
News
SpaceX's Falcon rockets might need a giant tower on wheels for US military launches
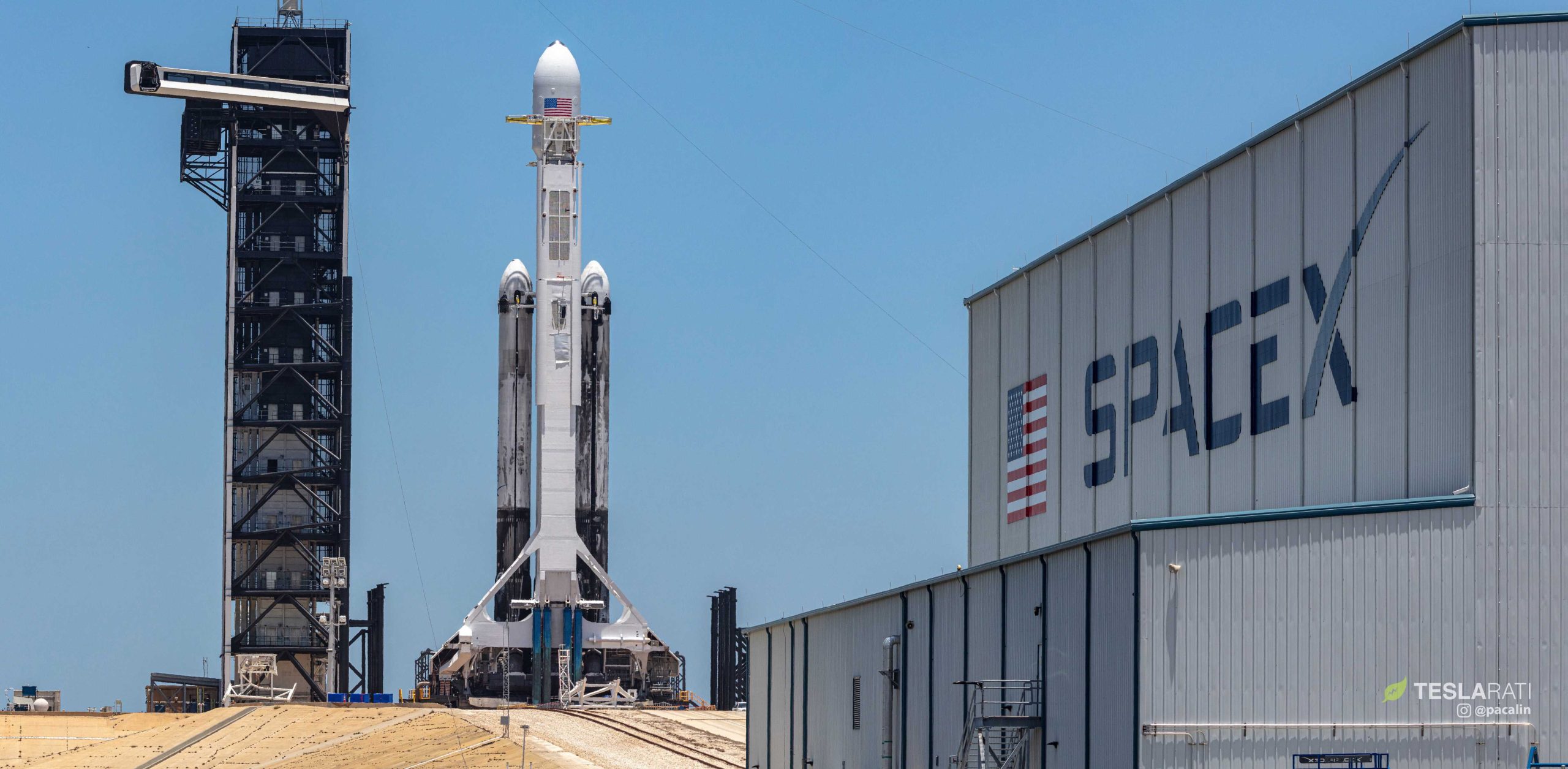
SpaceX reportedly plans to build a massive mobile gantry – effectively a tower on wheels – at one of its two Florida launch pads, a bid to meet obscure military launch criteria needed to secure highly lucrative Falcon 9 and Falcon Heavy launch contracts from the US government.
Although this is not the first time that SpaceX and vertical integration have been thrown around in the same sentence, it is the first time that the company is reportedly close to actually finalizing its plans along those lines and constructing a real solution at one or more of its three orbital-class launch pads.
Throughout the entirety of its active launch operations, SpaceX has relied exclusively on horizontal integration for its Falcon 1, 9, and Heavy rockets and the satellites they launch. CEO Elon Musk and other executives have maintained a consistent rationale for that preference over the years: ensuring that rockets and payloads can be horizontally integrated is the best possible solution so long as SpaceX’s primary motivation is improving access to space and lowering the cost of launch. As such, SpaceX has one and only one major motivation to jerry-rig a vertical integration solution for its Falcon family of rockets: necessity by way of arcane US military launch contract requirements.
Spaceflight Now broke the latest news first on January 3rd, 2020, revealing that SpaceX was at long last taking a substantial step towards actually building its own vertical integration infrastructure at Kennedy Space Center (KSC) Launch Complex 39A – a step that was long anticipated but has taken years to transpire into anything concrete. The gist is this: for a variety of seemingly shoehorned and far-from-obvious reasons, the secretive, ultra-expensive spy satellites that contractors like Lockheed Martin and Boeing build for the US Air Force (USAF) and the National Reconnaissance Office (NRO) builds itself are designed in such a way that they apparently cannot be flipped horizontally in a rocket’s payload fairing.
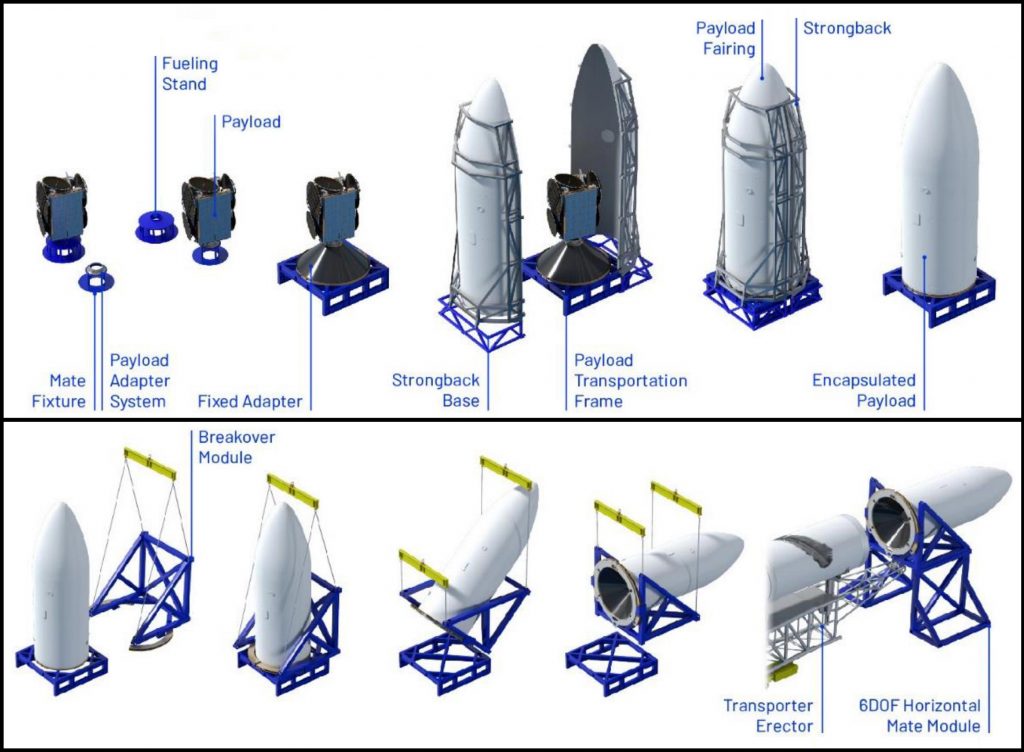
Identical to the process depicted above for Blue Origin’s in-development New Glenn rocket, up to now, SpaceX has encapsulated all satellite payloads vertically, sealed the payload fairing, rotated that integrated fairing and payload, and then attached that assembly to horizontal Falcon 9 and Falcon Heavy rockets. The rocket is then transported to the launch pad on a transporter erector (T/E), which – as the name suggests – raises the rocket and payload vertical before propellant loading and launch.
For certain USAF and NRO launch contracts, breakover (horizontal flip) is unacceptable and their preference is that the launch vehicle be brought vertical before the payload – also still vertical – is stacked on top. While it sounds simple in principle (i.e. “Just stick a crane out by the pad!”), vertical payload integration is exceptionally tedious unless you already have the infrastructure in place. Competitor United Launch Alliance (ULA), for example, already has that infrastructure – having held a decade-long monopoly over US military launches that only ended 5-7 years ago, depending on how it’s measured.
Both ULA’s Atlas V, Delta IV, and soon-to-be Vulcan Centaur rockets and the infrastructure used to launch them have all been designed around vertical payload integration – essentially requiring massive, expensive, and complicated buildings-on-wheels at each launch facility.
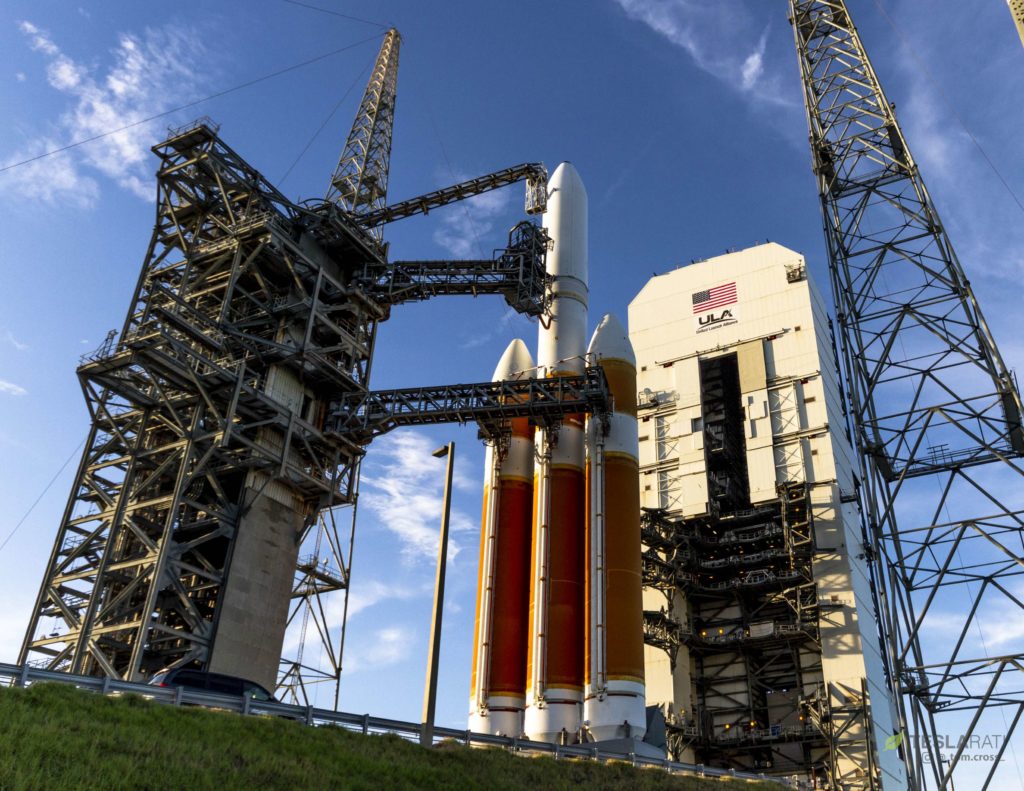

Per Spaceflight Now, SpaceX has plans to build a similar mobile tower at Pad 39A, currently dedicated Falcon 9/Crew Dragon missions for NASA and the occasional Falcon Heavy launch. That tower will ultimately roll up to Falcon 9 or Heavy rockets on the pad, fully covering the vehicles and giving technicians an array of work platforms and tools to support vertical payload integration, among other uses. SFN says that the mobile tower will be even taller than the existing Fixed Service Structure (FSS) tower at Pad 39A, measuring some 30 stories (100m/330ft) tall.
In line with a recent FSS redesign that saw that existing tower modified for Crew Dragon and outfitted with semi-transparent black glass or plastic and a black-and-white color scheme, the new mobile tower will apparently be built with a similar design language.
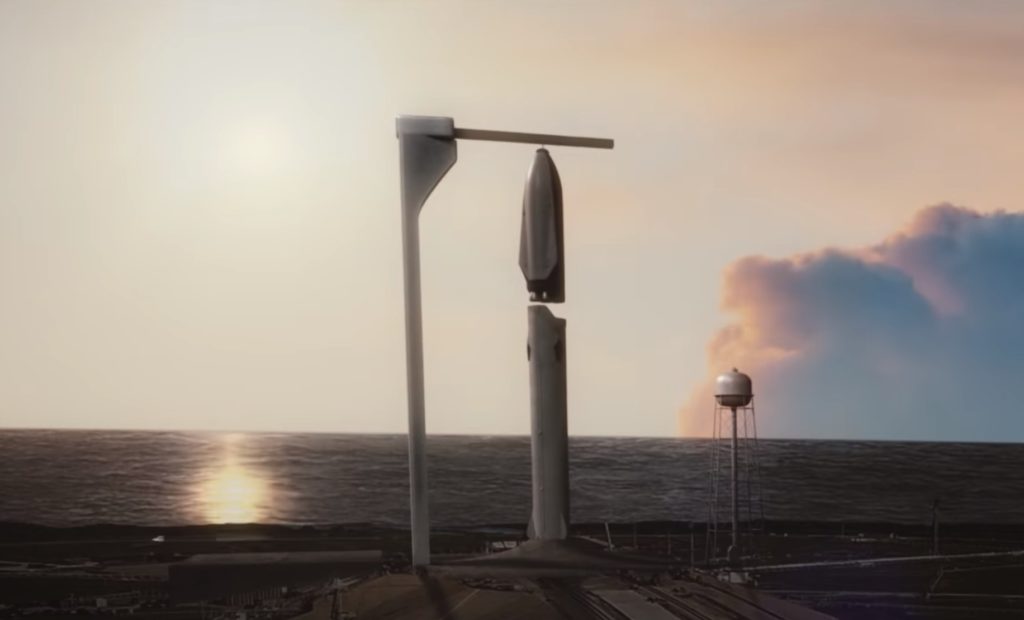

Ultimately, all of SpaceX’s plans for Starship – a massive next-generation, fully-reusable rocket – have relied on some form of vertical integration for Super Heavy boosters, Starships, and tankers. In a best-case scenario, all of those vehicles may one day land in reach of a giant crane situated at the launch pad, allowing SpaceX to lift them back to the pad and install ships and tankers on Super Heavy boosters just hours (maybe even minutes) after touchdown – truly rapid reuse.
For now, it’s unclear when exactly SpaceX wants to start cutting metal for its new Falcon 9/Heavy gantry, but it’s safe to say the company will move fast as usual once it begins.
Check out Teslarati’s Marketplace! We offer Tesla accessories, including for the Tesla Cybertruck and Tesla Model 3.

News
I figured out how to charge my Tesla at my rented townhouse – Here’s how
I hope that this article is able to help the prospective EV buyer or the current Tesla owner who is living in a rental and does not have a straightforward solution to home charging. My situation will be presented in this article, and I will tell you why I went with the solution I went with, and alternatives, because there is more than one way to do this.

When I bought my Tesla Model Y Premium All-Wheel-Drive last year, I knew I would have to try to figure out a way not become totally reliant on Superchargers. After about six months of ownership, it came time to resolve that problem once and for good, and being a tenant in a rented townhouse community definitely added to my challenge.
Before I even bought my Tesla, I emailed my leasing office to see if the community had any plans to bring EV charging to the neighborhood. I had made myself available to them as I am familiar with a lot of the solutions out there and how much of an advantage this could be for the community, and attracting new tenants. After months of trying, I bought my Tesla in August anyway, and figured I’d be able to find an answer — whether positive or negative — and go from there.
I hope that this article is able to help the prospective EV buyer or the current Tesla owner who is living in a rental and does not have a straightforward solution to home charging. My situation will be presented in this article, and I will tell you why I went with the solution I went with, and alternatives, because there is more than one way to do this.
My Challenge with Home Charging
In a rental community, apartment complex, or even townhouse row, parking spots are a little complicated. I have assigned parking at my house, and unfortunately, my parking spot is not right in front of my front door. Instead, it is staggered, so my car is parked in front of my neighbor’s front door.
Initially, I had spoken to my neighbor whose spot is right in front of my front door and had gotten permission to park in their spot during the day while it is vacant. However, I was not going to be able to upgrade my outlet from a 110v-120v to the typical and suggested 220v-240v alternative.
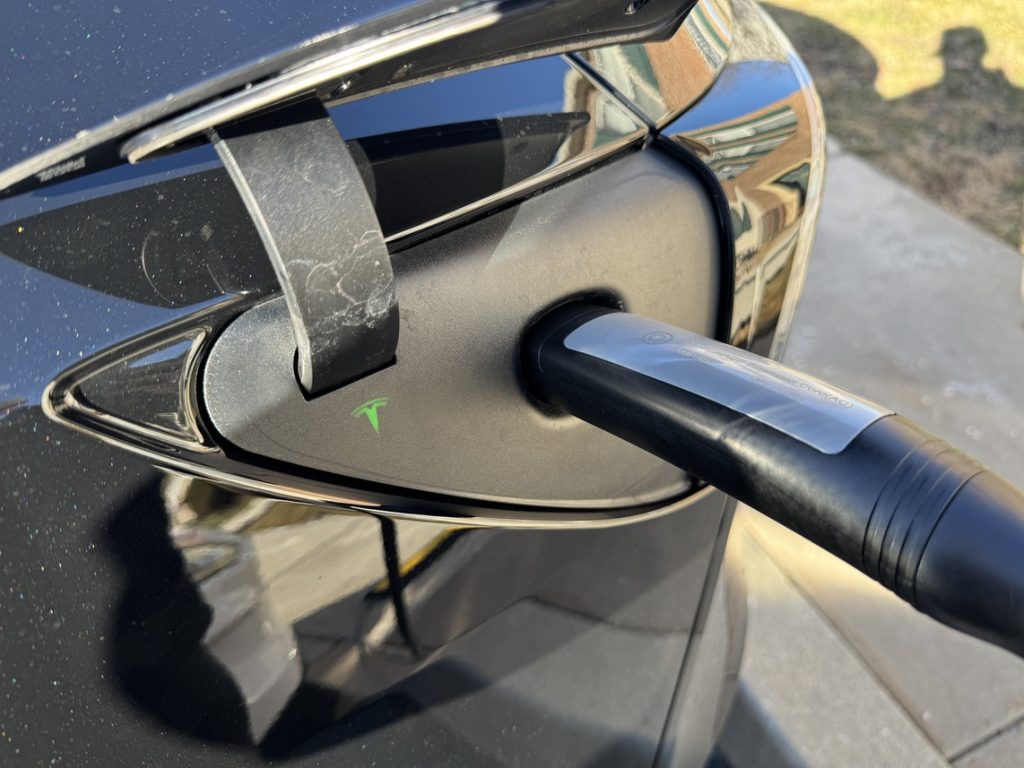

I knew that this would mean I would need to be in my permanent spot because charging sufficiently, especially in preparation for trips or errands, would require overnight charging.
The Tesla Mobile Connector is 20 feet long, which is sufficient for most applications. Mine, however, required about 30 feet, maybe even a little more, to charge.
My Options
I had a few options: Use the Mobile Connector and park in my neighbor’s spot and charge when I could, buy an 8 or 10-gauge extension cord that could handle moving power from the Mobile Connector to my car, or buy an NACS to NACS extension cord.
I didn’t really want to do the first option, considering I knew that spot would only be available when my neighbor was not there. It didn’t seem like a viable option, and I figured it would be better to figure out something from my personal, permanent parking spot anyway.
The 10-gauge extension cord option was what I first considered: it was less expensive than buying an NACS extension, it was more readily available, and it was the first thing my friends who are electricians recommended.
However, running this option would have put the Mobile Connector in the grass or on the ground, and I was not interested in doing that. Running the risk of having that $300 connector that came with the car in the grass and exposing it to dew, dogs, and various other things just did not seem like the best idea.
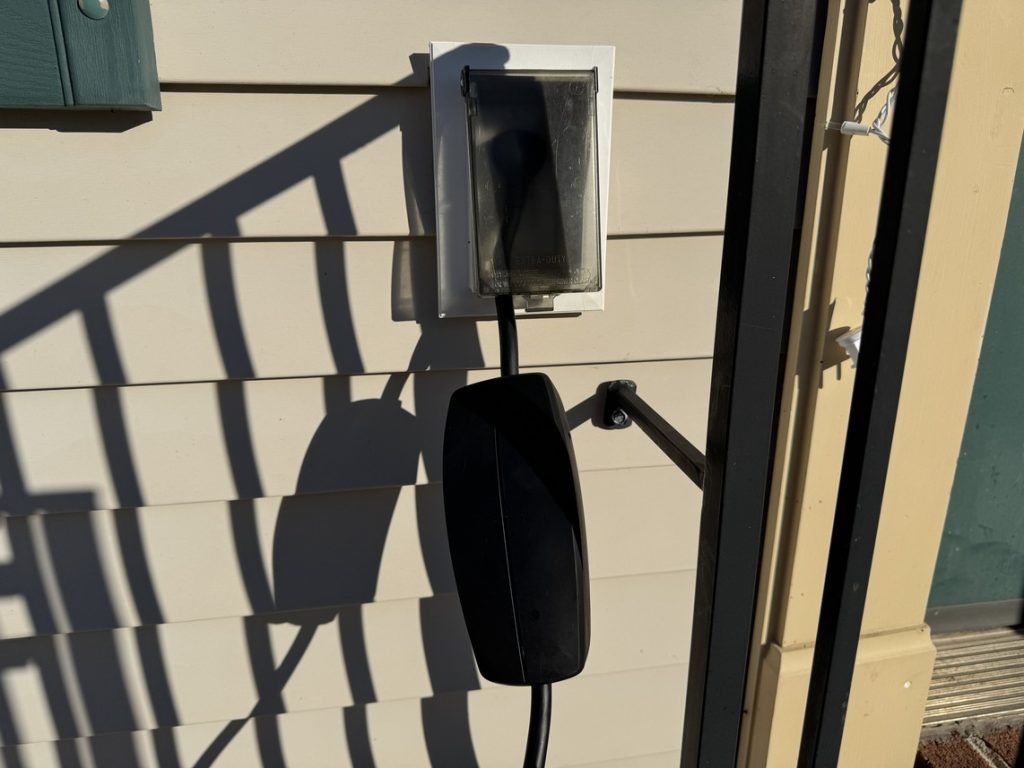

I looked around for some NACS to NACS connectors, and there are a lot of options. Given that this was something that was going to plug into a $50,000 car, I chose to spend the additional money on one that was not from Amazon, and I went with this one from A2Z, which was recommended by other owners, and their reputation seemed more than positive. I was leaning toward this option anyway because it would keep the Mobile Connector off the ground, and it gave me an additional 16 feet of length to work with.
This was the solution.
Putting It Into Action
It was a relatively simple process: Plug the Mobile Connector into my house, plug the NACS to NACS extension into the Mobile Connector, plug the NACS extension into the car. It all worked immediately, but there are some things you should know if you are also planning to do this.
The first is that you should be very aware that these cables are going to be a target of thieves. I don’t have too much of an issue with this in my area, but if you’re in a place where copper wiring is heavily sought after, be sure to keep these in a place where they won’t be stolen. I put mine away when they’re not charging, and at night, they’re visible from my Ring camera, so I’m not overly concerned. Definitely be aware of it, though.
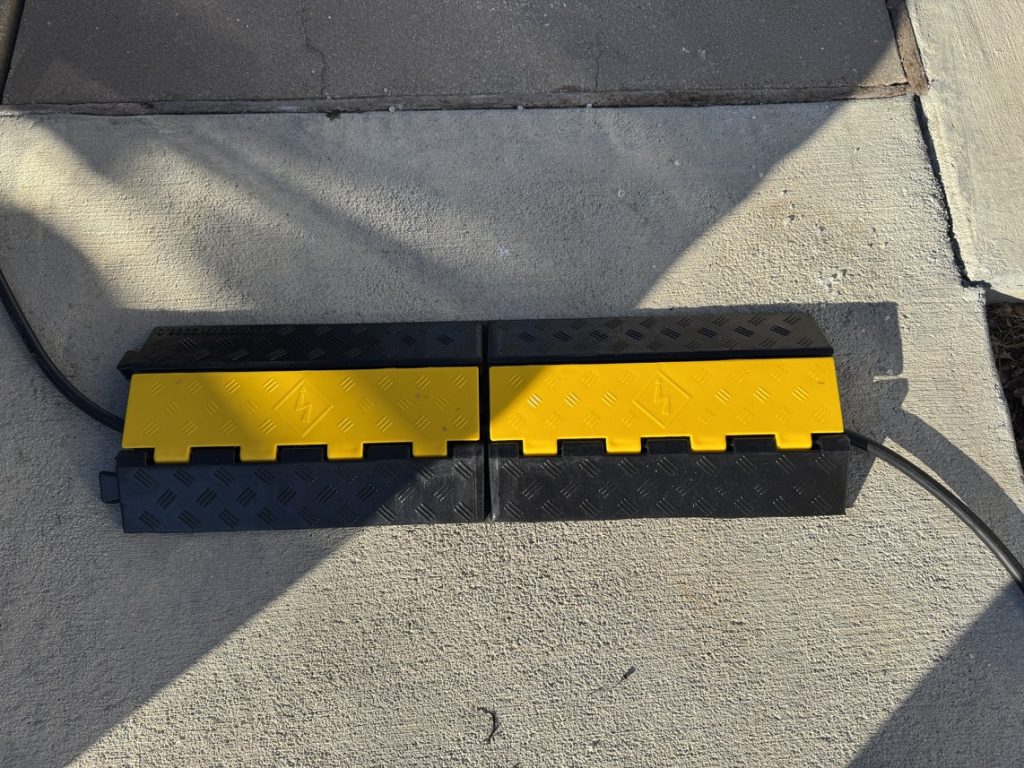
Additionally, if you’re going to run it across the sidewalk like I am, you’re going to want to pick up some sort of cable cover from a local hardware store. I picked up this one from Amazon because it was a little more heavy-duty, and it was big enough to cover the thicker gauge of the NACS to NACS extension:
I’ve considered picking up a second one for the visible cable, but I am undecided.
So far, I’ve been able to add some range to my car three times using this strategy, and while it is very slow, it is definitely worth it. It’s better than it sitting there stagnant.
Speed of Charging
Tesla says the Mobile Connector will provide you with between 3 and 5 miles of range per hour when plugged into a typical wall outlet. That is about what I’ve gotten with it. From 30 percent to 80 percent, be aware that it will take well over 24 hours to charge your car.
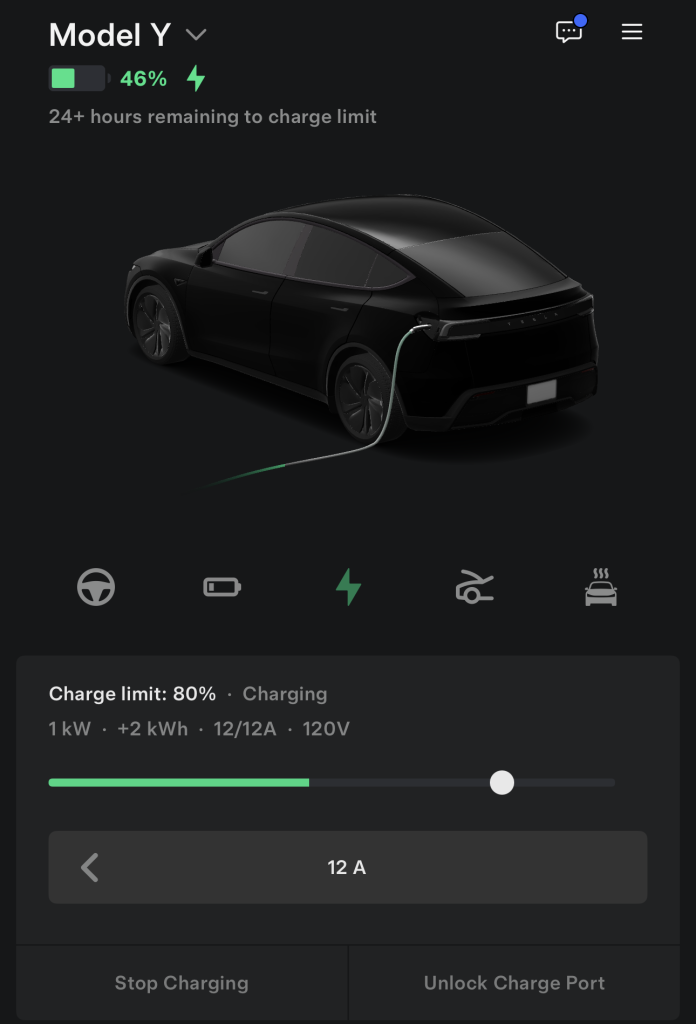
I plan to cover some additional details on this as time goes on, including any troubleshooting I might have to do, how much my electric bill goes up, and whether or not I run into any issues with my neighbors or my leasing office.
If you’re looking for some help on an at-home charging solution or have any questions about my setup, please email me at joey@teslarati.com.
🚨 I FINALLY figured out a way to charge my Tesla at home as a renter — Using Superchargers exclusively was inconvenient, tough on the battery, and expensive
Here’s how I did it: https://t.co/TZokpc6Fh3 pic.twitter.com/UtRYKLvB2Y
— TESLARATI (@Teslarati) March 2, 2026
Elon Musk
Starlink V2 to bring satellite-to-phone service to Deutsche Telekom in Europe
Starlink stated that the system is designed to deliver 5G speeds directly to compatible smartphones in remote areas.

Starlink is partnering with Deutsche Telekom to roll out satellite-to-mobile connectivity across Europe, extending coverage to more than 140 million subscribers across 10 countries.
The service, planned for launch in 2028 in several Telekom markets, including Germany, will use Starlink’s next-generation V2 satellites and Mobile Satellite Service (MSS) spectrum to enable direct-to-device connectivity.
In a post on X, the official Starlink account stated that the agreement will be the first in Europe to deploy its V2 next-generation satellite-to-mobile technology using new MSS spectrum. The company added that the system is designed to deliver 5G speeds directly to compatible smartphones in remote areas.
Abdu Mudesir, Board Member for Product and Technology at Deutsche Telekom, shared his excitement for the partnership in a press release. “We provide our customers with the best mobile network. And we continue to invest heavily in expanding our infrastructure. At the same time, there are regions where expansion is especially complex due to topographical conditions or official constraints,” he said.
“We want to ensure reliable connectivity for our customers in those areas as well. That is why we are strategically complementing our network with satellite-to-mobile connectivity. For us, it is clear: connectivity creates security and trust. And we deliver. Everywhere.”
Under the partnership, compatible smartphones will automatically switch to Starlink’s satellite network when terrestrial coverage is unavailable, enabling access to data, voice, video, and messaging services.
Telekom reports 5G geographic coverage approaching 90% in Germany, with LTE exceeding 92% and voice coverage reaching up to 99%. Starlink’s satellite layer is intended to extend connectivity beyond those terrestrial limits, particularly in topographically challenging or infrastructure-constrained areas.
Stephanie Bednarek, VP of Starlink Sales, also shared her thoughts on the partnership. “We’re so pleased to bring reliable satellite-to-mobile connectivity to millions of people across 10 countries in partnership with Deutsche Telekom. This agreement will be the first-of-its-kind in Europe to launch Starlink’s V2 next-generation technology that will expand on data, voice and messaging by providing broadband directly to mobile phones,” she said.
Starlink’s V2 constellation is designed to expand bandwidth and capacity compared to its predecessor. If implemented as outlined, the 2028 launch would mark one of the first large-scale European deployments of integrated satellite-to-phone connectivity by a major telecom operator.
News
Tesla back on top as Norway’s EV market surges to 98% share in February
Tesla became Norway’s top-selling brand with 1,210 registrations, representing a 16.6% share.

Tesla reclaimed the top spot in Norway’s auto market in February as electric vehicles captured more than 98% of all new car registrations.
The rebound follows a sharp January slump triggered by VAT rule changes, which prompted numerous car buyers to advance their purchases into late 2025.
As per data from the Norwegian Road Traffic Information Council (OFV), 7,127 new electric vehicles were registered in February, representing a 98.01% market share. Fossil-fuel vehicles and hybrids accounted for just 2% of total new registrations.
Total new car registrations reached 7,272 units in February, hinting at a rapid recovery after January sales fell nearly 75% year-over-year following VAT adjustments.
OFV Director Geir Inge Stokke noted that similar patterns were observed after previous VAT changes in 2022, with demand temporarily weakening before normalizing, as noted in an Allt Om Elbil report.
“We are now seeing signs that the market is returning to a more normal level of activity, which we also experienced after the VAT change in 2022. At that time, changes in demand led to a weak start to 2023. We have seen the same pattern this year,” he said.
Amidst this trend, the Tesla Model Y made a strong comeback in the domestic market. After an unusually weak January that saw the Tesla Model Y drop to seventh place, the model returned to the top of Norway’s sales chart in February.
The Model Y recorded 1,073 registrations, giving it a 14.8% market share for the month. Tesla also became Norway’s top-selling brand with 1,210 registrations, representing a 16.6% share. Toyota followed with 941 registrations, while Volkswagen, Volvo, and Skoda rounded out the top five brands.
The February data suggests that Tesla’s January dip was tied more to timing effects around VAT adjustments than to structural demand shifts. It would then be interesting to see how the rest of the year unfolds for Tesla, particularly as the company pushes for the release of its Full Self-Driving (Supervised) system to Europe this year.










