News
Watch Tesla Full Self-Driving Beta’s software operate without ‘rolling stops’
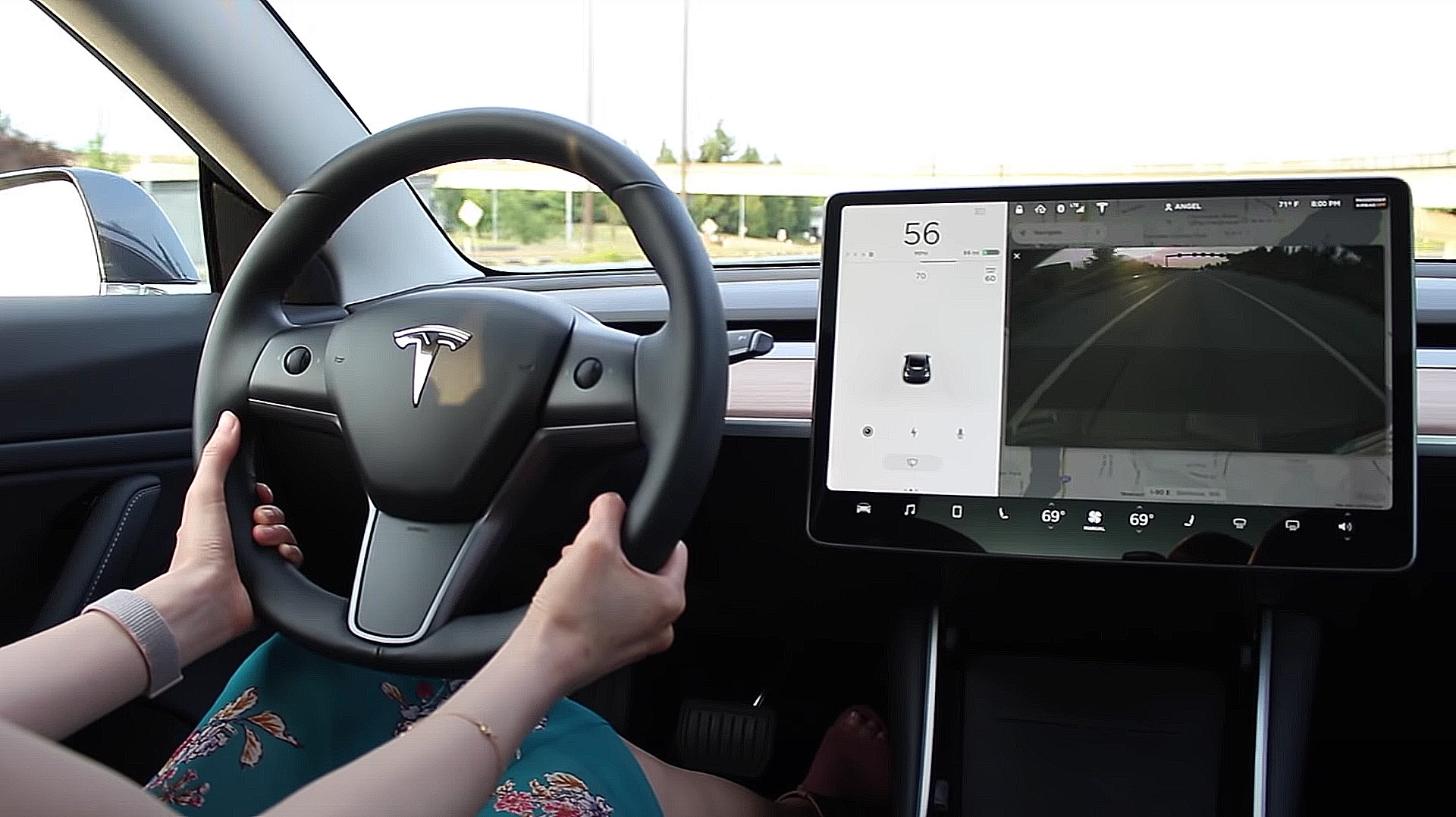
Tesla has rolled out Full Self-Driving Beta software version 10.10, which has eliminated the vehicle’s ability to perform “rolling stops.” The feature was required to be removed following a reprimand from the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA), who required Tesla to remove the feature from the Beta program via an update.
Earlier this week, the NHTSA required Tesla to recall 53,822 vehicles. The term recall is applicable here, according to the NHTSA. NHTSA recalls can include any required repair, which includes a software update, to remedy a potential safety risk. Software updates, while performed from the comfort of a garage or parking space, are still technically considered a recall as they are a manufacturer remedy to a problem that could cause a risk to safety.
The recall applies to Model S and Model X vehicles built from 2016 to 2022, Model 3s from 2017 to 2022, and Model Ys from 2020 to 2022.
Tesla stated that it would remedy the issue with a software update. The FSD Beta 10.10 release notes are as follows:
– Smoother fork maneuvers and turn-lane selection using high fidelity trajectory primitives.
– Disabled rolling-stop functionality in all FSD Profiles. This behavior used to allow the vehicle to roll through all-way-stop intersections, but only when several conditions were met, including: vehicle speed less than 5.6 mph, no relevant objects/pedestrians/bicyclists detected, sufficient visibility and all entering roads at the intersection have speed limits below 30 mph.
– Improved generalized static object network by 4% using improved ground truth trajectories.
– Improved smoothness when stopping for crossing objects at intersections by modeling soft and hard constraints to better represent urgency of the slowdown.
– Enabled lane changing into an oncoming lane to maneuver around static obstacles, when safe to do so.
– Improved smoothness for merge handling by enforcing more consistency with previous cycle’s speed control decisions.
– Improved handling of flashing red light traffic controls by adding more caution for events where crossing vehicles may not stop.
– Improved right of way understanding at intersections with better modeling of intersection extents.
The Full Self-Driving Beta’s “rolling stop” feature was designed to allow vehicles to travel through an all-way-stop intersection while maintaining speeds between 0.1 and 5.6 MPH. According to the NHTSA’s Safety Recall Report, Tesla met with the NHTSA met on January 19 to discuss the “rolling stop” feature and all of its related details. Tesla made the voluntary decision to disable the feature on January 20, 2022. The NHTSA stated that its main concern was “Entering an all-way-stop intersection without coming to a complete stop may increase the risk of collision.” Additionally, the agency said that “Tesla is not aware of any collisions, injuries or fatalities related to this condition.”
Tesla recently stated that its Beta program had exceeded 60,000 vehicles.
Check out the first videos of the new FSD Beta Version 10.10 update below, courtesy of owner James Locke.
Update 2:43 PM 2/7/2022: Second paragraph revised for accuracy. NHTSA definition of “recall” includes issues that could be remedied by software updates.

News
Tesla Cybercab spotted with interesting charging solution, stimulating discussion
The port is located in the rear of the vehicle and features a manual door and latch for plug-in, and the video shows an employee connecting to a Tesla Supercharger.
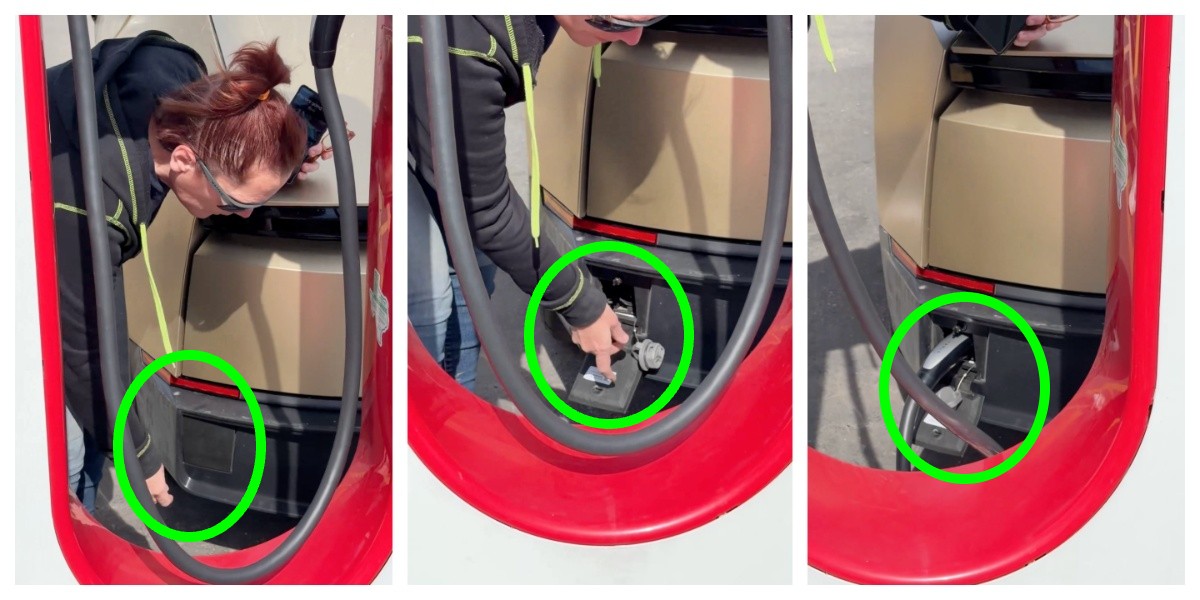
Tesla Cybercab units are being tested publicly on roads throughout various areas of the United States, and a recent sighting of the vehicle’s charging port has certainly stimulated some discussions throughout the community.
The Cybercab is geared toward being a fully-autonomous vehicle, void of a steering wheel or pedals, only operating with the use of the Full Self-Driving suite. Everything from the driving itself to the charging to the cleaning is intended to be operated autonomously.
But a recent sighting of the vehicle has incited some speculation as to whether the vehicle might have some manual features, which would make sense, but let’s take a look:
🚨 Tesla Cybercab charging port is in the rear of the vehicle!
Here’s a great look at plugging it in!!
— TESLARATI (@Teslarati) January 29, 2026
The port is located in the rear of the vehicle and features a manual door and latch for plug-in, and the video shows an employee connecting to a Tesla Supercharger.
Now, it is important to remember these are prototype vehicles, and not the final product. Additionally, Tesla has said it plans to introduce wireless induction charging in the future, but it is not currently available, so these units need to have some ability to charge.
However, there are some arguments for a charging system like this, especially as the operation of the Cybercab begins after production starts, which is scheduled for April.
Wireless for Operation, Wired for Downtime
It seems ideal to use induction charging when the Cybercab is in operation. As it is for most Tesla owners taking roadtrips, Supercharging stops are only a few minutes long for the most part.
The Cybercab would benefit from more frequent Supercharging stops in between rides while it is operating a ride-sharing program.
Tesla wireless charging patent revealed ahead of Robotaxi unveiling event
However, when the vehicle rolls back to its hub for cleaning and maintenance, standard charging, where it is plugged into a charger of some kind, seems more ideal.
In the 45-minutes that the car is being cleaned and is having maintenance, it could be fully charged and ready for another full shift of rides, grabbing a few miles of range with induction charging when it’s out and about.
Induction Charging Challenges
Induction charging is still something that presents many challenges for companies that use it for anything, including things as trivial as charging cell phones.
While it is convenient, a lot of the charge is lost during heat transfer, which is something that is common with wireless charging solutions. Even in Teslas, the wireless charging mat present in its vehicles has been a common complaint among owners, so much so that the company recently included a feature to turn them off.
Production Timing and Potential Challenges
With Tesla planning to begin Cybercab production in April, the real challenge with the induction charging is whether the company can develop an effective wireless apparatus in that short time frame.
It has been in development for several years, but solving the issue with heat and energy loss is something that is not an easy task.
In the short-term, Tesla could utilize this port for normal Supercharging operation on the Cybercab. Eventually, it could be phased out as induction charging proves to be a more effective and convenient option.
News
Tesla confirms that it finally solved its 4680 battery’s dry cathode process
The suggests the company has finally resolved one of the most challenging aspects of its next-generation battery cells.
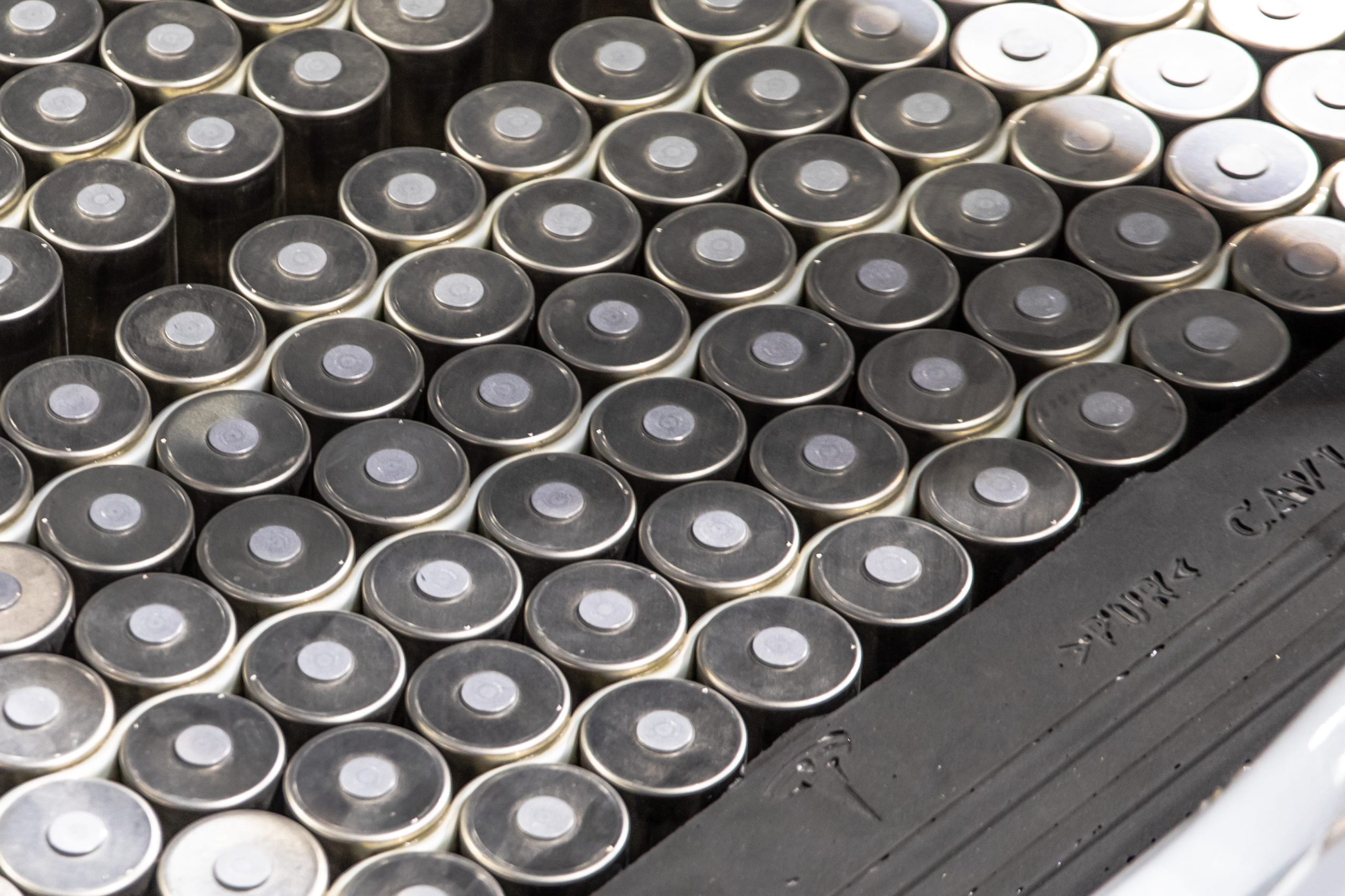

Tesla has confirmed that it is now producing both the anode and cathode of its 4680 battery cells using a dry-electrode process, marking a key breakthrough in a technology the company has been working to industrialize for years.
The update, disclosed in Tesla’s Q4 and FY 2025 update letter, suggests the company has finally resolved one of the most challenging aspects of its next-generation battery cells.
Dry cathode 4680 cells
In its Q4 and FY 2025 update letter, Tesla stated that it is now producing 4680 cells whose anode and cathode were produced during the dry electrode process. The confirmation addresses long-standing questions around whether Tesla could bring its dry cathode process into sustained production.
The disclosure was highlighted on X by Bonne Eggleston, Tesla’s Vice President of 4680 batteries, who wrote that “both electrodes use our dry process.”
Tesla first introduced the dry-electrode concept during its Battery Day presentation in 2020, pitching it as a way to simplify production, reduce factory footprint, lower costs, and improve energy density. While Tesla has been producing 4680 cells for some time, the company had previously relied on more conventional approaches for parts of the process, leading to questions about whether a full dry-electrode process could even be achieved.
4680 packs for Model Y
Tesla also revealed in its Q4 and FY 2025 Update Letter that it has begun producing battery packs for certain Model Y vehicles using its in-house 4680 cells. As per Tesla:
“We have begun to produce battery packs for certain Model Ys with our 4680 cells, unlocking an additional vector of supply to help navigate increasingly complex supply chain challenges caused by trade barriers and tariff risks.”
The timing is notable. With Tesla preparing to wind down Model S and Model X production, the Model Y and Model 3 are expected to account for an even larger share of the company’s vehicle output. Ensuring that the Model Y can be equipped with domestically produced 4680 battery packs gives Tesla greater flexibility to maintain production volumes in the United States, even as global battery supply chains face increasing complexity.
Elon Musk
Tesla Giga Texas to feature massive Optimus V4 production line
This suggests that while the first Optimus line will be set up in the Fremont Factory, the real ramp of Optimus’ production will happen in Giga Texas.
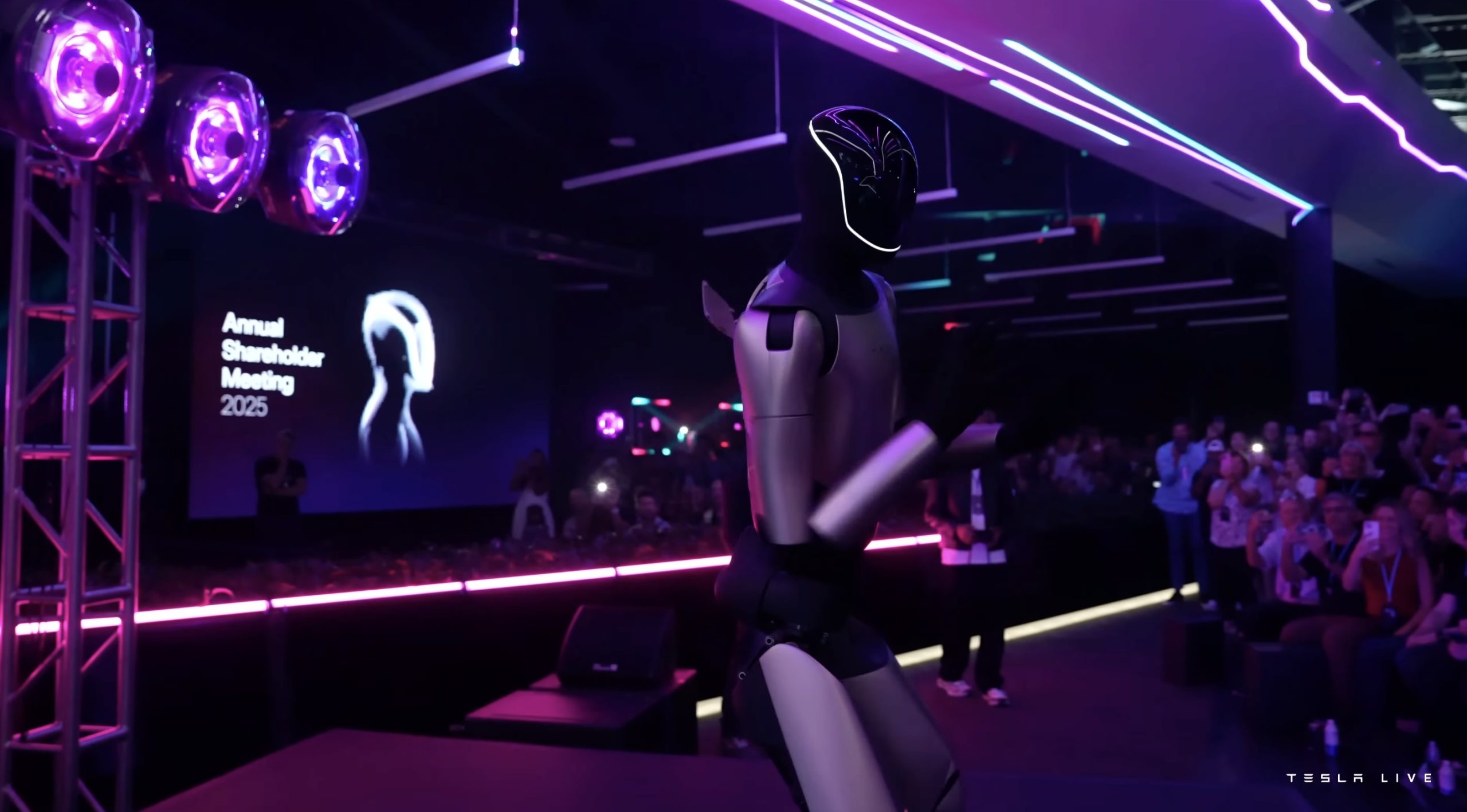

Tesla will build Optimus 4 in Giga Texas, and its production line will be massive. This was, at least, as per recent comments by CEO Elon Musk on social media platform X.
Optimus 4 production
In response to a post on X which expressed surprise that Optimus will be produced in California, Musk stated that “Optimus 4 will be built in Texas at much higher volume.” This suggests that while the first Optimus line will be set up in the Fremont Factory, and while the line itself will be capable of producing 1 million humanoid robots per year, the real ramp of Optimus’ production will happen in Giga Texas.
This was not the first time that Elon Musk shared his plans for Optimus’ production at Gigafactory Texas. During the 2025 Annual Shareholder Meeting, he stated that Giga Texas’ Optimus line will produce 10 million units of the humanoid robot per year. He did not, however, state at the time that Giga Texas would produce Optimus V4.
“So we’re going to launch on the fastest production ramp of any product of any large complex manufactured product ever, starting with building a one-million-unit production line in Fremont. And that’s Line one. And then a ten million unit per year production line here,” Musk stated.
How big Optimus could become
During Tesla’s Q4 and FY 2025 earnings call, Musk offered additional context on the potential of Optimus. While he stated that the ramp of Optimus’ production will be deliberate at first, the humanoid robot itself will have the potential to change the world.
“Optimus really will be a general-purpose robot that can learn by observing human behavior. You can demonstrate a task or verbally describe a task or show it a task. Even show it a video, it will be able to do that task. It’s going to be a very capable robot. I think long-term Optimus will have a very significant impact on the US GDP.
“It will actually move the needle on US GDP significantly. In conclusion, there are still many who doubt our ambitions for creating amazing abundance. We are confident it can be done, and we are making the right moves technologically to ensure that it does. Tesla, Inc. has never been a company to shy away from solving the hardest problems,” Musk stated.








