies to Great Britain.
The approval allows Tesla’s energy business to sell electricity directly to customers in the region, as noted in a Bloomberg News report.
Tesla has already expanded similar services in the United States. In Texas, the company offers electricity plans that allow Tesla owners to charge their vehicles at a lower cost while also feeding excess electricity back into the grid.
Tesla already has a sizable presence in the UK market. According to price comparison website U-switch, there are more than 250,000 Tesla electric vehicles in the country and thousands of Tesla home energy storage systems.
Ofgem also noted that Tesla Motors Ltd., a separate entity incorporated in England and Wales, received an electricity generation license in June 2020.
The new UK license arrives as Tesla continues expanding its global energy business.
Last year, Tesla Energy retained the top position in the global battery energy storage system (BESS) integrator market for the second consecutive year. According to Wood Mackenzie’s latest rankings, Tesla held about 15% of global market share in 2024.
The company also maintained a dominant position in North America, where it captured roughly 39% market share in the region.
At the same time, competition in the energy storage sector is increasing. Chinese companies such as Sungrow have been expanding their presence globally, particularly in Europe.








