News
SpaceX board member says Starlink prototype satellites “are working wonderfully”
Speaking in a Satellite Innovation 2018 keynote, long-time SpaceX investor and board member Steve Jurvetson made a quiet but significant comment about the company’s Starlink satellite constellation efforts, stating that the first two prototype spacecraft – currently in orbit – “are working wonderfully.”
Standing in contrast to recent speculation that SpaceX’s Starlink project had experienced major failures with on-orbit hardware, Jurvetson may be a biased source but still has a major vested interest in SpaceX’s long-term success – supporting billions dumped into a satellite constellation with no real returns in sight would serve to seriously harm his significant investments in the company.
He would say that? Maybe, but @dfjsteve Jurvetson, early @SpaceX & @planet investor, told Satellite Innovation conference Oct 10, regarding SpaceX's two Starlink test sats launched in February: pic.twitter.com/WHzJlPUEPA
— Peter B. de Selding (@pbdes) October 12, 2018
Perhaps the most trustworthy source of SpaceX information outside of the company itself, Jurvetson expressed considerable confidence in SpaceX’s Starlink achievements thus far.
“I personally think SpaceX is in the lead [with Ku- and Ka-band phased arrays that could make (global LEO satellite broadband) possible] … Tintin 1 and 2 [are working wonderfully].” – Steve Jurvetson, Satellite Innovation 2018
Previously discussed on Teslarati, SpaceX’s growing experience with phased array antennas is undoubtedly a boon for the company’s proposed Starlink internet constellation, just one of several companies actively pursuing the increasingly competitive low Earth orbit (LEO) satellite broadband market. Fundamentally, phased array antennas will eventually take over nearly all multipurpose orbital communications thanks to the sheer simplicity and potential technical superiority of the technology.
Phased array antennas get their name from the fact that they have no moving parts – rather than moving a physical dish or angling dedicated ‘beams’, phased arrays actively use signal interference to very precisely shape, direct, and regulate line-of-sight communications beams. Currently quite immature, the draw of the technology is the sheer simplicity and reliability of antennas that require no moving parts, eliminating a major mode of failure and the inherent physical limitations of current antenna tech. Without something like phased arrays, LEO communications satellites would struggle to accurately and reliably track ground stations and gateways while traveling multiple kilometers per second.
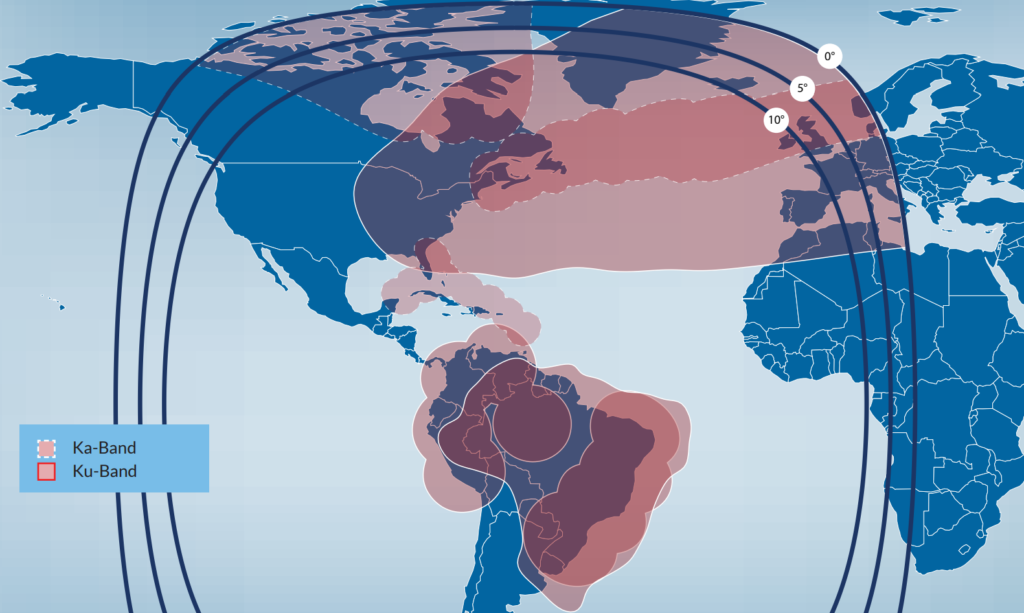
- Traditional geostationary commsats like Telstar 19V feature dish-style antennas. The weird lumps and bumps on each dish are there by design, enabling the oddly specific coverage footprints seen to the right. (Telstar)
- Telstar 19V’s coverage map. Each coverage blob is there by design and is accomplished by physically shaping the antenna dish.
- LEO communications satellites like Iridium’s NEXT constellation feature totally flat panels of phased array antennas, capable of forming beams digitally. (Harris)
Large communications satellites in geostationary orbit do not face this problem. Thanks to their inherently fixed positions over ground targets (hence “geostationary“), designers and manufacturers have learned to quite literally mold each satellite’s on-orbit antennas to explicitly prioritize certain areas on the ground. This process tends to involve a prior determination of markets where demand for satellite communications is or will be highest, while also avoiding wasted coverage over areas with no need for it. However, once the antenna is launched, its beams are almost completely permanent. If markets change, the satellite simply cannot adapt.
Phased arrays, on the other hand, can almost entirely change where their many beams are directed, how much bandwidth is dedicated to certain locations, and all while accurately tracking moving targets with very few limitations. As a result, satellites with phased array antennas are sort of the communications jacks of all trades, capable of offering high-bandwidth connectivity to stationary user terminals, large ground stations, and moving vehicles simultaneously from with the same antenna array.
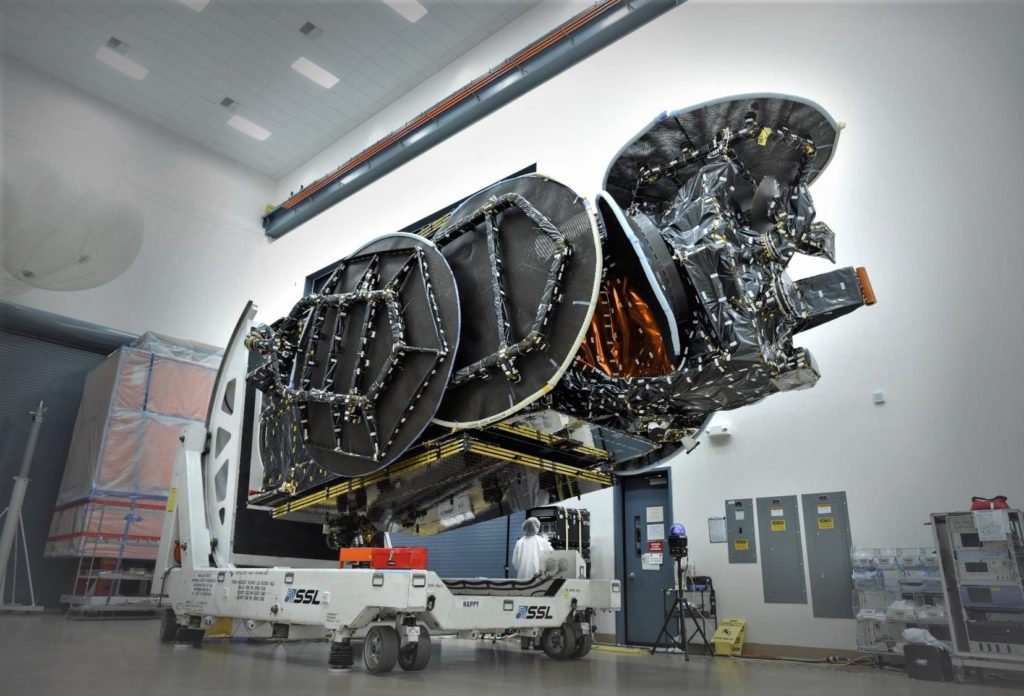
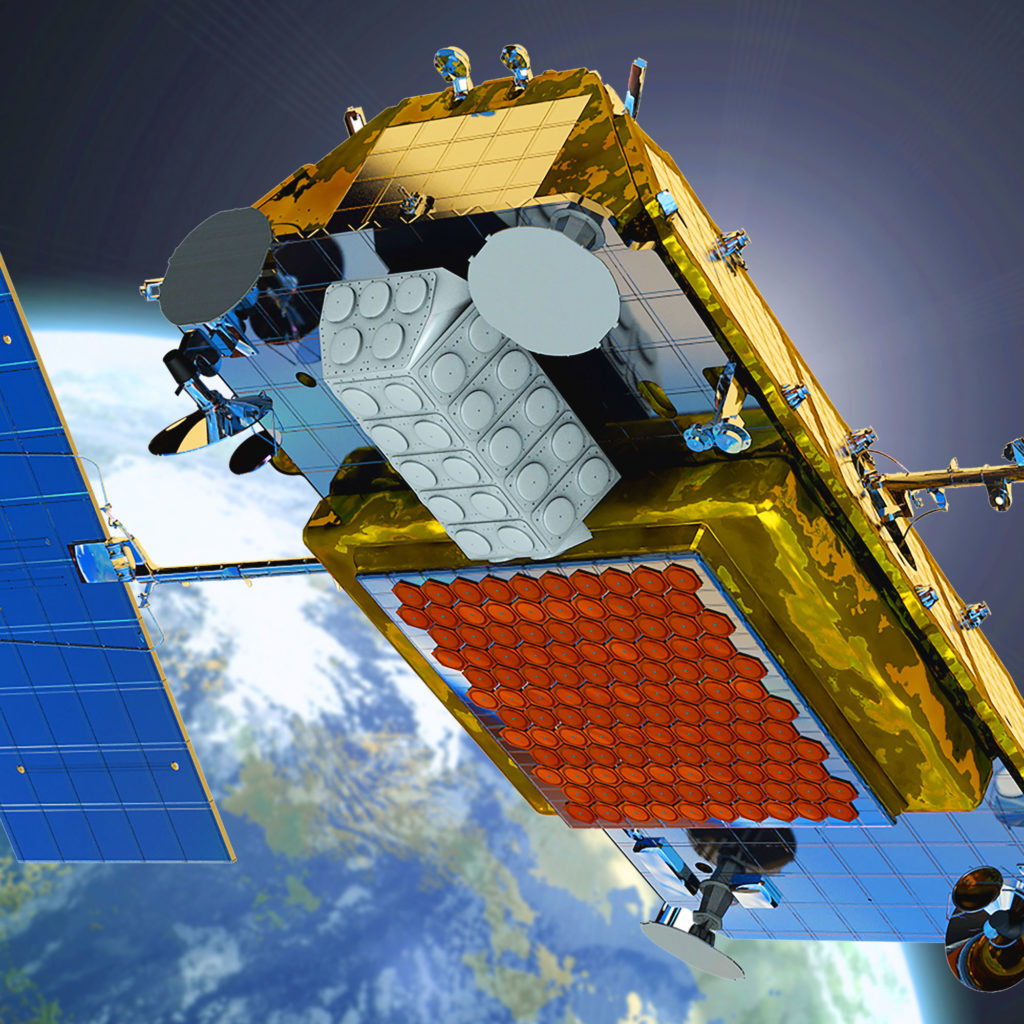
- SpaceX’s first two Starlink prototype satellites are pictured here before their inaugural launch, showing off a thoroughly utilitarian bus and several advanced components. (SpaceX)
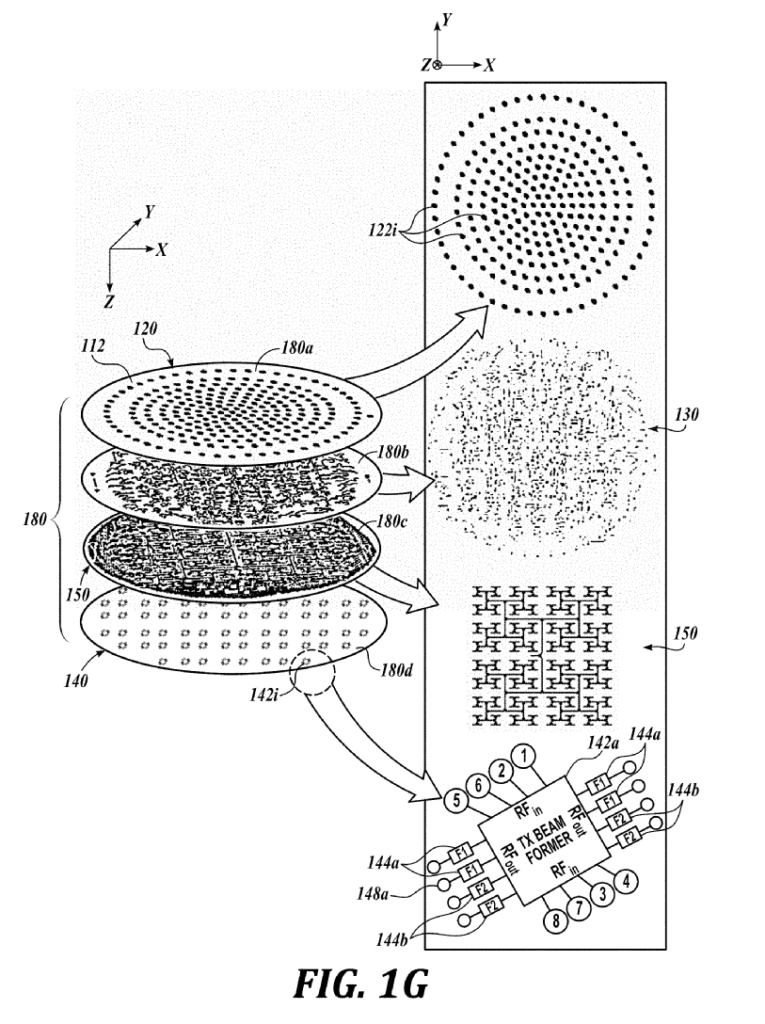
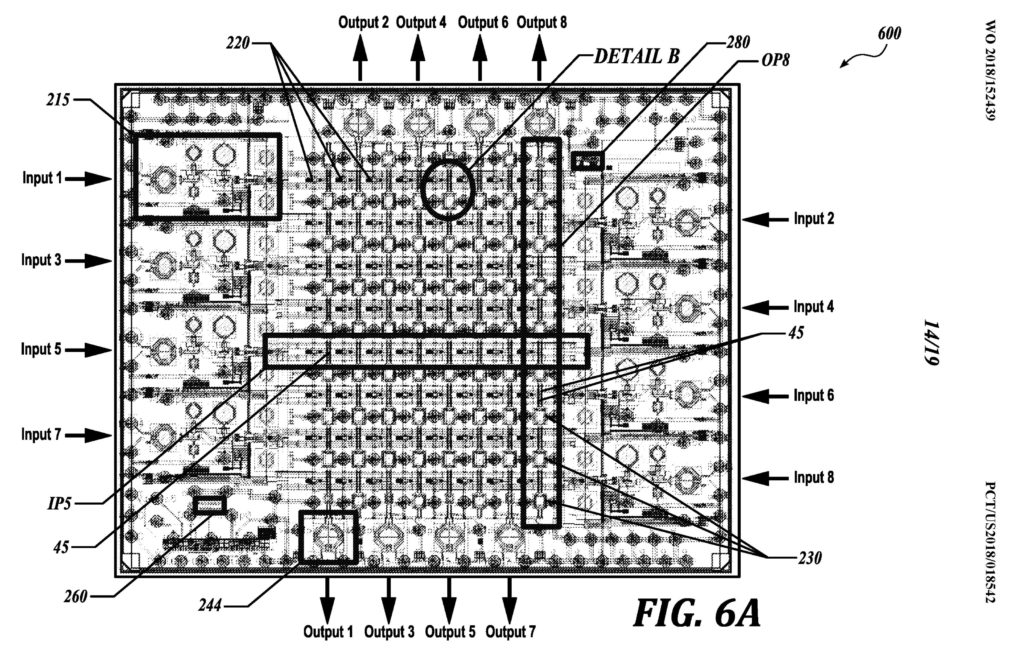
- Patent diagrams like this show various subcomponents of a sandwiched phased array antenna, comprised of multiple printed circuit boards. (SpaceX)
- The technical term for this is “science rectangle.” In all seriousness, this is actually an extraordinary glimpse at custom silicon developed in-house at SpaceX, in this case a semiconductor die. (SpaceX)
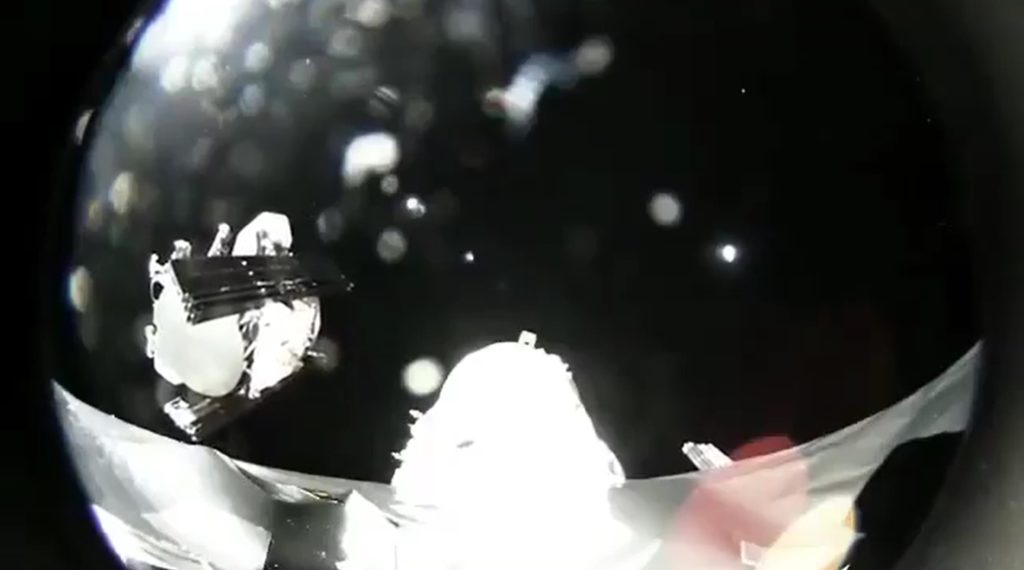
- One of the first two prototype Starlink satellites separates from Falcon 9’s upper stage in February 2018. (SpaceX)
If SpaceX can perfect this, they will be the only company in the world to have done so on-orbit, while other satellite operators like Iridium have managed to build and launch low-bandwidth phased arrays but have yet to attempt to do so with the bands optimal for broadband internet or at a scale that might work for constellations of hundreds or even thousands of satellites. If Jurvetson is to be believed, SpaceX’s first foray into dedicated communications satellites and specialized hardware design and manufacturing has been a major success.
Even if the orbits of Tintin A and B do suggest that some difficulties were had with at least one satellite’s electric propulsion thrusters, it’s obvious that the experience and data derived from testing the vast majority of each satellite’s non-propulsion-related systems were invaluable and well worth the effort. Another group of prototypes will likely be launched according to Elon Musk, but that’s simply how SpaceX develops complex systems – build, launch, learn, and repeat.
For prompt updates, on-the-ground perspectives, and unique glimpses of SpaceX’s rocket recovery fleet check out our brand new LaunchPad and LandingZone newsletters!

News
Tesla brings closure to flagship ‘sentimental’ models, Musk confirms

Tesla is bringing closure to its flagship Model S and Model X vehicles, which CEO Elon Musk said several years ago were only produced for “sentimental reasons.”
The Model S and Model X have been light contributors to Tesla’s delivery growth over the past few years, commonly contributing only a few percentage points toward the over 1.7 million cars the company has handed over to customers annually since 2022.
However, the Model S and Model X have remained in production because of their high-end performance and flagship status; they are truly two vehicles that are premium offerings and do not hold major weight toward Tesla’s future goals.
On Wednesday, during the Q4 2025 Earnings Call, Musk confirmed that Tesla would bring closure to the two models, ending their production and making way for the manufacturing efforts of the Optimus robot:
“It is time to bring the Model S and Model X programs to an end with an honorable discharge. It is time to bring the S/X programs to an end. It’s part of our overall shift to an autonomous future.”
Musk said the production lines that Tesla has for the Model S and Model X at the Fremont Factory in Northern California will be transitioned to Optimus production lines that will produce one million units per year.
Tesla Fremont Factory celebrates 15 years of electric vehicle production
Tesla will continue to service Model S and Model X vehicles, but it will officially stop deliveries of the cars in Q2, as inventory will be liquidated. When they’re gone, they’re gone.
BREAKING: Tesla will wind down Model S and Model X production next quarter, Elon Musk confirms.
“It is time to bring the Model S and Model X programs to an end with an honorable discharge.” pic.twitter.com/Czn7aQjJE1
— TESLARATI (@Teslarati) January 28, 2026
Tesla has been making moves to sunset the two vehicles for the better part of one year. Last July, it stopped taking any custom orders for vehicles in Europe, essentially pushing the idea that the program was coming to a close soon.
Musk said back in 2019:
“I mean, they’re very expensive, made in low volume. To be totally frank, we’re continuing to make them more for sentimental reasons than anything else. They’re really of minor importance to the future.”
That point is more relevant than ever as Tesla is ending the production of the cars to make way for Optimus, which will likely be Tesla’s biggest product in the coming years.
Musk added during the Earnings Call on Wednesday that he believes Optimus will be a major needle-mover of the United States’ GDP, as it will increase productivity and enable universal high income for humans.
Investor's Corner
LIVE BLOG: Tesla (TSLA) Q4 and FY 2025 earnings call
Tesla’s (NASDAQ:TSLA) earnings call follows the release of the company’s Q4 and full-year 2025 update letter.

Tesla’s (NASDAQ:TSLA) earnings call follows the release of the company’s Q4 and full-year 2025 update letter, which was published on Tesla’s Investor Relations website after markets closed on January 28, 2025.
The results cap a quarter in which Tesla produced more than 434,000 vehicles, delivered over 418,000 vehicles, and deployed 14.2 GWh of energy storage products. For the full year, Tesla produced 1.65 million vehicles and delivered 1.63 million, while total energy storage deployments reached 46.7 GWh.
Tesla’s Q4 and FY 2025 Results
According to Tesla’s Q4 and FY 2025 Update Letter, the company posted GAAP earnings per share of $0.24 and non-GAAP EPS of $0.50 in the fourth quarter. Total revenue for Q4 came in at $24.901 billion, while GAAP net income was reported at $840 million.
For full-year 2025, Tesla reported GAAP EPS of $1.08 and non-GAAP EPS of $1.66 per share. Total revenue reached $94.83 billion, including $69.53 billion from automotive operations and $12.78 billion from the company’s energy generation and storage business. GAAP net income for the year totaled $3.79 billion.
Earnings call updates
The following are live updates from Tesla’s Q4 and FY 2025 earnings call. I will be updating this article in real time, so please keep refreshing the page to view the latest updates on this story.
16:25 CT – Good day to everyone, and welcome to another Tesla earnings call live blog. There’s a lot to unpack from Tesla’s Q4 and FY 2025 update letter, so I’m pretty sure this earnings call will be quite interesting.
16:30 CT – The Q4 and FY 2025 earnings call officially starts. IR exec Travis Axelrod opens the call. Elon and other executives are present.
16:30 CT – Elon makes his opening statement and explains why Tesla changed its mission to “Amazing Abundance.” “With the continued growth of AI and robotics, I think we’re headed towards a future of universal high income,” Musk said, adding that along the way, Tesla will still be improving its products while keeping the environment safe and healthy.
16:34 CT – Elon noted that the first steps for this future are happening this year, thanks to Tesla’s autonomy and robotics programs, which will be launching and ramping this year. He also highlighted that Tesla will be making major investments this year, though the company will be very strategic when it comes to its funding. “I think it makes a ton of strategic sense,” Musk said.
16:36 CT – Elon also announces the end of the Model S and Model X programs “with an honorable discharge.” If you’re interested in buying a Model S or X, it’s best to do it now, Musk said. The Model S and Model X factory in Fremont will be replaced by an Optimus line. “It’s slightly sad, but it is time to bring the S and X program to an end. It’s part of our overall shift to an autonomous future,” Musk said.
16:38 CT – Elon discusses how Unsupervised FSD is now starting for the Robotaxi service. He noted that these Unsupervised Robotaxis don’t have any chase cars as of yesterday. He reiterated Tesla’s plans for owners to be able to add their own vehicles to the Robotaxi fleet. Autonomy target for the end of the year is about a quarter or half of the United States, Musk said.
16:41 CT – Elon noted that the Tesla Energy team is absolutely killing it. He also stated that Tesla expects its Energy business to continue growing, and that the “solar opportunity is underrated.”
16:43 CT –Elon also added that Tesla Optimus 3 will be unveiled in about three months, probably. The Model S and Model X line in Fremont will be a million-unit Optimus production line. Looks like Optimus is really coming out of the gate with large, meaningful volumes. “The normal S curve for manufacturing ramps is longer for Optimus,” Musk stated. “Long term, I think Optimus will have a significant impact on the US GDP.”
16:44 CT – Elon closes his opening statements with a sincere thanks to the Tesla team. He also noted that he feels fortunate to be able to work alongside such a talented workforce.
Elon ends his opening remarks with an optimistic prediction about the future.“The future is more exciting than you can imagine,” he concluded.
16:47 CT – Tesla CFO Vaibhav Taneja makes his opening remarks. He discusses several aspects of Tesla’s Q4 milestones. He noted that Tesla Energy achieved yet another gross profit record during the fourth quarter. There’s insane demand for the Megapack and Powerwall. Backlogs for these products are healthy this 2026. He also noted that Tesla ended 2025 with a bigger vehicle order backlog compared to recent years.
16:53 CT – Investor questions from Say begin. The first question is about Tesla’s expectations for the Robotaxi Network. Lars Moravy noted that it has the advantage of manufacturing and scale, and Tesla believes that the Robotaxi Network will significantly grow year over year. Elon highlighted that the Cybercab will be produced with no steering wheel or pedals. No fallback. Elon also noted that Tesla expects to produce more Cybercabs than all its other vehicles combined in the future.
16:51 CT – The next question is if Tesla still expects to launch new models, such as affordable cars. Lars Moravy noted that Tesla did release affordable variants last year, and Tesla is still pushing hard to lower its costs. That being said, Tesla is really pushing the Cybercab as its total addressable market is larger than consumer-owned cars. Lars also mentioned that Tesla will produce different vehicles for its Robotaxi services.
16:56 CT – Elon noted that eventually, Tesla will produce mostly autonomous cars. The exception would be the next-generation Roadster, which will be a true driver’s car.
17:03 CT – A question about Elon’s past comments about a potential next pickup truck was asked. Lars noted that the Cybertruck is still performing well in the electric pickup truck segment, though Tesla is known for flexibility. Elon added that Tesla will be transitioning the Cybertruck line to a fully autonomous vehicle line. He also stated that the Cybertruck is a useful vehicle. “An autonomous Cybertruck will be useful for that.”
17:10 CT – A question was asked about when FSD will be 100% Unsupervised. Elon noted that 100% Unsupervised FSD is already being used today, though only in the Austin Robotaxi program. Tesla is still being extremely careful with its rollout.
When asked about Tesla’s chip program, Elon noted that he feels pretty good about Tesla’s chip strategy. But in terms of selling Tesla’s chips outside Tesla, the company has to make sure it has enough chips for Optimus robots, data centers, and other programs first.
17:18 CT – Analyst questions begin. First up is Wolf Research. He asks about Tesla’s increasing Capex, specifically where the majority of it is going. The Tesla CFO noted that programs in six factories are going live this year, so that consumes Capex. The Optimus program also consumes a lot of resources. The growth of Tesla’s current capacity is also consuming a lot of resources. As for how these programs will be funded, the CFO pointed to Tesla’s massive war chest, as well as initiatives such as the Robotaxi Network.
17:21 CT – Morgan Stanley asks about Tesla’s xAI investment. The analyst asked about more information about how Tesla and xAI will work together. The CFO noted that this investment is part of Master Plan Part IV. Elon also mentioned some advantages for xAI’s technology for Tesla’s products, like Grok being used to manage a Robotaxi fleet or a group of Optimus robots.
17:24 CT – Barclays asks Elon about the constraints on memory. Does Tesla have any near term constraints for Tesla vehicles’ memory? Elon responded that the Tesla AI computer is already very compute and memory-efficient. The intelligence per gigabyte is important. Musk noted that Tesla is ahead of the industry by an order of magnitude or more.
17:29 CT – Cannacord asks about startups from China entering the humanoid market. What competitive advantage does Optimus have compared to these rivals? Elon stated that he believes China will be a key competitor in the humanoid robot market. China will be the toughest competitor for Tesla. That being said, Elon noted that Tesla believes Optimus will be ahead in real-world intelligence, electromechanical dexterity, and hand design.
News
Tesla announces massive investment into xAI
“On January 16, 2026, Tesla entered into an agreement to invest approximately $2 billion to acquire shares of Series E Preferred Stock of xAI as part of their recent publicly-disclosed financing round,” it said.

Tesla has announced a major development in its ventures outside of electric vehicles, as it confirmed today that it invested $2 billion into xAI on January 16.
The move is significant, as it marks the acquisition of shares of Series E Preferred Stock, executed on market terms alongside other investors. The company officially announced it in its Q4 2025 Shareholder Deck, which was released at market close on Wednesday.
The investment follows shareholder approval in 2025 for potential equity stakes in xAI and echoes SpaceX’s earlier $2 billion contribution to xAI’s $10 billion fundraising round.
Tesla said that, earlier this month, it entered an agreement to invest $2 billion to acquire shares of Series E Preferred Stock of xAI:
“Tesla’s investment was made on market terms consistent with those previously agreed to by other investors in the financing round. As set forth… pic.twitter.com/HgtrcHdB2U
— TESLARATI (@Teslarati) January 28, 2026
CEO Elon Musk, who is behind both companies, is now weaving what appears to be an even tighter ecosystem among his ventures, blending Tesla’s hardware prowess with xAI’s cutting-edge AI models, like Grok.
Tesla confirmed the investment in a statement in its Shareholder Deck:
“On January 16, 2026, Tesla entered into an agreement to invest approximately $2 billion to acquire shares of Series E Preferred Stock of xAI as part of their recent publicly-disclosed financing round. Tesla’s investment was made on market terms consistent with those previously agreed to by other investors in the financing round. As set forth in Master Plan Part IV, Tesla is building products and services that bring AI into the physical world. Meanwhile, xAI is developing leading digital AI products and services, such as its large language model (Grok).”
It continued:
“In that context, and as part of Tesla’s broader strategy under Master Plan Part IV, Tesla and xAI also entered into a framework agreement in connection with the investment. Among other things, the framework agreement builds upon the existing relationship between Tesla and xAI by providing a framework for evaluating potential AI collaborations between the companies. Together, the investment and the related framework agreement are intended to enhance Tesla’s ability to develop and deploy AI products and services into the physical world at scale. This investment is subject to customary regulatory conditions with the expectation to close in Q1’2026.”
The history of the partnership traces back to xAI’s founding in July 2023, as Musk launched the company as a counterweight to dominant AI players like OpenAI and Google.
xAI aimed to “understand the true nature of the universe” through unbiased, truth-seeking AI. Tesla, meanwhile, has long invested in AI for its Full Self-Driving (FSD) software and Optimus robots, training models on vast datasets from its vehicle fleet.
The investment holds profound significance for both companies.
For Tesla, it accelerates its Master Plan Part IV, which envisions AI-driven autonomy in vehicles and humanoid robots. xAI’s Grok could enhance Tesla’s real-world AI applications, from optimizing battery management to predictive maintenance, potentially giving Tesla an edge over its biggest rivals, like Waymo.
Investors, on the other hand, stand to gain from this symbiosis. Tesla Shareholders may see boosted stock value through AI innovations, with analysts projecting enhanced margins and significant future growth in robotics. xAI’s valuation could soar, attracting more capital.