News
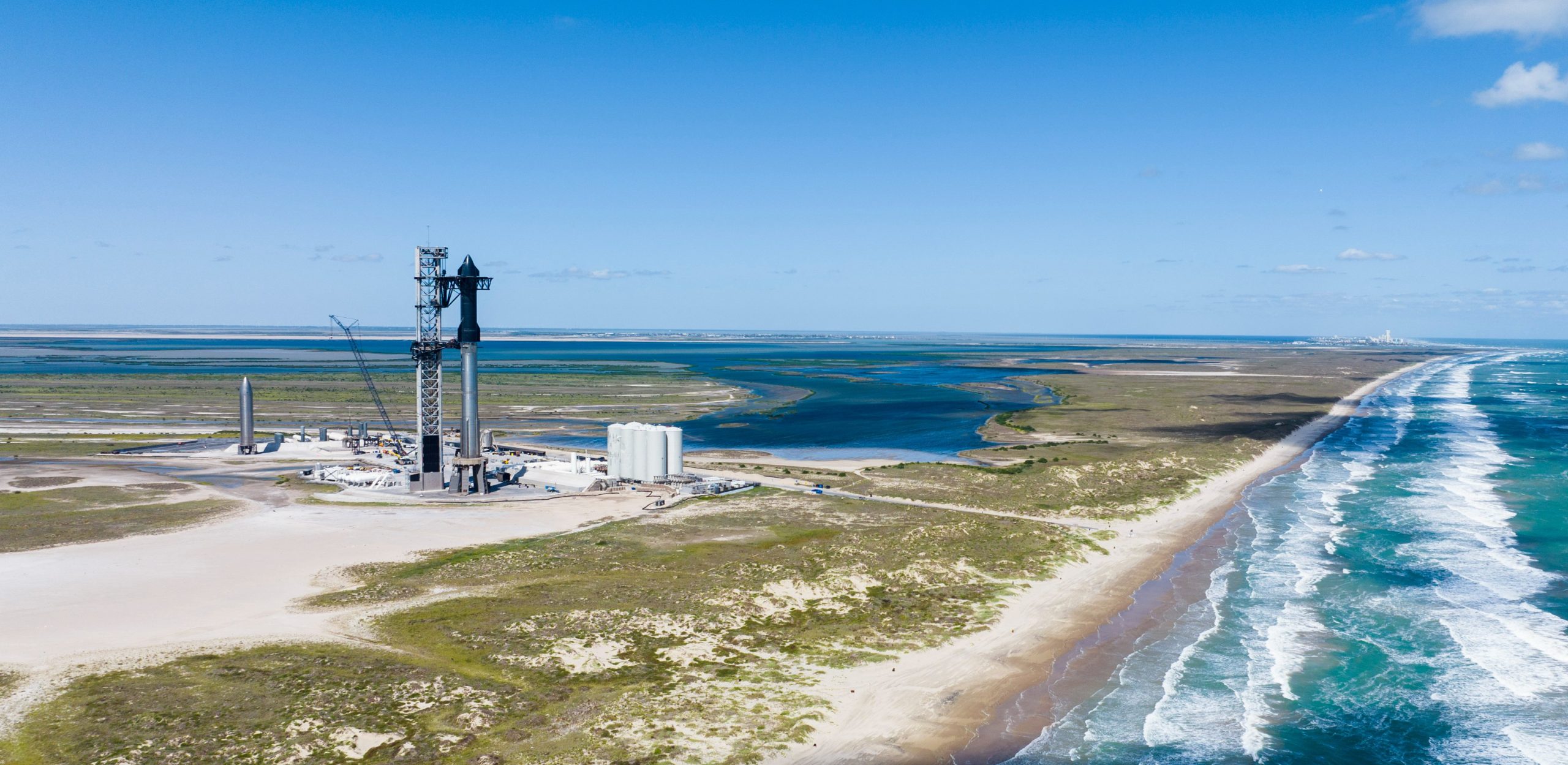
SpaceX Starship Integrated Flight Test 2: What to Expect
After a one-day delay to replace a failed grid fin actuator, SpaceX is now less than 24 hours from the second test flight of Starship. SpaceX will have a 20-minute launch window that opens at 7:00 AM CT (13:00 UTC).
Making this test flight is Ship 25 and Booster 9. Ship 25 is powered by 6 Raptor engines (3 sea level and 3 vacuum), and Booster 9 is powered by 33 Raptor engines.
Booster 9 features many upgrades over the last booster to take flight, including better engine shielding and a switch from hydraulic thrust vector controls to electric TVC. Ship 25 didn’t see as many upgrades as the booster, and not much has been shared of any major changes that were made. One change to both vehicles was the improvement of the Flight Termination System, which took much longer to destroy the rocket than expected during the first test.
Launch Day
T minus 2 hours before the scheduled liftoff, the SpaceX launch director will give the go for propellant loading. This process will begin at t minus 1 hour and 37 minutes, and at this point, Booster 9 will begin loading with both liquid oxygen and liquid methane.
T minus 1 hour and 17 minutes, liquid methane will begin loading onto Ship 25, followed by liquid oxygen 4 minutes later at t minus 1 hour and 13 minutes.
T minus 19 minutes and 40 seconds, the 39 Raptor engines on Booster 9 and Ship 25 will begin chilling to prepare for the extremely cold fuel to flow through and prevent thermal shock to engine hardware.
T minus 10 seconds, the flame deflector installed after the first IFT will begin flowing water.
Super Heavy Booster 9 static fire successfully lit all 33 Raptor engines, with all but two running for the full duration. Congratulations to the SpaceX team on this exciting milestone! pic.twitter.com/1hzs768vHg
— SpaceX (@SpaceX) August 25, 2023
T minus 3 seconds, Raptor engine ignition begins, and thrust begins to build to allow for liftoff.
LIFT OFF!
T+ 2 seconds, the 2nd Integrated Flight Test should now be officially underway, with Booster 9 thundering away from the orbital launch mount.
Liftoff from Starbase pic.twitter.com/rgpc2XO7Z9
— SpaceX (@SpaceX) April 20, 2023
T+ 52 seconds, Starship and Booster 9 reach Max Q, the area of maximum dynamic pressure on the vehicle will occur here. If (or most) all Raptor engines on Booster 9 are performing nominally, the vehicle will pass through this fairly quickly.
T+ 2 minutes and 39 seconds, Staging. This will be the first time SpaceX has ever attempted hot staging. Almost all of Booster 9 engines will cut out, and Ship 25 will ignite its Raptor engines to separate from the booster. This is all unknown territory from this point on for SpaceX, as the first test flight did not make it this far. SpaceX has yet to clarify how many Ship 25 engines will ignite during this process.
If all goes well, Booster 9 will begin its flip and boost backburn at t+ 2 minutes and 53 seconds, which will last ~54 seconds. Unlike the Falcon 9, the booster is not designed to perform an entry burn.
T+ 6 minutes and 30 seconds after lift-off, Booster 9 will begin its landing burn for a hopeful soft touchdown in the Gulf of Mexico 18 seconds after landing burn ignition. The planned landing area is ~20 miles (32 km) downrange.
Meanwhile, Ship 25 will continue burning its 6 Raptor engines until t+ 8 minutes and 33 seconds, inserted into a sub-orbital trajectory, and then enter a coast phase until its planned reentry North of the Hawaiian islands.
Landing!
At t+ 1 hour and 17 minutes, Starship will begin feeling the effects of the atmosphere, its first real test for the heatshield. If it survives atmospheric entry, Starship will splash down in the Pacific Ocean at t+ 1 hour and 30 minutes after lift off. SpaceX has said Ship 25 will not attempt a landing burn during this test.
If Starship is able to make it past staging, SpaceX will most likely consider this test a success, but it would be a major accomplishment for Ship 25 to survive entry back through the atmosphere and gather important data for the company.
If you have a chance to make it to South Texas or even the other side of the Rio Grande in Mexico, it’ll be a sight you’ll never forget. If you’re watching from home, SpaceX will begin streaming the launch on X and their website 35 minutes before lift-off.
Questions or comments? Shoot me an email at rangle@teslarati.com, or Tweet me @RDAnglePhoto.

Elon Musk
Tesla Full Self-Driving set to get an awesome new feature, Elon Musk says
Tesla Full Self-Driving is set to get an awesome new feature in the near future, CEO Elon Musk confirmed on X.
Full Self-Driving is the company’s semi-autonomous driving program, which is among the best available to the general public. It still relies on the driver to ultimately remain in control and pay attention, but it truly does make traveling less stressful and easier.
However, Tesla still continuously refines the software through Over-the-Air updates, which are meant to resolve shortcomings in the performance of the FSD suite. Generally, Tesla does a great job of this, but some updates are definitely regressions, at least with some of the features.
Tesla Cybertruck owner credits FSD for saving life after freeway medical emergency
Tesla and Musk are always trying to improve the suite’s performance by fixing features that are presently available, but they also try to add new things that would be beneficial to owners. One of those things, which is coming soon, is giving the driver the ability to prompt FSD with voice demands.
For example, asking the car to park close to the front door of your destination, or further away in an empty portion of the parking lot, would be an extremely beneficial feature. Adjusting navigation is possible through Grok integration, but it is not always effective.
Musk confirmed that voice prompts for FSD would be possible:
Coming
— Elon Musk (@elonmusk) February 21, 2026
Tesla Full Self-Driving is a really great thing, but it definitely has its shortcomings. Navigation is among the biggest complaints that owners have, and it is easily my biggest frustration with using it. Some of the routes it chooses to take are truly mind-boggling.
Another thing it has had issues with is being situated in the correct lane at confusing intersections or even managing to properly navigate through local traffic signs. For example, in Pennsylvania, there are a lot of stop signs with “Except Right Turn” signs directly under.
This gives those turning right at a stop sign the opportunity to travel through it. FSD has had issues with this on several occasions.
Parking preferences would be highly beneficial and something that could be resolved with this voice prompt program. Grocery stores are full of carts not taken back by customers, and many people choose to park far away. Advising FSD of this preference would be a great advantage to owners.
Cybertruck
Elon Musk clarifies Tesla Cybertruck ’10 day’ comment, fans respond
Some are arguing that the decision to confirm a price hike in ten days is sort of counterproductive, especially considering it is based on demand. Giving consumers a timeline of just ten days to make a big purchase like a pickup truck for $60,000, and basically stating the price will go up, will only push people to make a reservation.
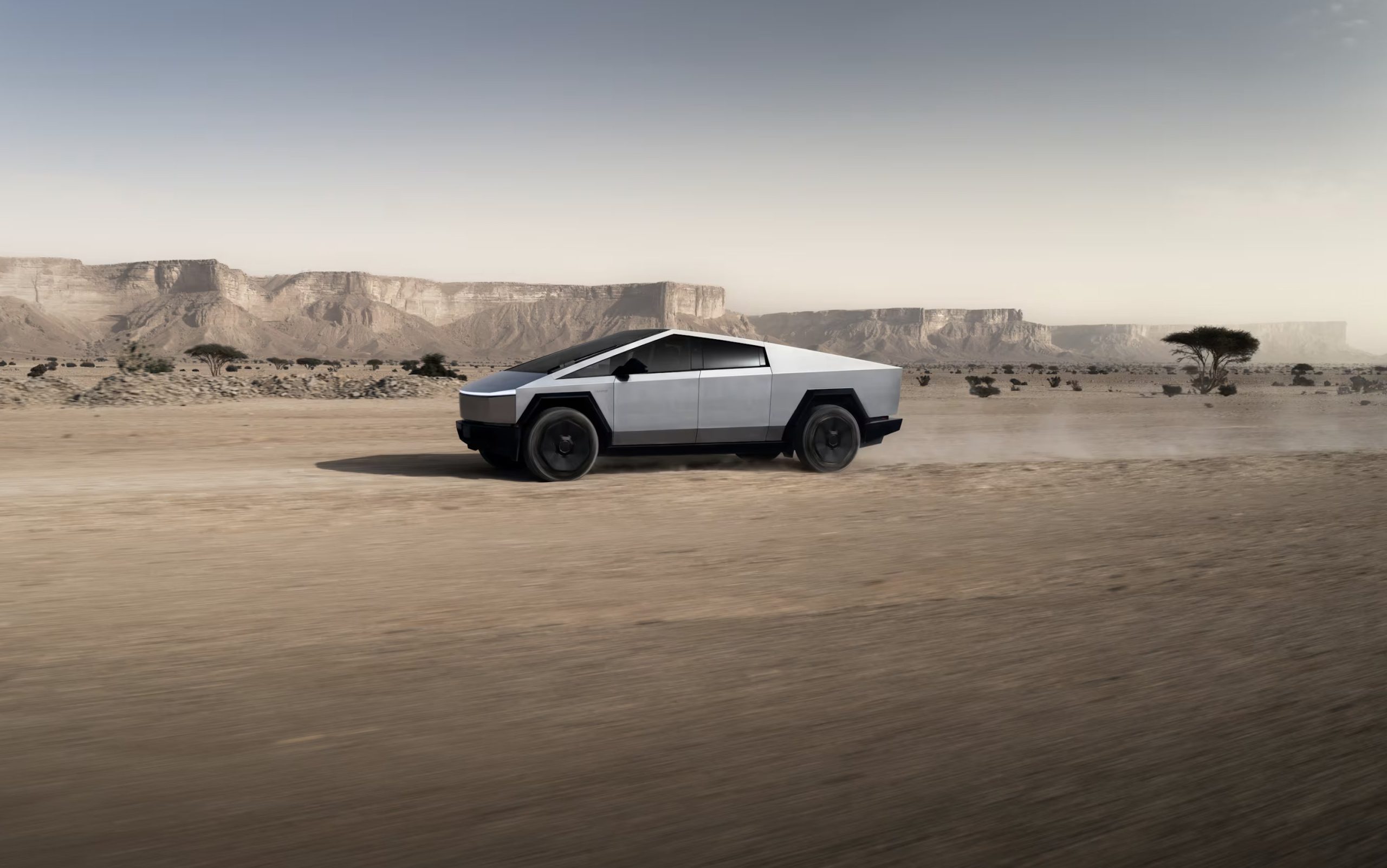

Elon Musk has clarified what he meant by his comment on X yesterday that seemed to indicate that Tesla would either do away with the new All-Wheel-Drive configuration of the Cybertruck or adjust the price.
The response was cryptic as nobody truly knew what Musk’s plans were for the newest Tesla Cybertruck trim level. We now have that answer, and fans of the company are responding in a polarizing fashion.
On Thursday night, Tesla launched the Cybertruck All-Wheel-Drive, priced competitively at $59,990. It was a vast improvement from the Rear-Wheel-Drive configuration Tesla launched last year at a similar price point, which was eventually cancelled just a few months later due to low demand.
Tesla launches new Cybertruck trim with more features than ever for a low price
However, Musk said early on Friday, “just for 10 days,” the truck would either be available or priced at $59,990. We can now confirm Tesla will adjust the price based on more recent comments from the CEO.
Musk said the price will fluctuate, but it “depends on how much demand we see at this price level.”
Depends on how much demand we see at this price level
— Elon Musk (@elonmusk) February 20, 2026
Some are defending the decision, stating that it is simply logical to see how the Cybertruck sells at this price and adjust accordingly.
Case 1: You don’t like it -> don’t buy it
Case 2 (me): You like it, it’s fits your situation and needs -> you buy it.
Case 3: Complain endlessly for no reason, you weren’t going to get one anyway, but you want people to know you’re mad, for some reason.Silly netizens.
— Ryan Scanlan 👥 (@Xenius) February 21, 2026
Others, not so much.
Alright I’m obviously not the one successful enough to be calling the shots at Tesla and worth almost a trillion dollars
But people were excited about the awesome Cybertruck news and then it got taken away, that’s why people are annoyed. The wording felt more like a threat.… pic.twitter.com/NWVNklcXoJ
— Dirty Tesla (@DirtyTesLa) February 21, 2026
No but fr wtf you doing dude???????
— Greggertruck (@greggertruck) February 20, 2026
It’s how it was communicated.
If it had been stated clearly on the website for everyone to see, everyone would be fine.— KiTT_2020 (@kitt_2020) February 20, 2026
Some are arguing that the decision to confirm a price hike in ten days is sort of counterproductive, especially considering it is based on demand. Giving consumers a timeline of just ten days to make a big purchase like a pickup truck for $60,000, and basically stating the price will go up, will only push people to make a reservation.
Demand will look strong because people want to lock in this price. The price will inevitably go up, and demand for the trim will likely fall a bit because of the increased cost.
Many are arguing Musk should have kept this detail internal, but transparency is a good policy to have. It is a polarizing move to confirm a price increase in just a week-and-a-half, but the community is obviously split on how to feel.
Cybertruck
Tesla Cybertruck’s newest trim will undergo massive change in ten days, Musk says
It appears as if the new All-Wheel-Drive trim of Cybertruck won’t be around for too long, however. Elon Musk revealed this morning that it will be around “only for the next 10 days.”
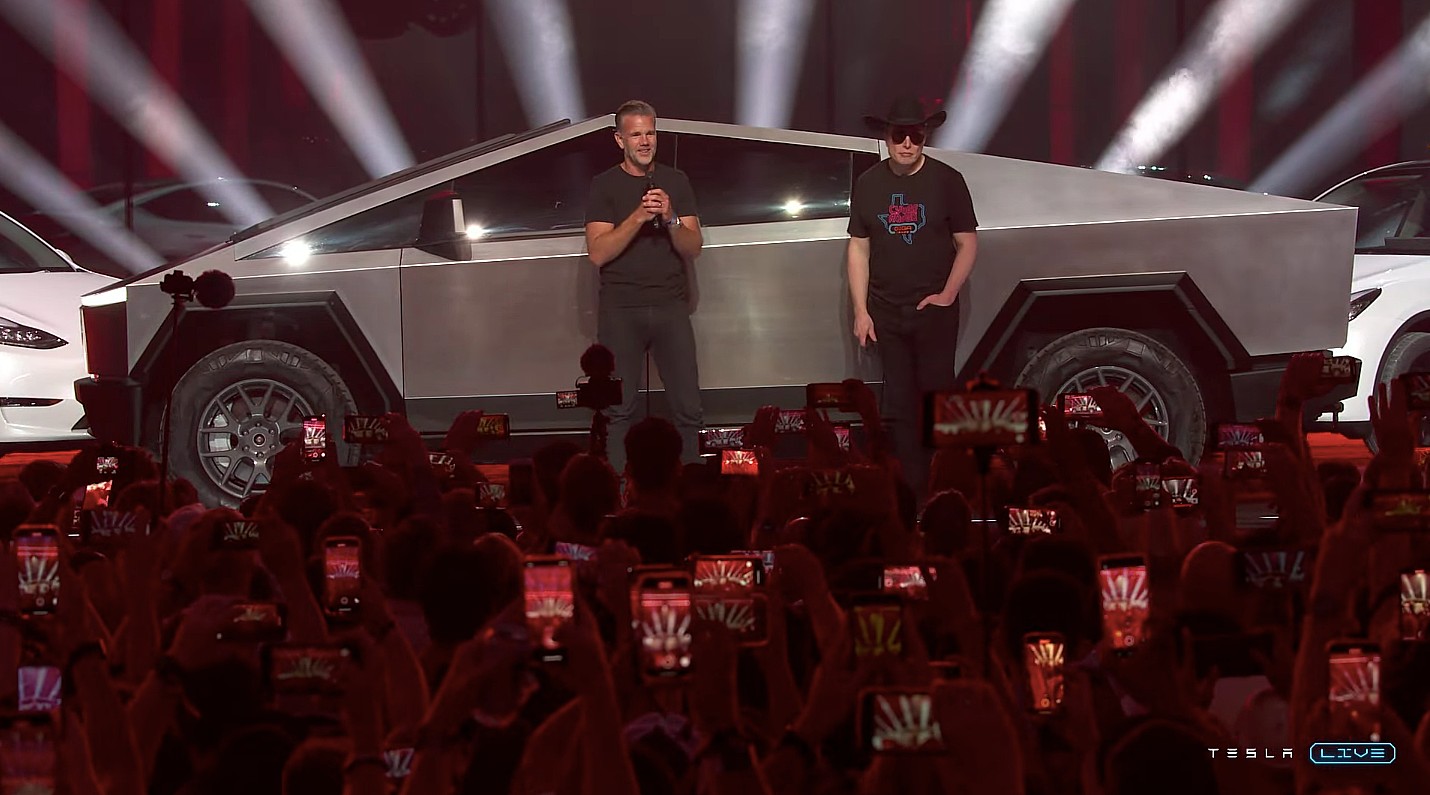

Tesla’s new Cybertruck trim has already gotten the axe from CEO Elon Musk, who said the All-Wheel-Drive configuration of the all-electric pickup will only be available “for the next ten days.”
Musk could mean the price, which is $59,990, or the availability of the trim altogether.
Last night, Tesla launched the All-Wheel-Drive configuration of the Cybertruck, a pickup that comes in at less than $60,000 and features a competitive range and features that are not far off from the offerings of the premium trim.
Tesla launches new Cybertruck trim with more features than ever for a low price
It was a nice surprise from Tesla, considering that last year, it offered a Rear-Wheel-Drive trim of the Cybertruck that only lasted a few months. It had extremely underwhelming demand because it was only $10,000 cheaper than the next trim level up, and it was missing a significant number of premium features.
Simply put, it was not worth the money. Tesla killed the RWD Cybertruck just a few months after offering it.
With the news that Tesla was offering this All-Wheel-Drive configuration of the Cybertruck, many fans and consumers were encouraged. The Cybertruck has been an underwhelming seller, and this seemed to be a lot of truck for the price when looking at its features:
- Dual Motor AWD w/ est. 325 mi of range
- Powered tonneau cover
- Bed outlets (2x 120V + 1x 240V) & Powershare capability
- Coil springs w/ adaptive damping
- Heated first-row seats w/ textile material that is easy to clean
- Steer-by-wire & Four Wheel Steering
- 6’ x 4’ composite bed
- Towing capacity of up to 7,500 lbs
- Powered frunk
It appears as if this trim of Cybertruck won’t be around for too long, however. Musk revealed this morning that it will be around “only for the next 10 days.”
Only for the next 10 days https://t.co/82JnvZQGh2
— Elon Musk (@elonmusk) February 20, 2026
Musk could mean the price of the truck and not necessarily the ability to order it. However, most are taking it as a cancellation.
If it is, in fact, a short-term availability decision, it is baffling, especially as Tesla fans and analysts claim that metrics like quarterly deliveries are no longer important. This seems like a way to boost sales short-term, and if so many people are encouraged about this offering, why would it be kept around for such a short period of time?
Some are even considering the potential that Tesla axes the Cybertruck program as a whole. Although Musk said during the recent Q4 Earnings Call that Cybertruck would still be produced, the end of the Model S and Model X programs indicates Tesla might be prepared to do away with any low-volume vehicles that do not contribute to the company’s future visions of autonomy.
The decision to axe the car just ten days after making it available seems like a true head-scratcher.