

News
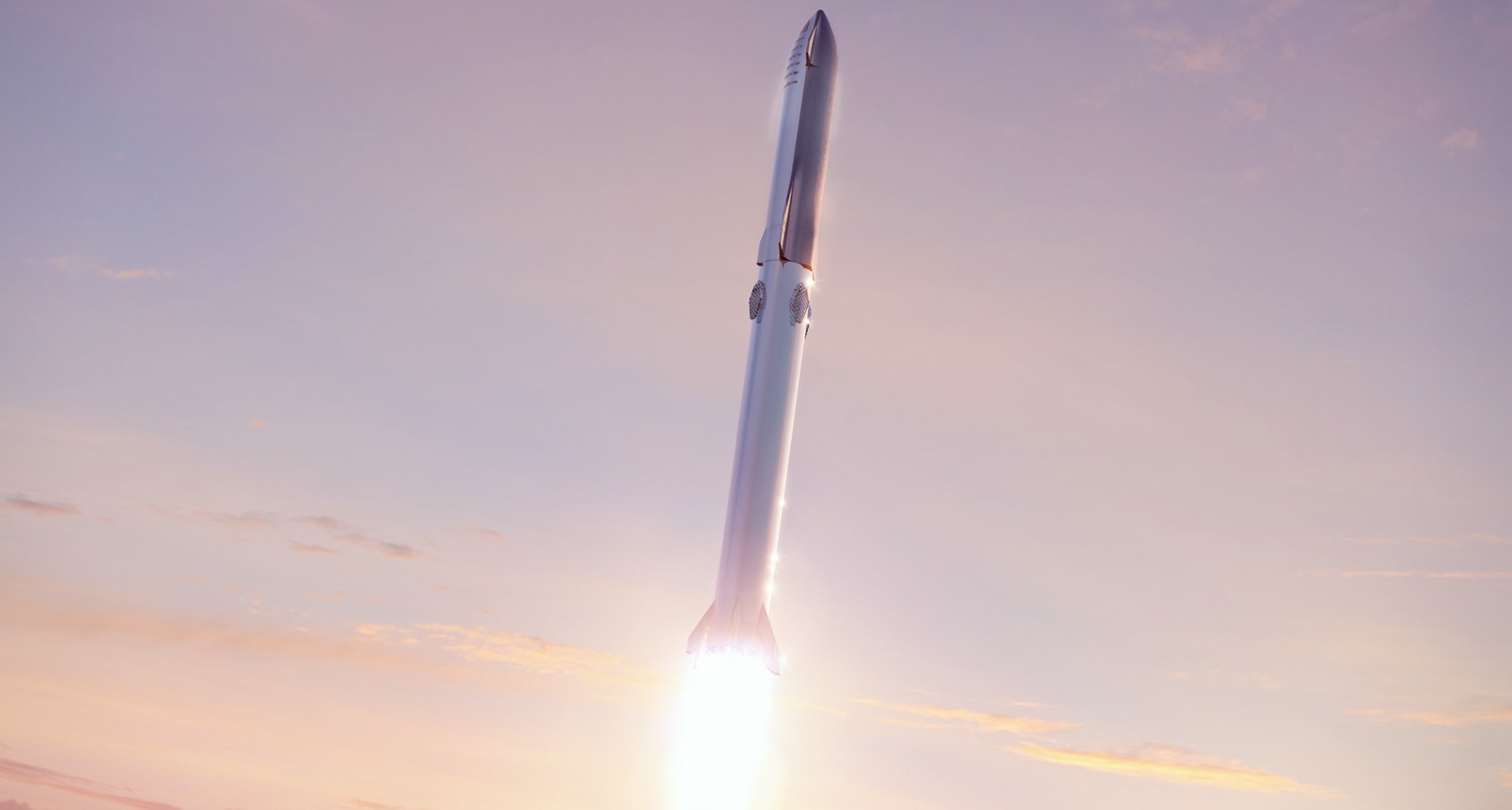
SpaceX to replace Falcon 9’s titanium grid fins with steel on Starship’s Super Heavy booster
Following a question on Twitter about how SpaceX intends to manufacture the truly massive grid fins shown in renders of Starship’s Super Heavy booster, CEO Elon Musk revealed that SpaceX will build them out of welded steel.
For the first several years of Falcon 9 and Falcon Heavy booster recovery operations, SpaceX built grid fins – used for maneuvering the rockets at high speeds – out of aluminum. With Falcon 9 Block 5, aluminum grid fins were phased out entirely in favor of larger titanium fins, necessitated by exceptionally high-speed reentries that nearly melted through the aluminum fins on several occasions. Now, SpaceX wants to move from titanium to steel fins for its next-generation Starship launch vehicle.
Welded steel— Elon Musk (@elonmusk) October 3, 2019
In response to the Twitter user’s question, Musk simply stated that Super Heavy’s grid fins would be manufactured out of “welded steel”, certainly keeping with the CEO’s now well-known love for the material. In October 2018, Musk finally managed to convince most of the senior engineers reporting to him that – despite years of work and full-scale testing – SpaceX needed to radically redesign Starship.

Prior to this radical change, SpaceX had spent at least 2-3 years on a Starship design (formerly Big F_____ Spaceship; BFS) made almost entirely out of carbon fiber composites, an extremely lightweight material that can be optimized for high strength. However, as Musk ultimately concluded in late 2018, although carbon composites are undeniably light and strong (optimal for spaceflight), they have extremely low heat tolerance and can react violently with supercooled liquid oxygen. Built almost entirely out of aluminum alloys with similarly low melting points, Falcon 9 has also struggled with the challenges posed by material choices, made far more difficult by the need to recover and reuse orbital-class rocket stages.
Musk ultimately decided that redesigning Starship with steel (alloys with particularly high melting points and good strength) was the right way to go. According to Musk, the high-quality carbon fiber composites SpaceX was originally pursuing cost something like $130,000 per metric ton, translating to a truly gobsmacking cost – accounting for unavoidable wastage – of $400M-$500M or more just to buy the materials needed to build a single Starship and Super Heavy booster. Steel, on the other hand, is quite literally 50 times cheaper, costing SpaceX around $2500 per ton, or as little as $10M in structural materials for each ship/booster pair.

Man of Stainless Steel
Speaking at a September 28th presentation on the 2019 status of Starship’s design, CEO Elon Musk couldn’t praise his decision to move to stainless steel enough, describing it as likely being the single best design decision he has ever made. It remains to be seen if the eccentric self-taught engineer’s decision was the correct one, but the progress SpaceX has made in just 10-11 months is undeniable. SpaceX has gone from a nearly blank slate to Starhopper’s 150m (500ft) test flight in ~6 months and gone from nothing to Starship Mk1 in another 6 or so months.
According to Musk, the properties of stainless steel – mainly a high melting point/working temperature and a tendency to strengthen at cryogenic temperatures – mean that the relatively heavy material is able to produce a launch vehicle that could eventually be far lighter and higher-performance than one made with carbon composites (BFR) or aluminum alloys (Falcon 9). Thanks to those properties, Starship/Super Heavy will become much stronger when filled with cold propellant and will also require little to no external heat shielding on its leeward half, whereas a reusable Al/composite rocket would require major thermal protection on nearly all exposed surfaces.
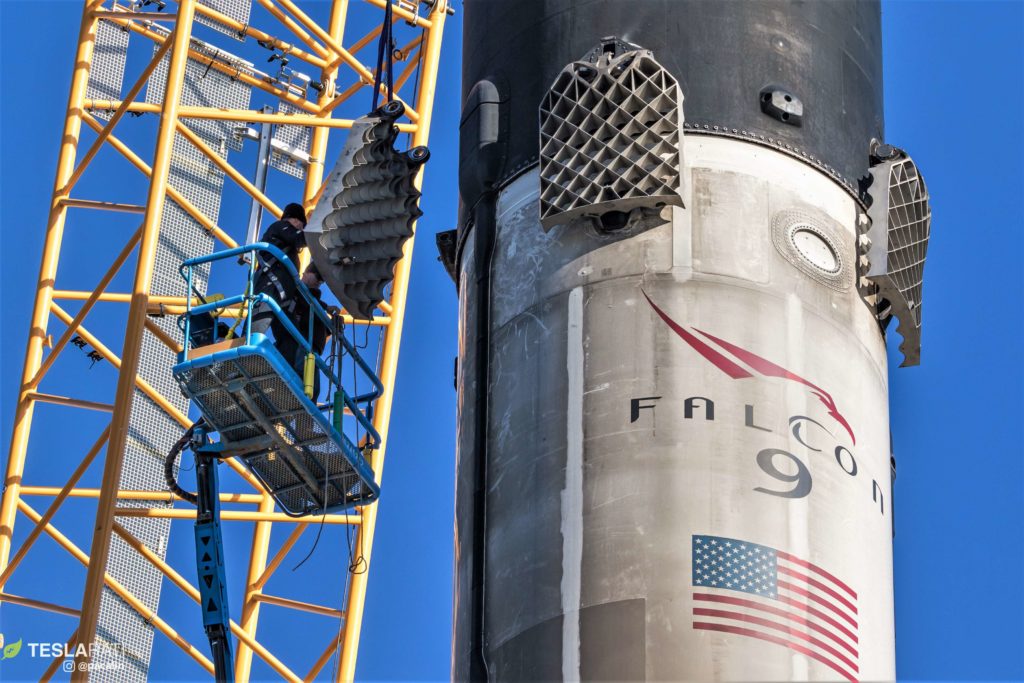

As part of the move to remove any ultra-expensive nonessential materials from the designs of Starship and Super Heavy, Musk has apparently also turned his gaze on the booster’s grid fins. As described at the top of this article, SpaceX replaced Falcon 9’s aluminum grid fins with titanium fins, requiring the company to create the largest single-piece titanium casting in the world. Musk has repeatedly indicated that each grid fin is extremely expensive.
In light of their expense, Musk (or SpaceX) has seemingly decided that future (larger?) SpaceX rockets will try to avoid large, titanium castings. Super Heavy nevertheless still needs massive grid fins: official renders published by SpaceX last month revealed a new diamond shape for the booster’s fins, and Musk later took to Twitter to reveal that they would be made out of welded steel instead of titanium.
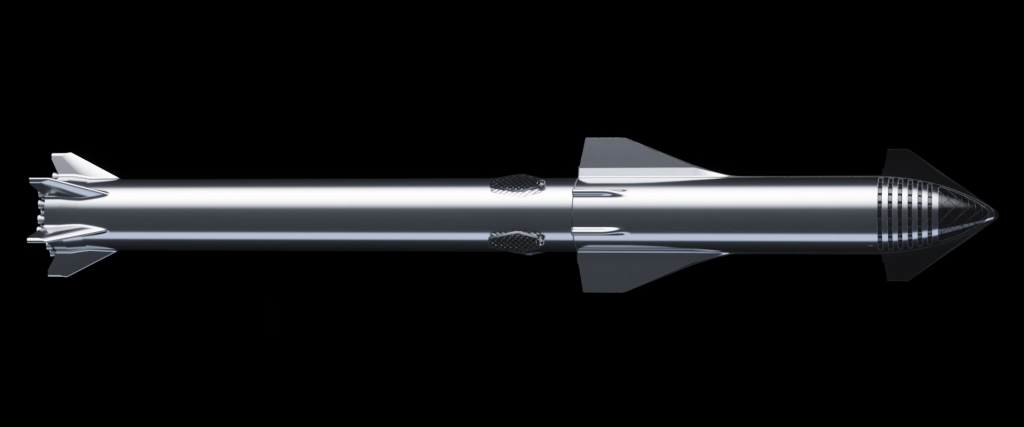
Based on SpaceX’s official 2019 Super Heavy renders, the booster’s grid fins measure approximately 7m by 3m (23 ft by 10 ft), dwarfing Falcon 9’s titanium fins (perhaps 2m by 1.2m) with something like 8-10 times the surface area. Although 301-series stainless steel has a melting point and heat capacity roughly 15% lower than Grade 5 titanium, its strength characteristics are otherwise similar, while also remaining mechanically functional at almost three times the working temperature of titanium (840C vs. 330C).
Most importantly, not only is 301 steel roughly 15-20 times cheaper than titanium, but the process of fabricating large steel components – particularly with welding instead of casting – is dramatically faster, easier, and cheaper than working with and forming titanium. With their reasonably similar properties and the increased size of Super Heavy, it’s likely that steel grid fins would exhibit little to no ablation during even the hottest atmospheric reentries, and it would nevertheless be extremely easy and cheap to either repair or replace fins in the unlikely event of damage.

Given just how quickly and relatively easily SpaceX has built full-scale flight hardware out of steel and assuming there are no technical showstoppers caused by changing scales, it wouldn’t be surprising in the slightest to see SpaceX fabricate and test welded steel grid fins on Falcon 9 boosters in the near future.
Check out Teslarati’s Marketplace! We offer Tesla accessories, including for the Tesla Cybertruck and Tesla Model 3.

News
Tesla influencers argue company’s polarizing Full Self-Driving transfer decision
Tesla maintains it will honor transfers for orders with initial delivery windows before the deadline and offers full deposit refunds otherwise, citing longstanding fine print that the program is “subject to change at any time.”

Tesla’s decision to tighten its Full Self-Driving (FSD) transfer promotion has ignited fierce debate among owners and enthusiasts.
The company quietly updated its terms in late February 2026, changing the eligibility from “order by March 31, 2026” to “take delivery by March 31, 2026.”
What began as a flexible incentive to boost sales, allowing buyers to transfer their paid FSD (Supervised) to a new vehicle, now excludes many, particularly Cybertruck owners facing delivery delays into summer or later.
Tesla maintains it will honor transfers for orders with initial delivery windows before the deadline and offers full deposit refunds otherwise, citing longstanding fine print that the program is “subject to change at any time.”
The reversal has polarized the Tesla community, with accusations of a “bait-and-switch” clashing against defenses of corporate pragmatism. Many owners who placed orders under the original wording feel betrayed, especially as production backlogs and new unsupervised FSD rollout complicate timelines.
However, Tesla has allowed them to cancel their orders and receive a refund.
Critics of the decision argue that the change disadvantages loyal customers who helped fund FSD development, calling it poor communication and a revenue grab as Tesla pivots toward subscriptions.
Popular influencers have amplified the divide. Whole Mars Catalog struck a measured but firm tone, acknowledging the original “order by” language but emphasizing Tesla’s right to adjust terms. He has continued to defend Tesla in this particular issue:
Sad to see so many fans trashing Tesla with such extreme language.
LIARS!!! PATHETIC!!! And if you aren’t as furious and angry as they are they are you’re “worshipping” and saying “they can do no wrong”.
Let’s get real here. They’re not liars. They offered FSD transfer to us… https://t.co/3Ay7vGaVR6
— Whole Mars Catalog (@wholemars) March 3, 2026
He criticized extreme backlash as “dramatization” and “spoiled kids,” noting the unsupervised FSD era and broader sales challenges make blanket transfers financially risky. Whole Mars advocated for polite outreach to CEO Elon Musk over the issue.
Rather than “calling them out”, I would simply say “Hey Elon, really hoped to be able to do FSD transfer on my cybertruck but the terms changed. Would really appreciate if Tesla could extend this to everyone who ordered before the terms changes”
that would probably work
— Whole Mars Catalog (@wholemars) March 3, 2026
In a contrasting perspective, Dirty TesLA voiced sharper frustration, posting that blocking transfers feels “crazy” and distancing himself from “people that want to worship a corporation and say they can do no wrong.” His stance resonated with owners who view the policy flip as disrespectful to early adopters.
Popular Tesla influencer Sawyer Merritt captured the frustration felt by thousands. In a widely shared thread viewed over 700,000 times, Merritt detailed how pre-change Cybertruck orders now risk losing FSD eligibility unless their initial delivery window falls before March 31.
It’s not a contradiction, it’s a change in policy that Tesla just made an hour ago. I am trying to check if the change is retroactive to all existing orders, including Cybertruck AWD orders, because if it is, that sucks big time.
— Sawyer Merritt (@SawyerMerritt) February 28, 2026
The controversy underscores deeper tensions—between Tesla’s need for revenue discipline and owners’ expectations of goodwill. As FSD evolves toward unsupervised capability, the community remains split: some see the change as necessary business, others as a broken promise. Whether Tesla reconsiders under pressure or holds firm remains to be seen, but it does not appear they are planning to budge.
News
Tesla Semi’s latest adoptee will likely encourage more of the same
Public visibility matters. When shoppers see a trusted name like Ralph’s running clean, high-tech trucks on public roads, skepticism fades. Competitors such as Albertsons, which pre-ordered Semis years ago, and other chains chasing ESG targets now have proof that electric autonomy works in real-world grocery fleets.

The latest adoptee of the Tesla Semi will likely encourage more businesses in the same realm to adopt the all-electric Class 8 truck, as a new company utilizing the Semi has been spotted in Southern California.
A sleek, futuristic Tesla Semi truck branded for Ralph’s Supermarkets was spotted cruising a Los Angeles highway in a viral 13-second dashcam video posted March 2, by X user ChargePozitive.
Tesla Semi Truck in the wild pic.twitter.com/SnQY8ShMMJ
— ChargePozitive ⚡️➕ (@ChargePozitive) March 2, 2026
This sighting confirms Kroger’s March 2025 partnership with Tesla to deploy up to 500 autonomous electric Semis.
While the initial announcement targeted Midwest supply chains, the California appearance under the Ralph’s banner shows the program expanding to Kroger’s West Coast operations. Ralph’s, a staple for millions of Southern California shoppers, is now hauling groceries with the Semi, which has zero tailpipe emissions and claims up to 500 miles of range per charge.
Tesla Semi pricing revealed after company uncovers trim levels
The timing could not be better for sustainable logistics. Traditional trucking accounts for a massive share of retail emissions, but Tesla’s Semi slashes fuel and maintenance costs while leveraging full autonomy to ease driver shortages and improve safety.
Tesla’s expanding Megacharger network, including new sites along major freight corridors and partnerships like the recently-announced one with Pilot Travel Centers, is removing range anxiety and making nationwide scaling realistic. There’s still a long way to go, but things are moving in the right direction.
Public visibility matters. When shoppers see a trusted name like Ralph’s running clean, high-tech trucks on public roads, skepticism fades. Competitors such as Albertsons, which pre-ordered Semis years ago, and other chains chasing ESG targets now have proof that electric autonomy works in real-world grocery fleets.
PepsiCo’s successful pilots already demonstrated viability, and Ralph’s sighting adds retail credibility.
As Tesla ramps high-volume Semi production through 2026, this isn’t an isolated curiosity. Instead, it’s a catalyst. More grocers adopting the platform will accelerate industry-wide decarbonization, cut operating expenses, and deliver tangible environmental wins.
The future of sustainable supply chains is already on the highway, and Ralph’s just made it impossible to ignore.
Moving forward, Tesla hopes to expand the Semi program into other regions, including Europe, which CEO Elon Musk recently said is a total possibility next year.
Elon Musk
Tesla ramps Cybercab test manufacturing ahead of mass production
Tesla still has plans for volume production, which remains between four and eight weeks away, aligning with Musk’s statements that early ramps would be deliberately measured given the Cybercab’s novel architecture and full reliance on Tesla’s vision-based Full Self-Driving technology.
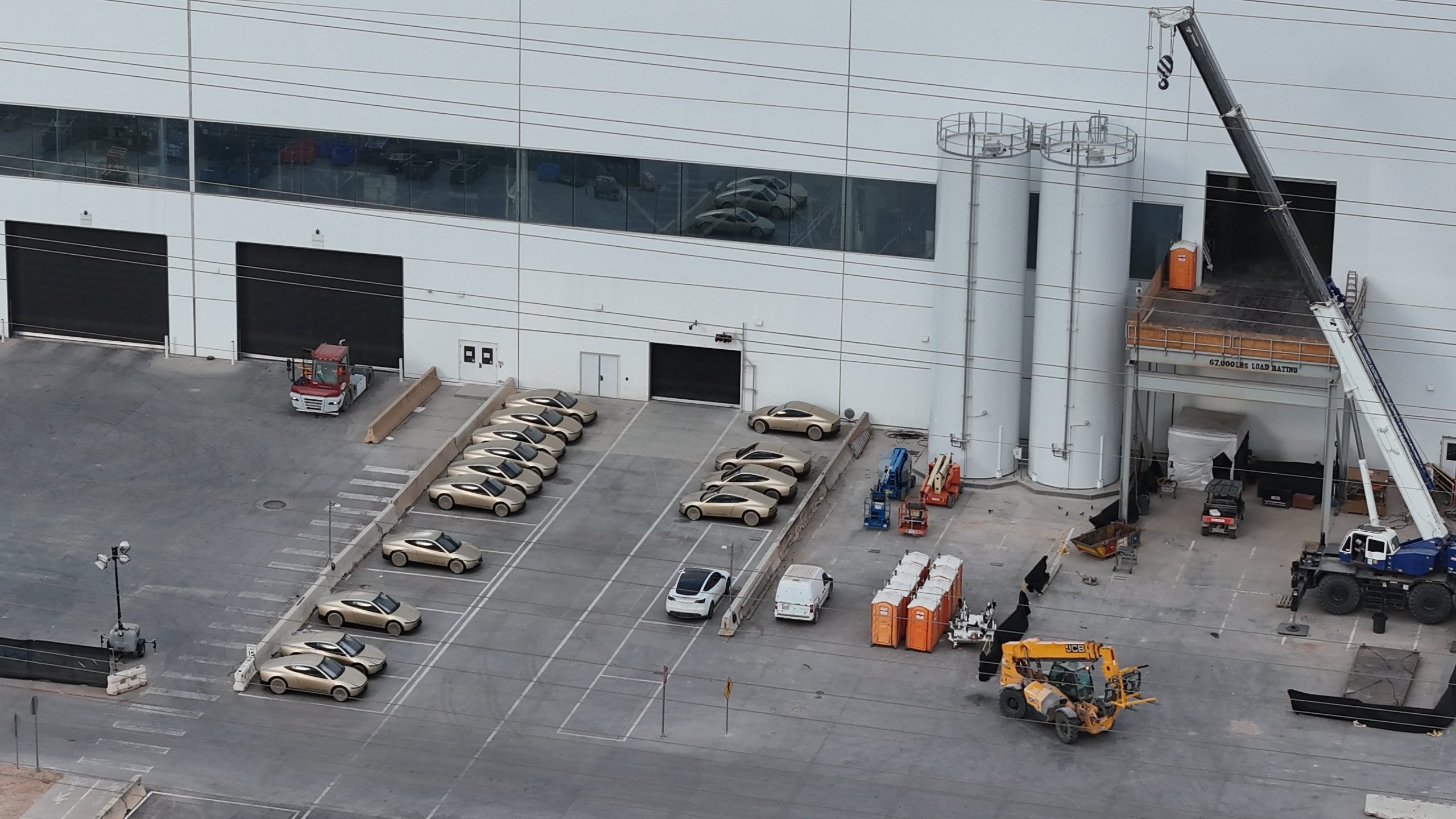

Tesla is seemingly ramping Cybercab test manufacturing ahead of mass production, which is scheduled to begin next month, the company said.
At Tesla’s Gigafactory Texas, production of the Cybercab, the company’s groundbreaking purpose-built Robotaxi vehicle, is accelerating markedly. Drone footage from Joe Tegtmeyer captured striking aerial footage today, revealing what appears to be the largest public sighting of Cyebrcabs to date.
A total of 25 units were observed by Tegtmeyer across the Gigafactory Texas property, marking a clear step-up in testing and validation activities as Tesla prepares for a broader output.
Tesla Cybercab production begins: The end of car ownership as we know it?
In the footage, 14 metallic gold Cybercabs were parked in a tight formation outside the factory exit, showcasing their sleek, autonomous-only design with no steering wheels, pedals, or traditional controls. Another 9 units sat at the crash testing facility, likely undergoing structural and safety validations, while two more appeared at the west end-of-line area for final checks.
Big day for Cybercab at Giga Texas today! Actually, yesterday to kick off March, the production line went into a higher volume & today we see 25 at three main locations, and there were several others I observed driving around too!
I think this may be the largest single grouping… pic.twitter.com/HZDMNv57lJ
— Joe Tegtmeyer 🚀 🤠🛸😎 (@JoeTegtmeyer) March 3, 2026
Tegtmeyer noted additional Cybercabs driving around the complex, hinting at active movement and real-world testing beyond static parking.
This surge follows the first production Cybercab rolling off the line in mid-February 2026, several weeks ahead of the originally anticipated April start.
That milestone, celebrated by Tesla employees and confirmed by CEO Elon Musk, kicked off low-volume builds on the dedicated “unboxed” manufacturing line, a modular process designed to slash costs, reduce factory footprint, and enable faster assembly compared to conventional methods.
Industry observers interpret the jump to dozens of visible units in early March as evidence that Tesla has transitioned into higher-volume test manufacturing.
Tesla still has plans for volume production, which remains between four and eight weeks away, aligning with Musk’s statements that early ramps would be deliberately measured given the Cybercab’s novel architecture and full reliance on Tesla’s vision-based Full Self-Driving technology.
The Cybercab, envisioned as a sub-$30,000 autonomous two-seater for robotaxi fleets, represents Tesla’s bold pivot toward scalable autonomy and robotics.
Tesla fans and enthusiasts on X praised the imagery, with many expressing excitement over the visible progress toward deployment. While challenges remain, including software maturity, regulatory hurdles, and supply chain scaling, the increased factory activity underscores Tesla’s momentum in turning the Cybercab vision into reality.
As Giga Texas continues expanding and refining the manufacturing process of the Cybercab, the coming months will prove to be a pivotal time in determining how quickly this revolutionary vehicle reaches roads in the U.S. and internationally.








