
News
Tesla Autopilot and artificial intelligence: The unfair advantage
Serial tech entrepreneur and Tesla CEO Elon Musk has had a longstanding fear of artificial intelligence, but his company’s investments in artificial intelligence have been noted as an attempt to keep track of developments in the field of AI. In an interview for Vanity Fair in April 2017, he outright expressed his concerns with AI and claimed that one of the reasons for the development of SpaceX was that it could be an interplanetary escape route for humanity if artificial intelligence goes rogue. However, even Musk realizes the importance of AI in real-world applications, specifically for self-driving cars. At the end of June, Musk hired Andrej Karpathy as the new Director of Artificial Intelligence at Tesla, and MIT Technology Review claims it is the start of a plan to rethink automated driving at Tesla.
Karpathy comes from OpenAI, a non-profit company founded by Musk that focuses on “discovering and enacting the path to safe artificial general intelligence.” Afterwards, he moved on to intern at DeepMind, a place that spotlighted reinforcement learning with AI. Karpathy’s previous research focuses are on image understanding and recognition, which directly translates into applying proven image recognitions algorithms in Tesla’s Autopilot.
Recently, the popular question of morality was brought up in context to AI learning in Autopilot cars. It’s very interesting to consider how to teach technology to respond to an innately human moral problem. The Moral Machine, hosted by Massachusetts Institute of Technology, is a platform built to “gather human perspectives on moral decisions made by machine intelligence, such as self-driving cars.” It questions how the machine would act in human decisions such as whether to crash the driver or keep driving into a pedestrian that is crossing the street where there are no traffic regulators. How exactly do you teach a logical machine the mechanisms of ethical decision-making?
Although Musk and Tesla are the leaders in the self-driving field, a number of other companies are also entering into the competition sphere. Google, Uber, and Intel’s Mobileye have all been considering the application of reinforcement learning in the context of self-driving cars. Uber, Waymo, GM (Cruise Automation), Mobileye (camera supplier), Mercedes and Velodyne (LiDAR Supplier) could be potential competitors in the realm of self-driving vehicles. However, most of the technology does not encompass full self-driving, which is Musk’s aim. While other companies are investing heavily in autonomous fleets, Tesla far outpaces them in terms of data collection and release of finished product.
What are the differentiators for Tesla in the growing field of AI directed driverless cars?
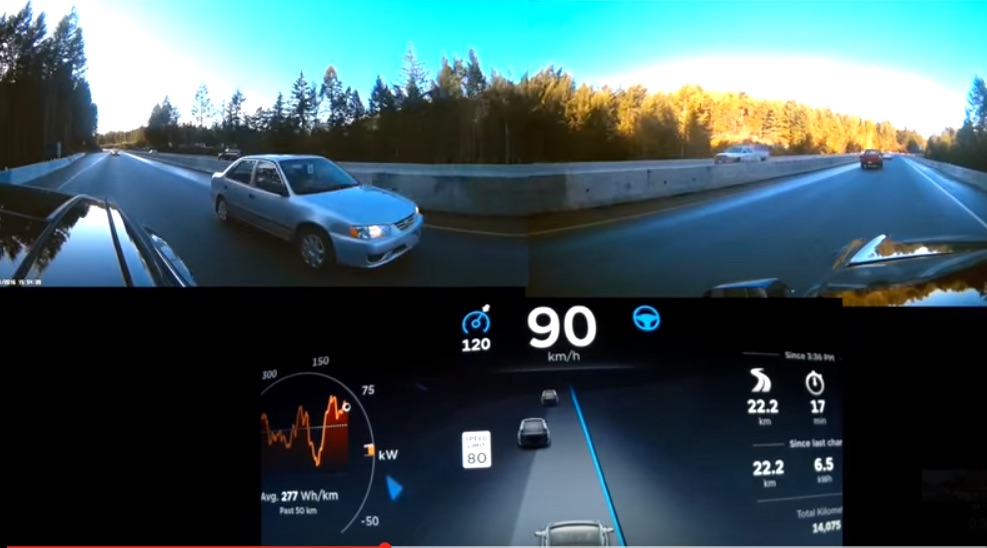
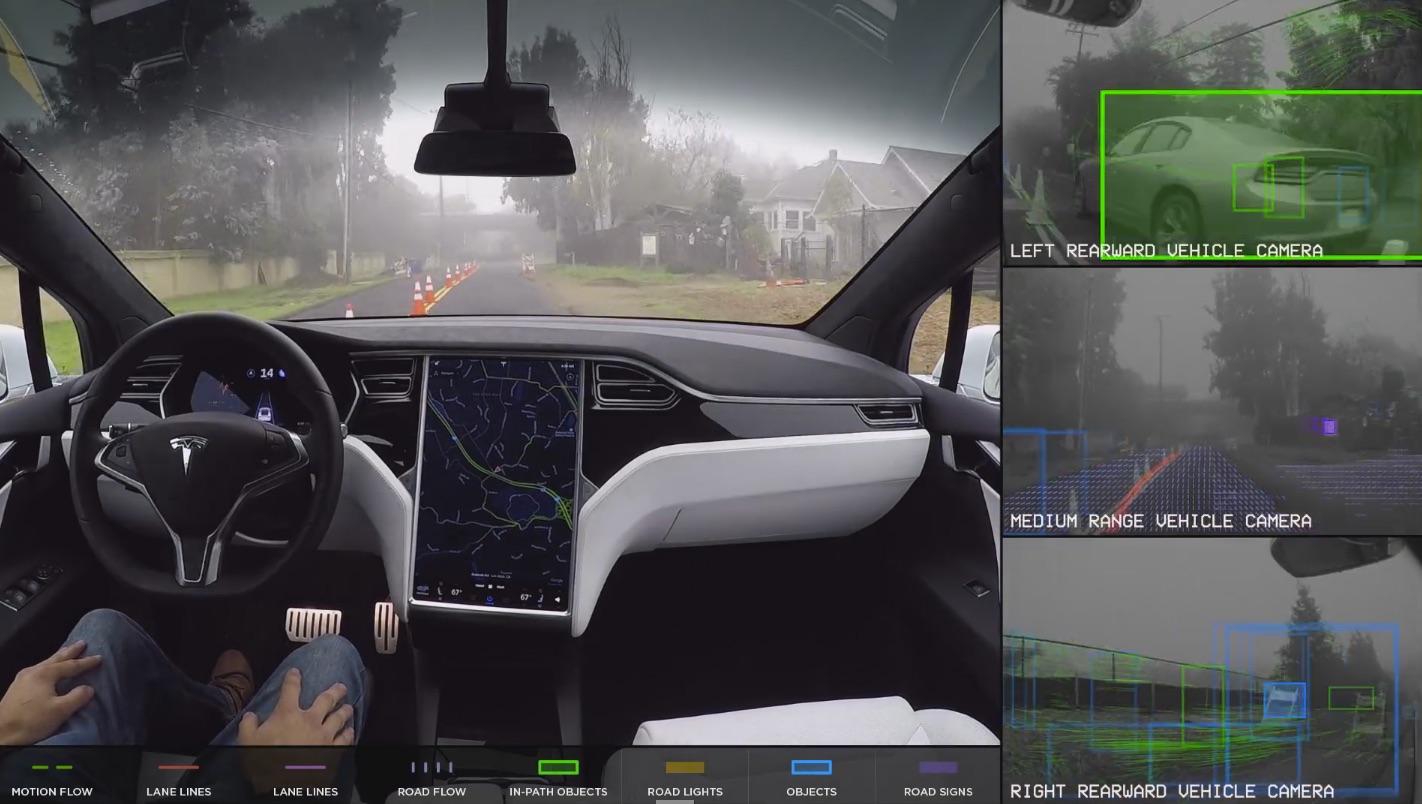
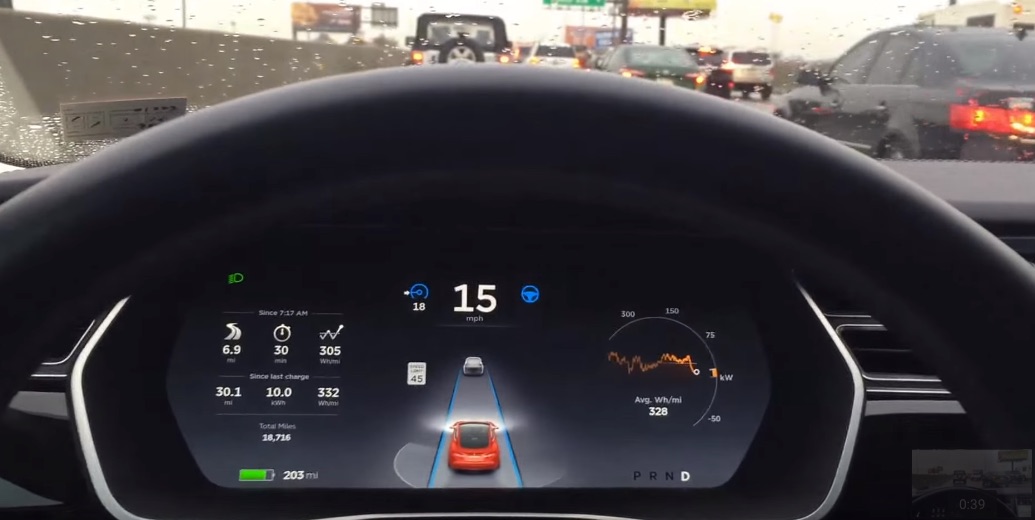
Historically, Musk has focused on “narrow AI” which can enable the car to make decisions without driver interference. The vehicles would increasingly rely on radar as well as ultrasonic technology for sensing and data-gathering to form the basis for Tesla’s Autopilot algorithms. A technology that isn’t derived from LiDAR, the combination of radar and camera system said to outperform LiDAR especially in adverse weather conditions such as fog.
With the introduction of Autopilot 2.0 and Tesla’s “Vision” system, and billions of miles real-world driving data collected by Model S and Model X drivers, Tesla continues to create a detailed 3D map of the world that has increasingly finer resolution as more vehicles are purchased, delivered and placed onto roadways. The addition of GPS allows Tesla to put together a visual driving map for AI vehicles to follow, paving the path for newer and more advanced vehicles.
The addition of Karpathy will be a notable asset for Tesla’s Autopilot team. In specific, the team will be able to apply Karpathy’s deep knowledge of reinforcement learning systems. Reinforcement learning for AI is similar to teaching animals via repetition of a behavior until a positive outcome is yielded. This type of machine learning will allow Tesla Autopilot to navigate complex and challenging scenarios. For example, AI will allow cars to determine in real-time how to navigate a four-way stop, a busy intersection or other difficult situations present on city streets. By making cars smarter with the way they navigate drivers, Tesla will put itself ahead of the curve with a fully-thinking, fully self-driving car.
Tesla is expected to demonstrate a fully autonomous cross-country drive from California to New York by the end of this year as a showcase for its upcoming Full Self-driving Capability. If you’re buying a Tesla Model 3, or an existing Model S or Model X owner, just know that you’re contributing to a self-driving future, mile by mile.

Elon Musk
Elon Musk hints Tesla investors will be rewarded heavily
“Hold onto your Tesla stock. It’s going to be worth a lot, I think. That’s my bet,” Musk said.

Elon Musk recently hinted that he believes Tesla investors will be rewarded heavily if they continue to hold onto their shares, and he reiterated that in a new interview that the company released on its social accounts this week.
Musk is one of the most successful CEOs in the modern era and has mammothed competitors on the Forbes Net Worth List over the past year as his holdings in his various companies have continued to swell.
Tesla investors, especially those who have been holding shares for several years, have also felt substantial gains in their portfolios. Over the past five years, the stock is up over 78 percent. Since February 2019, nearly seven years ago to the day, the stock is up over 1,800 percent.
Musk said in the interview:
“Hold onto your Tesla stock. It’s going to be worth a lot, I think. That’s my bet.”
Elon Musk in new interview: “Hold on to your $TSLA stock. It’s going to be worth a lot, I think. That’s my bet.” pic.twitter.com/cucirBuhq0
— Sawyer Merritt (@SawyerMerritt) February 26, 2026
It’s no secret Musk has been extremely bullish on his own companies, but Tesla in particular, because it is publicly traded.
However, the company has so many amazing projects that have an opportunity to revolutionize their respective industries. There is certainly a path to major growth on Wall Street for Tesla through its various future projects, including Optimus, Cybercab, Semi, and Unsupervised FSD.
- Optimus (Tesla’s humanoid robot): Musk has discussed its potential for tasks like childcare, walking dogs, or assisting elderly parents, positioning it as a massive long-term driver of company value.
- Cybercab (Tesla’s robotaxi/autonomous ride-hailing vehicle): a fully autonomous vehicle geared specifically for Tesla’s ride-sharing ambitions.
- Semi (Tesla’s electric truck, with mentions of expansion, like in Europe): brings Tesla into the commercial logistics sector.
- Unsupervised FSD (Full Self-Driving software achieving full autonomy without human supervision): turns every Tesla owner’s vehicle into a fully-autonomous vehicle upon release
These projects specifically are some of the highest-growth pillars Tesla has ever attempted to develop, especially in Musk’s eyes, as he has said Optimus will be the best-selling product of all-time.
Many analysts agree, but the bullish ones, like Cathie Wood of ARK Invest, are perhaps the one who believes Tesla has incredible potential on Wall Street, predicting a $2,600 price target for 2030, but this is not even including Optimus.
She told Bloomberg last March that she believes that the project will present a potential additive if Tesla can scale faster than anticipated.
Cybertruck
Tesla drops latest hint that new Cybertruck trim is selling like hotcakes
According to Tesla’s Online Design Studio, the new All-Wheel-Drive Cybertruck will now be delivered in April 2027. Earlier orders are still slated for early this Summer, but orders from here on forward are now officially pushed into next year:

Tesla’s new Cybertruck offering has had its delivery date pushed back once again. This is now the second time, and deliveries for the newest orders are now pushed well into 2027.
According to Tesla’s Online Design Studio, the new All-Wheel-Drive Cybertruck will now be delivered in April 2027. Earlier orders are still slated for early this Summer, but orders from here on forward are now officially pushed into next year:
🚨 Tesla has updated the $59,990 Cybertruck Dual Motor AWD’s estimated delivery date to April 2027.
First deliveries are still slated for June, but if you order it now, you’ll be waiting over a year.
Demand appears to be off the charts for the new Cybertruck and consumers are… pic.twitter.com/raDCCeC0zP
— TESLARATI (@Teslarati) February 26, 2026
Just three days ago, the initial delivery date of June 2026 was pushed back to early Fall, and now, that date has officially moved to April 2027.
The fact that Tesla has had to push back deliveries once again proves one of two things: either Tesla has slow production plans for the new Cybertruck trim, or demand is off the charts.
Judging by how Tesla is already planning to raise the price based on demand in just a few days, it seems like the company knows it is giving a tremendous deal on this spec of Cybertruck, and units are moving quickly.
That points more toward demand and not necessarily to slower production plans, but it is not confirmed.
Tesla Cybertruck’s newest trim will undergo massive change in ten days, Musk says
Tesla is set to hike the price on March 1, so tomorrow will be the final day to grab the new Cybertruck trim for just $59,990.
It features:
- Dual Motor AWD w/ est. 325 mi of range
- Powered tonneau cover
- Bed outlets (2x 120V + 1x 240V) & Powershare capability
- Coil springs w/ adaptive damping
- Heated first-row seats w/ textile material that is easy to clean
- Steer-by-wire & Four Wheel Steering
- 6’ x 4’ composite bed
- Towing capacity of up to 7,500 lbs
- Powered frunk
Interestingly, the price offering is fairly close to what Tesla unveiled back in late 2019.
Elon Musk
Elon Musk outlines plan for first Starship tower catch attempt
Musk confirmed that Starship V3 Ship 1 (SN1) is headed for ground tests and expressed strong confidence in the updated vehicle design.

Elon Musk has clarified when SpaceX will first attempt to catch Starship’s upper stage with its launch tower. The CEO’s update provides the clearest teaser yet for the spacecraft’s recovery roadmap.
Musk shared the details in recent posts on X. In his initial post, Musk confirmed that Starship V3 Ship 1 (SN1) is headed for ground tests and expressed strong confidence in the updated vehicle design.
“Starship V3 SN1 headed for ground tests. I am highly confident that the V3 design will achieve full reusability,” Musk wrote.
In a follow-up post, Musk addressed when SpaceX would attempt to catch the upper stage using the launch tower’s robotic arms.
“Should note that SpaceX will only try to catch the ship with the tower after two perfect soft landings in the ocean. The risk of the ship breaking up over land needs to be very low,” Musk clarified.
His remarks suggest that SpaceX is deliberately reducing risk before attempting a tower catch of Starship’s upper stage. Such a milestone would mark a major step towards the full reuse of the Starship system.
SpaceX is currently targeting the first Starship V3 flight of 2026 this coming March. The spacecraft’s V3 iteration is widely viewed as a key milestone in SpaceX’s long-term strategy to make Starship fully reusable.
Starship V3 features a number of key upgrades over its previous iterations. The vehicle is equipped with SpaceX’s Raptor V3 engines, which are designed to deliver significantly higher thrust than earlier versions while reducing cost and weight.
The V3 design is also expected to be optimized for manufacturability, a critical step if SpaceX intends to scale the spacecraft’s production toward frequent launches for Starlink, lunar missions, and eventually Mars.