
News
SpaceX begins testing first flightworthy Super Heavy booster
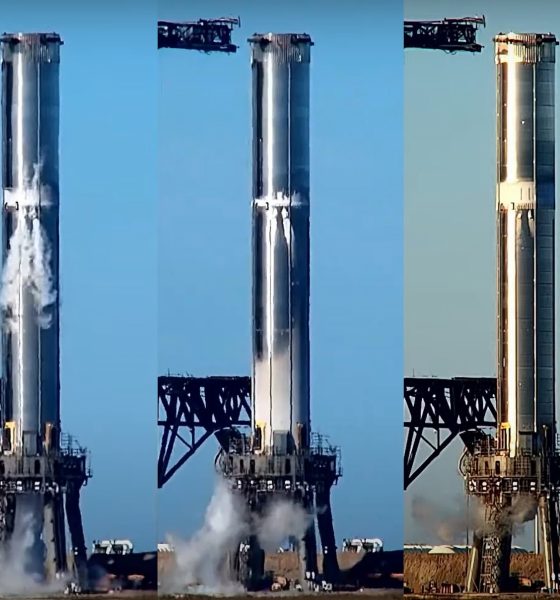
More than three months after the building-sized Starship booster’s latest return to Starbase’s orbital launch site, SpaceX has finally begun the process of testing what CEO Elon Musk says is still the first flightworthy Super Heavy.
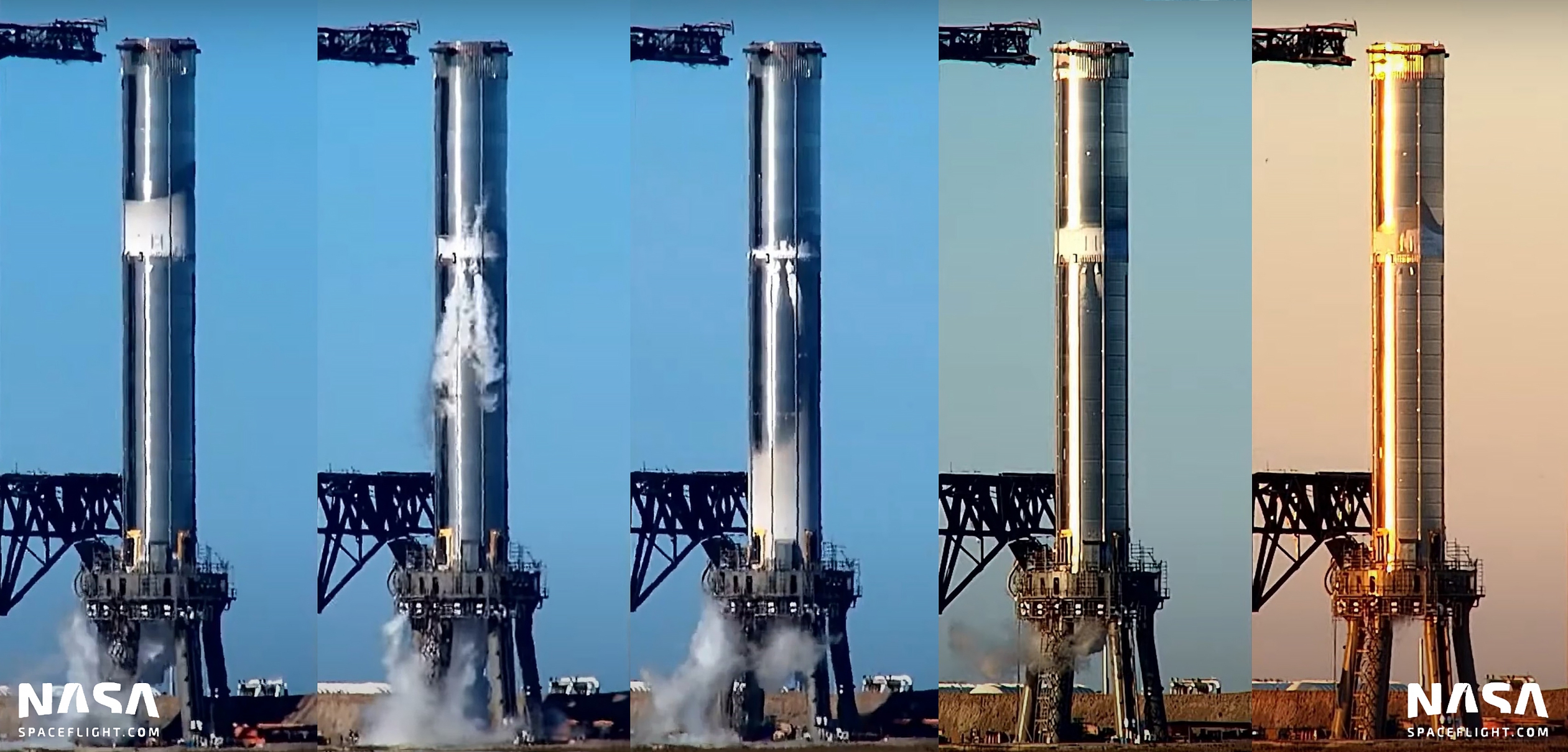
After completing a number of pad tests in the days prior, SpaceX began filling Super Heavy Booster 4 (B4) with liquid nitrogen – supplied by the first orbital-class Starship launch – for the first time on December 17th. It’s unclear exactly what was done during the test but regardless of what transpired, the test and B4’s survival were a major, long-awaited milestone for both the Starship booster and the orbital launch site (OLS).
At this point in time, the general consensus among close followers of SpaceX’s Starship program is that the unprecedented amount of time it’s taken the company to complete Booster 4’s first test was not because of the rocket itself but rather because the orbital launch site needed to fully test it had yet to be completed. While it was SpaceX’s choice to not perform some kind of initial testing with B4 at one of the site’s two suborbital test and launch mounts, it’s clear that the company ultimately concluded that Super Heavy Booster 3’s successful July 2021 tests – including a cryogenic proof virtually identical to Booster 4’s first test – made such partial testing redundant.
Put a different way, SpaceX must already be confident enough in the quality of the first few Super Heavies rolling out of its Starbase factory to deem it unnecessary to verify the structural integrity of the first truly completed Super Heavy booster before putting the one and only orbital Starship launch site directly in the line of fire. Nonetheless, depending on how far Super Heavy Booster 4’s first cryogenic proof test went, it appears that SpaceX’s presumptions were correct.
On December 17th, SpaceX subjected Super Heavy B4 to a cryogenic proof test about twice as ambitious as B3’s, filling the booster maybe a sixth of the way with a few hundred tons of liquid nitrogen (LN2). What isn’t clear is if that test also raised the booster’s propellant tanks to flight pressures (6-8 bar or 90-115 psi). If Booster 4 did reach those pressures, the test is even more significant – partially proving that the rocket is ready for flight. On December 21st, SpaceX performed a similar series of cryogenic tests, again partially filling Booster 4 with about the same amount of liquid nitrogen but doing so two or three times in a row. Again, the Super Heavy survived the several-hour ordeal without any obvious issues. Still, a number of additional tests – some even more important – are still in front of SpaceX and Super Heavy B4.
The most obvious is simple enough: SpaceX needs to fully fill a Super Heavy booster for the first time. Depending on the storage situation, that process will likely begin by filling Booster 4 with about 2500 tons (5.5M lb) of liquid nitrogen (LN2) – about two-thirds full. If SpaceX also temporarily fills one of the orbital tank farm’s liquid oxygen (LOx) or methane (LCH4) tanks with nitrogen, it could fully load Booster 4 with around 3500 tons (7.7M lb) of nitrogen. At least according to SpaceX’s own website, that’s about the same weight as the propellant (3400t/7.5M lb) Super Heavy is designed to lift off with. If that full cryoproof goes well, SpaceX will then likely perform one or several wet dress rehearsals, ultimately filling Booster 4 with approximately 2900 tons (6.4M lb) of cryogenic oxygen and 500 tons (1.1M lb) of cryogenic methane.
Finally, SpaceX will probably kick off static fire testing, likely beginning by igniting just one or a few of Super Heavy’s many engines. Eventually, that process could culminate in the ignition of all 29 of Booster 4’s Raptors, briefly producing a bit less than 5400 tons (~11.9M lbf) of thrust – 50% more powerful than NASA’s retired Saturn V Moon rocket.
According to Elon Musk, despite a number of recent signs and reports to the contrary, SpaceX still intends to fly Booster 4 and Ship 20 on Starship’s first orbital-velocity launch attempt, so the scope and scale of testing are only likely to grow over the next several weeks.

News
Tesla Model Y outsells everything in three states, but Ford dominates
The Model Y’s success here highlights accelerating mainstream adoption of electric SUVs, which offer spacious interiors, impressive range, rapid acceleration, and low operating costs.
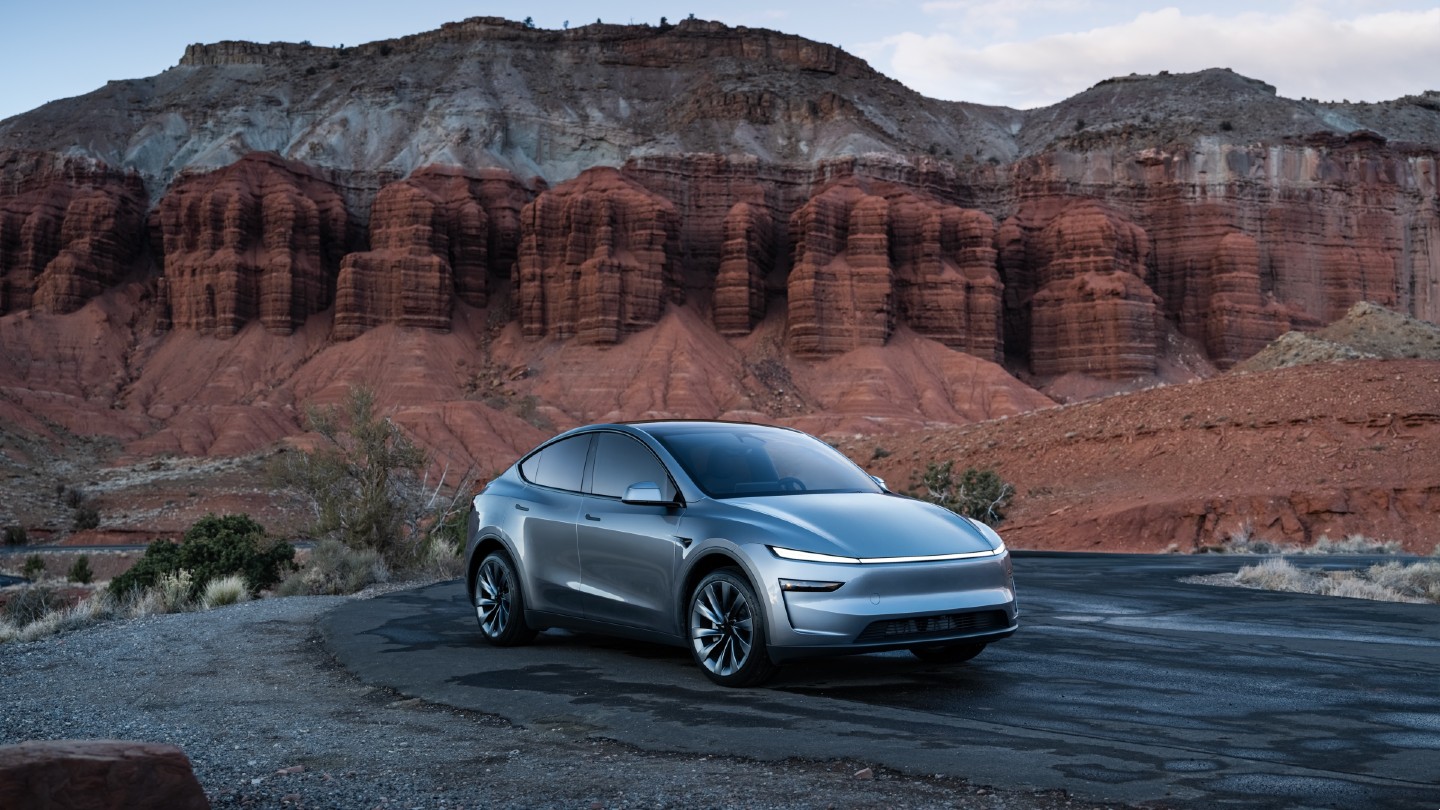

The Tesla Model Y was the best-selling vehicle in three different states in the U.S. last year, according to new data that shows the all-electric crossover outsold every other car in a few places. However, Ford widely dominated the sales figures with its popular F-Series of pickups.
According to new vehicle registration data compiled by Edmunds and visualized by Visual Capitalist, the Ford F-Series, encompassing models like the F-150, F-250, F-350, and F-450, claimed the title of best-selling vehicle in 29 states.
This dominance underscores the pickup truck’s unbreakable appeal across much of the country, particularly in rural, Midwestern, Southern, and Western states, where towing capacity, durability, and utility for work or recreation remain top priorities.
The Tesla Model Y is the best-selling vehicle in California, Washington, and Nevada
How many states will it dominate next year? https://t.co/ERyoyce42D
— TESLARATI (@Teslarati) March 9, 2026
The F-Series has held the crown as America’s overall best-selling vehicle for decades, a streak that continued strong into 2025 despite broader market shifts.
Yet, amid this truck-heavy reality, Tesla made a notable breakthrough. The Model Y emerged as the top-selling vehicle, not just the leading EV, but the outright best-seller in three key states: California, Nevada, and Washington.
These West Coast strongholds reflect regions with robust EV infrastructure, high environmental awareness, generous incentives, and tech-savvy populations. In California alone, nearly 50 percent of new vehicle registrations were electrified, far outpacing the national average of around 25 percent.
The Model Y’s success here highlights accelerating mainstream adoption of electric SUVs, which offer spacious interiors, impressive range, rapid acceleration, and low operating costs.
Elon Musk: Tesla Model Y is world’s best-selling car for 3rd year in a row
Elsewhere, Japanese crossovers filled many gaps: Toyota’s RAV4 and Honda’s CR-V topped charts in several urban and densely populated Northeastern and Midwestern states, where fuel efficiency, reliability, and family-friendly features win out over larger trucks.
While Ford’s broad reach shows traditional preferences persist, at least for now, Tesla’s Model Y victories in high-population, influential states signal a gradual but undeniable transition toward electrification. As charging networks expand and battery technology improves, more states could follow the West Coast’s lead in the coming years.
This 2025 map captures a pivotal moment: pickup trucks still rule the majority, but EVs are carving out meaningful territory where consumer priorities align with sustainability and innovation. The road ahead promises continued competition between legacy giants and electric disruptors.
Elon Musk
Elon Musk shares updated Starship V3 maiden launch target date
The comment was posted on Musk’s official account on social media platform X.
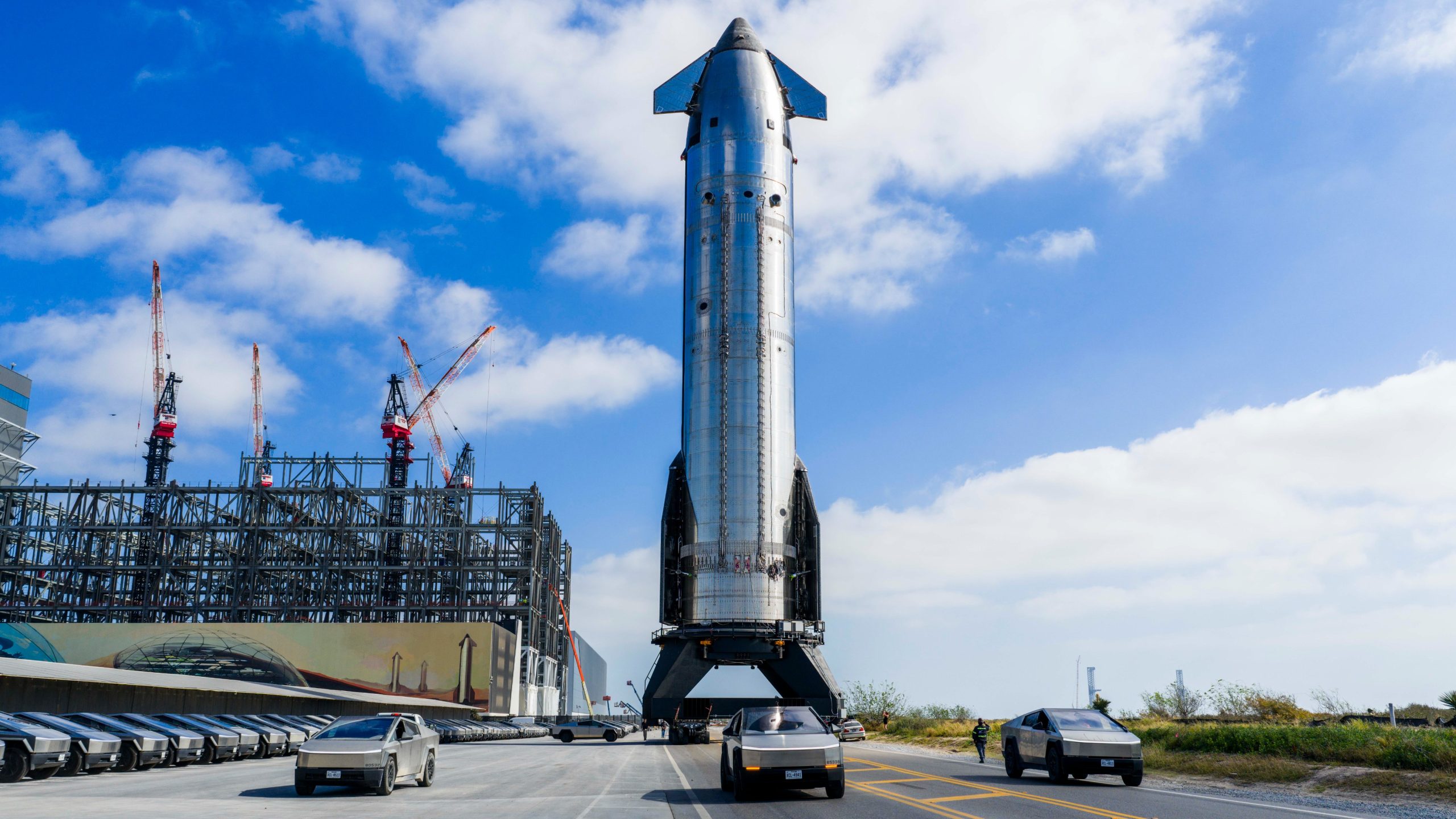

SpaceX CEO Elon Musk shared a brief Starship V3 update in a post on social media platform X, stating the next launch attempt of the spacecraft could take place in about four weeks.
The comment was posted on Musk’s official account on social media platform X.
Musk’s update suggests that Starship Flight 12 could target a launch around early April, though the schedule will depend on several remaining milestones at SpaceX’s Starbase launch facility in Texas.
Among the key steps is testing and certification of the site’s new launch tower, launch mount, and tank farm systems. These upgrades will support the next generation of Starship vehicles.
Booster 19 is expected to roll to the launch site and be placed on the launch mount before returning to the production facility to receive its 33 Raptor engines. The booster would then return for a static fire test, which could mark the first time a Super Heavy booster equipped with Raptor V3 engines is fired on the pad.
Ship 39 is expected to undergo a similar preparation process. The vehicle will likely return to the production site to receive its six engines before heading to Massey’s test site for static fire testing.
Once both stages are prepared, the booster and ship will roll out to the launch site for the first full stack of a V3 Super Heavy and V3 Starship. A full wet dress rehearsal is expected to follow before any launch attempt.
Elon Musk has previously shared how SpaceX plans to eventually recover Starship’s upper stage using the launch tower’s robotic arms. Musk noted that the company will only attempt to catch the Starship spacecraft after two successful soft landings in the ocean. The approach is intended to reduce risk before attempting a recovery over land.
“Should note that SpaceX will only try to catch the ship with the tower after two perfect soft landings in the ocean. The risk of the ship breaking up over land needs to be very low,” Musk wrote in a post on X.
Such a milestone would represent a major step toward the full reuse of the Starship system, which remains a central goal for SpaceX’s long-term launch strategy.
News
Tesla opens first public Tesla Semi Megacharger site in Los Angeles
The development was highlighted in a post on social media platform X by the official Tesla Semi account.
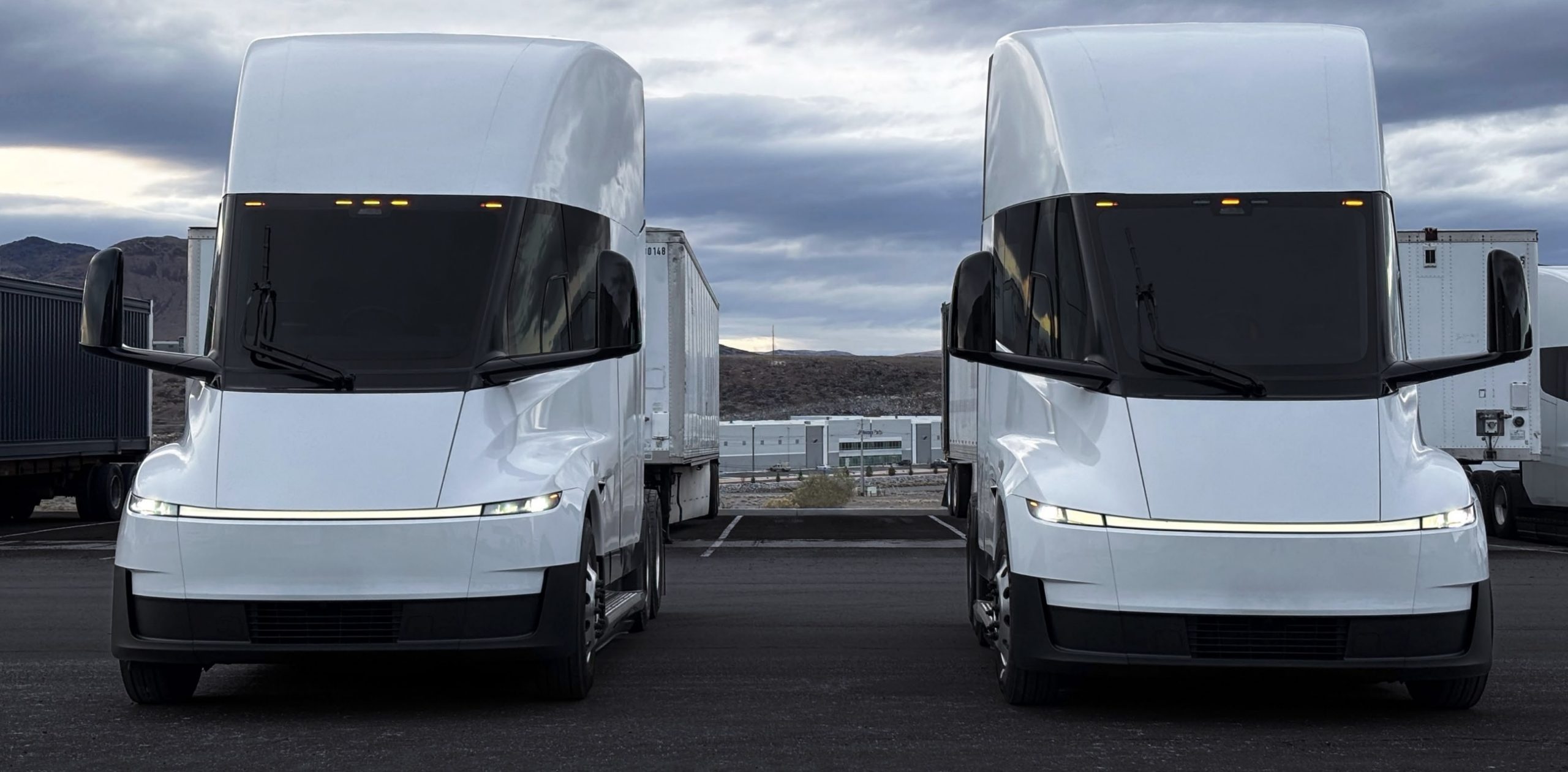

Tesla has opened its first public Tesla Semi Megacharger site in Los Angeles. The station reportedly offers up to 750 kW charging speeds and is open to Tesla Semi customers.
The development was highlighted in a post on social media platform X by the official Tesla Semi account.
Tesla Semi Megachargers
The Los Angeles site seems to be the first public Tesla Semi Megacharger that is not located at a Tesla factory. It is also the third Megacharger site currently visible on Tesla’s map.
The Megacharger system is designed specifically for the Tesla Semi and is capable of delivering extremely high charging speeds to support long-haul trucking operations. Infrastructure such as this will likely play a key role in making the Semi competitive with diesel-powered transport trucks.
Tesla’s progress with the Semi has also drawn attention in recent days after Elon Musk biographer Ashlee Vance shared photos from inside the Tesla Semi factory near Giga Nevada. The images suggested that preparations for higher production volumes may be underway, hinting that a broader ramp of the Tesla Semi’s production indeed be approaching.
New deployment strategies
Tesla has continued expanding its broader charging network through several new strategies aimed at accelerating infrastructure deployment. One of these initiatives is the Supercharger for Business program, which allows third parties to purchase Tesla Supercharger equipment and deploy charging stations while still integrating with Tesla’s network.
The program recently marked a milestone in Alpharetta, Georgia, where the city deployed four 325 kW city-branded Superchargers near the Alpharetta Department of Public Safety on Old Milton Parkway. The chargers support the city’s Tesla Model Y police vehicles while also remaining accessible to the public.
As per a report from EVwire, the project was designed not only to support fleet charging but also to generate economic returns that could offset the city’s investment. Tesla’s Supercharger for Business program has already attracted several participants, including businesses and charging providers such as Suncoast Charging, Pie Safe bakery in Idaho, Francis Energy in Oklahoma, and Wawa convenience stores.








