

News
SpaceX CEO Elon Musk explains why Falcon Heavy’s center core missed the drone ship
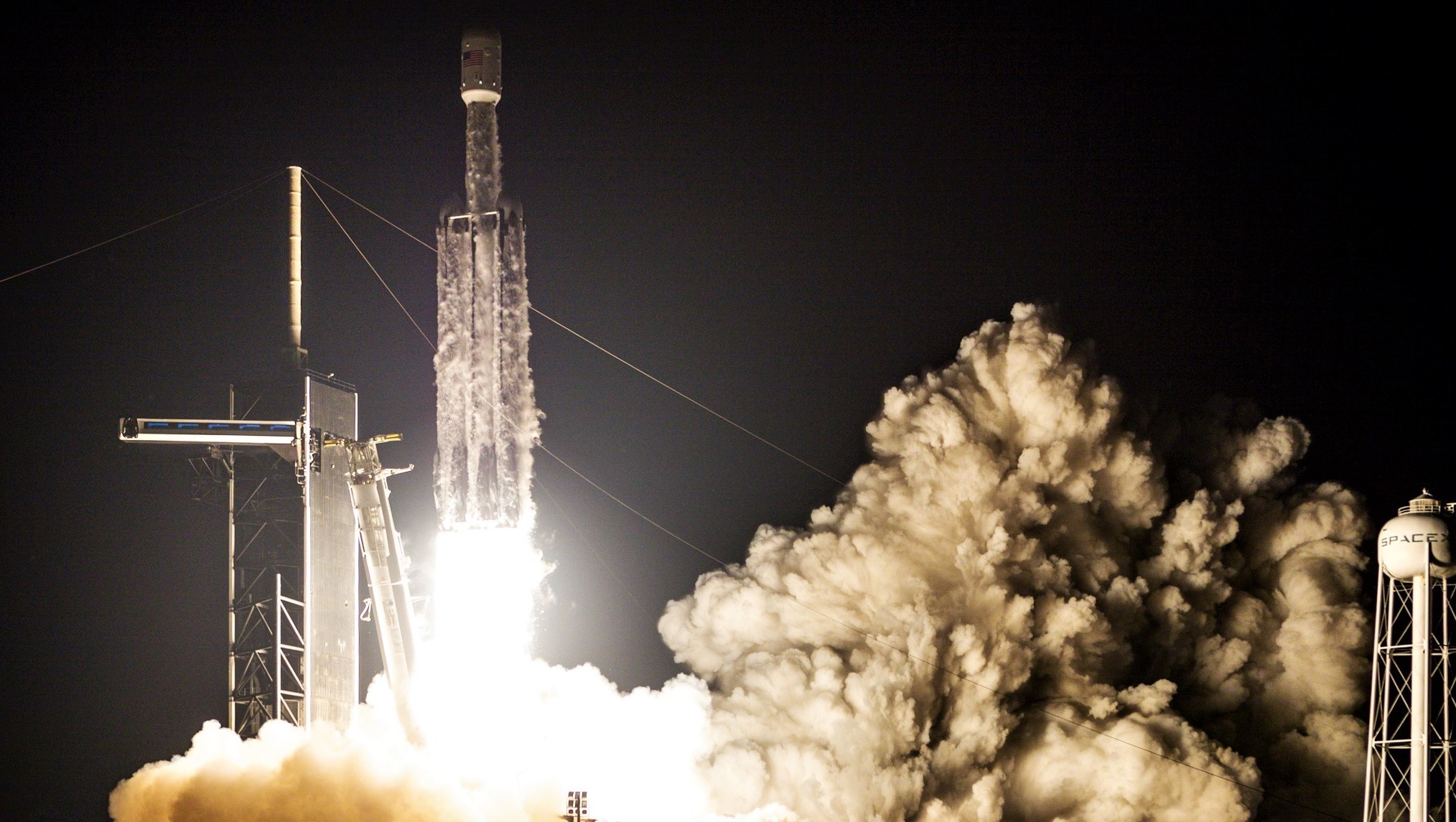
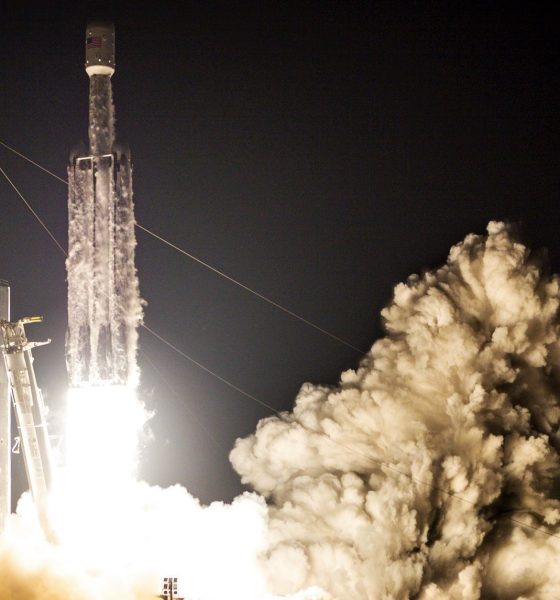
Some 12 hours after Falcon Heavy successfully completed what Elon Musk described as the SpaceX’s “most difficult launch ever”, the CEO took to Twitter to offer some insight into the mission’s only sad note – an unsuccessful center core recovery attempt.
The second Falcon Heavy Block 5 center core built by SpaceX, B1057 suffered an untimely demise shortly after its first (and last) launch, failing to successfully land aboard drone ship Of Course I Still Love You (OCISLY). Although an undeniable disappointment, the overall STP-2 mission was a spectacular success and will without a doubt serve SpaceX well as the company eyes its first certified Falcon Heavy launches for the US military. New center cores can and will be produced and there should be no doubt that SpaceX will eventually perfect center core recovery (or transcend the need entirely with Starship).
As noted by both CEO Elon Musk and several SpaceX engineers-turned-webcast-hosts, aside from the fact that the overall mission was by far the company’s most challenging yet, center core B1057’s recovery was also expected to be the most challenging booster landing ever. The booster’s landing target was drone ship OCISLY, stationed a record-smashing 1240 km (770 mi) off the coast of Florida – almost 30% further than any previous recovery attempt.
Sadly, SpaceX either chose not to broadcast the center core’s onboard camera during reentry or the booster could not maintain a downlink connection during the ordeal. However, based on basic info that was included in the webcast, B1057 completed its boost burn and separated from the upper stage and Space Test Program-2 (STP-2) payload some 3 minutes and 40 seconds after lifting off from Pad 39A. At MECO (main-engine cutoff), the building-sized booster was traveling a blistering 3.1 km/s (Mach 9) at an altitude of more than 120 km (75 mi).

Running on slim propellant margins, the booster coasted through vacuum almost the entire way to drone ship OCISLY. Around 9 minutes after launch, B1057 began its entry burn, likely igniting three Merlin 1D engines to effectively cushion it against the worst of atmospheric reentry heating. Unintuitively, much of the actual benefit of that burn derives from that cushioning effect, while the burn only slows the booster down by a few hundred meters per second (mph).
Effectively falling in near-vacuum conditions, pulled by gravity, B1057 could easily have been traveling 3.5-4 km/s (Mach 10-12) by the time Earth’s atmosphere began to slow it down. Described by Musk himself, back-of-the-envelope analysis of available telemetry apparently indicated that that spectacularly fast and hot reentry either burned through B1057’s heavy titanium heat shield or broke through the smaller heat shield surrounding its M1D engine bells.
In short, the brutal heating and buffeting of hypersonic atmospheric reentry damaged the rocket’s central M1D engine, necessary for an accurately controlled drone ship landing. Incredibly, B1057 actually appeared to make it almost all the way to a successful recovery, veering off course just a few hundred meters above OCISLY. Musk also noted that this may have actually been an instance of the rocket’s autonomous guidance computer intentionally abort a landing attempt to protect the drone ship. It’s possible that the reentry didn’t fully destroy components, but rather damaged them to the point that they failed only after a sustained landing burn.

Regardless, the end result is unambiguous. Falcon Heavy center core B1057 did its job perfectly, supporting the STP-2 launch, boosting the upper stage and payload almost half the way to orbit, and eventually sacrificing itself to avoid potentially damaging OCISLY. SpaceX’s next Falcon Heavy launch is currently scheduled to launch the very large AFSPC-52 military satellite no earlier than September 2020, a full 15 months away. The company should have no trouble manufacturing multiple new center cores between now and then.
Check out Teslarati’s Marketplace! We offer Tesla accessories, including for the Tesla Cybertruck and Tesla Model 3.

News
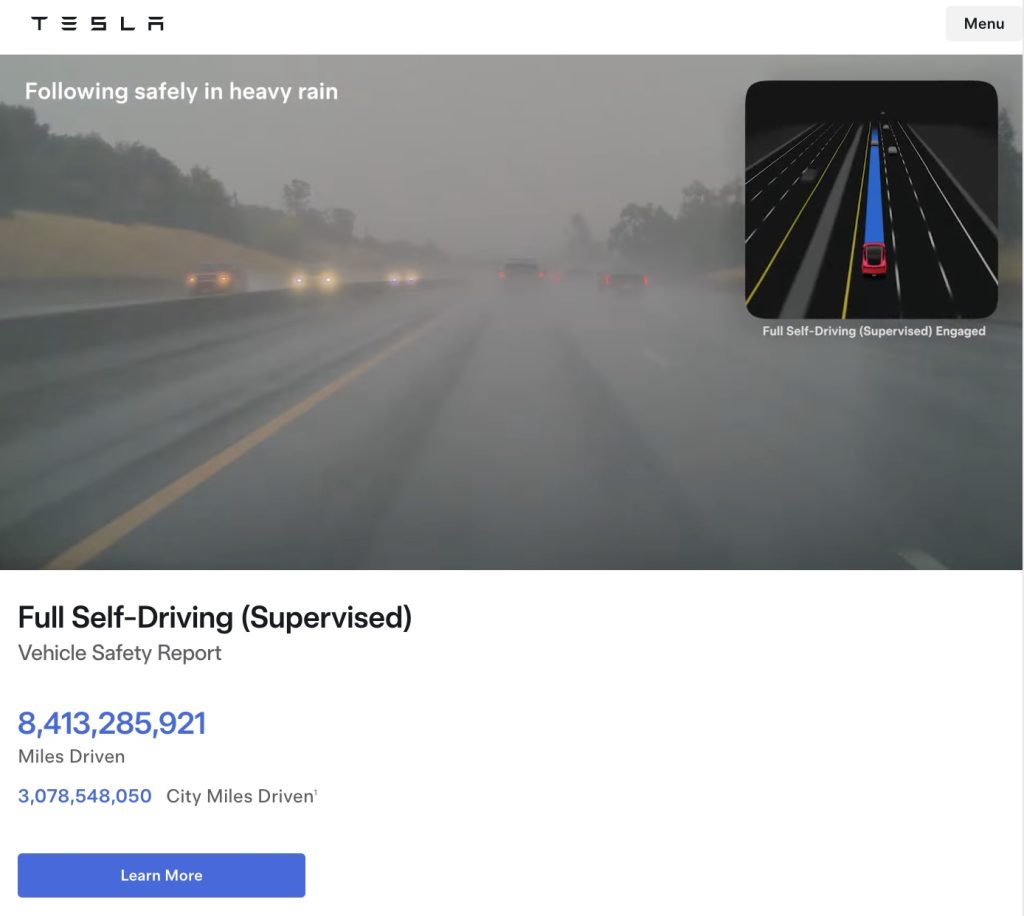
Tesla FSD (Supervised) fleet passes 8.4 billion cumulative miles
The figure appears on Tesla’s official safety page, which tracks performance data for FSD (Supervised) and other safety technologies.

Tesla’s Full Self-Driving (Supervised) system has now surpassed 8.4 billion cumulative miles.
The figure appears on Tesla’s official safety page, which tracks performance data for FSD (Supervised) and other safety technologies.
Tesla has long emphasized that large-scale real-world data is central to improving its neural network-based approach to autonomy. Each mile driven with FSD (Supervised) engaged contributes additional edge cases and scenario training for the system.
The milestone also brings Tesla closer to a benchmark previously outlined by CEO Elon Musk. Musk has stated that roughly 10 billion miles of training data may be needed to achieve safe unsupervised self-driving at scale, citing the “long tail” of rare but complex driving situations that must be learned through experience.
The growth curve of FSD Supervised’s cumulative miles over the past five years has been notable.
As noted in data shared by Tesla watcher Sawyer Merritt, annual FSD (Supervised) miles have increased from roughly 6 million in 2021 to 80 million in 2022, 670 million in 2023, 2.25 billion in 2024, and 4.25 billion in 2025. In just the first 50 days of 2026, Tesla owners logged another 1 billion miles.
At the current pace, the fleet is trending towards hitting about 10 billion FSD Supervised miles this year. The increase has been driven by Tesla’s growing vehicle fleet, periodic free trials, and expanding Robotaxi operations, among others.
With the fleet now past 8.4 billion cumulative miles, Tesla’s supervised system is approaching that threshold, even as regulatory approval for fully unsupervised deployment remains subject to further validation and oversight.
Elon Musk
Elon Musk fires back after Wikipedia co-founder claims neutrality and dubs Grokipedia “ridiculous”
Musk’s response to Wales’ comments, which were posted on social media platform X, was short and direct: “Famous last words.”

Elon Musk fired back at Wikipedia co-founder Jimmy Wales after the longtime online encyclopedia leader dismissed xAI’s new AI-powered alternative, Grokipedia, as a “ridiculous” idea that is bound to fail.
Musk’s response to Wales’ comments, which were posted on social media platform X, was short and direct: “Famous last words.”
Wales made the comments while answering questions about Wikipedia’s neutrality. According to Wales, Wikipedia prides itself on neutrality.
“One of our core values at Wikipedia is neutrality. A neutral point of view is non-negotiable. It’s in the community, unquestioned… The idea that we’ve become somehow ‘Wokepidea’ is just not true,” Wales said.
When asked about potential competition from Grokipedia, Wales downplayed the situation. “There is no competition. I don’t know if anyone uses Grokipedia. I think it is a ridiculous idea that will never work,” Wales wrote.
After Grokipedia went live, Larry Sanger, also a co-founder of Wikipedia, wrote on X that his initial impression of the AI-powered Wikipedia alternative was “very OK.”
“My initial impression, looking at my own article and poking around here and there, is that Grokipedia is very OK. The jury’s still out as to whether it’s actually better than Wikipedia. But at this point I would have to say ‘maybe!’” Sanger stated.
Musk responded to Sanger’s assessment by saying it was “accurate.” In a separate post, he added that even in its V0.1 form, Grokipedia was already better than Wikipedia.
During a past appearance on the Tucker Carlson Show, Sanger argued that Wikipedia has drifted from its original vision, citing concerns about how its “Reliable sources/Perennial sources” framework categorizes publications by perceived credibility. As per Sanger, Wikipedia’s “Reliable sources/Perennial sources” list leans heavily left, with conservative publications getting effectively blacklisted in favor of their more liberal counterparts.
As of writing, Grokipedia has reportedly surpassed 80% of English Wikipedia’s article count.
News
Tesla Sweden appeals after grid company refuses to restore existing Supercharger due to union strike
The charging site was previously functioning before it was temporarily disconnected in April last year for electrical safety reasons.

Tesla Sweden is seeking regulatory intervention after a Swedish power grid company refused to reconnect an already operational Supercharger station in Åre due to ongoing union sympathy actions.
The charging site was previously functioning before it was temporarily disconnected in April last year for electrical safety reasons. A temporary construction power cabinet supplying the station had fallen over, described by Tesla as occurring “under unclear circumstances.” The power was then cut at the request of Tesla’s installation contractor to allow safe repair work.
While the safety issue was resolved, the station has not been brought back online. Stefan Sedin, CEO of Jämtkraft elnät, told Dagens Arbete (DA) that power will not be restored to the existing Supercharger station as long as the electric vehicle maker’s union issues are ongoing.
“One of our installers noticed that the construction power had been backed up and was on the ground. We asked Tesla to fix the system, and their installation company in turn asked us to cut the power so that they could do the work safely.
“When everything was restored, the question arose: ‘Wait a minute, can we reconnect the station to the electricity grid? Or what does the notice actually say?’ We consulted with our employer organization, who were clear that as long as sympathy measures are in place, we cannot reconnect this facility,” Sedin said.
The union’s sympathy actions, which began in March 2024, apply to work involving “planning, preparation, new connections, grid expansion, service, maintenance and repairs” of Tesla’s charging infrastructure in Sweden.
Tesla Sweden has argued that reconnecting an existing facility is not equivalent to establishing a new grid connection. In a filing to the Swedish Energy Market Inspectorate, the company stated that reconnecting the installation “is therefore not covered by the sympathy measures and cannot therefore constitute a reason for not reconnecting the facility to the electricity grid.”
Sedin, for his part, noted that Tesla’s issue with the Supercharger is quite unique. And while Jämtkraft elnät itself has no issue with Tesla, its actions are based on the unions’ sympathy measures against the electric vehicle maker.
“This is absolutely the first time that I have been involved in matters relating to union conflicts or sympathy measures. That is why we have relied entirely on the assessment of our employer organization. This is not something that we have made any decisions about ourselves at all.
“It is not that Jämtkraft elnät has a conflict with Tesla, but our actions are based on these sympathy measures. Should it turn out that we have made an incorrect assessment, we will correct ourselves. It is no more difficult than that for us,” the executive said.








