SpaceX
SpaceX goes all-in on steel Starship, scraps expensive carbon fiber BFR tooling
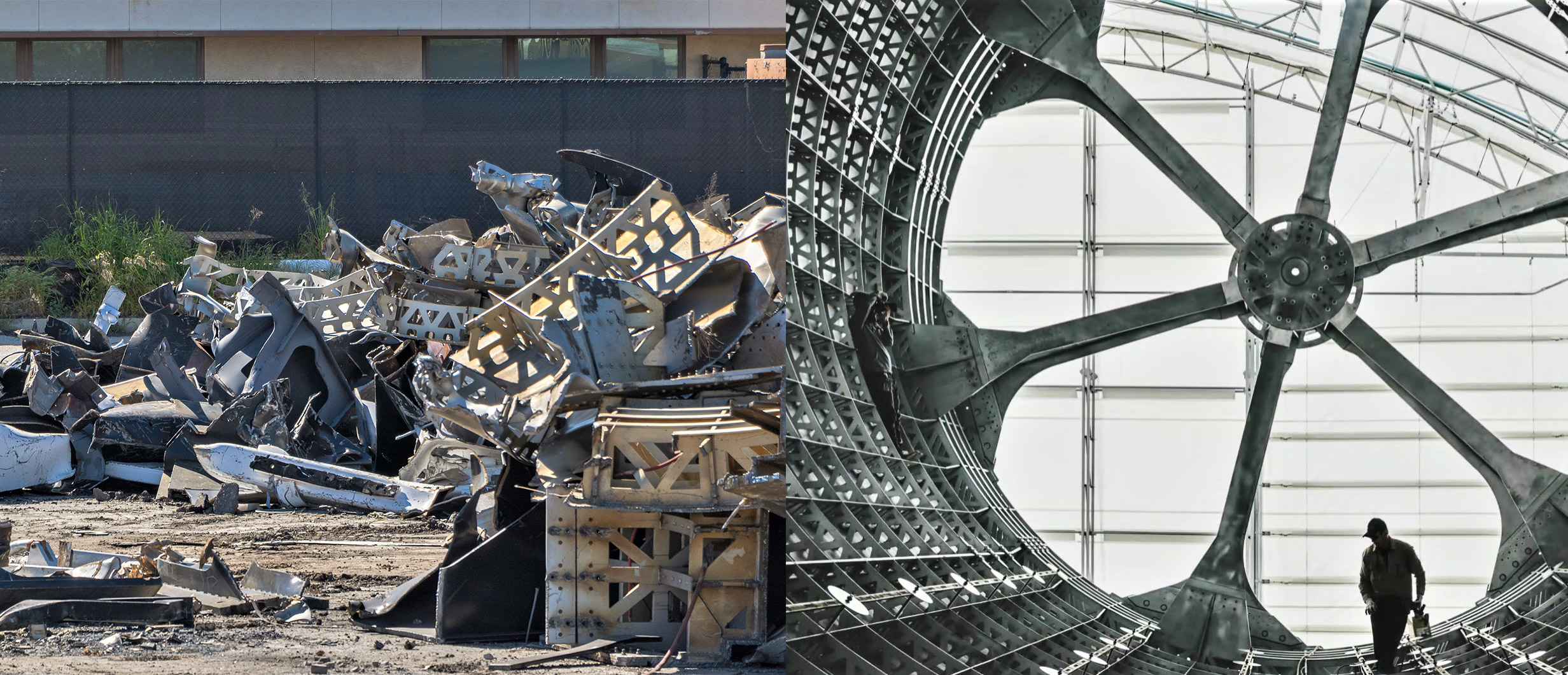
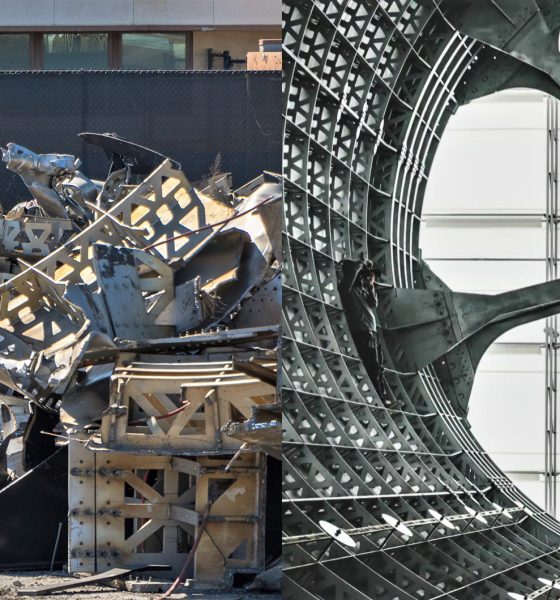
In a wholly unforeseen turn of events, SpaceX has taken the extraordinary step of permanently scrapping both its Port of Los Angeles-based BFR development tent and what seem to be the majority of what it contained, irreparably destroying custom-built tooling meant to support the fabrication of carbon composite BFR spaceships and boosters.
Likely worth anywhere from several to tens of millions of dollars (USD), SpaceX’s advanced BFR production tools were procured from industry-expert Ascent Aerospace sometime in 2017 before being officially delivered to the rocket company’s newly-erected Port of LA tent around April 2018. Situated at the port specifically due to logistical concerns about the high cost of transporting 9m/30ft-diameter objects from SpaceX’s main Hawthorne facilities to a barge for transport east, the company has decided to unequivocally destroy its aerospace-grade composite tooling less than 12 months after accepting delivery. Put simply, this is the best evidence yet that SpaceX – willing or not – has gone all-in on build Starship and Super Heavy out of stainless steel less than six months after CEO Elon Musk began to hint at the program’s utterly radical pivot.

From the very beginning of SpaceX and Elon Musk’s serious pursuit of an entirely reusable launch vehicle capable of transporting dozens of astronauts and passengers to and from Earth and Mars, the plan had been to build the vast majority of the rocket’s booster and spacecraft structures out of advanced carbon fiber composite materials. Above all else, this fundamental architecture was motivated largely by the significant performance gains a rocket could achieve by replacing traditional aluminum tanks and structures with carbon fiber.
For a rocket (and especially an orbital spaceship) meant to somehow make Earth-Mars transport both routine and at least minutely affordable, focusing primarily on the optimization of the mass of cargo delivered relative to the empty weight of the spaceship and booster made (and still does make) a great deal of sense. Assuming that the reusability of a system is roughly constant, the only conceivable way to further lower the cost of price per unit of cargo or passenger ticket would be to increase the usable cargo/passenger capacity for each individual launch, making an extremely light and high-performance rocket the low-hanging fruit target.


The centrality of carbon fiber composites remained with SpaceX’s Sept. 2017 iteration of BFR, downsized by 25% to a diameter of 9m (~30 ft). Around six months later, that commitment to composites was further solidified by the delivery of the first 9m-diameter carbon fiber tooling in March or April 2018. The tooling used to mold and
In the subsequent months of 2018, SpaceX’s BFR and composite R&D team spent tens of thousands of hours building out an ad-hoc advanced composites workshop inside a temporary tent in an industrial area, and ultimately managed to build a number of full-scale carbon fiber segments, including at least one large tank barrel section and the beginnings of a tank dome. In September 2018, that progress was partially revealed alongside the announcement that Japanese billionaire Yasuka Maezawa had purchased the first crewed lunar launch of BFR for several hundred million dollars, set to occur no earlier than 2023.
Two months after indicating that the first BFR “airframe/tank barrel section” would be built out of a “new carbon fiber material”, Musk provided the very first teaser for a “counterintuitive” development that would later be identified as the CEO’s decision to wholly replace BFR’s proposed used of composites with stainless steel and an advanced metallic heat shield. Still more than a little controversial and hard to follow almost half a year later, the feeling at the time was that SpaceX’s eccentric leader had decided to throw away more than 24 months of composite BFR design and development work for an almost entirely unproven alternative approach.
For better or for worse, it appears that SpaceX (or maybe just Musk) has quite literally trashed the most concrete demonstration of a prior commitment to advanced carbon fiber composites, scrapping the vast majority of its composite tooling and perhaps even the prototype BFR segments built in 2018.


It remains to be seen whether the now-permanent decision to pursue a stainless steel design in place of carbon fiber was a very expensive mistake, a stroke of genius, or something in between, However, the undeniably brisk progress made with the BFR’s steel variant in last four or so months bodes well – at a minimum – for Musk’s optimism that this radical change will ultimately result in an operational vehicle far sooner (and presumably cheaper) than the composites route.
Generally speaking, it seems safe to – on the face of it – agree with Musk’s argument that steel should ultimately lend itself far more easily to reusability thanks to its high tolerance for extreme temperatures. Unlike Falcon 9’s aluminum structures (and even the most exotic, advanced carbon fiber composites), certain varieties of stainless steel can weather heating approaching that experienced during orbital reentry with minimal erosion or damage to its mechanical properties. As Musk puts it, the Super Heavy booster’s suborbital trajectory could require almost no heat shielding – and perhaps even paint – at all.
Only time will tell whether the inevitably harsher realities of real-life engineering are so kind. In the meantime, SpaceX is perhaps just hours away from the first attempted static-fire test of a Raptor installed on something approaching flight-hardware, in this case a full-scale Starship hop test prototype.
Check out Teslarati’s Marketplace! We offer Tesla accessories, including for the Tesla Cybertruck and Tesla Model 3.

Elon Musk
SpaceX targets 150Mbps per user for upgraded Starlink Direct-to-Cell
If achieved, the 150Mbps goal would represent a significant jump from the current performance of Starlink Direct-to-Cell.

SpaceX is targeting peak download speeds of 150Mbps per user for its next-generation Direct-to-Cell Starlink service. The update was shared by SpaceX Spectrum & Regulatory Affairs Lead Udrivolf Pica during the International Telecommunication Union’s Space Connect conference.
“We are aiming at peak speeds of 150Mbps per user,” Pica said during the conference. “So something incredible if you think about the link budgets from space to the mobile phone.”
If achieved, the 150Mbps goal would represent a significant jump from the current performance of Starlink Direct-to-Cell.
Today, SpaceX’s cellular Starlink service, offered in partnership with T-Mobile under the T-Satellite brand, provides speeds of roughly 4Mbps per user. The service is designed primarily for texts, low-resolution video calls, and select apps in locations that traditionally have no cellular service.
By comparison, Ookla data shows median 5G download speeds of approximately 309Mbps for T-Mobile and 172Mbps for AT&T in the United States, as noted in a PCMag report. While 150Mbps would still trail the fastest terrestrial 5G networks, it would place satellite-to-phone broadband much closer to conventional carrier performance, even in remote areas.
Pica indicated that the upgraded system would support “video, voice, and data services, clearly,” moving beyond emergency connectivity and basic messaging use cases.
To reach that target, SpaceX plans to upgrade its existing Starlink Direct-to-Cell satellites and add significant new capacity. The company recently acquired access to radio spectrum from EchoStar, which Pica described as key to expanding throughput.
“More spectrum means a bigger pipeline, and this means that we can expand what we can do with partners. We can expand the quality of service. And again, we can do cellular broadband basically, cellular broadband use cases, like AI or daily connectivity needs,” he stated.
SpaceX has also requested regulatory approval to deploy 15,000 additional Direct-to-Cell satellites, beyond the roughly 650 currently supporting the system. The upgraded architecture is expected to begin rolling out in late 2027.
Elon Musk
Microsoft partners with Starlink to expand rural internet access worldwide
The update was shared ahead of Mobile World Congress.

Microsoft has announced a new collaboration with Starlink as part of its expanding digital access strategy, following the company’s claim that it has extended internet connectivity coverage to more than 299 million people worldwide.
The update was shared ahead of Mobile World Congress, where Microsoft detailed how it surpassed its original goal of bringing internet access to 250 million people by the end of 2025.
In a blog post, Microsoft confirmed that it is now working with Starlink to expand connectivity in rural and hard-to-reach regions.
“Through our collaboration with Starlink, Microsoft is combining low-Earth orbit satellite connectivity with community-based deployment models and local ecosystem partnerships,” the company wrote.
The partnership is designed to complement Microsoft’s existing work with local internet providers and infrastructure companies across Africa, Latin America, and India, among other areas. Microsoft noted that traditional infrastructure alone cannot meet demand in some regions, making low-Earth orbit satellite connectivity an important addition.
Kenya was cited as an early example. Working with Starlink and local provider Mawingu Networks, Microsoft is supporting connectivity for 450 community hubs in rural and underserved areas. These hubs include farmer cooperatives, aggregation centers, and digital access facilities intended to support agricultural productivity and AI-enabled services.
Microsoft stated that 2.2 billion people globally remain offline, and that connectivity gaps risk widening as AI adoption accelerates.
Starlink’s expanding constellation, now numbering more than 9,700 satellites in orbit, provides near-global coverage, making it one of the few systems capable of delivering broadband to remote regions without relying on terrestrial infrastructure.
Starlink is expected to grow even more in the coming years as well, especially as SpaceX transitions its fleet to Starship, which is capable of carrying significantly larger payloads compared to its current workhorse, the Falcon 9.
Elon Musk
Elon Musk denies Starlink’s price cuts are due to Amazon Kuiper
“This has nothing to do with Kuiper, we’re just trying to make Starlink more affordable to a broader audience,” Musk wrote in a post on X.

Elon Musk has pushed back on claims that Starlink’s recent price reductions are tied to Amazon’s Kuiper project.
In a post on X, Musk responded directly to a report suggesting that Starlink was cutting prices and offering free hardware to partners ahead of a planned IPO and increased competition from Kuiper.
“This has nothing to do with Kuiper, we’re just trying to make Starlink more affordable to a broader audience,” Musk wrote in a post on X. “The lower the cost, the more Starlink can be used by people who don’t have much money, especially in the developing world.”
The speculation originated from a post summarizing a report from The Information, which ran with the headline “SpaceX’s Starlink Makes Land Grab as Amazon Threat Looms.” The report stated that SpaceX is aggressively cutting prices and giving free hardware to distribution partners, which was interpreted as a reaction to Amazon’s Kuiper’s upcoming rollout and possible IPO.
In a way, Musk’s comments could be quite accurate considering Starlink’s current scale. The constellation currently has more than 9,700 satellites in operation today, making it by far the largest satellite broadband network in operation. It has also managed to grow its user base to 10 million active customers across more than 150 countries worldwide.
Amazon’s Kuiper, by comparison, has launched approximately 211 satellites to date, as per data from SatelliteMap.Space, some of which were launched by SpaceX’s Falcon 9 rocket. Starlink surpassed that number in early January 2020, during the early buildout of its first-generation network.
Lower pricing also aligns with Starlink’s broader expansion strategy. SpaceX continues to deploy satellites at a rapid pace using Falcon 9, and future launches aboard Starship are expected to significantly accelerate the constellation’s growth. A larger network improves capacity and global coverage, which can support a broader customer base.
In that context, price reductions can be viewed as a way to match expanding supply with growing demand. Musk’s companies have historically used aggressive pricing strategies to drive adoption at scale, particularly when vertical integration allows costs to decline over time.








