

News
SpaceX’s Starship to spar with Blue Origin for NASA Moon landing contracts
On November 18th, NASA announced that it had added commercial Moon lander offerings from SpaceX, Blue Origin, Sierra Nevada Corporation, and others to a pool of companies that will be able to compete to affordably deliver cargo to the surface of the Moon. With this latest addition of landers, competition could get very interesting, very quickly.
In November 2018, NASA revealed a big step forward in its plans to kickstart robotic exploration and utilization of the Moon, announcing nine new partners in its Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) initiative. Designed first and foremost to encourage the commercial development of unprecedentedly affordable Moon landers, the program’s first nine partners included Lockheed Martin, Astrobotic, Intuitive Machines, Masten Space, Orbit Beyond, and several others.
In May 2019, NASA announced the next step, contracting with three of those nine aforementioned providers to bring their proposed Moon landers to fruition and attempt their first lunar landings. Orbit Beyond dropped out shortly after but Astrobotic and Intuitive Machines continue to work towards that goal and aim to attempt the first Moon landings with their respective Peregrine and Nova-C spacecraft no earlier than (NET) July 2021. Intuitive Machines has contracted a SpaceX Falcon 9 for its first Nova-C Moon launch, while Astrobotic side with the very first launch of United Launch Alliance’s (ULA) next-generation Vulcan rocket.
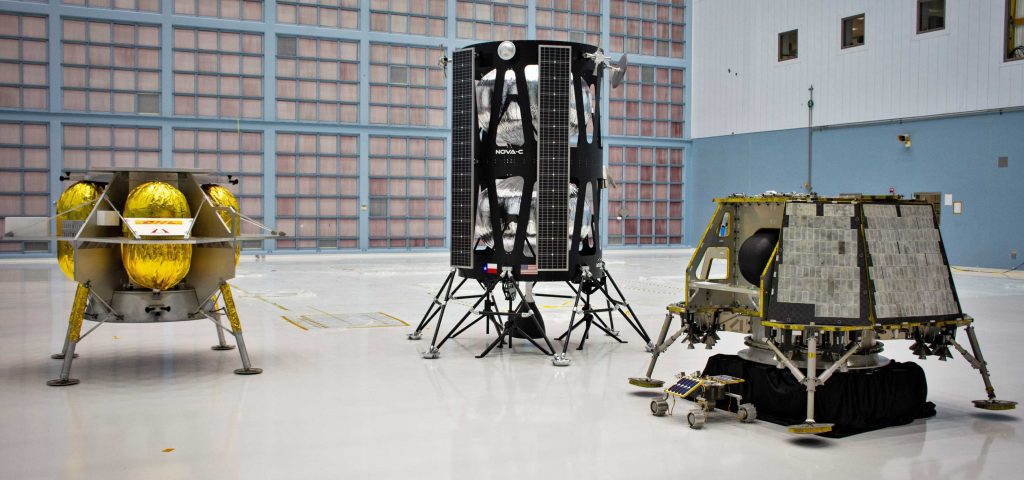

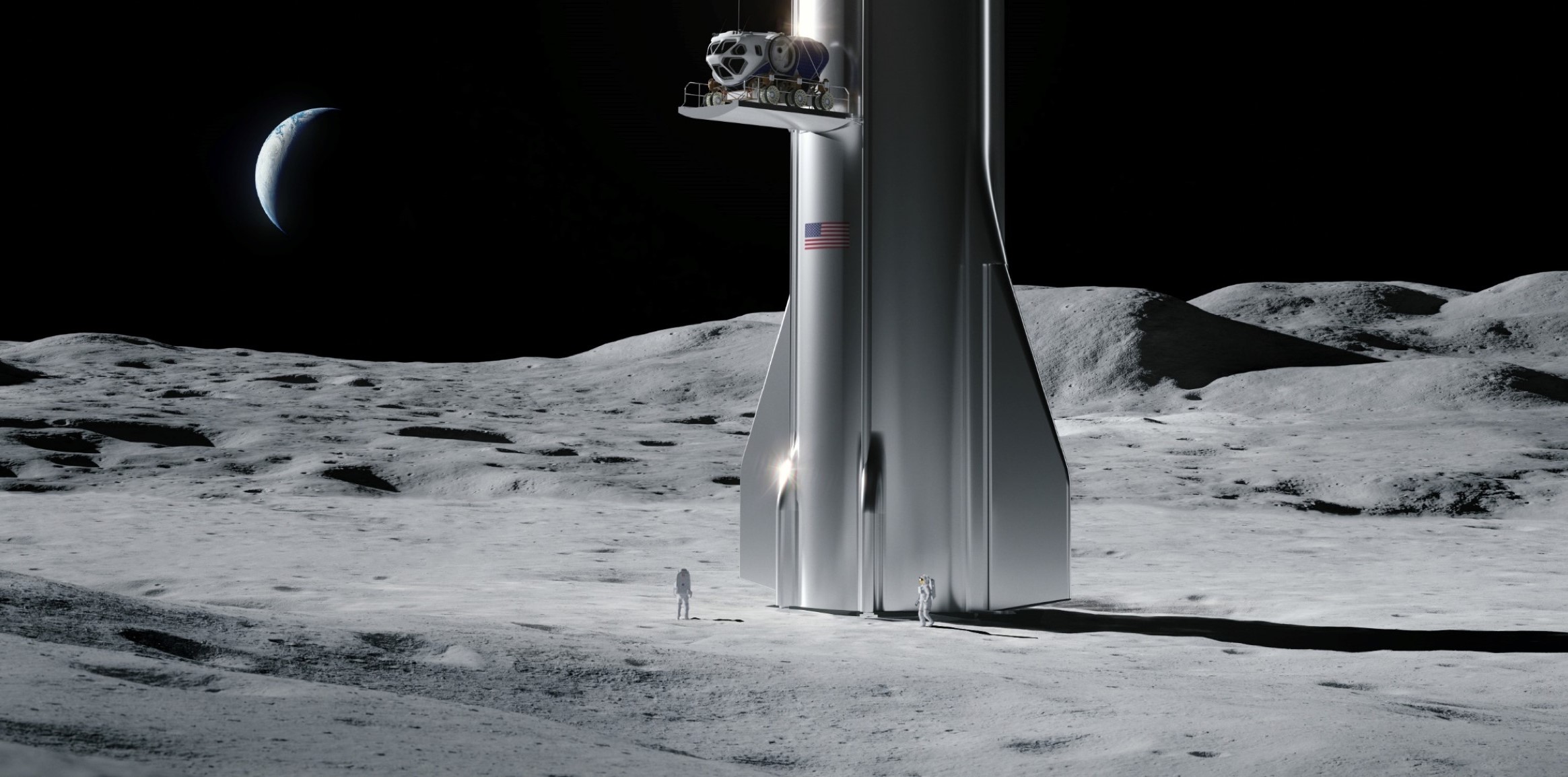
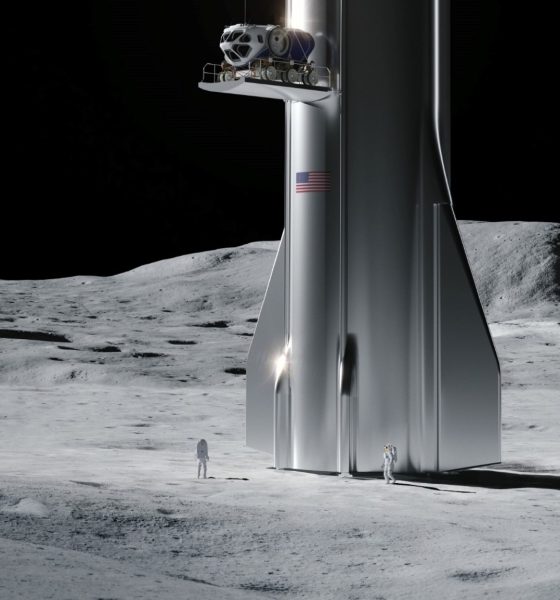
Generally speaking, the landers offered by the first nine CLPS partners were on the smaller side of the spectrum, capable of delivering around 50-100 kg (100-200 lb) of useful cargo to the surface of the Moon with launch masses around 1500-3000 kg (3300-6600 lb). On November 18th, NASA announced that a second group of partners would be added to the competitive ‘pool’ of CLPS-eligible Moon landers, all of which can technically compete to land a range of NASA payloads on the Moon. The new five are Ceres Robotics, Tyvak Nano-Satellite Systems, Sierra Nevada Corporation, Blue Origin, and SpaceX.
Next to nothing is known about Tyvak’s or Ceres Robotics’ apparently proposed landers, but a render of SNC’s Moon lander concept shares some obvious similarities with its Dream Chaser spacecraft and expendable power and propulsion module, implying that it’s likely on the larger side. Blue Origin and SpaceX, of course, proposed their Blue Moon and Starship spacecraft.
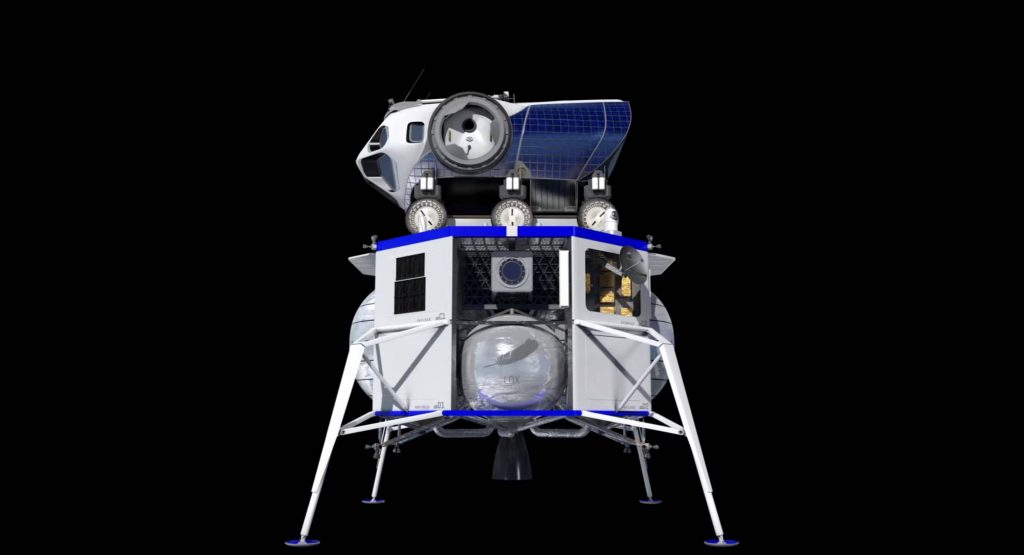


As a 100%-speculative guess, Ceres and Tyvak’s landers are likely in the same ~100 kg-class range as the nine CLPS providers selected before it, while Sierra Nevada’s lander concept is probably closer to 500 kg (1100 lb). According to Blue Origin, it’s recently-updated Blue Moon lander is designed to deliver up to 4500 kg (9900 lb) to the lunar surface and is expected to attempt its first Moon landing no earlier than 2024.
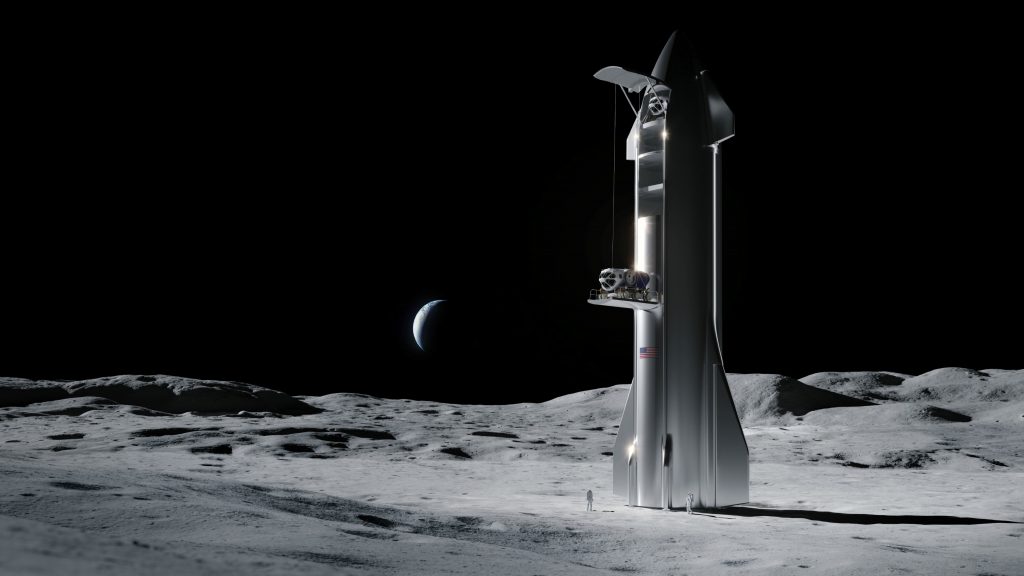
Unsurprisingly, SpaceX’s Starship blows all 13 other lander proposals out of the water and, in the context of the CLPS program, is a bit like bringing a Gatling gun to a paintball match. According to SpaceX, a fully-refueled Starship should be able to land 100 metric tons (220,000 lb) of cargo on the Moon, although it’s unclear if that would allow the Starship to return to Earth.
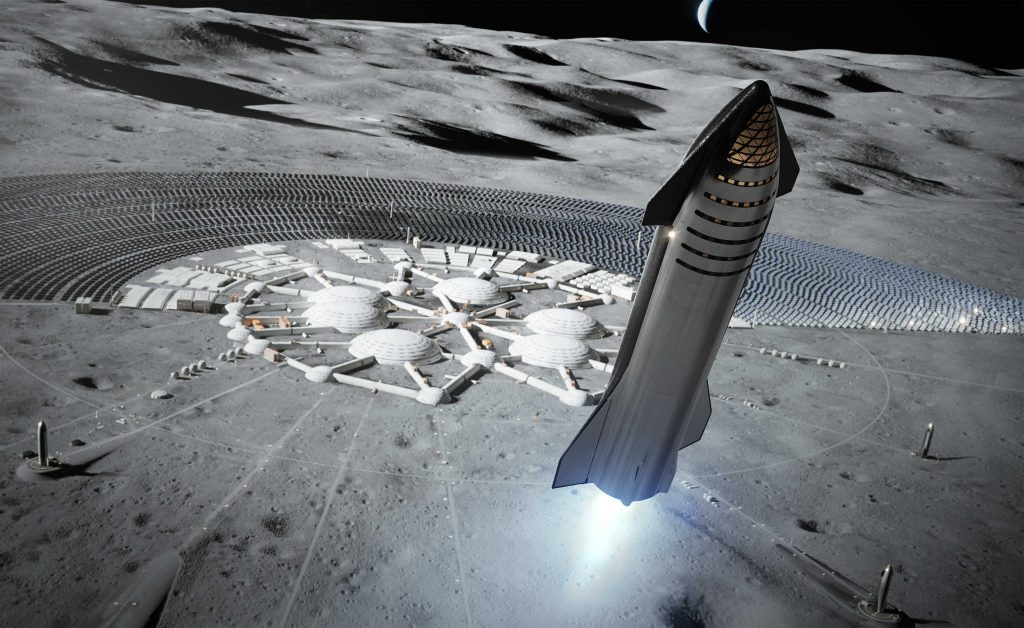
In simpler terms, there is just no chance whatsoever that the practical scope of NASA’s CLPS program could possibly warrant more than a few metric tons delivered to the surface of the Moon. NASA as a whole doesn’t have the budget needed to build useful several-dozen-ton spacecraft or experiments, let alone CLPS. In that sense, the real question to ask is what could Starship manage if the useful payloads it needs to deliver are no more than a few metric tons?
Assuming SpaceX’s technical know-how is mature enough to allow Starship to preserve cryogenic propellant for weeks or months after launch, it’s entirely conceivable that a Moon launch with, say, 10 tons of cargo could be achieved with just one or two in-orbit refuelings, all while leaving that Starship enough margin to safely return to Earth. Given that NASA awarded Intuitive Machines and Astrobotic approximately $80M apiece to land 50-100 kg on the Moon, it’s far too easy to imagine SpaceX quoting a similar price to deliver 10+ tons to the Moon by enabling full Starship reuse.
All things considered, politics still looms in the distance and there is just as much of a chance that SpaceX (and maybe even Blue Origin) will be passed over by CLPS when the time comes to award the next round of Moon delivery contracts. Still, the odds of something far out of the ordinary happening are much higher with a program like CLPS. Stay tuned!
Check out Teslarati’s Marketplace! We offer Tesla accessories, including for the Tesla Cybertruck and Tesla Model 3.

News
Lucid unveils Lunar Robotaxi in bid to challenge Tesla’s Cybercab in the autonomous ride hailing race
Lucid’s Lunar robotaxi is gunning for Tesla’s Cybercab in the autonomous ride hailing race
![Lucid Lunar robotaxi concept [Credit: Rendering by TESLARATI]](https://www.teslarati.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/03/lucid-lunar-robotaxi-concept-teslarati-rendering.jpg)
Lucid Group pulled back the curtain on its purpose-built autonomous robotaxi platform dubbed the Lunar Concept. Announced at its New York investor day event, Lunar is arguably the company’s most ambitious concept yet, and a direct line of sight toward the autonomous ride haling market that Tesla looks to control.
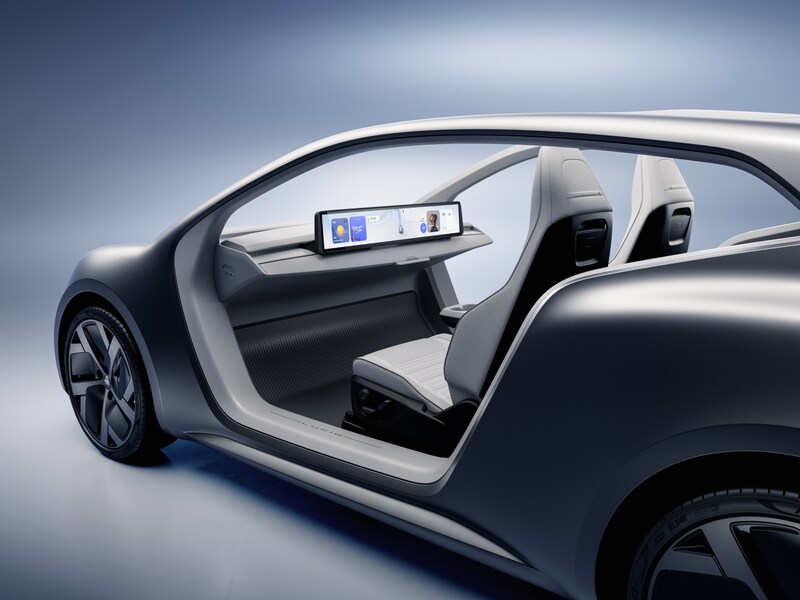

At Lucid Investor Day 2026, the company introduced Lunar, a purpose-built robotaxi concept based on the Midsize platform.
A comparison to Tesla’s Cybercab is unavoidable. The concept of a Tesla robotaxi was first introduced by Elon Musk back in April 2019 during an event dubbed “Autonomy Day,” where he envisioned a network of self-driving Tesla vehicles transporting passengers while not in use by their owners. That vision took another major step in October 2024 when, Musk unveiled the Cybercab at the Tesla “We, Robot” event held at Warner Bros. Studios in Burbank, California, where 20 concept Cybercabs autonomously drove around the studio lot giving rides to attendees.
Fast forward to today, and Tesla’s ambitions are finally materializing, but not without friction. As we recently reported, the Cybercab is being spotted with increasing frequency on public roads and across the grounds of Gigafactory Texas, suggesting that the company’s road testing and validation program is ramping meaningfully ahead of mass production. Tesla already operates a small scale robotaxi service in Austin using supervised Model Ys, but the Cybercab is designed from the ground up for high-volume, low-cost production, with Musk stating an eventual goal of producing one vehicle every 10 seconds.
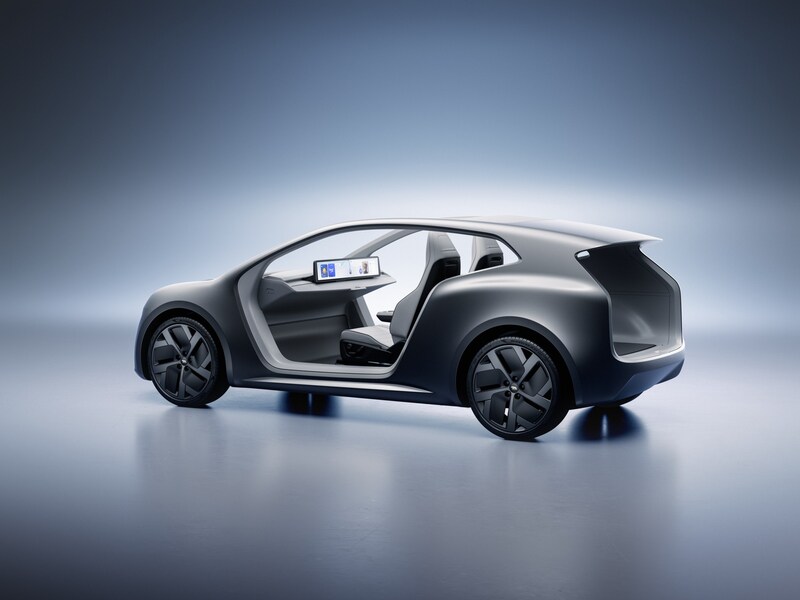

At Lucid Investor Day 2026, the company introduced Lunar, a purpose-built robotaxi concept based on the Midsize platform.
Into this landscape steps Lucid’s Lunar. Built on the company’s all-new Midsize EV platform, which will also underpin consumer SUVs starting below $50,000. The Lunar mirrors the Cybercab’s core philosophy of having two seats, no driver controls, and a focus on fleet economics. The platform introduces Lucid’s redesigned Atlas electric drive unit, engineered to be smaller, lighter, and cheaper to manufacture at scale.
Unlike Tesla’s strategy of building its own ride hailing network from scratch, Lucid is partnering with Uber. The companies are said to be in advanced discussions to deploy Midsize platform vehicles at large scale, with Uber CEO Dara Khosrowshahi publicly backing Lucid’s engineering credentials and autonomous-ready architecture.
In the investor day event, Lucid also outlined a recurring software revenue model, with an in-vehicle AI assistant and monthly autonomous driving subscriptions priced between $69 and $199. This can be seen as a nod to the software revenue stream that Tesla has long championed with its Full Self-Driving subscription.
Tesla’s Cybercab is targeting a price point below $30k and with operating costs as low as 20 cents per mile. But with regulatory hurdles still ahead, the window for competition is open. Lucid’s Lunar may not have a launch date yet, but it arrives at a pivotal moment, and when the robotaxi race is no longer viewed as hypothetical. Rather, every serious EV player needs to come to bat on the same plate that Tesla has had countless practice swings on over the last seven years.
Elon Musk
Brazil Supreme Court orders Elon Musk and X investigation closed
The decision was issued by Supreme Court Justice Alexandre de Moraes following a recommendation from Brazil’s Prosecutor-General Paulo Gonet.

Brazil’s Supreme Federal Court has ordered the closure of an investigation involving Elon Musk and social media platform X. The inquiry had been pending for about two years and examined whether the platform was used to coordinate attacks against members of the judiciary.
The decision was issued by Supreme Court Justice Alexandre de Moraes following a recommendation from Brazil’s Prosecutor-General Paulo Gonet.
According to a report from Agencia Brasil, the investigation conducted by the Federal Police did not find evidence that X deliberately attempted to attack the judiciary or circumvent court orders.
Prosecutor-General Paulo Gonet concluded that the irregularities identified during the probe did not indicate fraudulent intent.
Justice Moraes accepted the prosecutor’s recommendation and ruled that the investigation should be closed. Under the ruling, the case will remain closed unless new evidence emerges.
The inquiry stemmed from concerns that content on X may have enabled online attacks against Supreme Court justices or violated rulings requiring the suspension of certain accounts under investigation.
Justice Moraes had previously taken several enforcement actions related to the platform during the broader dispute involving social media regulation in Brazil.
These included ordering a nationwide block of the platform, freezing Starlink accounts, and imposing fines on X totaling about $5.2 million. Authorities also froze financial assets linked to X and SpaceX through Starlink to collect unpaid penalties and seized roughly $3.3 million from the companies’ accounts.
Moraes also imposed daily fines of up to R$5 million, about $920,000, for alleged evasion of the X ban and established penalties of R$50,000 per day for VPN users who attempted to bypass the restriction.
Brazil remains an important market for X, with roughly 17 million users, making it one of the platform’s larger user bases globally.
The country is also a major market for Starlink, SpaceX’s satellite internet service, which has surpassed one million subscribers in Brazil.
Elon Musk
FCC chair criticizes Amazon over opposition to SpaceX satellite plan
Carr made the remarks in a post on social media platform X.

U.S. Federal Communications Commission (FCC) Chairman Brendan Carr criticized Amazon after the company opposed SpaceX’s proposal to launch a large satellite constellation that could function as an orbital data center network.
Carr made the remarks in a post on social media platform X.
Amazon recently urged the FCC to reject SpaceX’s application to deploy a constellation of up to 1 million low Earth orbit satellites that could serve as artificial intelligence data centers in space.
The company described the proposal as a “lofty ambition rather than a real plan,” arguing that SpaceX had not provided sufficient details about how the system would operate.
Carr responded by pointing to Amazon’s own satellite deployment progress.
“Amazon should focus on the fact that it will fall roughly 1,000 satellites short of meeting its upcoming deployment milestone, rather than spending their time and resources filing petitions against companies that are putting thousands of satellites in orbit,” Carr wrote on X.
Amazon has declined to comment on the statement.
Amazon has been working to deploy its Project Kuiper satellite network, which is intended to compete with SpaceX’s Starlink service. The company has invested more than $10 billion in the program and has launched more than 200 satellites since April of last year.
Amazon has also asked the FCC for a 24-month extension, until July 2028, to meet a requirement to deploy roughly 1,600 satellites by July 2026, as noted in a CNBC report.
SpaceX’s Starlink network currently has nearly 10,000 satellites in orbit and serves roughly 10 million customers. The FCC has also authorized SpaceX to deploy 7,500 additional satellites as the company continues expanding its global satellite internet network.
![Lucid Lunar robotaxi concept [Credit: Rendering by TESLARATI]](https://www.teslarati.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/03/lucid-lunar-robotaxi-concept-teslarati-rendering-80x80.jpg)







