

News
First living tissue 3D printed in space aboard International Space Station
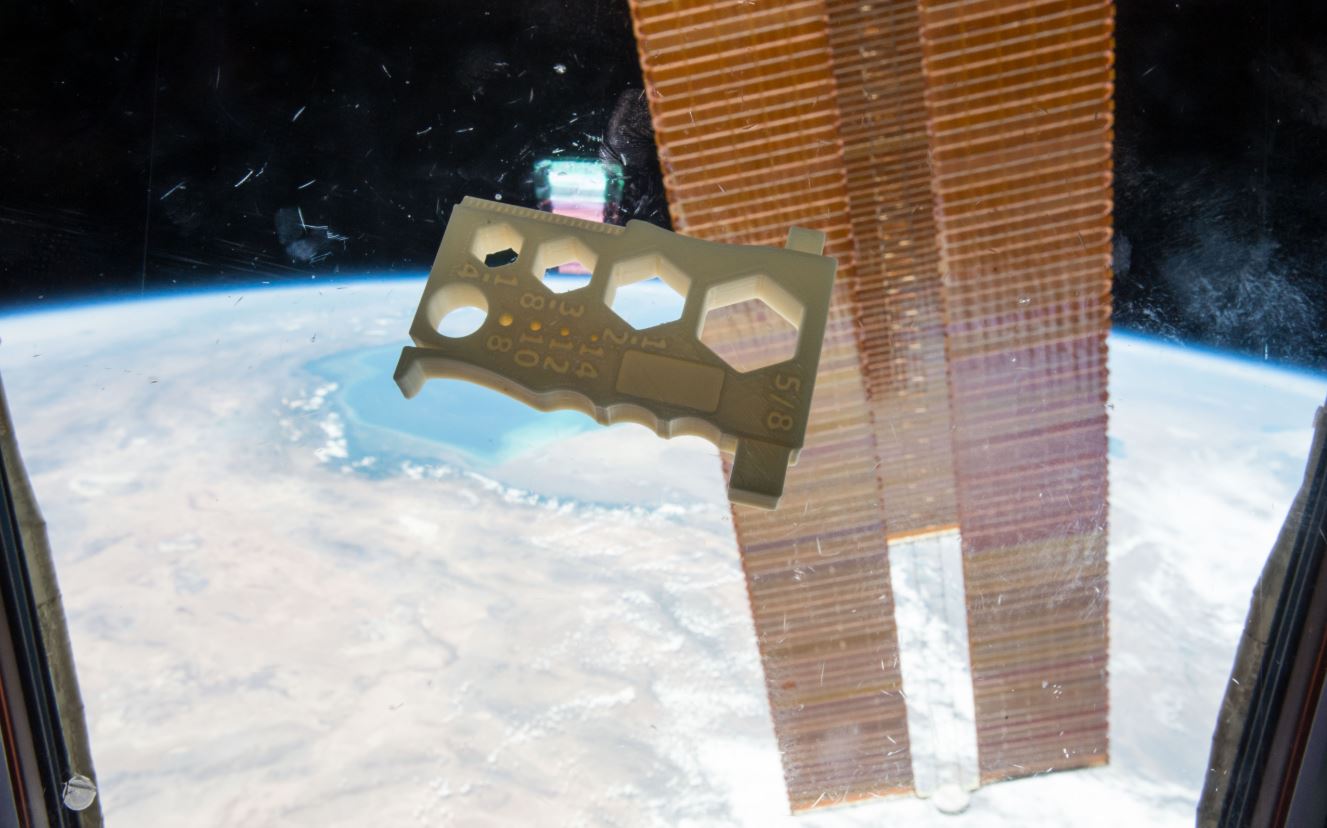
Using the “Organaut”, a 3D bioprinter designed for microgravity, Russia has become the first country to print living tissue in space. After a December 3rd cargo delivery to the International Space Station (ISS), cosmonaut Oleg Kononenko completed an experiment with the machine in the Russian sector of the station, successfully producing human cartilage tissue and a rodent thyroid gland. The Organaut was designed via a collaboration with the printer’s maker, 3D Bioprinting Solutions, and Russia’s national space agency, Roscosmos. The United States also has its own bioprinting mission scheduled for the first half of 2019, joining in the march to develop biological solutions for problems that space is well suited to solve.
A 3D bioprinter operates by creating one layer at a time of specified tissue or stem cell material arranged as needed to grow and form as biologically programmed to do. As summarized by Aryeh Batt, the CEO of Precise Bio, a company dedicated to 3D printed bioproducts for human eyes, “Essentially, the biology does the work, but you have to put them in the correct environment to make it happen.” In the case of Organaut, an internal robotic mechanism drips living cell fabric layers from an automatic syringe. When living tissue is bioprinted under Earth’s gravity, the artificial cells grow in a flatter structure than their natural state in the human body. In microgravity, however, they form a shape closer to their normal dimensions.
Along with demonstrating the growth advantages of microgravity, Organaut’s tissue samples will provide the ability to study the effect of radiation on the body. “We will look at how the constructs came together, and how they behaved,” confirmed Usef Hesuani, head of laboratory projects and a managing partner of 3D Bioprinting Solutions in a recent press conference. The original Organaut printer was aboard the Soyuz MS-10 spacecraft which experienced an launch failure on October 11, 2018, forcing the U.S. and Russian crew to make an emergency landing. A second one was quickly put together for the subsequent mission.
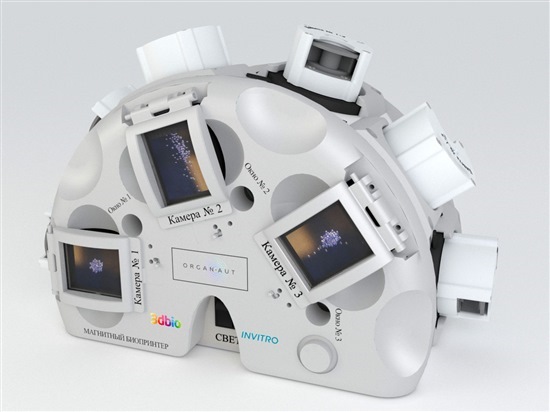
The parent company of 3D Bioprinting Solutions is INVITRO, the largest private medical company in Russia. Founded in 1995 by Aleksandr Ostrovsky, it has 8 laboratories and over 1000 medical offices in eastern Europe, but is primarily based in Skolkovo, a high technology business area in Moscow. Bioprinting Solutions made headlines in 2015 when it printed and transplanted a functioning mouse thyroid gland. The experiment performed aboard the ISS with Organaut was a modified version of their prior work.
Unlike NASA, Roscosmos does not generally partner with private companies for its research endeavors. In an effort to inspire Russian students to enter STEM fields within their country, the agency sought to spotlight the developing bioprinting industry by using the Organaut. The successful partnership with 3D Bioprinting Solutions has now motivated the agency to continue partnering with private companies in the future. The company itself also sees advantages to collaborations of its own with other Skolkova-area manufacturers. “We have companies that are making satellite platforms…it is possible to conduct a similar experiment amid microgravity on small spacecraft [like satellites]…smaller and cheaper,” noted Ivan Kosenkov, 3D Bioprinting Solutions’ project manager.
Organaut’s printed tissues were returned to Earth with the Soyuz MS-09 spacecraft on December 20th, and the results of the experiment are expected to be published at the end of January 2019. In February, NASA plans to send a bioprinter capable of producing beating heart tissue to the ISS. Named the 3D BioFabrication Facility (BFF), the machine was developed through a partnership with two companies well-established in 3D printing and on-orbit hardware, nScrypt and Techshot. Since the thickness of heart tissue is difficult to build under gravity without structural assistance that could impede functionality, the companies developed the BFF with the hypothesis that microgravity would overcome this limitation. Thus far, the concept has been proven during parabolic flight tests, i.e., aboard the “Vomit Comet” airplane that performs multiple parabolic maneuvers in an airliner to create 20-30 seconds of weightlessness each.

News
Tesla’s global fleet surpasses 9 million vehicles worldwide
The update was posted by Tesla China, which competes in the world’s most competitive electric vehicle market.

Tesla’s global fleet has now exceeded 9 million vehicles, a major milestone for the electric vehicle maker.
The update was posted by Tesla China, which competes in the world’s most competitive electric vehicle market.
Tesla’s global fleet crosses 9 million vehicles
The milestone was highlighted in a graphic shared by Tesla China, which thanked the over nine million Tesla owners worldwide for their support over the years. To celebrate the milestone, Tesla China announced several incentives for select owners, from Model Y L test drives to Tesla Bot Premium Gift Sets to Supercharging perks.
The milestone comes 16 years after the company started delivering its first vehicle, the original Tesla Roadster, as observed by members of the Tesla community. The first production Roadster was delivered to Elon Musk, who was serving as chairman at the time.
Reaching a global fleet of more than 9 million vehicles reflects the cumulative impact of Tesla’s growth over the past decade, particularly following the introduction of high-volume models such as the Model 3 and Model Y. The Model 3 and Model Y have allowed Tesla to transform from a niche automaker into one of the world’s largest producers of electric cars.
Strong China sales help drive fleet growth
Tesla’s expanding global footprint has been supported by solid performance in China, where the company posted a strong finish to 2025. In December, the Model Y ranked as the country’s top-selling new energy vehicle, as per sales data compiled by Chinese auto industry aggregator Yiche.
The Model Y led China’s NEV rankings with approximately 65,874 units sold during the month, outperforming a field dominated by domestic manufacturers such as BYD, SAIC-GM-Wuling, and Xiaomi. Tesla’s Model 3 also delivered an impressive result, ranking eighth overall with just under 28,000 units sold, ahead of numerous locally produced competitors despite its premium pricing.
Tesla China’s broader performance in December was equally notable. The company sold 97,171 vehicles wholesale during the month, based on data from the China Passenger Car Association. The result marked Tesla China’s second-highest monthly total on record, trailing only November 2022’s peak of 100,291 units.
News
Tesla launches new affordable Model Y configuration in the U.S.
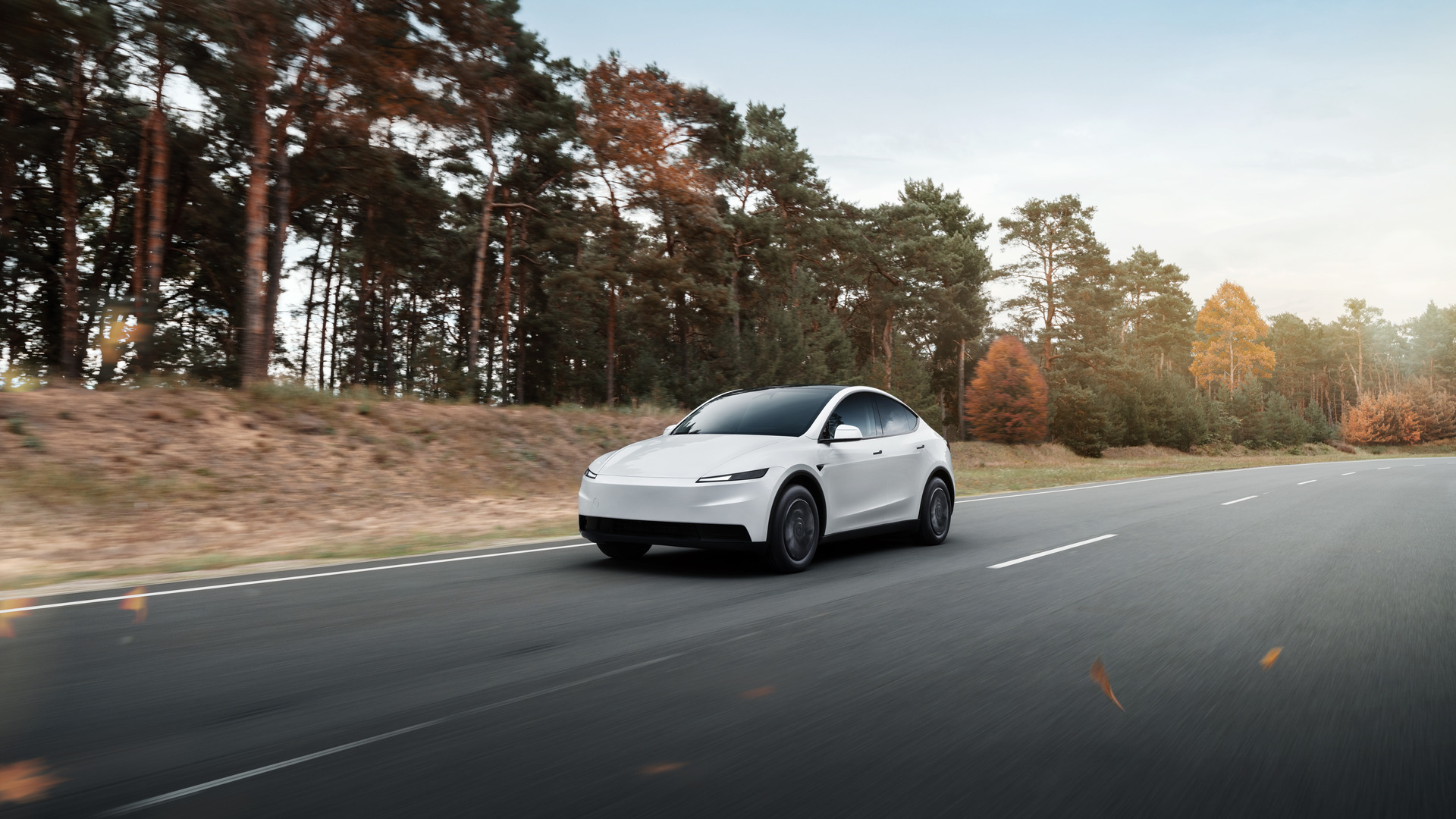

Tesla has launched another new affordable Model Y configuration in the United States, now adding a fifth version of the all-electric crossover to its lineup, diversifying the car’s options and giving consumers more choices at the time of purchase.
Tesla launched the Model Y All-Wheel-Drive on Monday night, pricing it at $41,990. It features 294 miles of range, a 125 MPH top speed, and a 0-60 MPH acceleration rate of 4.6 seconds.
The vehicle is the second most-affordable configuration of the Model Y, only eclipsing the Model Y Rear-Wheel-Drive, which is priced at $39,990.
The move to expand the Model Y lineup comes just a week after CEO Elon Musk confirmed the company would remove the Model S and Model X from production, making way for manufacturing of the Optimus robot at the company’s Fremont, California, factory.
🚨 Tesla has just launched the Model Y All-Wheel-Drive, a new configuration, in the U.S. for $41,990
It has 294 miles of range, a 4.6s 0-60 MPH acceleration rate, and a 125 MPH top speed pic.twitter.com/cyd81m26vB
— TESLARATI (@Teslarati) February 3, 2026
The Model Y All-Wheel-Drive fits the bill of the “Standard” offerings of the vehicle that Tesla launched last year. It is void of many of the more luxurious features, which are available in the “Premium” trim levels, available in Rear-Wheel-Drive, All-Wheel-Drive, and Performance.
The differences between the Standard and Premium configurations can be found in the video below:
@teslarati There are some BIG differences between the Tesla Model Y Standard and Tesla Model Y Premium #tesla #teslamodely ♬ Sia – Xeptemper
With five configurations now available in the Model Y, it certainly seems as if Tesla is attempting to get the vehicle available in more options than ever before.
With the Model S and Model X being removed from production due to their irrelevance to the future and Tesla’s focus on autonomy, diversifying the Model Y portfolio seems to align with the idea that the company is okay with making more variations of its most popular car.
Tesla Model Y Standard: first impressions from a Premium owner
Removing the Model S and Model X and replacing them with a new Model Y configuration is not exactly what fans have been wanting; many have been wondering what Tesla will do to replace the need for a bigger SUV for large families.
Nevertheless, Tesla’s relentless attitude toward solving autonomy and its preparation to launch a self-driving ride-hailing service seem to fit the bill for this move. Soon, it will be the Model 3, Model Y, and Cybercab playing the main parts of this autonomous future. The Cybertruck will be sticking around for other things, like local hauling.
Elon Musk
SpaceX officially acquires xAI, merging rockets with AI expertise

SpaceX has officially acquired xAI, merging rockets with AI expertise in what is the first move to bring Elon Musk’s companies under one umbrella.
On February 2, SpaceX officially announced the acquisition of xAI, uniting two powerhouse companies under a single entity, creating what the space exploration company called in a blog post “one of the most ambitious, vertically integrated innovation engines on (and off) Earth.”
🚨 BREAKING: Elon Musk has posted a new blog on SpaceX’s website confirming the acquisition of xAI pic.twitter.com/TFgeHGMpXc
— TESLARATI (@Teslarati) February 2, 2026
The deal will integrate xAI’s advanced AI capabilities, including the Grok chatbot and massive training infrastructure, with SpaceX’s rocket technology, Starlink satellite network, and ambitious space exploration goals.
The acquisition comes at a pivotal moment: xAI is valued at around $230 billion as of late 2025, and has been racing to scale AI compute amid global competition from companies like OpenAI, Google, and Meta. Meanwhile, SpaceX, which was recently valued at $800 billion, is facing escalating costs for its multiplanetary ambitions.
By combining forces, the merged entity gains a unified approach to tackle one of AI’s biggest bottlenecks: the enormous energy and infrastructure demands of next-gen models.
Musk wrote in a blog post on SpaceX’s website that:
“In the long term, space-based AI is obviously the only way to scale. To harness even a millionth of our Sun’s energy would require over a million times more energy than our civilization currently uses! The only logical solution therefore is to transport these resource-intensive efforts to a location with vast power and space. I mean, space is called “space” for a reason.”
Musk details the need for orbital data centers, stating that his estimate is that “within 2 to 3 years, the lowest cost way to generate AI compute will be in space.
This cost-efficiency alone will enable innovative companies to forge ahead in training their AI models and processing data at unprecedented speeds and scales, accelerating breakthroughs in our understanding of physics and invention of technologies to benefit humanity.”
SpaceX recently filed for approval from the FCC to launch up to one million solar-powered satellites configured as high-bandwidth, optically linked compute platforms.
These facilities would harness near-constant sunlight with minimal maintenance, delivering what the company projects as transformative efficiency.
Musk has long argued that space offers the ultimate solution for power-hungry AI projects. But that’s not all the merger will take care of.
Additionally, it positions the company to fund broader goals. Revenue from the Starlink expansion, potential SpaceX IPO, and AI-driven applications could accelerate the development of lunar bases, as Musk believes multiplanetary life will be crucial to saving civilization.
Critics question the feasibility of massive constellations amid orbital debris concerns and regulatory hurdles. Yet, proponents see it as a bold step toward a multiplanetary computing infrastructure that extends human civilization beyond Earth.








