

SpaceX
SpaceX’s crewed Dragon launch debut likely to slip into 2020 as NASA pursues “realistic” dates
In a recent blog post, NASA made it clear that changes happening to leadership within the agency – specifically within the Human Exploration and Operations Directorate – are impacting the timelines to return astronauts to the International Space Station(ISS) from US soil. Agency conflicts are just the latest of several setbacks that have impacted the schedule of SpaceX’s crewed Crew Dragon launch debut.
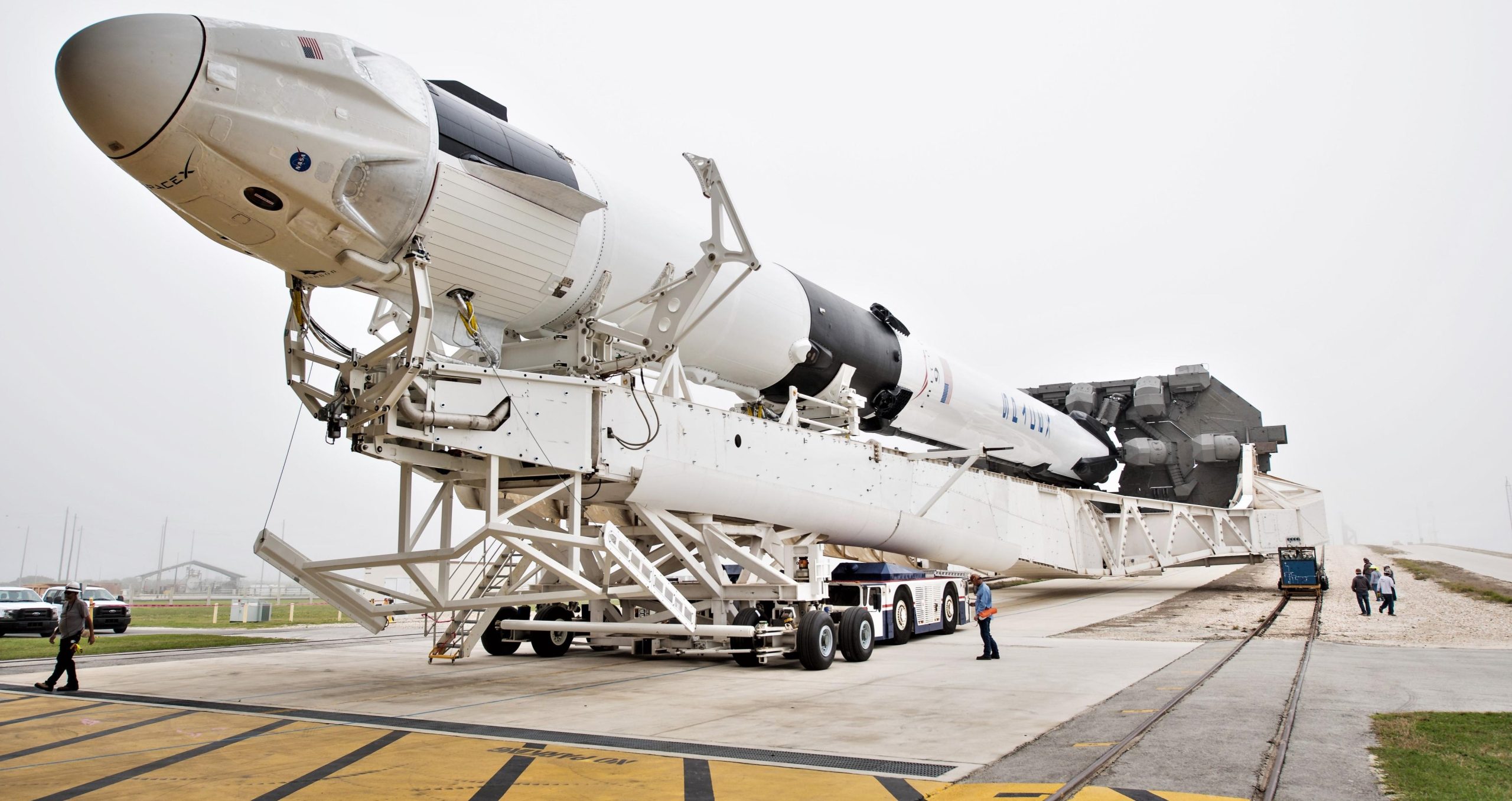
Initially, the SpaceX Demo-2 mission set to carry NASA astronauts Bob Behnken and Doug Hurley to the ISS was slated to occur in the summer of 2019. That demonstration flight has since dropped off of the NASA launches and landings schedule, at least through October. SpaceX is now targeting a Demo-2 launch no earlier than December 2019 but an array of critical milestones must be completed to achieve that goal and both SpaceX and NASA have been keen to express that a crewed Crew Dragon launch in 2019 is a huge stretch.

According to the recent blog post, “NASA Administrator (Jim Bridenstine) has directed all programs in the Human Exploration and Operations Directorate to reexamine flight dates once new leadership is in place to deliver realistic schedule plans.” It is very likely that these new schedule plans will push the Demo-2 launch target into 2020.
Another roadblock that affects the timeline is the fact that SpaceX has yet to conduct an in-flight abort (IFA) test of the Crew Dragon capsule, meant to demonstrate the ability of the capsule’s SuperDraco thruster abort system to safely return crewmembers back to Earth in the event of an in-flight failure. SpaceX’s IFA has been delayed by multiple months after a catastrophic anomaly during an attempted April 2019 static fire test of the abort system resulted in the complete loss of the Crew Dragon capsule (C201), originally assigned to support the IFA. Although the capsule was destroyed, valuable lessons were learned about the pressurization and propulsion systems of Crew Dragon, particular “the flammability of the check valve’s titanium internal components” according to a July 15th statement released by SpaceX.
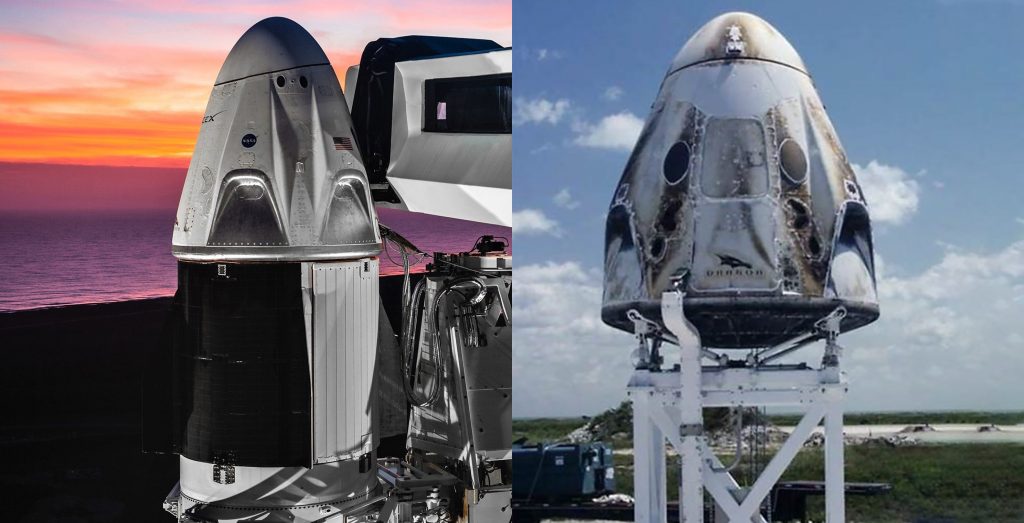
As a result of the loss of C201, the in-flight abort test must now use the Crew Dragon capsule (C205) originally intended for the Demo-2 to transport Behnken and Hurley to the ISS. The findings from the anomaly investigation identified changes to the SuperDraco thruster abort system that would need to be made to all capsules currently in production prior to any future flights. SpaceX states that “thorough testing and analysis of these mitigations has already begun in close coordination with NASA, and will be completed well in advance of future flights.”
Pending SpaceX’s modification of Dragon 2 hardware and NASA’s approval, a new launch date for the in-flight abort test could be announced as early as August. According to SpaceX CEO, Elon Musk, Falcon 9 Block 5 booster B1048.3 – the second booster to successfully complete three launches and landings – will likely support Crew Dragon’s in-flight abort test, although there have been indications from NASASpaceflight.com that B1046.3 is also a candidate.
Step by step
Following a successful in-flight abort test and recovery of the Crew Dragon capsule, a joint flight readiness review will be conducted by SpaceX, NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Directorate (HEOD), the Commercial Crew Program (CCP), and the International Space Station Program to settle on a launch date for Demo-2. This meeting will ensure that all parties are well-versed in the procedures required to support crewed spaceflight missions from US soil after an almost decade-long hiatus.
Another anticipated safety procedure that is assumed to be tested prior to the designation of a crewed flight date is a full rehearsal of emergency escape procedures at Launch Complex 39A (LC-39A), located at Kennedy Space Center, Florida. A joint version of this test was recently completed by NASA, Boeing, and United Launch Alliance in anticipation of crewed flights launching from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. As an escape system has not been necessary at LC-39A since the retirement of the Shuttle program, SpaceX and NASA may participate in a similar demonstration utilizing a recently installed zip-line egress system on the Fixed Service Structure of LC-39A.

Although there is some time remaining in the year for SpaceX and NASA to meet all pre-flight objectives, it seems more likely that a crewed SpaceX demonstration mission to the ISS will occur sometime in 2020. As NASA said “we are testing, learning and incorporating changes to improve the design and operation of these next-generation human space transportation systems. As a result, our providers have improved the safety of these systems, and the effect of these changes have impacted schedules.”
Finally, according to recent reports from a handful of Russian media outlets, Crew Dragon’s inaugural crewed launch is believed to be scheduled for absolutely no earlier than (NET) mid-December 2019, although all signs point to that date being purely for planning purposes. In short, Crew Dragon’s Demo-2 mission is all but guaranteed to slip into 2020, but those delays will (hopefully) result in a significantly safer and more reliable spacecraft.
Check out Teslarati’s Marketplace! We offer Tesla accessories, including for the Tesla Cybertruck and Tesla Model 3.

Elon Musk
Rumored SpaceX-xAI merger gets apparent confirmation from Elon Musk
The comment follows reports that the rocket maker is weighing a transaction that could further consolidate Musk’s space and AI ventures.

Elon Musk appeared to confirm reports that SpaceX is exploring a potential merger with artificial intelligence startup xAI by responding positively to a post about the reported transaction on X.
Musk’s comment follows reports that the rocket maker is weighing a transaction that could further consolidate his space and AI ventures.
SpaceX xAI merger
As per a recent Reuters report, SpaceX has held discussions about merging with xAI, with the proposed structure potentially involving an exchange of xAI shares for SpaceX stock. The value, structure, and timing of any deal have not been finalized, and no agreement has been signed.
Musk appeared to acknowledge the report in a brief reply on X, responding “Yeah” to a post that described SpaceX as a future “Dyson Swarm company.” The comment references a Dyson Swarm, a sci-fi megastructure concept that consists of a massive network of satellites or structures that orbit a celestial body to harness its energy.
Reuters noted that two entities were formed in Nevada on January 21 to facilitate a potential transaction for the possible SpaceX-xAI merger. The discussions remain ongoing, and a transaction is not yet guaranteed, however.
AI and space infrastructure
A potential merger with xAI would align with Musk’s stated strategy of integrating artificial intelligence development with space-based systems. Musk has previously said that space-based infrastructure could support large-scale computing by leveraging continuous solar energy, an approach he has framed as economically scalable over time.
xAI already has operational ties to Musk’s other companies. The startup develops Grok, a large language model that holds a U.S. Department of Defense contract valued at up to $200 million. AI also plays a central role in SpaceX’s Starlink and Starshield satellite programs, which rely on automation and machine learning for network management and national security applications.
Musk has previously consolidated his businesses through share-based transactions, including Tesla’s acquisition of SolarCity in 2016 and xAI’s acquisition of X last year. Bloomberg has also claimed that Musk is considering a merger between SpaceX and Tesla in the future.
Elon Musk
SpaceX reportedly discussing merger with xAI ahead of blockbuster IPO

In a groundbreaking new report from Reuters, SpaceX is reportedly discussing merger possibilities with xAI ahead of the space exploration company’s plans to IPO later this year, in what would be a blockbuster move.
The outlet said it would combine rockets and Starlink satellites, as well as the X social media platform and AI project Grok under one roof. The report cites “a person briefed on the matter and two recent company filings seen by Reuters.”
Musk, nor SpaceX or xAI, have commented on the report, so, as of now, it is unconfirmed.
With that being said, the proposed merger would bring shares of xAI in exchange for shares of SpaceX. Both companies were registered in Nevada to expedite the transaction, according to the report.
On January 21, both entities were registered in Nevada. The report continues:
“One of them, a limited liability company, lists SpaceX and Bret Johnsen, the company’s chief financial officer, as managing members, while the other lists Johnsen as the company’s only officer, the filings show.”
The source also stated that some xAI executives could be given the option to receive cash in lieu of SpaceX stock. No agreement has been reached, nothing has been signed, and the timing and structure, as well as other important details, have not been finalized.
SpaceX is valued at $800 billion and is the most valuable privately held company, while xAI is valued at $230 billion as of November. SpaceX could be going public later this year, as Musk has said as recently as December that the company would offer its stock publicly.
The plans could help move along plans for large-scale data centers in space, something Musk has discussed on several occasions over the past few months.
At the World Economic Forum last week, Musk said:
“It’s a no-brainer for building solar-powered AI data centers in space, because as I mentioned, it’s also very cold in space. The net effect is that the lowest cost place to put AI will be space and that will be true within two to three years, three at the latest.”
He also said on X that “the most important thing in the next 3-4 years is data centers in space.”
If the report is true and the two companies end up coming together, it would not be the first time Musk’s companies have ended up coming together. He used Tesla stock to purchase SolarCity back in 2016. Last year, X became part of xAI in a share swap.
Elon Musk
SpaceX Starship V3 gets launch date update from Elon Musk
The first flight of Starship Version 3 and its new Raptor V3 engines could happen as early as March.

Elon Musk has announced that SpaceX’s next Starship launch, Flight 12, is expected in about six weeks. This suggests that the first flight of Starship Version 3 and its new Raptor V3 engines could happen as early as March.
In a post on X, Elon Musk stated that the next Starship launch is in six weeks. He accompanied his announcement with a photo that seemed to have been taken when Starship’s upper stage was just about to separate from the Super Heavy Booster. Musk did not state whether SpaceX will attempt to catch the Super Heavy Booster during the upcoming flight.
The upcoming flight will mark the debut of Starship V3. The upgraded design includes the new Raptor V3 engine, which is expected to have nearly twice the thrust of the original Raptor 1, at a fraction of the cost and with significantly reduced weight. The Starship V3 platform is also expected to be optimized for manufacturability.
The Starship V3 Flight 12 launch timeline comes as SpaceX pursues an aggressive development cadence for the fully reusable launch system. Previous iterations of Starship have racked up a mixed but notable string of test flights, including multiple integrated flight tests in 2025.
Interestingly enough, SpaceX has teased an aggressive timeframe for Starship V3’s first flight. Way back in late November, SpaceX noted on X that it will be aiming to launch Starship V3’s maiden flight in the first quarter of 2026. This was despite setbacks like a structural anomaly on the first V3 booster during ground testing.
“Starship’s twelfth flight test remains targeted for the first quarter of 2026,” the company wrote in its post on X.








