News
SpaceX Falcon 9 booster spotted in Southern California on journey to Florida
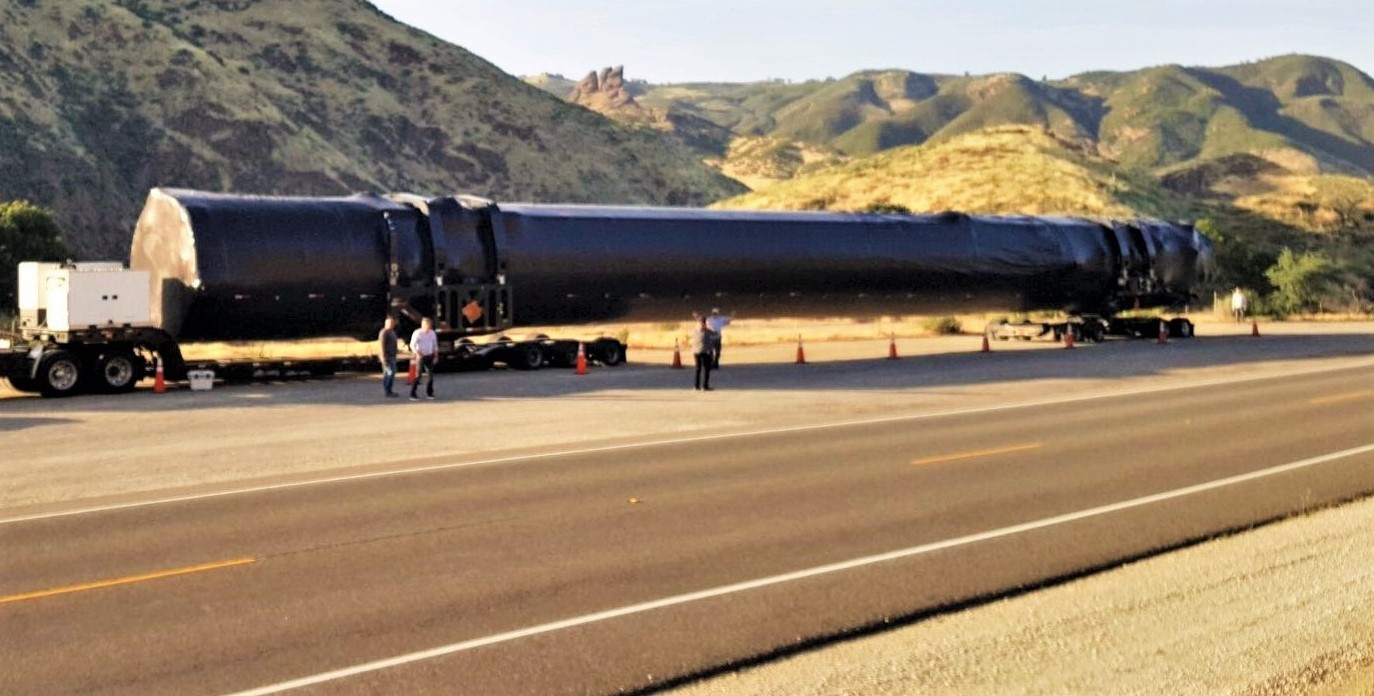
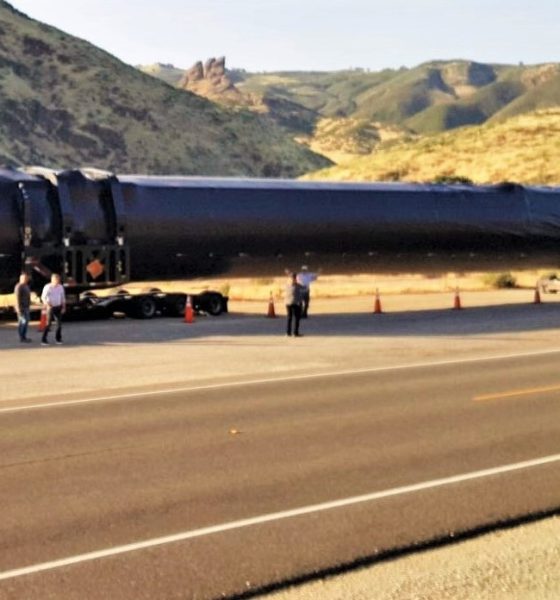
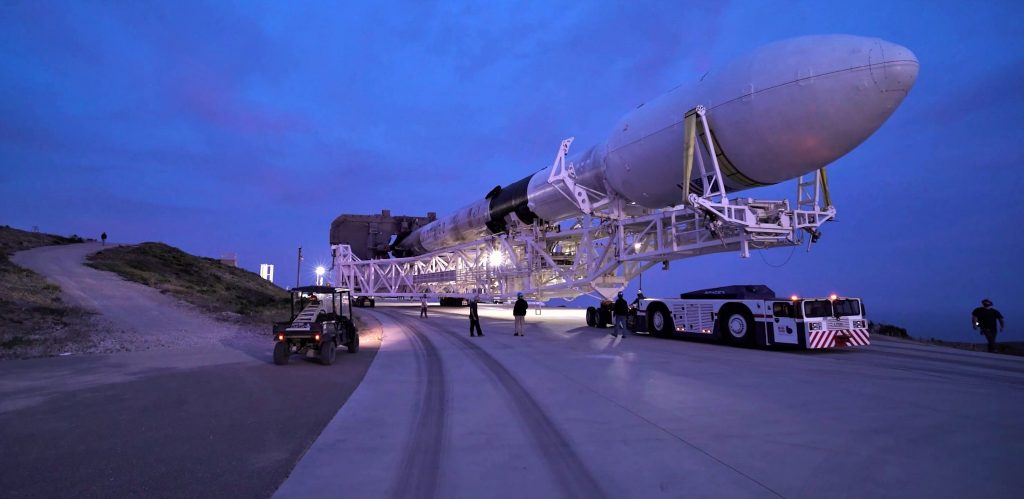
On August 20th, a member of a local California Facebook group happened to spot a SpaceX Falcon 9 booster in transit, an exceedingly rare sight as of late. Moving east, the booster is almost certainly heading to Florida to support a major cluster of 6-8 launches in Q4 2019.
This marks the first time in nearly four months that a flight-proven Falcon 9 booster has been spotted in transit, excluding a lone (unflown) booster captured on its way to McGregor, Texas last month. This also serves as an opportunity to reexamine the status of SpaceX’s expansive fleet of reusable Falcon 9 Block 5 rockets as the company prepares for a busy end of 2019 in the midst of a rare multi-month lull in launch activities.

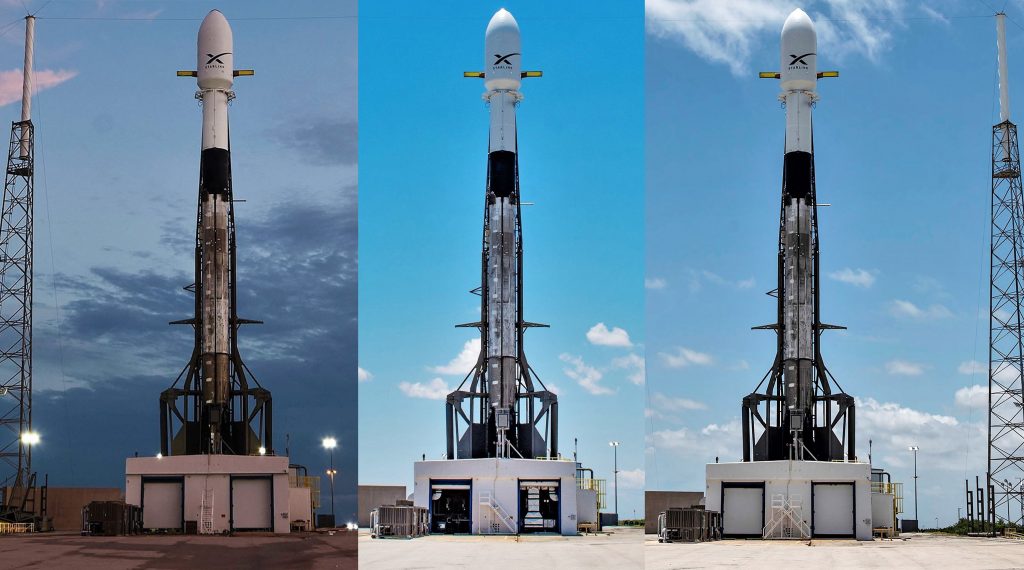
Based on the timing, its location (Southern California), and the direction it was headed (Eastbound), the rocket spotted on August 20th is almost certainly twice-flown Falcon 9 booster B1051. The booster was likely departing SpaceX’s Vandenberg Air Force Base (VAFB) launch facilities after some two months post-launch inspections and refurbishment, having completed its second launch and landing on June 12th, 2019 in support of the Radarsat Constellation Mission (RCM).


Prior to its successful launch of RCM, B1051 had the historic privilege of supporting the inaugural orbital launch of SpaceX’s Crew Dragon spacecraft, putting the next-gen crew capsule through its paces before a crewed launch debut expected to occur absolutely no earlier than (NET) December 2019. Known as DM-1 (Demo-1), B1051 was subjected to an exceptionally strenuous suite of inspections, analysis, and testing for the mission – from the very first welding sparks to the booster’s McGregor, TX and Florida static fires and launch debut.
Said debut occurred on March 2nd, 2019, after which B1051 landed at sea aboard drone ship Of Course I Still Love You (OCISLY).
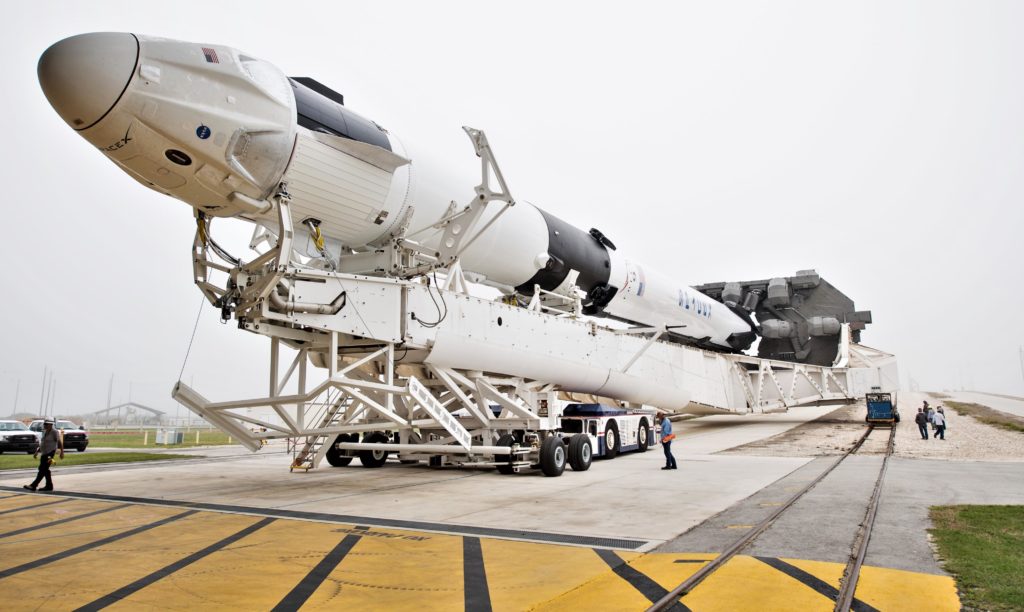

SpaceX production experienced an exceptionally frenetic period from early-2018 to mid-2019, in which the company averaged the completion of almost an entire Falcon 9 or Heavy rocket every 1-2 months, building, delivering, launching, and relaunching Falcon boosters B1046 through B1057 from ~January 2018 to April 2019. In the last 3-4 months, the (publicly visible) rate of rocket production has dramatically slowed, presumably an intentional slow-down triggered by SpaceX’s rapidly growing fleet of flight-proven boosters.
In the last four or so months, unaffiliated observers have spotted a grand total of one new Falcon 9 booster on its way from SpaceX’s Hawthorne, CA factory to its McGregor, TX testing facilities. That booster – likely either B1058 for Crew Dragon’s crewed launch debut (Demo-2) or B1059 for SpaceX’s next USAF GPS III launch – was spotted twice headed east in Arizona on July 29th. Prior to that, the next most recent ‘core spottings’ occurred in mid-to-late April, while the most recent since July 29th’s instance is B1051.2’s August 20th appearance. In short, things are unusually quiet on the SpaceX booster transport front.

Rocket fleet logistics
This apparent slowdown in production can be relatively easily explained by the nature of SpaceX’s fleet of boosters, as well as the company’s growing confidence in the extreme reusability nominally permitted by Falcon 9’s Block 5 upgrade. Just a few days ago, SpaceX Vice President of Build and Flight Reliability Hans Koenigsmann reiterated the belief that Falcon 9 Block 5 boosters will be more than capable of safely performing 10 or more launches apiece.
At the moment, SpaceX’s fleet of flightworthy Block 5 boosters is seven strong, composed of B1046.3, B1048.3, B1049.3, B1051.2, B1052.2, B1053.2, B1056.2. Altogether, they have supported a full 17 launches in 15 months, averaging 2.4 launches apiece with a maximum of three launches achieved by three separate boosters. Under the extremely conservative assumption that 60-90 days are needed for post-flight inspections and refurbishment, anywhere from 2-6 of those boosters are already ready for their next launches.

In simple terms, it appears that even a fleet as small as seven Falcon 9 Block 5 boosters may be capable of supporting a vast majority of SpaceX’s commercial launch contracts, while even NASA has come to support launching uncrewed Cargo Dragon missions on flight-proven boosters. In fact, Koenigsmann revealed that a number of customers had nearly come a full 180 degrees in the less than three years that SpaceX has been reflying boosters. Many now actively prefer a flight-proven booster and have come to view them as a more known quantity relative to unproven (i.e. new) hardware.
Aside from a handful of customers – primarily the US military – that explicitly demand new hardware, the rare need for entirely expendable Falcon 9 launches, and the equally rare loss of boosters during unsuccessful landings, SpaceX just doesn’t need nearly as high of a Falcon 9 or Heavy booster production rate to support the same (or even greater) launch cadences.
Check out Teslarati’s Marketplace! We offer Tesla accessories, including for the Tesla Cybertruck and Tesla Model 3.

News
Tesla makes latest move to remove Model S and Model X from its lineup
Tesla’s latest decisive step toward phasing out its flagship sedan and SUV was quietly removing the Model S and Model X from its U.S. referral program earlier this week.

Tesla has made its latest move that indicates the Model S and Model X are being removed from the company’s lineup, an action that was confirmed by the company earlier this quarter, that the two flagship vehicles would no longer be produced.
Tesla has ultimately started phasing out the Model S and Model X in several ways, as it recently indicated it had sold out of a paint color for the two vehicles.
Now, the company is making even more moves that show its plans for the two vehicles are being eliminated slowly but surely.
Tesla’s latest decisive step toward phasing out its flagship sedan and SUV was quietly removing the Model S and Model X from its U.S. referral program earlier this week.
The change eliminates the $1,000 referral discount previously available to new buyers of these vehicles. Existing Tesla owners purchasing a new Model S or Model X will now only receive a halved loyalty discount of $500, down from $1,000.
The updates extend beyond the two flagship vehicles. New Cybertruck buyers using a referral code on Premium AWD or Cyberbeast configurations will no longer get $1,000 off. Instead, both referrer and buyer receive three months of Full Self-Driving (Supervised).
The loyalty discount for Cybertruck purchases, excluding the new Dual Motor AWD trim level, has also been cut to $500.
NEWS: Tesla has removed the Model S and Model X from the referral program.
New owners also no longer get a $1,000 referral discount on a new Cybertruck Premium AWD or Cyberbeast. Instead, you now get 3 months of FSD (Supervised).
Additionally, Tesla has reduced the loyalty… pic.twitter.com/IgIY8Hi2WJ
— Sawyer Merritt (@SawyerMerritt) March 6, 2026
These adjustments apply only in the United States, and reflect Tesla’s broader strategy to optimize margins while boosting adoption of its autonomous driving software.
The timing is no coincidence. Tesla confirmed earlier this year that Model S and Model X production will end in the second quarter of 2026, roughly June, as the company reallocates factory capacity toward its Optimus humanoid robot and next-generation vehicles.
With annual sales of the low-volume flagships already declining (just 53,900 units in 2025), incentives are no longer needed to drive demand. Production is winding down, and Tesla expects strong remaining interest without subsidies.
Industry observers see this as the clearest sign yet of an “end-of-life” phase for the vehicles that once defined Tesla’s luxury segment. Community reactions on X range from nostalgia, “Rest in power S and X”, to frustration among long-time owners who feel perks are eroding just as the models approach discontinuation.
Some buyers are rushing orders to lock in final discounts before they vanish entirely.
Doug DeMuro names Tesla Model S the Most Important Car of the last 30 years
For Tesla, the move prioritizes efficiency: fewer discounts on outgoing models, a stronger push for FSD subscriptions, and a focus on high-margin Cybertruck trims amid surging orders.
Loyalists still have a narrow window to purchase a refreshed Plaid or Long Range model with remaining incentives, but the message is clear: Tesla’s lineup is evolving, and the era of the original flagships is drawing to a close.
News
Tesla Australia confirms six-seat Model Y L launch in 2026
Compared with the standard five-seat Model Y, the Model Y L features a longer body and extended wheelbase to accommodate an additional row of seating.
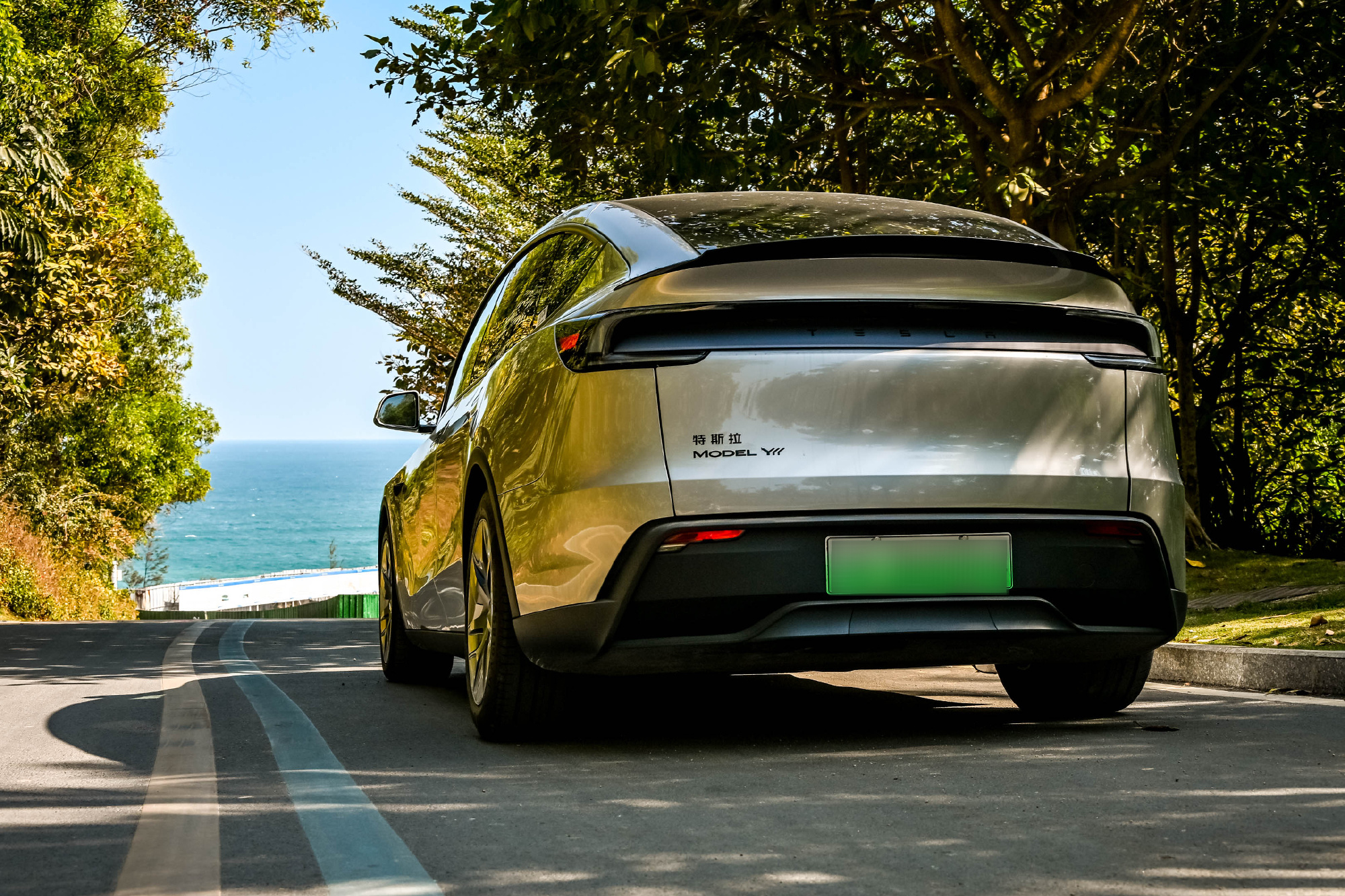

Tesla has confirmed that the larger six-seat Model Y L will launch in Australia and New Zealand in 2026.
The confirmation was shared by techAU through a media release from Tesla Australia and New Zealand.
The Model Y L expands the Model Y lineup by offering additional seating capacity for customers seeking a larger electric SUV. Compared with the standard five-seat Model Y, the Model Y L features a longer body and extended wheelbase to accommodate an additional row of seating.
The Model Y L is already being produced at Tesla’s Gigafactory Shanghai for the Chinese market, though the vehicle will be manufactured in right-hand-drive configuration for markets such as Australia and New Zealand.
Tesla Australia and New Zealand confirmed the vehicle will feature seating for six passengers.
“As shown in pictures from its launch in China, Model Y L will have a new seating configuration providing room for 6 occupants,” Tesla Australia and New Zealand said in comments shared with techAU.
Instead of a traditional seven-seat arrangement, the Model Y L uses a 2-2-2 layout. The middle row features two individual seats, allowing easier access to the third row while providing additional space for passengers.
Tesla Australia and New Zealand also confirmed that the Model Y L will be covered by the company’s updated warranty structure beginning in 2026.
“As with all new Tesla Vehicles from the start of 2026, the Model Y L will come with a 5-year unlimited km vehicle warranty and 8 years for the battery,” the company said.
The updated policy increases Tesla’s vehicle warranty from the previous four-year or 80,000-kilometer coverage.
Battery and drive unit warranties remain unchanged depending on the variant. Rear-wheel-drive models carry an eight-year or 160,000-kilometer warranty, while Long Range and Performance variants are covered for eight years or 192,000 kilometers.
Tesla has not yet announced official pricing or range figures for the Model Y L in Australia.
News
Tesla Roadster patent hints at radical seat redesign ahead of reveal
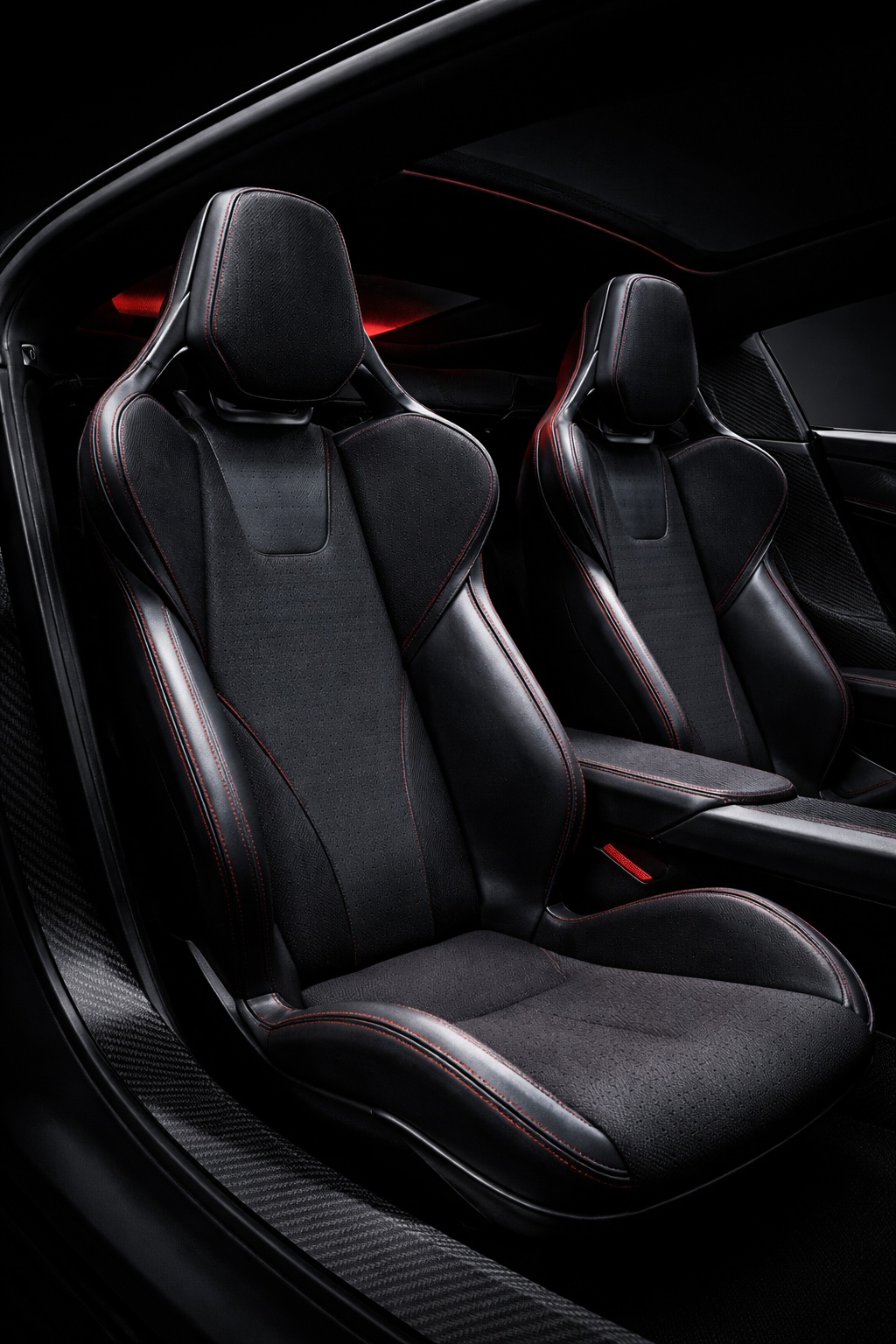

A newly published Tesla patent could offer one of the clearest signals yet that the long-awaited next-generation Roadster is nearly ready for its public debut.
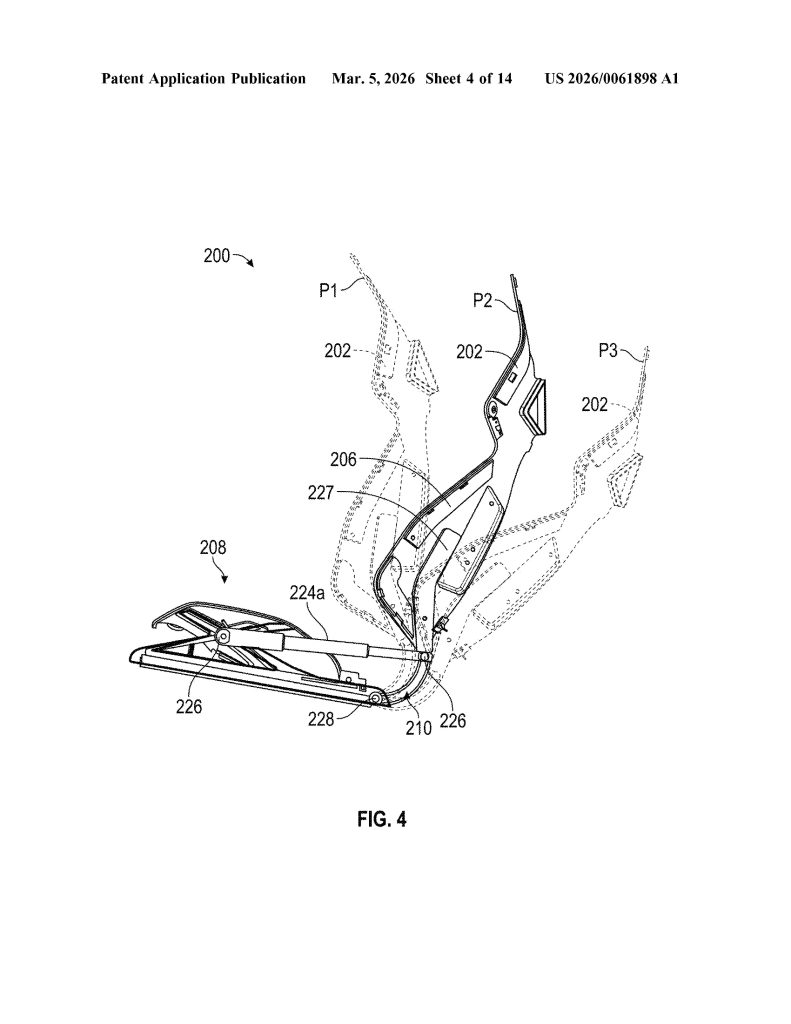
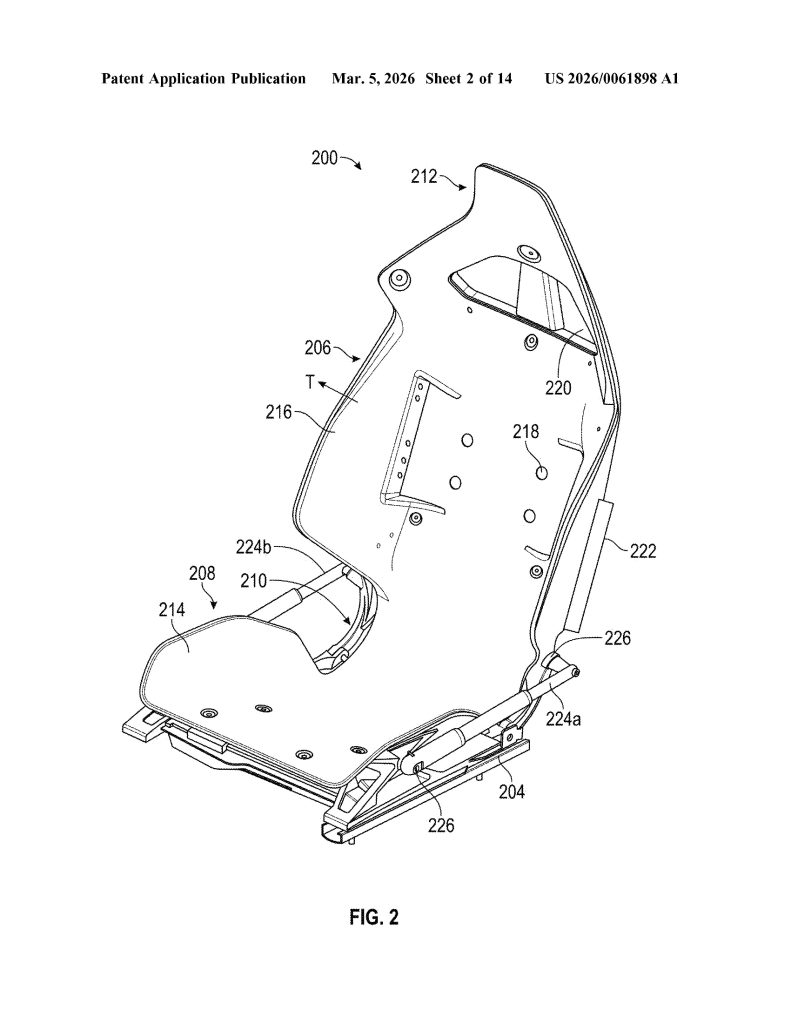
Patent No. US 20260061898 A1, published on March 5, 2026, describes a “vehicle seat system” built around a single continuous composite frame – a dramatic departure from the dozens of metal brackets, recliner mechanisms, and rivets that make up a traditional car seat. Tesla is calling it a monolithic structure, with the seat portion, backrest, headrest, and bolsters all thermoformed as one unified piece.
The approach mirrors Tesla’s broader manufacturing philosophy. The same company that pioneered massive aluminum castings to eliminate hundreds of body components is now applying that logic to the cabin. Fewer parts means fewer potential failure points, less weight, and a cleaner assembly process overall.
Tesla ramps hiring for Roadster as latest unveiling approaches
The timing of the filing is difficult to ignore. Elon Musk has publicly targeted April 1, 2026 as the date for an “unforgettable” Roadster design reveal, and two new Roadster trademarks were filed just last month. A patent describing a seat architecture suited for a hypercar, and one that Tesla has promised will hit 60 mph in under two seconds.
The Roadster, originally unveiled in 2017, has been one of Tesla’s most anticipated yet most delayed products. With a target price around $200,000 and engineering ambitions to match, it is being positioned as the ultimate showcase for what Tesla’s technology can do.
The patent was first flagged by @seti_park on X.
Tesla Roadster Monolithic Seat: Feature Highlights via US Patent 20260061898 A1
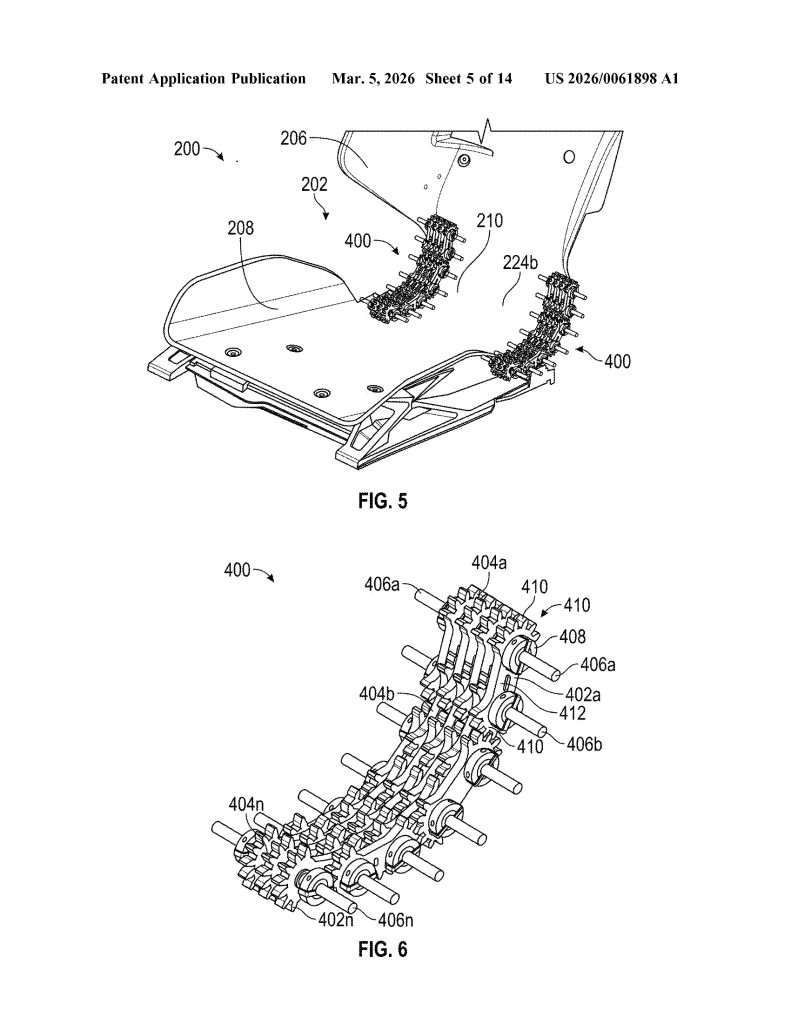
- Single Continuous Frame (Monolithic Construction). The core invention is a seat assembly built from one continuous frame that integrates the seat portion, backrest portion, and hinge into a single component — eliminating the need for separate structural parts and mechanical joints typical in conventional seats.
- Integrated Flexible Hinge. Rather than a traditional mechanical recliner, the hinge is built directly into the continuous frame and is designed to flex, and allowing the backrest to move relative to the seat portion. The hinge can be implemented as a fiber composite leaf spring or an assembly of rigid linkages.
- Thermoformed Anisotropic Composite Material. The continuous frame is manufactured via thermoforming from anisotropic composite materials, including fiberglass-nylon, fiberglass-polymer, nylon carbon composite, Kevlar-nylon, or Kevlar-polymer composites, enabling a molded-to-shape monolithic structure.
- Regionally Tuned Stiffness Zones. The frame is engineered with up to six distinct stiffness regions (R1–R6) across the seat, backrest, hinge, headrest, and bolsters. Each zone can have a different stiffness, allowing precise ergonomic and structural tuning without adding separate components.
- Linkage Assembly Hinge Mechanism. The hinge incorporates one or more linkage assemblies consisting of multiple interlocking links with gears, connected by rods. When driven by motors or actuators, these linkages act as a flexible member to control backrest movement along a precise, ergonomically optimized trajectory.
- Multi-Actuator Six-Degree-of-Freedom Positioning System. The seat uses four distinct actuator pairs, all controlled by a central controller. These actuators work in coordinated combinations to achieve fore/aft, height, cushion tilt, and backrest rotation adjustments simultaneously.
- ECU-Based Controller Architecture. An Electronic Control Unit (ECU) and programmable controller manage all seat actuators, receive user input via a user interface (touchscreen, buttons, or switches), and incorporate sensor feedback to confirm and maintain desired seat positions, essentially making this a software-driven seat system.
- Airbag-Integrated Bolster Deployment System. The backrest bolsters (216) are geometrically shaped and sized to guide airbag deployment along a specific, pre-configured trajectory. Left and right bolsters can have different shapes so that each guides its respective airbag along a distinct trajectory, improving occupant protection.
- Ventilation Holes Formed into the Backrest. The continuous frame includes one or more ventilation holes formed directly into the backrest portion, configured to either receive airflow into or deliver airflow from the seat frame — enabling passive or active thermal comfort without requiring separate ventilation components.
- Soft Trim Recess for Tool-Free Integration. The headrest and backrest portions together define a molded recess, specifically designed to receive and secure a soft trim component (foam, fabric, or cushioning) directly into the continuous frame, eliminating the need for separate attachment hardware and simplifying final assembly.