Investor's Corner
Why Tesla Autopilot will ultimately prove the self-driving industry leader
Tesla took an early lead in the race to develop vehicle autonomy, and its Autopilot system remains the state of the art. However, the technology is advancing more slowly than the company predicted – Elon Musk promised a coast-to-coast driverless demo run for 2018, and we’re still waiting. Meanwhile, competitors are hard at work on their own autonomy tech – GM’s Super Cruise, is now available on the CT6 luxury sedan.
Is Tesla in danger of falling behind in the self-driving race? Trent Eady, writing in Medium, takes a detailed look at the company’s Autopilot technology, and argues that the California automaker will continue to set the pace.
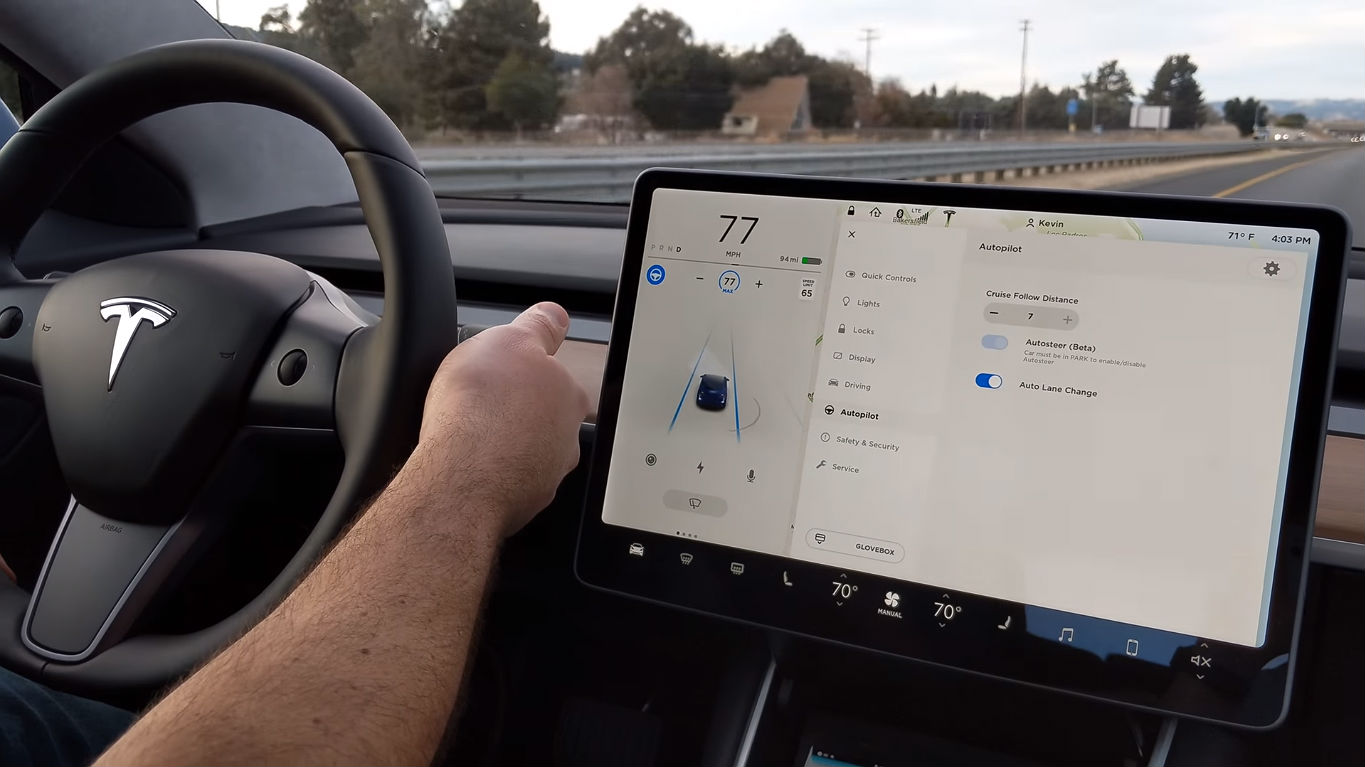
Every Tesla vehicle produced since October 2016 is equipped with a hardware suite designed for Full Self-Driving, including cameras, radar, ultrasonic sensors and an upgradable onboard computer. Around 150,000 of these “Hardware 2” Teslas are currently on the road, and could theoretically be upgraded to self-driving vehicles via an over-the-air software update.
Above: In its current state, Tesla’s Autopilot requires a hands-on approach (Youtube: Tesla)
Tesla disagrees with most of the other players in the self-driving game on the subject of Lidar, a technology that calculates distances using pulses of infrared laser light. Waymo, Uber and others seem to regard lidar as a necessary component of any self-driving system. However, Tesla’s Hardware 2 sensor suite doesn’t include it, instead relying on radar and optical cameras.
Lidar’s strength is its high spatial precision – it can measure distances much more precisely than current camera technology can (Eady believes that better software could enable cameras to close the gap). Lidar’s weakness is that it functions poorly in bad weather. Heavy rain, snow or fog causes lidar’s laser pulses to refract and scatter. Radar works much better in challenging weather conditions.
According to Eady, the reason that Tesla eschews lidar may be the cost: “Autonomy-grade lidar is prohibitively expensive, so it’s not possible for Tesla to include it in its production cars. As far as I’m aware, no affordable autonomy-grade lidar product has yet been announced. It looks like that is still years away.”
If Elon Musk and his autonomy team are convinced that lidar isn’t necessary, why does everyone else seem so sure that it is? “Lidar has accrued an aura of magic in the popular imagination,” opines Mr. Eady. “It is easier to swallow the new and hard-to-believe idea of self-driving cars if you tell the story that they are largely enabled by a cool, futuristic laser technology…It is harder to swallow the idea that if you plug some regular ol’ cameras into a bunch of deep neural networks, somehow that makes a car capable of driving itself through complicated city streets.”
Those deep neural networks are the real reason that Eady believes Tesla will stay ahead of its competitors in the autonomy field. The flood of data that Tesla is gathering through the sensors of the 150,000 or so existing Hardware 2 vehicles “offers a scale of real-world testing and training that is new in the history of computer science.”
Competitor Waymo has a computer simulation that contains 25,000 virtual cars, and generates data from 8 million miles of simulated driving per day. Tesla’s real-world data is of course vastly more valuable than any simulation data could ever be, and the company uses it to feed deep neural networks, allowing it to continuously improve Autopilot’s capabilities.
A deep neural network is a type of computing system that’s loosely based on the way the human brain is organized (sounds like the kind of AI that Elon Musk is worried about, but we’ll have to trust that Tesla has this under control). Deep neural networks are good at modeling complex non-linear relationships. The more data that’s available to train the network, the better its performance will be.
“Deep neural networks started to gain popularity in 2012, after a deep neural network won the ImageNet Challenge, a computer vision contest focused on image classification,” Eady explains. “For the first time in 2015, a deep neural network slightly outperformed the human benchmark for the ImageNet Challenge…The fact that computers can outperform humans on even some visual tasks is exciting for anyone who wants computers to do things better than humans can. Things like driving.”
By the way, who was the human benchmark who was bested by a machine in the ImageNet Challenge? Andrej Karpathy, who is now Director of AI at Tesla.
===
Note: Article originally published on evannex.com by Charles Morris; Source: Medium

Elon Musk
Tesla to a $100T market cap? Elon Musk’s response may shock you

There are a lot of Tesla bulls out there who have astronomical expectations for the company, especially as its arm of reach has gone well past automotive and energy and entered artificial intelligence and robotics.
However, some of the most bullish Tesla investors believe the company could become worth $100 trillion, and CEO Elon Musk does not believe that number is completely out of the question, even if it sounds almost ridiculous.
To put that number into perspective, the top ten most valuable companies in the world — NVIDIA, Apple, Alphabet, Microsoft, Amazon, TSMC, Meta, Saudi Aramco, Broadcom, and Tesla — are worth roughly $26 trillion.
Will Tesla join the fold? Predicting a triple merger with SpaceX and xAI
Cathie Wood of ARK Invest believes the number is reasonable considering Tesla’s long-reaching industry ambitions:
“…in the world of AI, what do you have to have to win? You have to have proprietary data, and think about all the proprietary data he has, different kinds of proprietary data. Tesla, the language of the road; Neuralink, multiomics data; nobody else has that data. X, nobody else has that data either. I could see $100 trillion. I think it’s going to happen because of convergence. I think Tesla is the leading candidate [for $100 trillion] for the reason I just said.”
Musk said late last year that all of his companies seem to be “heading toward convergence,” and it’s started to come to fruition. Tesla invested in xAI, as revealed in its Q4 Earnings Shareholder Deck, and SpaceX recently acquired xAI, marking the first step in the potential for a massive umbrella of companies under Musk’s watch.
SpaceX officially acquires xAI, merging rockets with AI expertise
Now that it is happening, it seems Musk is even more enthusiastic about a massive valuation that would swell to nearly four-times the value of the top ten most valuable companies in the world currently, as he said on X, the idea of a $100 trillion valuation is “not impossible.”
It’s not impossible
— Elon Musk (@elonmusk) February 6, 2026
Tesla is not just a car company. With its many projects, including the launch of Robotaxi, the progress of the Optimus robot, and its AI ambitions, it has the potential to continue gaining value at an accelerating rate.
Musk’s comments show his confidence in Tesla’s numerous projects, especially as some begin to mature and some head toward their initial stages.
Elon Musk
Tesla director pay lawsuit sees lawyer fees slashed by $100 million
The ruling leaves the case’s underlying settlement intact while significantly reducing what the plaintiffs’ attorneys will receive.

The Delaware Supreme Court has cut more than $100 million from a legal fee award tied to a shareholder lawsuit challenging compensation paid to Tesla directors between 2017 and 2020.
The ruling leaves the case’s underlying settlement intact while significantly reducing what the plaintiffs’ attorneys will receive.
Delaware Supreme Court trims legal fees
As noted in a Bloomberg Law report, the case targeted pay granted to Tesla directors, including CEO Elon Musk, Oracle founder Larry Ellison, Kimbal Musk, and Rupert Murdoch. The Delaware Chancery Court had awarded $176 million to the plaintiffs. Tesla’s board must also return stock options and forego years worth of pay.
As per Chief Justice Collins J. Seitz Jr. in an opinion for the Delaware Supreme Court’s full five-member panel, however, the decision of the Delaware Chancery Court to award $176 million to a pension fund’s law firm “erred by including in its financial benefit analysis the intrinsic value” of options being returned by Tesla’s board.
The justices then reduced the fee award from $176 million to $70.9 million. “As we measure it, $71 million reflects a reasonable fee for counsel’s efforts and does not result in a windfall,” Chief Justice Seitz wrote.
Other settlement terms still intact
The Supreme Court upheld the settlement itself, which requires Tesla’s board to return stock and options valued at up to $735 million and to forgo three years of additional compensation worth about $184 million.
Tesla argued during oral arguments that a fee award closer to $70 million would be appropriate. Interestingly enough, back in October, Justice Karen L. Valihura noted that the $176 award was $60 million more than the Delaware judiciary’s budget from the previous year. This was quite interesting as the case was “settled midstream.”
The lawsuit was brought by a pension fund on behalf of Tesla shareholders and focused exclusively on director pay during the 2017–2020 period. The case is separate from other high-profile compensation disputes involving Elon Musk.
Investor's Corner
Tesla (TSLA) Q4 and FY 2025 earnings call: The most important points
Executives, including CEO Elon Musk, discussed how the company is positioning itself for growth across vehicles, energy, AI, and robotics despite near-term pressures from tariffs, pricing, and macro conditions.

Tesla’s (NASDAQ:TSLA) Q4 and FY 2025 earnings call highlighted improving margins, record energy performance, expanding autonomy efforts, and a sharp acceleration in AI and robotics investments.
Executives, including CEO Elon Musk, discussed how the company is positioning itself for growth across vehicles, energy, AI, and robotics despite near-term pressures from tariffs, pricing, and macro conditions.
Key takeaways
Tesla reported sequential improvement in automotive gross margins excluding regulatory credits, rising from 15.4% to 17.9%, supported by favorable regional mix effects despite a 16% decline in deliveries. Total gross margin exceeded 20.1%, the highest level in more than two years, even with lower fixed-cost absorption and tariff impacts.
The energy business delivered standout results, with revenue reaching nearly $12.8 billion, up 26.6% year over year. Energy gross profit hit a new quarterly record, driven by strong global demand and high deployments of MegaPack and Powerwall across all regions, as noted in a report from The Motley Fool.
Tesla also stated that paid Full Self-Driving customers have climbed to nearly 1.1 million worldwide, with about 70% having purchased FSD outright. The company has now fully transitioned FSD to a subscription-based sales model, which should create a short-term margin headwind for automotive results.
Free cash flow totaled $1.4 billion for the quarter. Operating expenses rose by $500 million sequentially as well.
Production shifts, robotics, and AI investment
Musk further confirmed that Model S and Model X production is expected to wind down next quarter, and plans are underway to convert Fremont’s S/X line into an Optimus robot factory with a capacity of one million units.
Tesla’s Robotaxi fleet has surpassed 500 vehicles, operating across the Bay Area and Austin, with Musk noting a rapid monthly expansion pace. He also reiterated that CyberCab production is expected to begin in April, following a slow initial S-curve ramp before scaling beyond other vehicle programs.
Looking ahead, Tesla expects its capital expenditures to exceed $20 billion next year, thanks to the company’s operations across its six factories, the expansion of its fleet expansion, and the ramp of its AI compute. Additional investments in AI chips, compute infrastructure, and future in-house semiconductor manufacturing were discussed but are not included in the company’s current CapEx guidance.
More importantly, Tesla ended the year with a larger backlog than in recent years. This is supported by record deliveries in smaller international markets and stronger demand across APAC and EMEA. Energy backlog remains strong globally as well, though Tesla cautioned that margin pressure could emerge from competition, policy uncertainty, and tariffs.








