News
Indiana is back with another bill to ban Tesla’s direct sales model

If a proposed Indiana House bill is passed, manufacturers of “all-electric vehicles” would be banned from selling directly to consumers. The bill does not direct any specific language to Tesla Motors, Inc., but the innovative vehicle manufacturer is clearly the target of the legislation. Add Indiana into the mix of Tesla’s long list of court cases pending in which car dealers and automakers claim that they, as intermediaries, have sole right to sell vehicles to consumers.
Indiana House Bill 1592
Indiana automakers have traditionally used an established network of dealers who negotiate with buyers and provide automotive repair services. These automakers are part of a large umbrella of politically influential groups. They argue that Tesla’s model allows the company to evade laws, which confers an unfair advantage to Tesla and provides no accountability to its buyers.
Here is the synopsis of the Indiana House Bill 1592.
Automobile sales requirements. Provides that a manufacturer may engage in sales directly to the public only if the manufacturer meets certain requirements. Provides that a manufacturer can no longer engage in sales directly to the public after the earlier of: (1) reaching 1,000 units in cumulative annual sales; or (2) six years after the initial dealer’s license is granted.
Additionally, Sec. 20. of the bill reads:
A manufacturer licensed under this article may engage in sales directly to the general public only if the manufacturer (1) has exclusively offered for sale to the general public in Indiana all-electric vehicles on a continuous basis since July 15, 2015; (2) has never offered for sale to the general public in Indiana a line make of new motor vehicles through a franchised motor vehicle dealer.
Tesla is the only vehicle manufacturer which meets these particular criteria. Tesla sells its electric vehicles directly to consumers, while other manufacturers like General Motors, Ford, Subaru, and Toyota sell through Indiana dealerships. If passed, the bill would severely limit Tesla’s ability as a manufacturer to sell to the public:
Subject to the expiration schedule under IC 9-32-11-12.5, a manufacturer can no longer sell to the public after the earlier of the following: (1) A manufacturer described in this section reaches cumulative annual sales of one thousand (1,000) units to the general public from its licensed location in Indiana.
The author of the bill, Rep. Edmond Soliday, a Republican, has authored or co-authored several transportation bills, including transportation infrastructure funding, automated traffic enforcement, vehicle excise taxes, and department of transportation property matters. He defeated Midwest Environmental Systems CEO Pamela Fish in the November, 2016 elections. House Bill 1592 will be heard by the Roads and Transportation committee.
Last year another Republican, Rep. Kevin Mahan, supported a similar bill that would have forced manufacturers to sell their vehicles through a dealership. “For the average Hoosier, purchasing an automobile can be daunting and a big investment,” Mahan said. “A greater variety of vehicles are now available and can be brought directly to consumers virtually anywhere in the country. In the event of a recall or malfunction, consumers should be protected.”
Arguments against limiting manufacturer sales
Tesla Motors, Inc.’s Vice President of Corporate and Business Development Diarmuid O’Connell testified against House Bill 1592. “Tesla does not operate through some kind of loophole in Indiana law,” O’Connell said. “The current law is explicit in Tesla’s ability to sell directly and, as written today, it is not broken.” O’Connell’s remarks point to current Indiana law in which an auto manufacturer is not allowed to open a store in direct competition with an affiliated franchised dealer. Tesla has no direct competition franchise dealers in Indiana and has always sold directly to consumers. O’Connell added that Tesla’s presence in Indiana has “brought only good to the consumer welfare without harming anyone — not even the dealers.”
At stake is more than a corporate tug-of-war between automakers. Tesla’s electric vehicles are at the heart of that vision for tomorrow’s consumer domestic transportation and will continue to flourish and change the way automakers in the U.S. and abroad have conducted business as usual.
If “you’re interested in promoting competition and free market principles … you recognize direct distribution, particularly for a company like Tesla, is critically important,” said Todd Maron, the company’s chief counsel, during remarks at a 2016 Federal Trade Commission event. “We don’t simply believe that [electric vehicles] represent a nice complement to gas powered cars. We believe that it’s imperative that they are replaced entirely by electric vehicles.” An end to franchising laws would advance that goal and place low-mileage gas-powered vehicles at risk of obsolescence.
Arguments in favor of limiting manufacturer sales
A coalition of free market groups, led by Americans for Tax Reform President Grover Norquist, argues that ending or restricting automotive franchising would actually decrease consumer choice. Norquist believes that reducing competition among dealers selling the same car brands hurts consumers. Franchising laws were actually created by anti-trust efforts at the Federal Trade Commission and “they sustain market competition rather than undermine it.” Last year, the group accused federal regulators of ignoring evidence that would undermine proposed measures governing automotive sales that stand to enrich what they saw as a “politically-powerful company” at consumers’ expense.
Harry Tepe, owner of Tom Tepe Auto Center in Milan, Indiana, supports legislation that would further protect consumers in the auto industry. “We just want to make sure there are protections in place for the consumers,” Tepe said. “The issue at hand is that the loophole is still open that allows any manufacturer to come in and market a vehicle and sell directly to the public without having any protections in place for the consumer.” He takes the position that dealerships are responsible for being a liaison between the consumer and the manufacturer.
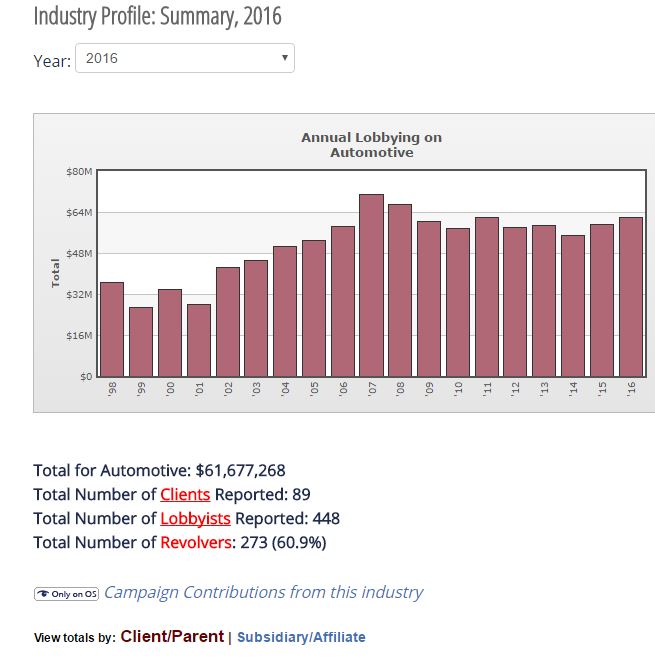
Lobbying on behalf of the automotive industry
Proponents and opponents of Indiana House Bill 1592 are, in many cases, influenced by a powerful automotive lobby in the U.S. Automotive industry lobbyists use a combination of strategies to gain influence. They do a lot of research, sit down with lawmakers one-on-one, deliver messages in writing, and call Congressmen and members of the administration on the phone.
“If you’re a big company, like a carmaker, and you’re lobbying lawmakers, you’re almost like a pro sports team. You want to get the big names, the most talented, most knowledgeable people,” said David Levinthal, communications director for the Center for Responsive Politics, a non-partisan research group that tracks the money spent in the U.S. political system and its effect on elections and public policy. “So, these big companies, in the major industries, hire former Congressmen and top Congressional staffers and other high-ranking government officials to be their lobbyists, because those are the folks who know who all the other major players are and they know the ways of Washington.”

News
Tesla preps to build its most massive Supercharger yet: 400+ V4 stalls
The project will be an expansion of the current Eddie World Supercharger in Yermo, California, and will take place in several stages.

Tesla is preparing to build its most massive Supercharger yet, as it recently submitted plans for an over 400-stall Supercharging station in California, which would dwarf its massive 168-stall location in Lost Hills, California.
The project will be an expansion of the current Eddie World Supercharger in Yermo, California, and will take place in several stages.
The expansion, adjacent to the existing Eddie World Supercharger, which is currently comprised of 22 older V2 and V3 stalls limited to 150 kW, unfolds across six phases.
Construction on Phase 1 begins later this year with 72 V4 stalls. Subsequent stages will progressively add hundreds more, culminating in over 400 next-generation chargers. Site plans label expansive parking arrays across Phases 1–5 along Calico Boulevard, with Phase 6 design still to be determined.
Tesla is planning an absolutely massive Supercharger expansion in Yermo, California!!
Over the course of 6 phases, Tesla is set to add over 400 V4 stalls in a commercial development known as Eddie World 2.
The first phase, which should begin construction sometime this year,… pic.twitter.com/ks5Y5dE8lR
— MarcoRP (@MarcoRPi1) March 6, 2026
The project was first flagged by MarcoRP, a notable Tesla Supercharger watcher.
Strategically located midway on I-15 between Los Angeles and Las Vegas, the station targets heavy EV traffic on this high-demand corridor.
The surrounding 20-mile stretch already hosts over 200 high-power stalls (including 40 at 250 kW, 120 at 325 kW, and more), plus 96 in nearby Baker—yet bottlenecks persist during peak travel.
In scale, it eclipses all existing Tesla Superchargers. The current record holder, the solar- and Megapack-powered “Project Oasis” in Lost Hills, California, offers 164 stalls. Barstow’s former leader had 120. Eddie World 2 will be more than double that size, cementing Tesla’s dominance in ultra-high-capacity charging.
Tesla finishes its biggest Supercharger ever with 168 stalls
Development blends charging with convenience. Architectural drawings show integrated retail: a 10,100 square foot Cracker Barrel, a 4,300 square foot McDonald’s, a 3,800 square foot convenience store, additional restaurants, drive-thrus, outdoor dining, and lease space.
EV-centric features include pull-through bays for Cybertrucks and trailers, ensuring accessibility for larger vehicles and future Semi trucks.
News
Tesla makes latest move to remove Model S and Model X from its lineup
Tesla’s latest decisive step toward phasing out its flagship sedan and SUV was quietly removing the Model S and Model X from its U.S. referral program earlier this week.

Tesla has made its latest move that indicates the Model S and Model X are being removed from the company’s lineup, an action that was confirmed by the company earlier this quarter, that the two flagship vehicles would no longer be produced.
Tesla has ultimately started phasing out the Model S and Model X in several ways, as it recently indicated it had sold out of a paint color for the two vehicles.
Now, the company is making even more moves that show its plans for the two vehicles are being eliminated slowly but surely.
Tesla’s latest decisive step toward phasing out its flagship sedan and SUV was quietly removing the Model S and Model X from its U.S. referral program earlier this week.
The change eliminates the $1,000 referral discount previously available to new buyers of these vehicles. Existing Tesla owners purchasing a new Model S or Model X will now only receive a halved loyalty discount of $500, down from $1,000.
The updates extend beyond the two flagship vehicles. New Cybertruck buyers using a referral code on Premium AWD or Cyberbeast configurations will no longer get $1,000 off. Instead, both referrer and buyer receive three months of Full Self-Driving (Supervised).
The loyalty discount for Cybertruck purchases, excluding the new Dual Motor AWD trim level, has also been cut to $500.
NEWS: Tesla has removed the Model S and Model X from the referral program.
New owners also no longer get a $1,000 referral discount on a new Cybertruck Premium AWD or Cyberbeast. Instead, you now get 3 months of FSD (Supervised).
Additionally, Tesla has reduced the loyalty… pic.twitter.com/IgIY8Hi2WJ
— Sawyer Merritt (@SawyerMerritt) March 6, 2026
These adjustments apply only in the United States, and reflect Tesla’s broader strategy to optimize margins while boosting adoption of its autonomous driving software.
The timing is no coincidence. Tesla confirmed earlier this year that Model S and Model X production will end in the second quarter of 2026, roughly June, as the company reallocates factory capacity toward its Optimus humanoid robot and next-generation vehicles.
With annual sales of the low-volume flagships already declining (just 53,900 units in 2025), incentives are no longer needed to drive demand. Production is winding down, and Tesla expects strong remaining interest without subsidies.
Industry observers see this as the clearest sign yet of an “end-of-life” phase for the vehicles that once defined Tesla’s luxury segment. Community reactions on X range from nostalgia, “Rest in power S and X”, to frustration among long-time owners who feel perks are eroding just as the models approach discontinuation.
Some buyers are rushing orders to lock in final discounts before they vanish entirely.
Doug DeMuro names Tesla Model S the Most Important Car of the last 30 years
For Tesla, the move prioritizes efficiency: fewer discounts on outgoing models, a stronger push for FSD subscriptions, and a focus on high-margin Cybertruck trims amid surging orders.
Loyalists still have a narrow window to purchase a refreshed Plaid or Long Range model with remaining incentives, but the message is clear: Tesla’s lineup is evolving, and the era of the original flagships is drawing to a close.
News
Tesla Australia confirms six-seat Model Y L launch in 2026
Compared with the standard five-seat Model Y, the Model Y L features a longer body and extended wheelbase to accommodate an additional row of seating.

Tesla has confirmed that the larger six-seat Model Y L will launch in Australia and New Zealand in 2026.
The confirmation was shared by techAU through a media release from Tesla Australia and New Zealand.
The Model Y L expands the Model Y lineup by offering additional seating capacity for customers seeking a larger electric SUV. Compared with the standard five-seat Model Y, the Model Y L features a longer body and extended wheelbase to accommodate an additional row of seating.
The Model Y L is already being produced at Tesla’s Gigafactory Shanghai for the Chinese market, though the vehicle will be manufactured in right-hand-drive configuration for markets such as Australia and New Zealand.
Tesla Australia and New Zealand confirmed the vehicle will feature seating for six passengers.
“As shown in pictures from its launch in China, Model Y L will have a new seating configuration providing room for 6 occupants,” Tesla Australia and New Zealand said in comments shared with techAU.
Instead of a traditional seven-seat arrangement, the Model Y L uses a 2-2-2 layout. The middle row features two individual seats, allowing easier access to the third row while providing additional space for passengers.
Tesla Australia and New Zealand also confirmed that the Model Y L will be covered by the company’s updated warranty structure beginning in 2026.
“As with all new Tesla Vehicles from the start of 2026, the Model Y L will come with a 5-year unlimited km vehicle warranty and 8 years for the battery,” the company said.
The updated policy increases Tesla’s vehicle warranty from the previous four-year or 80,000-kilometer coverage.
Battery and drive unit warranties remain unchanged depending on the variant. Rear-wheel-drive models carry an eight-year or 160,000-kilometer warranty, while Long Range and Performance variants are covered for eight years or 192,000 kilometers.
Tesla has not yet announced official pricing or range figures for the Model Y L in Australia.