News
SpaceX hits new Falcon 9 reusability milestone, retracts all four landing legs
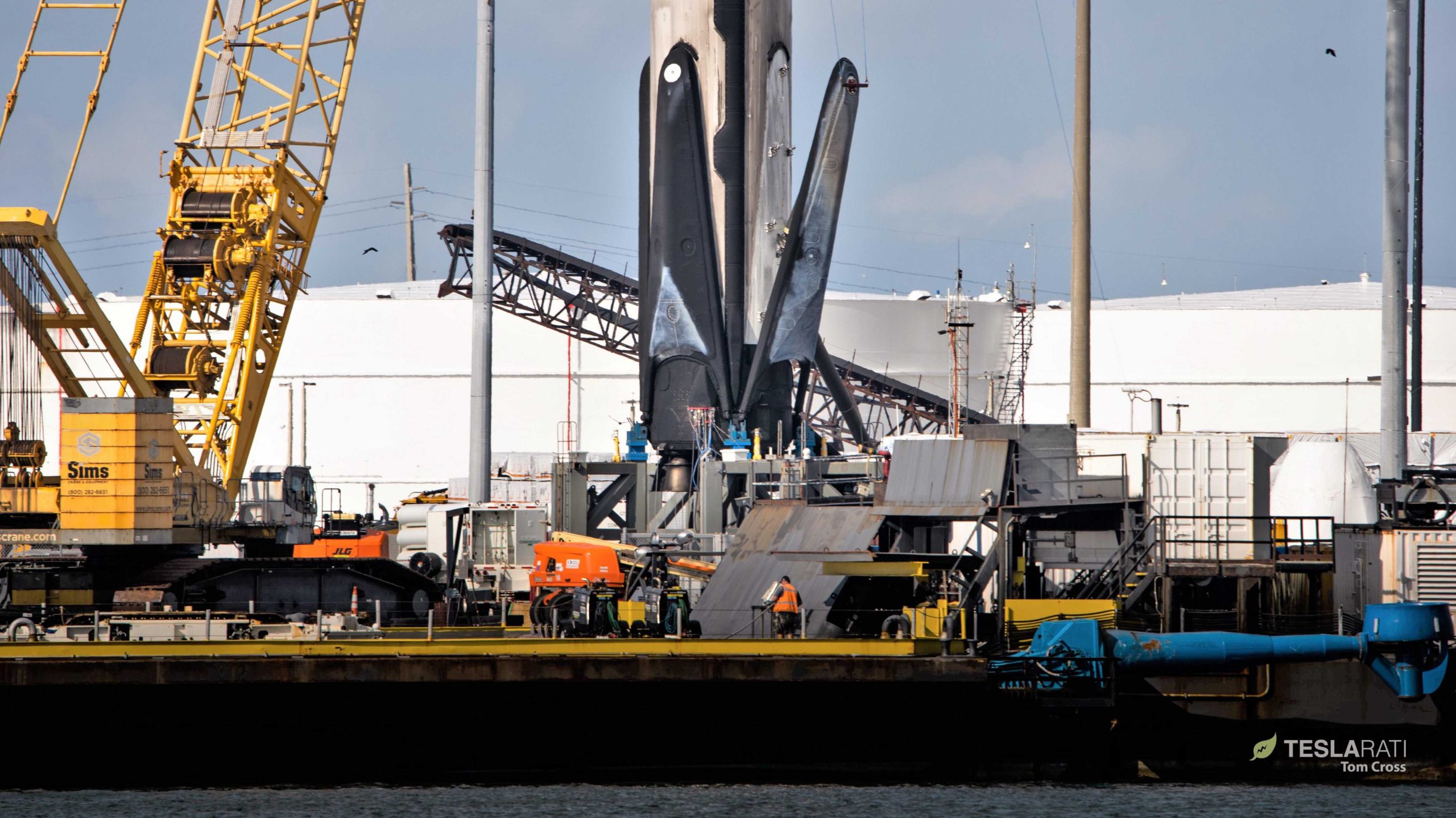
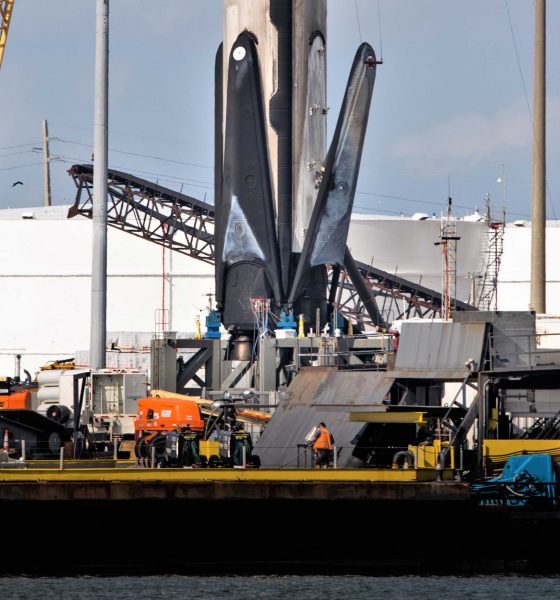
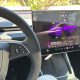
SpaceX appears to have selected Falcon 9 B1056 to become the first booster to have all four landing legs retracted and stowed. While relatively minor in the scope full Falcon 9 booster reuse, in-situ leg retraction could save SpaceX days of recovery and preflight work, a big help for truly rapid reusability.
A handful of prior retraction attempts have been made on Block 5 boosters but unknown issues prevented the process from taking hold. With some modifications to the legs and their deployment/retraction mechanisms, SpaceX seems to have solved those issues and is ready to graduate to a new level of rapid and easy rocket reusability. Teslarati photographer Tom Cross was on site in Port Canaveral, Florida when SpaceX began its first operational leg retractions and was able to capture photos and videos of the process.
Falcon 9 doesn’t even lift
The crux of the need for a relatively complex crane-and-jig method of leg retraction rests on SpaceX’s landing leg design. Put simply, after rapidly deploying with a combination of gravity and hydraulics, Falcon 9 landing legs have no built-in way to return to their stowed state. Each of the four legs are quite large, weighing around 600 kg (1300 lb) and stretching about 10m (33 ft) from hinge to tip. They use an intricate telescoping carbon fiber deployment mechanism to give the legs enough strength to stand up to the forces of Falcon 9 booster landings.
Combined, the legs’ size and telescoping mechanism makes the addition of an onboard retraction mechanism impractical. All the needed hardware would struggle to find a good place for installation and would quite literally be dead weight during launches and landings, stealing from Falcon 9/Heavy payload capacity and generally serving no purpose until a booster has been lifted off the ground with a giant crane.

As a result, SpaceX engineers instead decided to separate leg retraction hardware from the rocket itself and designed a custom crane jig. Pictured above, the jig attaches to Falcon 9’s interstage and allows the crane operator to lift the entire booster as needed. It also features four independent motors and pulleys that are meant to attach to a specific port on the outside of each booster landing leg. The jig then lifts the landing legs up, nominally retracting the telescoping deployment mechanism, at which point latches should be able to safely secure the legs to the booster’s body.
This has been significantly more difficult than expected, judging from a number of retraction attempts over the past six or so months. Falcon 9 Block 5 debuted in May 2018 – in fact, almost exactly one year ago – and SpaceX has since built 11 boosters that have supported 15 launches. SpaceX has thus taken ~12 months to get to a point where Falcon 9’s landing legs can be safely retracted, perhaps owing more to the fact that said legs are of minimal monetary value relative to the rest of a recovered booster. Improving leg retractibility is a bit of a luxury in that sense, as retracting legs offers little value proposition in terms of significantly lowering the cost of launch or reuse.


What leg retraction does do, however, is shave a significant amount of time off of the process of booster recovery and post-recovery processing. Instead of the normal process of totally dismantling and removing the legs piece by piece, stowing Falcon 9’s legs saves not only the time it takes to remove them but also the time it then takes to reinstall said legs for the next launch. At a minimum, this could save 12-24 hours of dedicated work, up to as much as several days according to CEO Elon Musk. Taken to the extreme, it’s likely that SpaceX’s ultimate goal is to lift a booster off the drone ship, retract its landing legs mid-air (or close), flip the booster horizontal, and lower it onto a transporter in one fluid movement.
If SpaceX can arrive at something approximating that in the near future, the company will be well on its way accomplish Musk’s goal of launching the same Falcon 9 booster twice in ~24 hours. Even further down the road, if or when SpaceX manages to optimize the reusability of its Falcon 9 boosters to the extent that almost zero refurbishment or in-depth inspection is needed between launches, minimizing the amount of human effort that goes into something as basic as preparing landing legs may actually have a significant impact on launch costs. For the time being, we get to enjoy the new and unusual spectacle of a giant reusable booster carefully stowing its landing legs for another launch attempt.
Check out Teslarati’s Marketplace! We offer Tesla accessories, including for the Tesla Cybertruck and Tesla Model 3.

News
Tesla hiring for Commercial Charging role hints at Semi push in Europe
The job opening was highlighted by David Forer, Senior Project Developer for Charging at Tesla, on LinkedIn.

Tesla appears to be expanding its Commercial Charging efforts in Central Europe. The job opening was highlighted by David Forer, Senior Project Developer for Charging at Tesla, on LinkedIn.
In a post on LinkedIn, Forer stated that Tesla is looking for a “high-energy executer to own Commercial Charging Sales in Central Europe.” He added that the role will involve closing commercial deals across Tesla’s “entire product range (Supercharging & Megacharging).”
The job listing specifies that the hire will lead the sale of Tesla’s high-power charging products, including Supercharger and Heavy Duty Charging, to major partners such as charge point operators, real estate owners, and retail companies. The role requires fluency in German and English and is based onsite in Munich.
Tesla already operates more than 75,000 Superchargers globally, though the Semi’s Megacharger network is still in its early stages. The inclusion of Heavy Duty Charging in the job description is notable, then, as it aligns with Tesla’s Megacharger infrastructure, which is designed to support the Tesla Semi.
Tesla CEO Elon Musk recently confirmed that the Tesla Semi is moving into high-volume production this 2026. In a post on X, Musk noted that “Tesla Semi starts high volume production this year.”
Aerial footage of the Tesla Semi Factory near Giga Nevada also shows that the facility looks nearly complete, with work now underway inside the facility.
Tesla has also refreshed the Semi lineup on its official website, listing two variants: Standard and Long Range. The Standard trim offers up to 325 miles of range with an energy consumption rating of 1.7 kWh per mile, while the Long Range version provides up to 500 miles.
Both variants support fast charging and can recover up to 60% of range in 30 minutes using compatible infrastructure such as the Megacharger Network.
The presence of Heavy Duty Charging in a Central Europe-focused sales role could indicate that Tesla is preparing charging infrastructure ahead of wider Semi deployment in the region. While Tesla has not formally announced a European launch timeline for the Semi, the vehicle, particularly its range, makes it an ideal fit for the area.
Elon Musk
Tesla Full Self-Driving set to get an awesome new feature, Elon Musk says
Tesla Full Self-Driving is set to get an awesome new feature in the near future, CEO Elon Musk confirmed on X.
Full Self-Driving is the company’s semi-autonomous driving program, which is among the best available to the general public. It still relies on the driver to ultimately remain in control and pay attention, but it truly does make traveling less stressful and easier.
However, Tesla still continuously refines the software through Over-the-Air updates, which are meant to resolve shortcomings in the performance of the FSD suite. Generally, Tesla does a great job of this, but some updates are definitely regressions, at least with some of the features.
Tesla Cybertruck owner credits FSD for saving life after freeway medical emergency
Tesla and Musk are always trying to improve the suite’s performance by fixing features that are presently available, but they also try to add new things that would be beneficial to owners. One of those things, which is coming soon, is giving the driver the ability to prompt FSD with voice demands.
For example, asking the car to park close to the front door of your destination, or further away in an empty portion of the parking lot, would be an extremely beneficial feature. Adjusting navigation is possible through Grok integration, but it is not always effective.
Musk confirmed that voice prompts for FSD would be possible:
Coming
— Elon Musk (@elonmusk) February 21, 2026
Tesla Full Self-Driving is a really great thing, but it definitely has its shortcomings. Navigation is among the biggest complaints that owners have, and it is easily my biggest frustration with using it. Some of the routes it chooses to take are truly mind-boggling.
Another thing it has had issues with is being situated in the correct lane at confusing intersections or even managing to properly navigate through local traffic signs. For example, in Pennsylvania, there are a lot of stop signs with “Except Right Turn” signs directly under.
This gives those turning right at a stop sign the opportunity to travel through it. FSD has had issues with this on several occasions.
Parking preferences would be highly beneficial and something that could be resolved with this voice prompt program. Grocery stores are full of carts not taken back by customers, and many people choose to park far away. Advising FSD of this preference would be a great advantage to owners.
Cybertruck
Elon Musk clarifies Tesla Cybertruck ’10 day’ comment, fans respond
Some are arguing that the decision to confirm a price hike in ten days is sort of counterproductive, especially considering it is based on demand. Giving consumers a timeline of just ten days to make a big purchase like a pickup truck for $60,000, and basically stating the price will go up, will only push people to make a reservation.

Elon Musk has clarified what he meant by his comment on X yesterday that seemed to indicate that Tesla would either do away with the new All-Wheel-Drive configuration of the Cybertruck or adjust the price.
The response was cryptic as nobody truly knew what Musk’s plans were for the newest Tesla Cybertruck trim level. We now have that answer, and fans of the company are responding in a polarizing fashion.
On Thursday night, Tesla launched the Cybertruck All-Wheel-Drive, priced competitively at $59,990. It was a vast improvement from the Rear-Wheel-Drive configuration Tesla launched last year at a similar price point, which was eventually cancelled just a few months later due to low demand.
Tesla launches new Cybertruck trim with more features than ever for a low price
However, Musk said early on Friday, “just for 10 days,” the truck would either be available or priced at $59,990. We can now confirm Tesla will adjust the price based on more recent comments from the CEO.
Musk said the price will fluctuate, but it “depends on how much demand we see at this price level.”
Depends on how much demand we see at this price level
— Elon Musk (@elonmusk) February 20, 2026
Some are defending the decision, stating that it is simply logical to see how the Cybertruck sells at this price and adjust accordingly.
Case 1: You don’t like it -> don’t buy it
Case 2 (me): You like it, it’s fits your situation and needs -> you buy it.
Case 3: Complain endlessly for no reason, you weren’t going to get one anyway, but you want people to know you’re mad, for some reason.
Silly netizens.— Ryan Scanlan 👥 (@Xenius) February 21, 2026
Others, not so much.
Alright I’m obviously not the one successful enough to be calling the shots at Tesla and worth almost a trillion dollars
But people were excited about the awesome Cybertruck news and then it got taken away, that’s why people are annoyed. The wording felt more like a threat.… pic.twitter.com/NWVNklcXoJ— Dirty Tesla (@DirtyTesLa) February 21, 2026
No but fr wtf you doing dude???????
— Greggertruck (@greggertruck) February 20, 2026
It’s how it was communicated.
If it had been stated clearly on the website for everyone to see, everyone would be fine.
— KiTT_2020 (@kitt_2020) February 20, 2026
Some are arguing that the decision to confirm a price hike in ten days is sort of counterproductive, especially considering it is based on demand. Giving consumers a timeline of just ten days to make a big purchase like a pickup truck for $60,000, and basically stating the price will go up, will only push people to make a reservation.
Demand will look strong because people want to lock in this price. The price will inevitably go up, and demand for the trim will likely fall a bit because of the increased cost.
Many are arguing Musk should have kept this detail internal, but transparency is a good policy to have. It is a polarizing move to confirm a price increase in just a week-and-a-half, but the community is obviously split on how to feel.