SpaceX
SpaceX’s Falcon 9 faced its most challenging reentry and landing yet
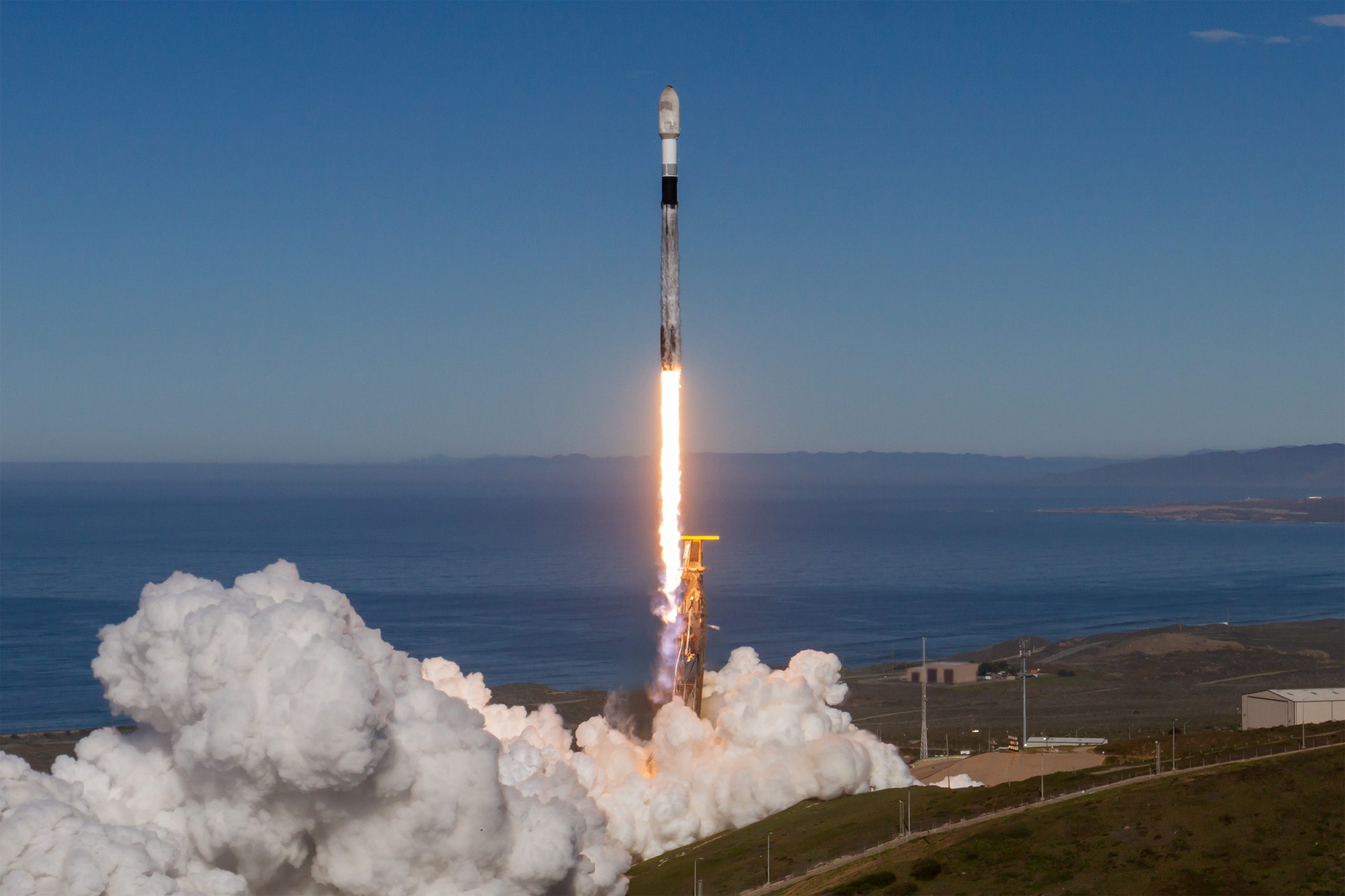
SpaceX has completed its second successful launch of 2019, sending the first commercial Moon lander on the first leg of its journey to the lunar surface with a sooty Falcon 9 Block 5 rocket.
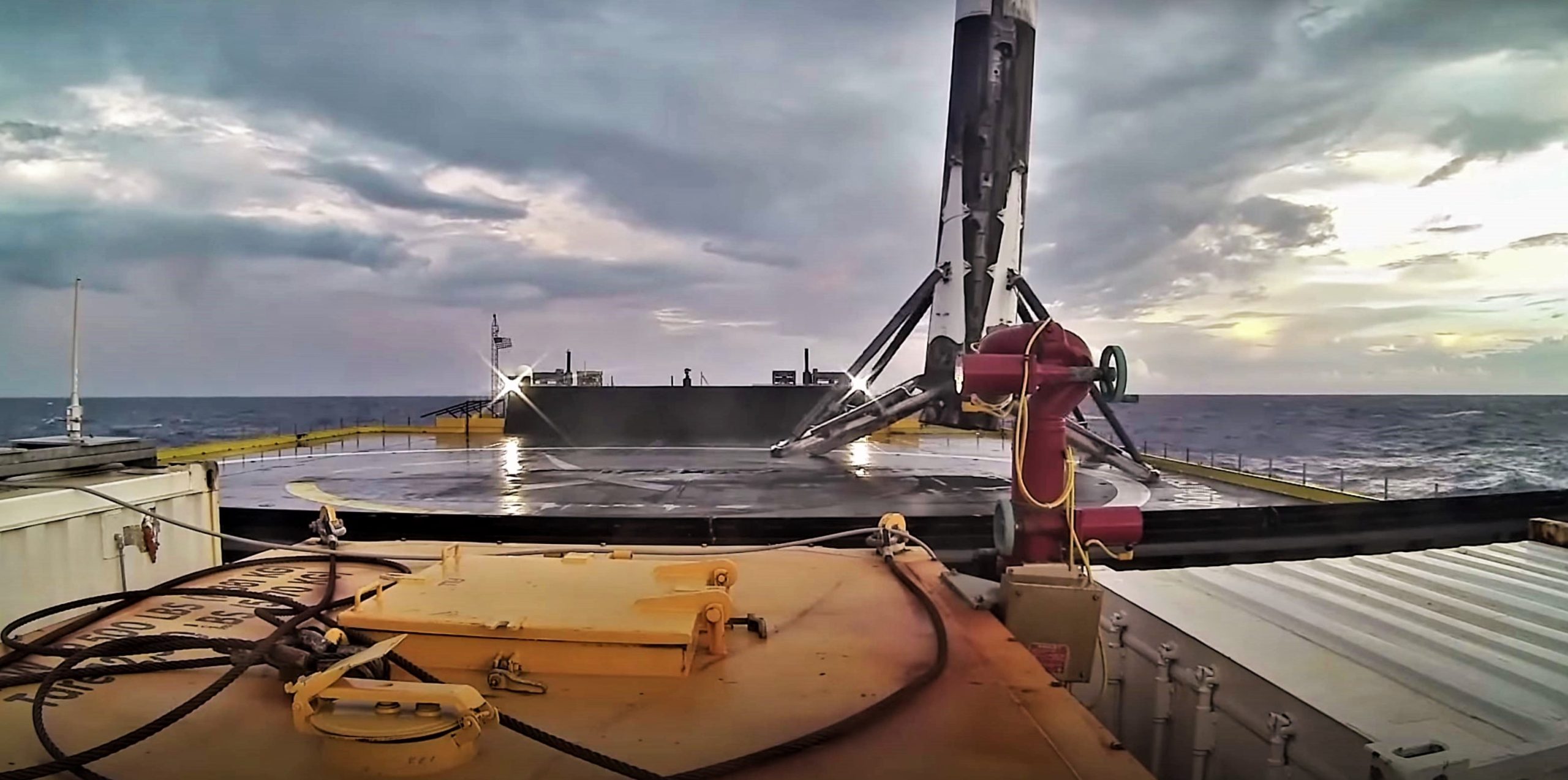
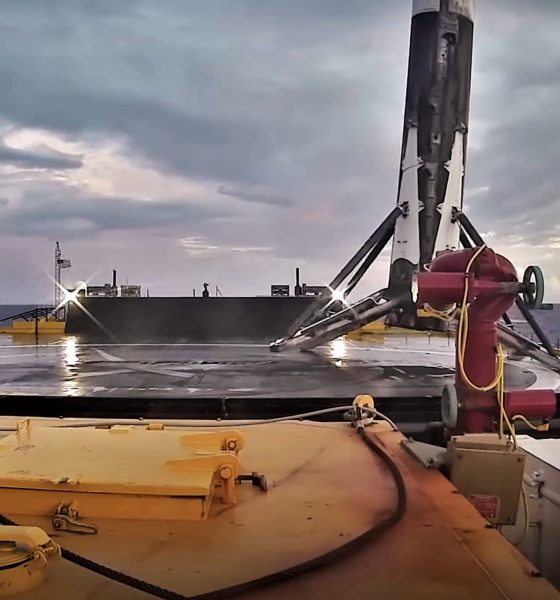
Built by Israeli aerospace company IAI for customer SpaceIL, the Moon lander – named Beresheet, Hebrew for “in the beginning” – is just one of three payloads present on this launch, gently perched with Air Force satellite S5 atop Indonesian communications satellite PSN-6. According to SpaceX, Falcon 9 B1048’s third successful launch and landing faced the Block 5 booster with “some of the most challenging reentry conditions to date”.
https://twitter.com/_TomCross_/status/1098766636780261378
After separating from Falcon 9’s upper stage and payload at an altitude of 68 km (43 mi) and a velocity of nearly 2.4 km/s (1.5 mi/s, Mach 7+), B1048 continued on in the near-vacuum of suborbital space, likely peaking at 80-100 km before heading back down into the thicker parts of Earth’s atmosphere. Despite what one SpaceX engineer described as “the most challenging reentry conditions to date”, B1048 appeared to perform perfectly over the course of its third launch and landing.
According to SpaceX CEO Elon Musk, the booster could fly again as early as April in support of Crew Dragon’s in-flight abort mission, although his implication that that test will occur in April directly contradicts a recent NASA schedule update that pegged the test no earlier than (NET) June 2019.
Highest reentry heating to date. Burning metal sparks from base heat shield visible in landing video. Fourth relight scheduled for April. https://t.co/uq6TdMhgFN
— Elon Musk (@elonmusk) February 22, 2019
Shortly before the main PSN-6 satellite was deployed from Falcon 9’s upper stage, one of SpaceX’s launch network operators verbally confirmed that SpaceIL’s Beresheet lander had established communications with the ground and successfully deployed its landing legs in orbit, one tangible step closer to the first attempted commercial Moon landing. Beresheet and PSN-6 will now take opposite paths forward, with the lunar lander raising its orbit quite literally to the Moon while PSN-6 drops its high end down and circularizes at approximately 35,800 km (22,250 mi) above Earth.
Combined with Musk’s apparent belief that B1048 – having just experienced what he described as the “highest reentry heating to date” – could be ready to launch again as few as 40-70 days from now, this successful launch and landing of a flight-proven Falcon 9 booster (the second time a SpaceX rocket as flown for the third time) suggests that the Block 5 upgrade continues to operate nominally. Designed to radically improve the ease and speed of Falcon 9 booster reuse, Block 5 debuted in May 2018 and has now launched 12 times, with half of those missions flying on flight-proven boosters. The proportion of flight-proven to new booster launches is likely to continue to grow in 2019, ultimately reaching a point where new boosters are limited to inaugural hardware debuts or specific contractual requests from conservative US government customers.
https://twitter.com/_TomCross_/status/1098734999027752961?
Up next for SpaceX is the imminent orbital launch debut of Crew Dragon, set to occur no earlier than March 2nd. While a slip of several days or more is not out of the question, the lack of date movement less than ten days out from the target launch date suggests that this particular date is far more confident than the several that preceded it. Regardless, we’ll find out tomorrow just how confident NASA and SpaceX are in DM-1’s March 2nd launch plan.
Check out Teslarati’s newsletters for prompt updates, on-the-ground perspectives, and unique glimpses of SpaceX’s rocket launch and recovery processes!

Elon Musk
SpaceX officially acquires xAI, merging rockets with AI expertise

SpaceX has officially acquired xAI, merging rockets with AI expertise in what is the first move to bring Elon Musk’s companies under one umbrella.
On February 2, SpaceX officially announced the acquisition of xAI, uniting two powerhouse companies under a single entity, creating what the space exploration company called in a blog post “one of the most ambitious, vertically integrated innovation engines on (and off) Earth.”
🚨 BREAKING: Elon Musk has posted a new blog on SpaceX’s website confirming the acquisition of xAI pic.twitter.com/TFgeHGMpXc
— TESLARATI (@Teslarati) February 2, 2026
The deal will integrate xAI’s advanced AI capabilities, including the Grok chatbot and massive training infrastructure, with SpaceX’s rocket technology, Starlink satellite network, and ambitious space exploration goals.
The acquisition comes at a pivotal moment: xAI is valued at around $230 billion as of late 2025, and has been racing to scale AI compute amid global competition from companies like OpenAI, Google, and Meta. Meanwhile, SpaceX, which was recently valued at $800 billion, is facing escalating costs for its multiplanetary ambitions.
By combining forces, the merged entity gains a unified approach to tackle one of AI’s biggest bottlenecks: the enormous energy and infrastructure demands of next-gen models.
Musk wrote in a blog post on SpaceX’s website that:
“In the long term, space-based AI is obviously the only way to scale. To harness even a millionth of our Sun’s energy would require over a million times more energy than our civilization currently uses! The only logical solution therefore is to transport these resource-intensive efforts to a location with vast power and space. I mean, space is called “space” for a reason.”
Musk details the need for orbital data centers, stating that his estimate is that “within 2 to 3 years, the lowest cost way to generate AI compute will be in space.
This cost-efficiency alone will enable innovative companies to forge ahead in training their AI models and processing data at unprecedented speeds and scales, accelerating breakthroughs in our understanding of physics and invention of technologies to benefit humanity.”
SpaceX recently filed for approval from the FCC to launch up to one million solar-powered satellites configured as high-bandwidth, optically linked compute platforms.
These facilities would harness near-constant sunlight with minimal maintenance, delivering what the company projects as transformative efficiency.
Musk has long argued that space offers the ultimate solution for power-hungry AI projects. But that’s not all the merger will take care of.
Additionally, it positions the company to fund broader goals. Revenue from the Starlink expansion, potential SpaceX IPO, and AI-driven applications could accelerate the development of lunar bases, as Musk believes multiplanetary life will be crucial to saving civilization.
Critics question the feasibility of massive constellations amid orbital debris concerns and regulatory hurdles. Yet, proponents see it as a bold step toward a multiplanetary computing infrastructure that extends human civilization beyond Earth.
Elon Musk
Rumored SpaceX-xAI merger gets apparent confirmation from Elon Musk
The comment follows reports that the rocket maker is weighing a transaction that could further consolidate Musk’s space and AI ventures.

Elon Musk appeared to confirm reports that SpaceX is exploring a potential merger with artificial intelligence startup xAI by responding positively to a post about the reported transaction on X.
Musk’s comment follows reports that the rocket maker is weighing a transaction that could further consolidate his space and AI ventures.
SpaceX xAI merger
As per a recent Reuters report, SpaceX has held discussions about merging with xAI, with the proposed structure potentially involving an exchange of xAI shares for SpaceX stock. The value, structure, and timing of any deal have not been finalized, and no agreement has been signed.
Musk appeared to acknowledge the report in a brief reply on X, responding “Yeah” to a post that described SpaceX as a future “Dyson Swarm company.” The comment references a Dyson Swarm, a sci-fi megastructure concept that consists of a massive network of satellites or structures that orbit a celestial body to harness its energy.
Reuters noted that two entities were formed in Nevada on January 21 to facilitate a potential transaction for the possible SpaceX-xAI merger. The discussions remain ongoing, and a transaction is not yet guaranteed, however.
AI and space infrastructure
A potential merger with xAI would align with Musk’s stated strategy of integrating artificial intelligence development with space-based systems. Musk has previously said that space-based infrastructure could support large-scale computing by leveraging continuous solar energy, an approach he has framed as economically scalable over time.
xAI already has operational ties to Musk’s other companies. The startup develops Grok, a large language model that holds a U.S. Department of Defense contract valued at up to $200 million. AI also plays a central role in SpaceX’s Starlink and Starshield satellite programs, which rely on automation and machine learning for network management and national security applications.
Musk has previously consolidated his businesses through share-based transactions, including Tesla’s acquisition of SolarCity in 2016 and xAI’s acquisition of X last year. Bloomberg has also claimed that Musk is considering a merger between SpaceX and Tesla in the future.
Elon Musk
SpaceX reportedly discussing merger with xAI ahead of blockbuster IPO

In a groundbreaking new report from Reuters, SpaceX is reportedly discussing merger possibilities with xAI ahead of the space exploration company’s plans to IPO later this year, in what would be a blockbuster move.
The outlet said it would combine rockets and Starlink satellites, as well as the X social media platform and AI project Grok under one roof. The report cites “a person briefed on the matter and two recent company filings seen by Reuters.”
Musk, nor SpaceX or xAI, have commented on the report, so, as of now, it is unconfirmed.
With that being said, the proposed merger would bring shares of xAI in exchange for shares of SpaceX. Both companies were registered in Nevada to expedite the transaction, according to the report.
On January 21, both entities were registered in Nevada. The report continues:
“One of them, a limited liability company, lists SpaceX and Bret Johnsen, the company’s chief financial officer, as managing members, while the other lists Johnsen as the company’s only officer, the filings show.”
The source also stated that some xAI executives could be given the option to receive cash in lieu of SpaceX stock. No agreement has been reached, nothing has been signed, and the timing and structure, as well as other important details, have not been finalized.
SpaceX is valued at $800 billion and is the most valuable privately held company, while xAI is valued at $230 billion as of November. SpaceX could be going public later this year, as Musk has said as recently as December that the company would offer its stock publicly.
The plans could help move along plans for large-scale data centers in space, something Musk has discussed on several occasions over the past few months.
At the World Economic Forum last week, Musk said:
“It’s a no-brainer for building solar-powered AI data centers in space, because as I mentioned, it’s also very cold in space. The net effect is that the lowest cost place to put AI will be space and that will be true within two to three years, three at the latest.”
He also said on X that “the most important thing in the next 3-4 years is data centers in space.”
If the report is true and the two companies end up coming together, it would not be the first time Musk’s companies have ended up coming together. He used Tesla stock to purchase SolarCity back in 2016. Last year, X became part of xAI in a share swap.