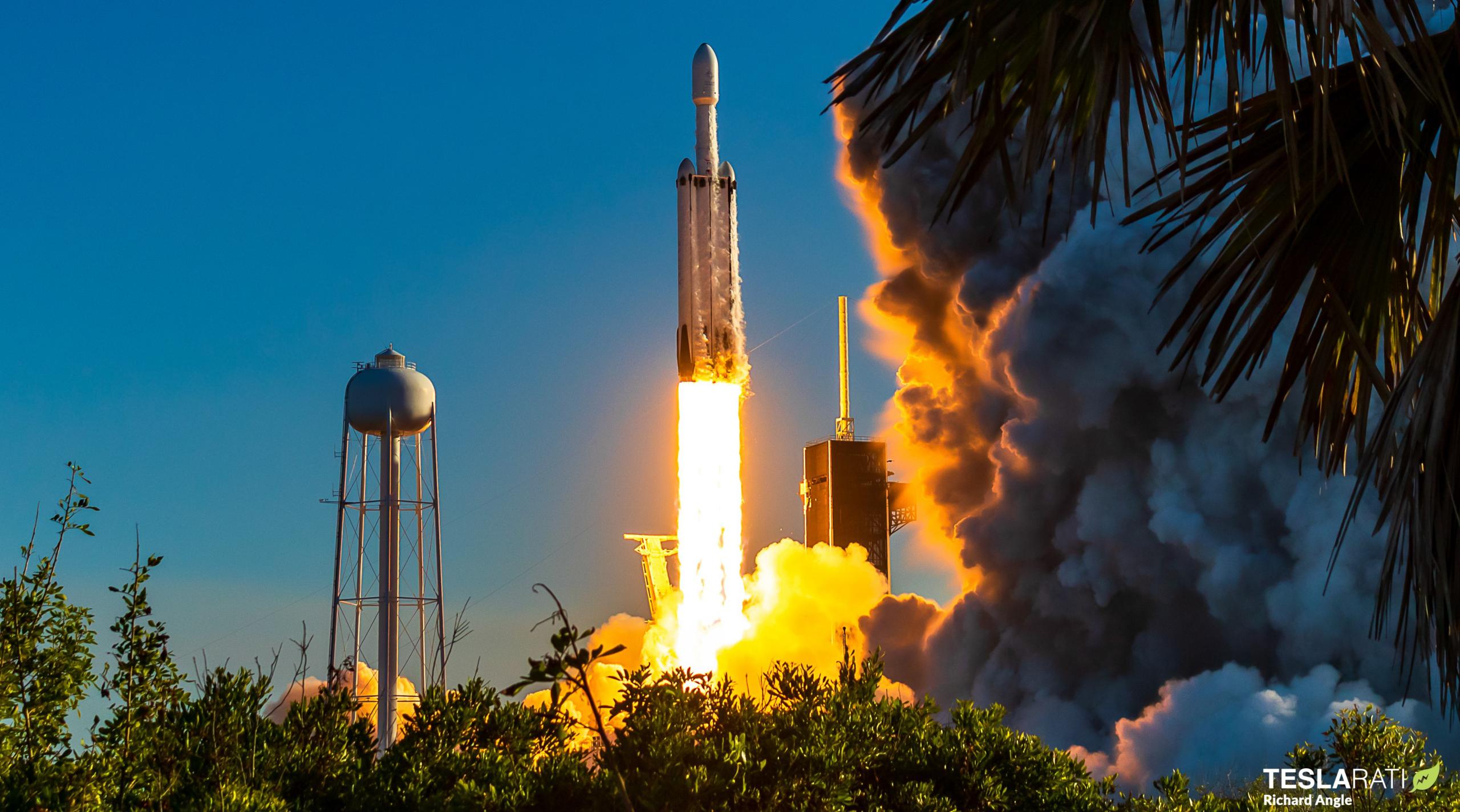
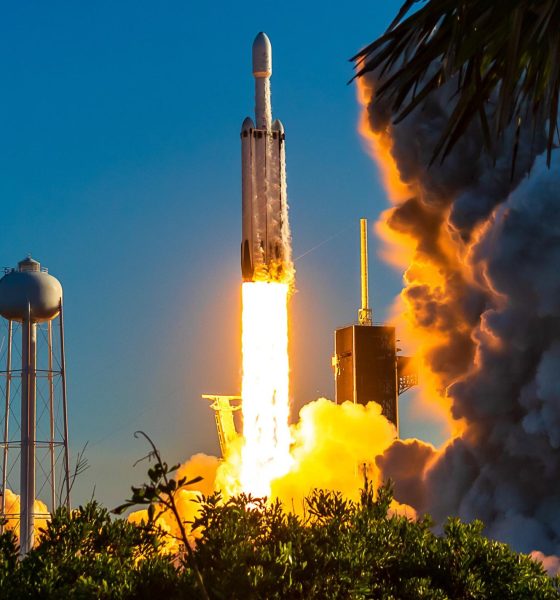
In a statement issued to Bloomberg, the US Space Force says that SpaceX’s Falcon Heavy rocket could still conduct its first operational launch for the military before the end of the year.
That’s a large downgrade from late 2021 and early 2022, when – lacking any new information from the US military – it appeared that SpaceX could launch up to three Falcon Heavy rockets for military customers over the course of the year. Around eight months later, the world’s most powerful and capable operational rocket – backed by a strong manifest of 11 firm launch contracts – hasn’t flown once since June 2019. At that time, the rocket’s next launch was already expected no earlier than late 2020 – a roughly 18-month gap.
Instead, thanks to largely unspecified problems that have relentlessly delayed the completion of the satellites Falcon Heavy is supposed to launch, the rocket’s fourth flight is now unlikely to occur less than ~40 months after its third. Thankfully, a new Space Force decision should at least dull the pain caused by the endless shuffling of Falcon Heavy’s near-term launch manifest.
Alongside a slight schedule update stating that SpaceX’s first operational Falcon Heavy launch for the US military could still happen sometime from “October to December” 2022, the Space Force statement issued to Bloomberg mainly revealed the military branch’s June decision to permit SpaceX’s use of reused Falcon Heavy boosters on upcoming launches. While Bloomberg did not publish the statement in full or explain what the decision truly entails, the implication is that the Space Force will now let SpaceX assign flight-proven Falcon boosters – with US military oversight – to its military missions.
The US military will likely retain the ability to veto or modify SpaceX’s booster assignments and reuse sequencing, but the Space Force told Bloomberg that it’s confident that the “recovery, refurbishment, and launch of SpaceX boosters utilizes well-established processes.” In fact, the US military has already approved the use of flight-proven Falcon 9 boosters, several launches of which have since occurred, and even allowed SpaceX to fly two reused Falcon Heavy side booster’s on the rocket’s first (test) launch for the military.
It’s no surprise that that acceptance would eventually grow to include Falcon Heavy, which is similar to Falcon 9 in many ways. That it took the USSF until June 2022, three full years after STP-2 demonstrated the successful reuse of two Falcon Heavy boosters at once, to fully approve it is arguably far more surprising.
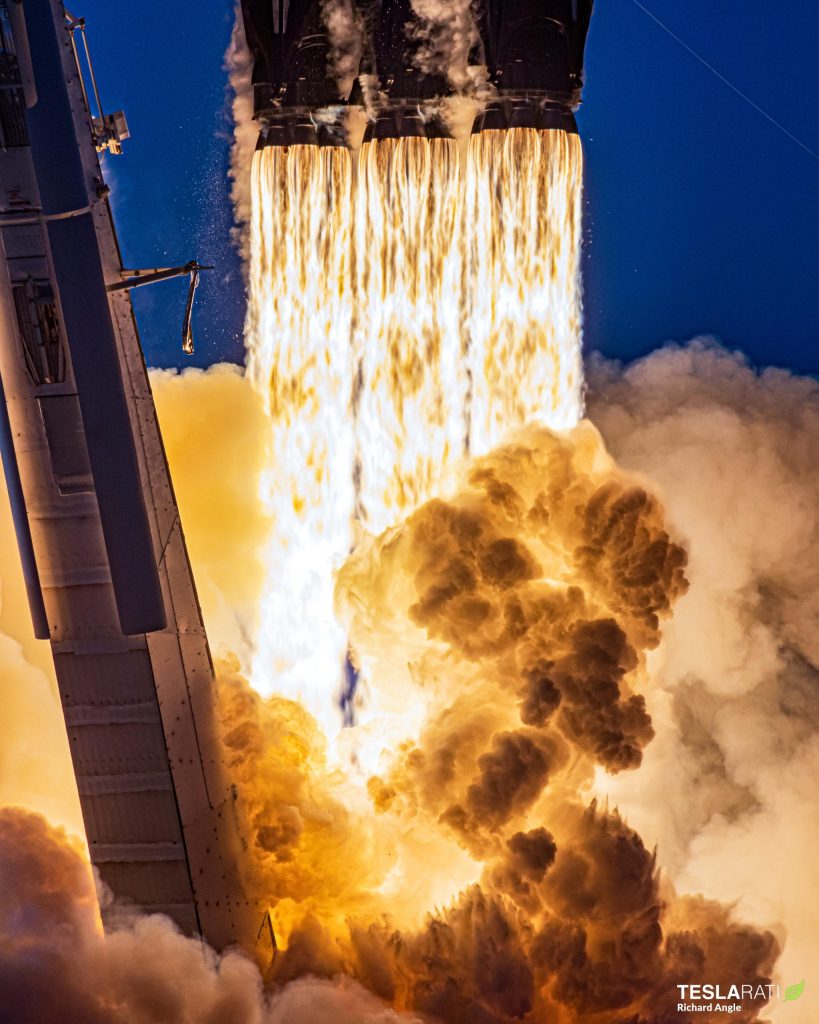

SpaceX will likely be able to plan for future Falcon Heavy launches more easily knowing that the US military should – in theory – be okay with the company reusing boosters on upcoming launches. That would be especially true if the military is comfortable with SpaceX reusing Falcon Heavy boosters that have supported non-military launches. After numerous delays, only one non-military mission – ViaSat’s first ViaSat-3 geostationary communications satellite – still claims to have a shot at a 2022 launch, but that target has slipped from spring, late-summer, and September 2022 to Q4 2022 since late 2021.
At one point, the US military’s USSF-44, USSF-52, and USSF-67 missions were all scheduled to launch on Falcon Heavy in 2022. Now, one reliable source states that USSF-44 and USSF-52 are indefinitely delayed, while another indicates that USSF-44 has slipped to December 2022 and USSF-52 to April 2023. Meanwhile, EchoStar’s Jupiter-3 commsat recently slipped to Q1 2023 and NASA’s Psyche asteroid explorer ran into software issues that delayed its Falcon Heavy launch from August/September 2022 to July or September 2023.
That leaves ViaSat-3 and USSF-67, both of which could launch in Q4 2022. But given just how delay-ridden ViaSat-3 has been and how temperamental all military Falcon Heavy payloads have been, the most likely outcome may already be zero Falcon Heavy launches in 2022.

Elon Musk
SpaceX pursues 5G-level connectivity with Starlink Mobile V2 expansion
SpaceX noted that the upcoming Starlink V2 satellites will deliver up to 100 times the data density of the current first-generation system.

SpaceX has previewed a major upgrade to Starlink Mobile, outlining next-generation satellites that aim to deliver significantly higher capacity and full 5G-level connectivity directly to mobile phones.
The update comes as Starlink rebrands its Direct-to-Cell service to Starlink Mobile, positioning the platform as a scalable satellite-to-mobile solution that’s integrated with global telecom partners.
SpaceX noted that the upcoming Starlink V2 satellites will deliver up to 100 times the data density of the current first-generation system. The company also noted that the new V2 satellites are designed to provide significantly higher throughput capability compared to its current iteration.
“The next generation of Starlink Mobile satellites – V2 – will deliver full cellular coverage to places never thought possible via the highest performing satellite-to-mobile network ever built.
“Driven by custom SpaceX-designed silicon and phased array antennas, the satellites will support thousands of spatial beams and higher bandwidth capability, enabling around 20x the throughput capability as compared to a first-generation satellite,” SpaceX wrote in its official Starlink Mobile page.
Thanks to the higher bandwidth of Starlink Mobile, users should be able to stream, browse the internet, use high-speed apps, and enjoy voice services comparable to terrestrial cellular networks.
In most environments, Starlink says the upgraded system will enable full 5G cellular connectivity with a user experience similar to existing ground-based networks.
The satellites function as “cell towers in space,” using advanced phased-array antennas and laser interlinks to integrate with terrestrial infrastructure in a roaming-like architecture.
“Starlink Mobile works with existing LTE phones wherever you can see the sky. The satellites have an antenna that acts like a cellphone tower in space, the most advanced phased array antennas in the world that connect seamlessly over lasers to any point in the globe, allowing network integration similar to a standard roaming partner,” SpaceX wrote.
Starlink Mobile currently operates with approximately 650 satellites in low-Earth orbit and is active across more than 32 countries, representing over 1.7 billion people through partnerships with mobile network operators. Starlink Mobile’s current partnerships span North America, Europe, Asia, Africa, and Oceania, allowing reciprocal access across participating nations.
News
Tesla FSD (Supervised) fleet passes 8.4 billion cumulative miles
The figure appears on Tesla’s official safety page, which tracks performance data for FSD (Supervised) and other safety technologies.

Tesla’s Full Self-Driving (Supervised) system has now surpassed 8.4 billion cumulative miles.
The figure appears on Tesla’s official safety page, which tracks performance data for FSD (Supervised) and other safety technologies.
Tesla has long emphasized that large-scale real-world data is central to improving its neural network-based approach to autonomy. Each mile driven with FSD (Supervised) engaged contributes additional edge cases and scenario training for the system.
The milestone also brings Tesla closer to a benchmark previously outlined by CEO Elon Musk. Musk has stated that roughly 10 billion miles of training data may be needed to achieve safe unsupervised self-driving at scale, citing the “long tail” of rare but complex driving situations that must be learned through experience.
The growth curve of FSD Supervised’s cumulative miles over the past five years has been notable.
As noted in data shared by Tesla watcher Sawyer Merritt, annual FSD (Supervised) miles have increased from roughly 6 million in 2021 to 80 million in 2022, 670 million in 2023, 2.25 billion in 2024, and 4.25 billion in 2025. In just the first 50 days of 2026, Tesla owners logged another 1 billion miles.
At the current pace, the fleet is trending towards hitting about 10 billion FSD Supervised miles this year. The increase has been driven by Tesla’s growing vehicle fleet, periodic free trials, and expanding Robotaxi operations, among others.
With the fleet now past 8.4 billion cumulative miles, Tesla’s supervised system is approaching that threshold, even as regulatory approval for fully unsupervised deployment remains subject to further validation and oversight.
Elon Musk
Elon Musk fires back after Wikipedia co-founder claims neutrality and dubs Grokipedia “ridiculous”
Musk’s response to Wales’ comments, which were posted on social media platform X, was short and direct: “Famous last words.”

Elon Musk fired back at Wikipedia co-founder Jimmy Wales after the longtime online encyclopedia leader dismissed xAI’s new AI-powered alternative, Grokipedia, as a “ridiculous” idea that is bound to fail.
Musk’s response to Wales’ comments, which were posted on social media platform X, was short and direct: “Famous last words.”
Wales made the comments while answering questions about Wikipedia’s neutrality. According to Wales, Wikipedia prides itself on neutrality.
“One of our core values at Wikipedia is neutrality. A neutral point of view is non-negotiable. It’s in the community, unquestioned… The idea that we’ve become somehow ‘Wokepidea’ is just not true,” Wales said.
When asked about potential competition from Grokipedia, Wales downplayed the situation. “There is no competition. I don’t know if anyone uses Grokipedia. I think it is a ridiculous idea that will never work,” Wales wrote.
After Grokipedia went live, Larry Sanger, also a co-founder of Wikipedia, wrote on X that his initial impression of the AI-powered Wikipedia alternative was “very OK.”
“My initial impression, looking at my own article and poking around here and there, is that Grokipedia is very OK. The jury’s still out as to whether it’s actually better than Wikipedia. But at this point I would have to say ‘maybe!’” Sanger stated.
Musk responded to Sanger’s assessment by saying it was “accurate.” In a separate post, he added that even in its V0.1 form, Grokipedia was already better than Wikipedia.
During a past appearance on the Tucker Carlson Show, Sanger argued that Wikipedia has drifted from its original vision, citing concerns about how its “Reliable sources/Perennial sources” framework categorizes publications by perceived credibility. As per Sanger, Wikipedia’s “Reliable sources/Perennial sources” list leans heavily left, with conservative publications getting effectively blacklisted in favor of their more liberal counterparts.
As of writing, Grokipedia has reportedly surpassed 80% of English Wikipedia’s article count.










