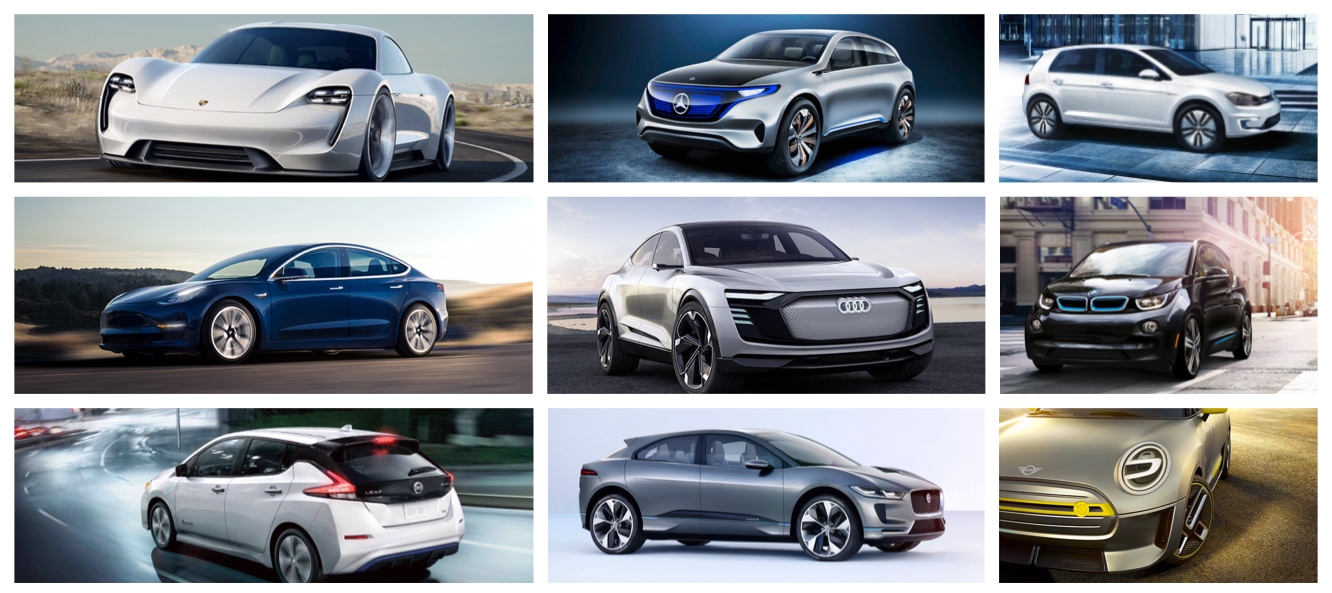

News
Automakers come to accept that the EV revolution has begun
The last several months have been busy in the electric vehicle revolution. Governments have been announcing their phase out plans for petrol vehicles and automakers have committed billions of dollars to electrification programs. At this point automakers are practically falling over each other racing to get out their announcements. How many electric vehicles they’re developing, how much they’re investing, are they going fully electrified, and when. Suddenly no one wants to be perceived as falling behind in this revolution. And why should they? Nokia and Blackberry can attest to what happens if you do.
In the past, established automakers have been very cautious with electrification, with many simply watching to see how the situation developed. Generally, their investments could be best described as vague or immaterial to their core business of making cars. That’s clearly changed – take a look at the timeline of announcements below.
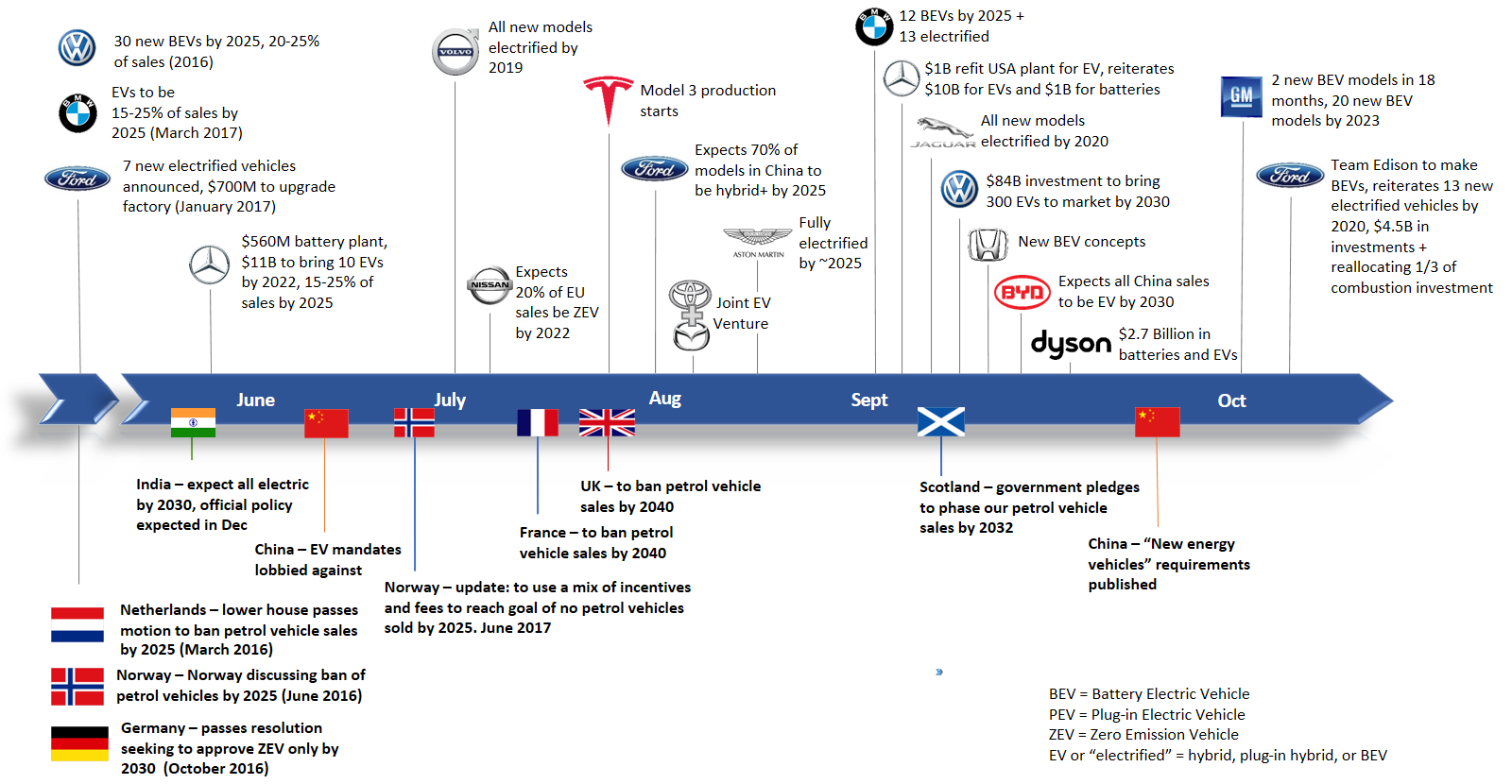
Taken as a whole these announcements are really quite striking. Most recently it was GM and Ford that released their competing declarations of electrification. GM with twenty new fully electric vehicles by 2023 and Ford quickly following up to say they had a new dedicated team for fully electric vehicles, while reiterating their previously committed $4.5 billion in investments for 13 new electrified vehicle options. Ford followed up the next day to say they were also diverting one third of their investments from combustion vehicle development.
The month prior was filled with even more announcements, including tweets between Elon Musk and Mercedes about the size of the latter’s investments. Volkswagen, BMW, Mercedes, Jaguar, Honda, BYD, and Dyson all made significant announcements about their EV programs that month, but it was Volvo’s “fully electrified” announcement that first caught the media’s attention back in July. It was a clever, if somewhat misleading PR move, but it did set important targets for their company and the competition. The fact that Tesla started producing their mass market Model 3 was almost lost amongst all this news. That’s an exaggeration of course, but only a year ago many believed their plans were impossible.
Government announcements have been another important part of the narrative, with targets that provide direction and impetus to the industry. Based on some of the lobbying it hasn’t been entirely welcome, but that’s to be expected. Anytime an entire country is talking about completely phasing out your current business model, it’s going give an industry pause. In this case there were multiple, with China, the UK, France, India, and several others weighing in with their plans to phase out combustion vehicles.
Looking at these announcements together suggests that a new phase in the electric vehicle revolution has begun. The fundamentals behind this shift are what I will argue here. My proposition is that the combined macro-economic drivers of regulation, competition, and market growth are pushing EVs to the mainstream. Be forewarned, it’s a long post, but analyzing any of these factors in isolation loses the bigger picture. Electric vehicles are coming, of that there can be no doubt.
Regulation, competition, and market growth.
You’ll notice the analysis below centers around plug-in electric vehicles (PEVs). Today a little more than 60% of new EV sales are pure battery electric vehicles (BEVs) and the rest are plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs). PHEV’s are a transitionary technology, which currently offer some benefits that will disappear as battery costs continue to fall and range continues to increase. Note that the analysis doesn’t include hybrids without plugs, they’re old news. Also note that in talking about vehicles and vehicle sales, these are always in reference to passenger vehicles (i.e. no freight trucks). Annual passenger vehicles sales data was taken from the International Organization of Motor Vehicle Manufacturers and electric sales information is from the International Energy Agency.
Regulation:
The 2015 Paris climate agreement requires country specific greenhouse gas reductions by 2030 or sooner. As part of the agreement countries must also submit annual reports on their progress. Transport is a key part of each country’s emissions and it’s one that has a solution at hand, hence the plans to phase out combustion vehicles. France and UK announced for bans by 2040, Scotland by 2032, Netherlands 2025, Norway 2025, and India and China in development. There’s some subtlety to each. Norway for example is leaning towards economic levers to achieve their goals in lieu of outright restrictions, while India has said they expect all vehicles to be electric by 2030 without regulation being necessary, though their official policy is expected later this year.
Personally I tend to agree. I expect we will all be buying electric vehicles long before 2040 largely due to economics, especially with carbon pricing. That said, all of the government announcements are important. They provide both the public and automakers a framework in which to operate, while the more aggressive targets are actually moving the industry forward.
California and nine east coast states have long mandated a portion of sales be zero emission vehicles (ZEVs), administered through a credit system. The system gives partial credit to plug-in electric vehicles (PEVs) and more credits to long range zero emission vehicles (ZEVs). It’s basically the reason automakers have produced ZEVs in the USA. In quite possibly the biggest announcement of the year China is now doing something similar. They’ve mandated a ‘new energy vehicle’ credit requirement of 10% of sales in 2019 and 12% in 2020. Since one EV can be responsible for multiple credits it means that less than 12% of all vehicles sold will be required to be zero emission vehicles. For example, if the requirement was met with vehicles like the BMW i3, it would mean 4.6% of all vehicle sales in China would be ZEV in 2020, about 1.4 million that year. For reference there are about 2.5 million PEVs on the planet right now.
China is also looking at establishing a date for complete phase out of petrol vehicles, which has caught California’s attention. California is not eager to lose their leadership position in electric vehicles and is now looking to increase their own targets and establish their own timeline for complete phase out. I believe the quote from their governor was “Why haven’t we done something already?”. It seems that an EV target race has begun and that means mandated growth for the EV market.

source: BMW
Market Growth:
This one has always been a bit of ‘chicken or the egg’ scenario. Historically demand for electric vehicles was low, which automakers referenced as the reason for their limited offerings. Others argued that there could be no demand when so few options were available, especially when those that did exist had such weird aesthetics (which was an effective way to prevent scavenging from more profitable combustion sales). Tesla flipped this around with their preorders of the Model 3 and showed everyone the latent demand to the tune of nearly 400,000 preorders. Other automakers took notice. BMW even started having widespread video presentations depicting the threat of Tesla to motivate their employees.
If you’ve only heard the rhetoric of how electric vehicles constitute a small fraction of the world’s annual sales, you might have missed something important. Exponential growth. Since 2012 growth of plug-in electric vehicles has been over 40% every year. Cumulatively that means 10x more PEVs will be sold in 2017 than 2012, as shown in the graph below.
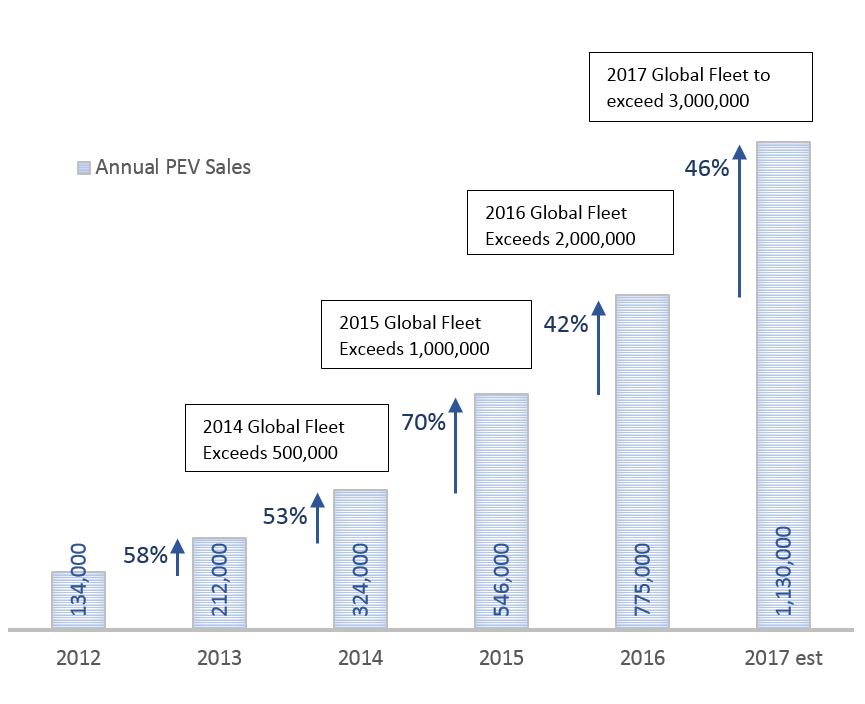
Historical data from the IEA, 2017 estimate from EVvolumes.com
Don’t get me wrong, the existing market share is almost laughably low at 1.1% worldwide (2016 data from the IEA), but over the last three years sales have grown at an average 54.6% compound annual growth rate (CAGR).
To illustrate the effect of exponential growth consider the following example about bacteria in a jar. If the number of bacteria doubles every minute and after 1 hour the jar is full of bacteria, that means at 59 minutes the jar is half-full, at 58 minutes ¼ full, at 57 minutes 1/8 full, etc. At 54 minutes that jar is only 1.6% full and everyone is thinking that bacterial will never fill the jar. It’s simplistic and exaggerated but that’s where we are today, at 54 minutes.
The example shows the power of exponential growth but also the challenge in forecasting it. Over the long term, small changes in annual growth rates can have big impacts. Solar power projections were notoriously underestimated and each year forecasts had to be revised upwards. That’s not to disparage the forecasters, it’s incredibly difficult to do what they do and certainly some caution in forecasting is warranted. But it is worth considering that electric vehicles may be in a similar situation. For example, Bloomberg New Energy Finance (BNEF) posted an EV outlook report in 2016, estimating that annual sales in 2040 would be 35% of all vehicles sold and the total PEV fleet would be 410 million. This year they revised those projections up, to 54% and 600 million. That’s 200 million more EVs, on a starting estimate of 410 million, after one year of new data. Will the next years’ forecasts also be revised upwards?
Shorter timeframes are usually more accurate, BNEF’s numbers indicate they expect approximately 2.5 million PEVs to be sold in 2020. That seems reasonable, but it would mean that PEV sales growth slows to 35% annually for the next few years. With more models coming that have better features and lower costs, and with governments now pushing the market with more aggressive targets, it seems unlikely growth will slow. So as an experiment what happens if the 54.6% growth rate over the last three years continues, to 2020 and 2025?
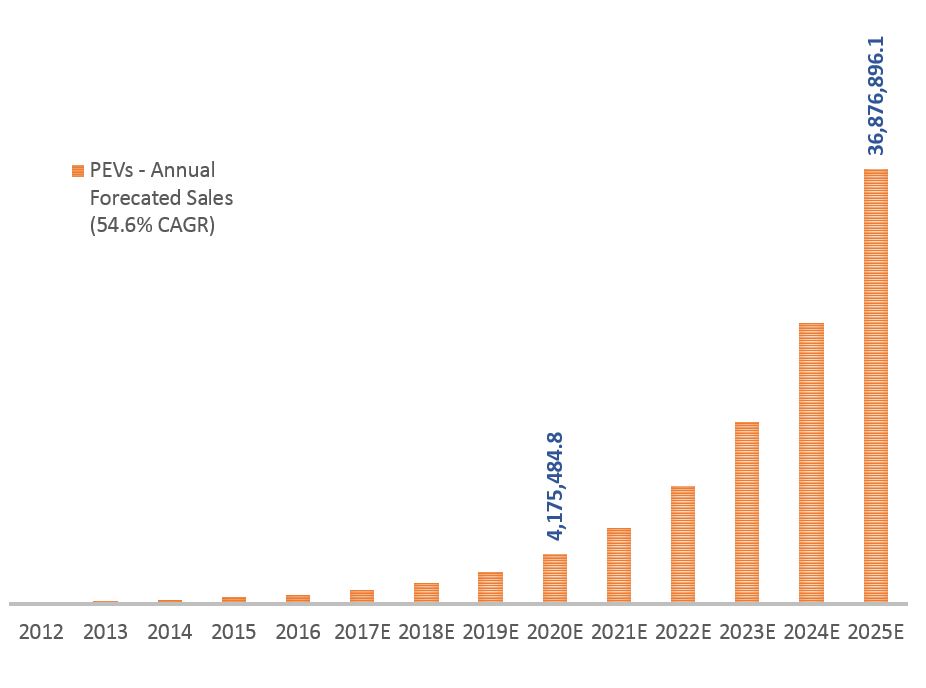 The impact would be impressive. The graph indicates that over 4 million PEVs would be sold in 2020, for 5% of total vehicle sales. That jumps to 37 million PEVs sold in 2025, nearly 40% of the total vehicle sales predicted. Contrast that with BNEF numbers, of 3% of sales in 2020 and 8% in 2025. Personally I think 8% is a low estimate for 2025, it works out to a compound annual growth rate of approximately 25%. Interestingly UBS increased their 2025 PEV estimate upwards by 50% this year (from 2016) to 14% of total sales – showing that short-term projections can be just as uncertain.
The impact would be impressive. The graph indicates that over 4 million PEVs would be sold in 2020, for 5% of total vehicle sales. That jumps to 37 million PEVs sold in 2025, nearly 40% of the total vehicle sales predicted. Contrast that with BNEF numbers, of 3% of sales in 2020 and 8% in 2025. Personally I think 8% is a low estimate for 2025, it works out to a compound annual growth rate of approximately 25%. Interestingly UBS increased their 2025 PEV estimate upwards by 50% this year (from 2016) to 14% of total sales – showing that short-term projections can be just as uncertain.
Perhaps 54.6% isn’t feasible, although Tesla has nearly managed it with a 47% growth rate since 2013. They did this while building up their staff, infrastructure, technology, and procedures virtually from scratch all at the same time. It’s also worth considering the history of smartphones. Globally smartphone sales grew at a rate of 46.4% year over year for ten years from 2004 to 2014, growing from sales of 27 million a year to over a billion. It was even more dramatic in China, where smartphone users accounted for about 5% of mobile subscribers in 2010 but were 70% by 2015 (Statista). That’s in just 5 years.
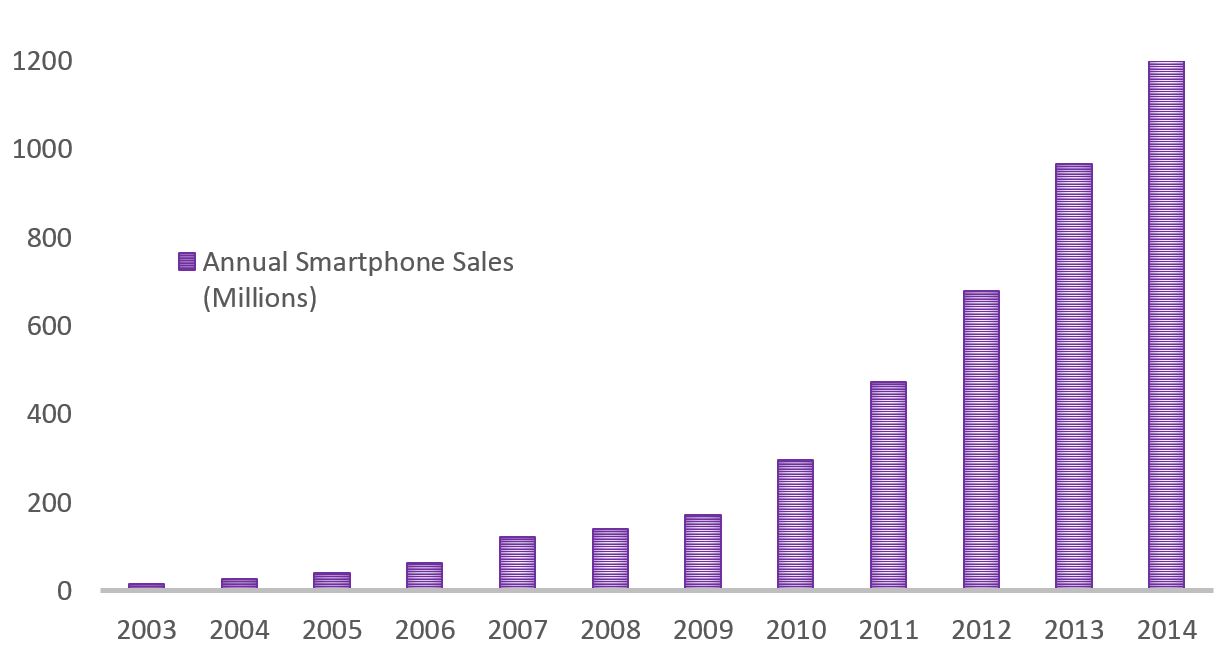
Data from www.gartner.com
Granted smartphones are not cars. The average smartphone costs orders or magnitude less and is traded in every two years, while the average car is traded in every 6.5 years (in the USA). A smartphone apparently has an average total lifespan of 4.7 years and a car can last to ~200,000 miles, approximately 15 years of average driving.
But electric cars do offer something cell phones never have. A lower cost. Cell phones provide a wealth of new functionality in our lives, but generally at a premium. Today, electric cars already cost less to operate than combustion vehicles, by 2018 they are expected to reach cost parity on total cost of ownership (UBS report), and by 2025 Bloomberg expects them to cost less upfront than combustion vehicles. That’s battery only electric vehicles (BEVs). Perhaps the changeover is longer than it was for cellphones, but once BEVs have an upfront cost less than petrol, why would anyone buy anything else?
Competition:
More and more manufacturers are entering the electric vehicle field with legitimate programs and their EVs are getting excellent reviews. At the end of 2016 the Chevy Bolt came out and won the North American and Motor Trend car of the year awards. Be prepared to see future EVs dominate the awards. VW already has a new e-Golf, Nissan a new Leaf, BMW an updated i3, Hyundai released their Ionic, and Audi, Porsche, and Jaguar are all coming out with pure EV models in 2018. Then there are the massive “electrification” shifts from the likes of Mercedes, BWM, Volvo, Austin Martin, VW, Ford, GM, and others. All now committing to reshaping their companies and the industry by moving to electric vehicles. There’s also that company Tesla which started making their game changing Model 3. Suddenly there’s a lot of competition and if your company isn’t one of those competing…. what are you doing? Those automakers on the sidelines are starting to look obsolete and it’s a short road from obsolete to ‘out of business’. 
With automakers and governments committing to electrification of vehicles, we are going to see a significant ramp up in the electric vehicle market. More plug-in options are coming out, billions are being invested, and governments are seriously planning the end of combustion vehicles. It really is a paradigm shift. In large part we have Tesla to thank. If they hadn’t shown the world what was possible, who knows when this would have happened. Certainly the future would be a bit darker.

News
Tesla loses Director who designed one of the company’s best features
Thomas Dmytryk, who has spent over 11 years with Tesla and helped to develop Over-the-Air updates and the company’s vehicles’ ability to utilize them to improve, has decided to leave.

Tesla has lost the director who designed one of the company’s best features: Over-the-Air updates.
Thomas Dmytryk, who has spent over 11 years with Tesla and helped to develop Over-the-Air updates and the company’s vehicles’ ability to utilize them to improve, has decided to leave. In a lengthy statement on LinkedIn, Dmytryk said that he’s “closing the book.” He had nothing but good things to say:
“After 11 incredible years at Tesla, I’m closing the book. It’s been the ride of a lifetime: always on the news, innovating relentlessly, constantly pushing the limits. Tesla is THE place for talented, passionate people. I feel insanely lucky to have been part in that culture for so long.”
It appears the intense lifestyle of developing and creating intensively for so long might have caught up to Dmytryk, who did not give his definitive plans for the future, and it appears he may be taking some time off before jumping into a new venture:
“The future? Extremely bright. Ambitions intact, just getting started as a transformative company that could elevate billions of lives. So why leave now?! Human life’s always been my North Star, right now I need to be with mines. I’ve always admired Tesla’s top leadership and vision. But what I’ve always found incredible is the tenacity, brilliance and devotion of people on the front line. YOU make Tesla unstoppable. I wish you all the best and of course EPIC wins.”
The move was first reported by NotaTeslaApp.
Over-the-Air updates are among Tesla’s best features. They are used to improve the Full Self-Driving suite, add features, remedy recalls, and more. Many vehicles have the ability to receive OTA updates, as I did in a Ford Bronco previous to my Model Y. However, Tesla does them better than anyone else: they’re seamless, effective, and frequent. Your car always improves.
The move is a blow to Tesla, of course, considering Dmytryk’s massive contribution to the company and extremely long tenure spent, but not something that is overwhelmingly detrimental. Tesla deals with a lot of extremely intelligent people, some of whom are the best in their field, so they are sure to find a suitable replacement.
However, it’s no secret that the company has been losing some of its top talent, some of whom were in executive roles. Some have left to take on new projects, and others have not revealed their career plans.
It seems at least some of those employees are simply deciding to walk away and try new things after working so hard for so long. According to Dmytryk’s LinkedIn, he also played a large part in Musk’s acquisition of X, as he stated he “worked at Twitter/X ~45/week while working at the same pace for Tesla.”
That averages a 13-hour day, seven days a week, or 18 hours for the normal five-day work week.
News
Tesla’s most wanted Model Y heads to new region with no sign of U.S. entry
Unlike the standard Model Y, the “L” stretches the wheelbase by roughly 150 mm and the overall length by about 177 mm to 4,976 mm. The result is a genuine 2-2-2 seating layout that gives six adults proper legroom and cargo space — a true family hauler without the cramped third-row compromises of many three-row SUVs.
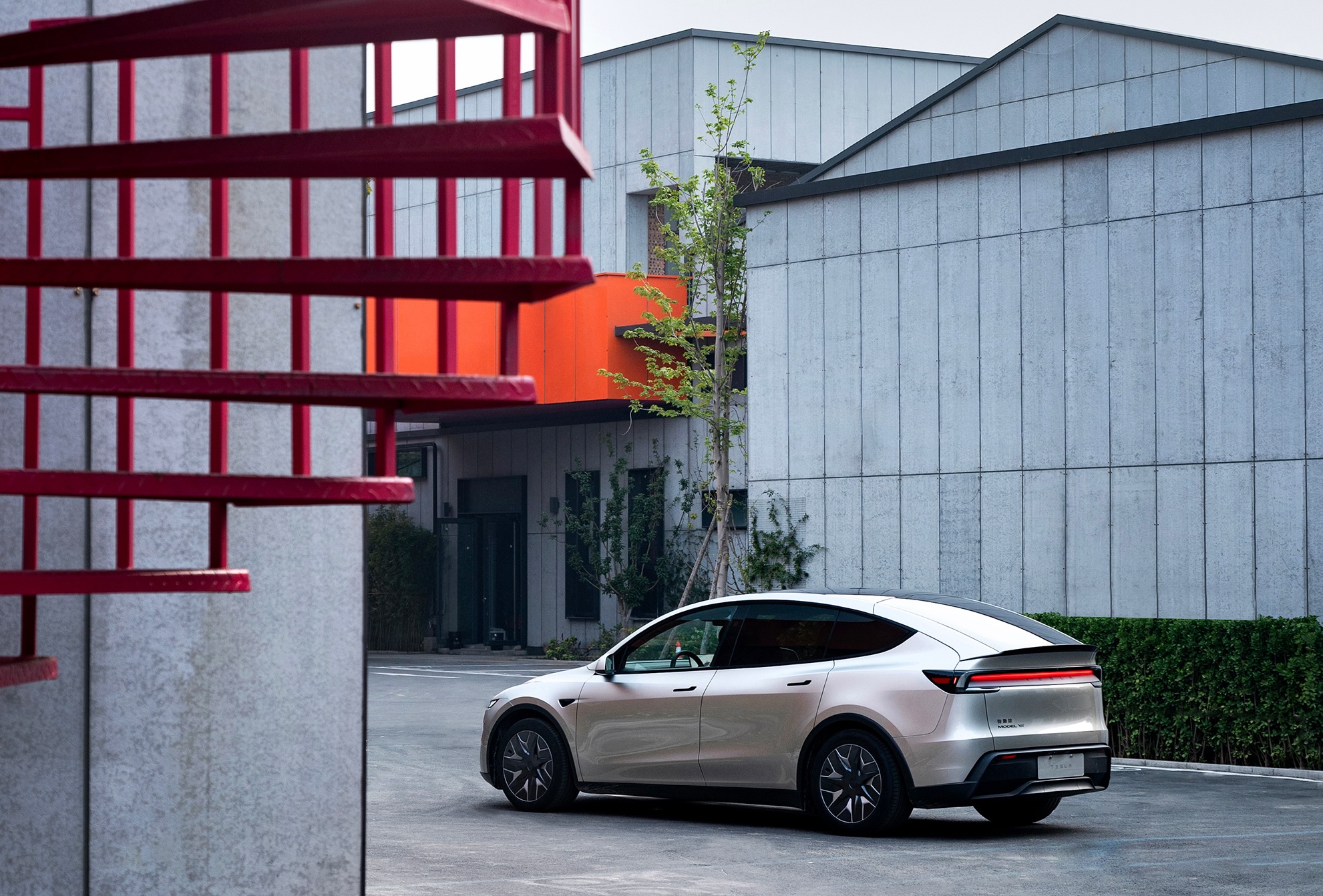

Tesla’s most wanted Model Y configuration is heading to a new region, and although U.S. fans and owners have requested the vehicle since its release last year, it appears the company has no plans to bring it to the market.
According to fresh regulatory filings, the six-seat Model Y L is coming to South Korea with signs indicating an imminent launch. The extended-wheelbase configuration, already a hit in China, just cleared energy-efficiency certification from the Korea Energy Agency, paving the way for deliveries as early as the first half of 2026.
The vehicle is already built at Tesla’s Giga Shanghai facility in China, making it an ideal candidate for the Asian market, as well as the European one, as the factory has been known as a bit of an export hub in the past.
$TSLA
BREAKING: The official launch of Tesla Model Y L in S.Korea seems to be quite imminent.Additional credentials related to Model YL were released today.
✅ Battery Manufacturer: LG Energy Solutions
✅ Number of passengers: 6 people
✅ Total battery capacity: 97.25 kWh… pic.twitter.com/hmy64XYi80— Tsla Chan (@Tslachan) March 6, 2026
It seems like Tesla was prepping for this release anyway, as the timing was no accident. A camouflaged Model Y L prototype was spotted testing on Korean highways the same day the certification dropped. Tesla has already secured similar approvals for Australia and New Zealand, with both markets expecting the larger Model Y in 2026.
Unlike the standard Model Y, the “L” stretches the wheelbase by roughly 150 mm and the overall length by about 177 mm to 4,976 mm. The result is a genuine 2-2-2 seating layout that gives six adults proper legroom and cargo space — a true family hauler without the cramped third-row compromises of many three-row SUVs.
South Korean filings list it as an all-wheel-drive imported electric passenger vehicle with a 97.25 kWh total battery capacity supplied by LG Energy Solution. Local tests show an impressive 543 km (337 miles) combined range at room temperature and 454 km (282 miles) in colder conditions, easing one of the biggest concerns for Korean EV buyers.
Tesla Model Y lineup expansion signals an uncomfortable reality for consumers
But for U.S. fans, things are not looking good for a launch in the market.
CEO Elon Musk has been blunt. The six-seater “wouldn’t arrive in the U.S. until late 2026, if ever,” he said, pointing to the company’s heavy bet on unsupervised Full Self-Driving and robotaxi platforms like the Cybercab. With the Model X slated for discontinuation, many families hoped the stretched Model Y would slide into the lineup as an affordable three-row bridge. So far, that hope remains unfulfilled.
For now, South Korean drivers will be among the first buyers outside China to enjoy the spacious, efficient Model Y L. Tesla continues its global rollout strategy, tailoring vehicles to regional tastes while North American customers keep refreshing their apps and crossing their fingers.
The Model Y L proves the appetite for practical, family-sized electric SUVs is stronger than ever. Hopefully, Tesla will listen to its fans and bring the vehicle to the U.S. where it would likely sell well.
Elon Musk
Tesla is ramping up its advertising strategy on social media
Tesla has long stood out in the automotive world for its unconventional approach to advertising—or, more accurately, its near-total avoidance of it. For over a decade, the company spent virtually nothing on traditional marketing.

Tesla seems to be ramping up its advertising strategy on social media once again. Marketing and advertising have not been a major focus of Tesla’s, something that has brought some criticism to the company from its fans.
However, the company looks to be making adjustments to that narrative, as it has at times in the past, as ads were spotted on several different platforms over the past few days.
On Facebook and YouTube, ads were spotted that were evidently placed by Tesla. On Facebook, Tesla was advertising Full Self-Driving, and on YouTube, an ad for its Energy Division was spotted:
Tesla also threw up some ads on YouTube for Energy https://t.co/19DGQMjBsA pic.twitter.com/XQRfgaDKxY
— TESLARATI (@Teslarati) March 9, 2026
Tesla has long stood out in the automotive world for its unconventional approach to advertising—or, more accurately, its near-total avoidance of it. For over a decade, the company spent virtually nothing on traditional marketing.
In 2022, Tesla’s U.S. ad spend was roughly $152,000, a rounding error compared to General Motors’ $3.6 billion the following year.
Traditional automakers averaged about $495 per vehicle on ads; Tesla spent $0. CEOElon Musk’s stance was explicit: “Tesla does not advertise or pay for endorsements,” he posted on X in 2019. “Instead, we use that money to make the product great.”
The strategy relied on word-of-mouth from delighted owners, Elon’s massive X following, viral product launches, media frenzy, and customer referrals. A great product, Musk argued, sells itself. It does not need Super Bowl spots or billboards. Resources poured into R&D instead, with Tesla investing nearly $3,000 per car, far more than rivals.
Tesla counters jab at lack of advertising with perfect response
This reluctance wasn’t arrogance; it was philosophy, and Musk made it clear that the money was better spent on the product. Heavy spending on ads was seen as wasteful when innovation and authenticity drove organic demand. Shareholder calls for marketing budgets were ignored.
The current shift, paid Facebook ads promoting Full Self-Driving (Supervised) and YouTube Shorts offering up to $1,000 back on Powerwall batteries, marks a pragmatic evolution.
These targeted campaigns coincide with the end of one-time FSD purchases and a March 31 deadline for FSD transfer eligibility on new vehicles.
This move likely signals Tesla adapting to scale, as well as a more concerted effort to stop misinformation regarding its platform. As EV competition intensifies and the company bets big on robotaxis and energy storage, pure organic buzz may not suffice to hit adoption targets. Selective digital ads allow precise, cost-effective reach without abandoning core principles.
If successful, it could foreshadow measured expansion into marketing, boosting high-margin software and home energy revenue while preserving Tesla’s innovative edge. But, it’s nice to see the strategy return, especially as Tesla has been reluctant to change its mind in the past.









