News
Tesla’s approach to battery technology keeps it ahead in the EV industry
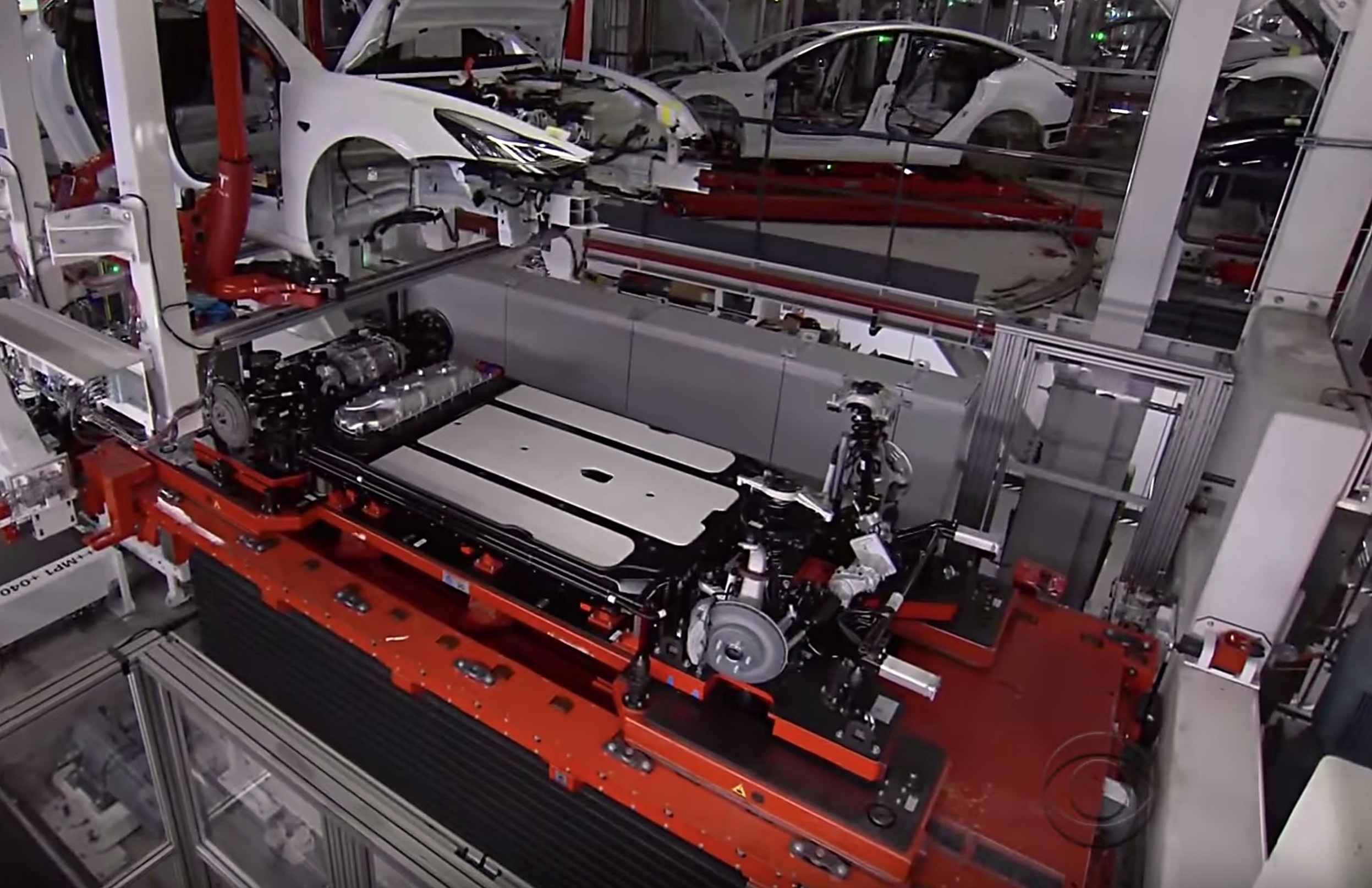
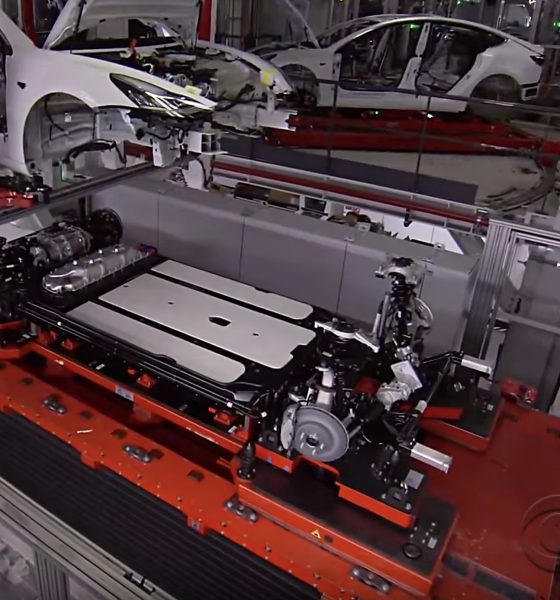
Tesla’s dominance in the growing electric vehicle (EV) industry is largely attributed to its unique approach to its battery technology. The engineering behind the all-electric car maker’s cylindrical cells speaks for itself in terms of the performance and range achieved, but in a recent interview with a battery technology researcher, a few things detailed about Tesla’s batteries stood out in particular.
Ravindra Kempaiah is a Ph.D. scholar at the University of Illinois Chicago focusing on advanced battery materials for his thesis. In his interview with Tesla owner and host of All Things EV, Sean Mitchell, Kempaiah explained lithium-ion technology in EVs and the primary issues faced in their development. Overall, the biggest challenge is balancing the three main components in battery production: energy density, cost, and cycle life. Increasing one area will significantly impact the other, and the ideal equation is always being sought after. For example, if you increase energy density for higher range and lower cost, the cycle life takes a major hit. If you increase density and life cycle, the battery alone can cost as much as $100k, as described by Kempaiah.
“We always want more range. We always want higher cycle life. We want our batteries to last 15-20 years and the car to go 500 miles, but this is a problem every battery scientist has faced for the last 30 years,” Kempaiah commented in the interview.
Tesla deals with the same balancing act as other battery-electric car makers; however, there are key factors which seem to have kept the company ahead in the industry.

First, Tesla’s choice of cylindrical cells sets it apart from every other electric vehicle on the market. This provides several advantages that drive performance, flexibility, and cost control. Notably, Rivian is also using cylindrical cells, although their vehicles are not yet under production.
Out of the three types of cells available (cylindrical, prismatic, and pouch cells), cylindrical is the most cost-effective to produce. Namely, the cost per kWh is lower in cylindrical cells versus other types. The metallic jacket around the 18650 and 2170 cylindrical cells used in the Tesla Model S/X and Model 3, respectively, acts as scaffolding and provides structural rigidity to the battery. Additionally, in high powered situations, current draw and distribution of power is over the entirety of the battery pack instead of concentrated in a certain section, according to Kempaiah.
Second, Tesla uses a liquid-cooled thermal management system to manage battery temperatures whereas other automakers take a more economical air cooling approach. By adjusting the temperature of the battery pack, Tesla is able to ensure that cells are operating in their most efficient and optimal states, thereby maximizing battery longevity as well as performance. While reducing cost is an important factor in accelerating the growth of the electric vehicle market, Tesla’s investment in thermal management technology provides an upside for owners who may be looking for longevity and long-term affordability of their cars.

Third, Tesla has actively sought to limit the amount of cobalt it uses in its batteries and already uses less of the element than other companies in the Model 3 batteries. The scarcity of cobalt and its mining sources have subjected it to socioeconomic situations that are more than problematic in the United States, i.e., child labor and similar abuses are widespread in its sourcing. With this in mind, Tesla has been working on the question, “Is cobalt really needed?”
Cobalt is used as a cathode in battery technology, and out of all cathode materials available, it has the highest cost both fiscally and politically. Current consensus on battery technology says that without cobalt, the structural integrity and cycle life in batteries is compromised, as described in the interview. However, some recent scientific literature was cited by Kempaiah that indicated higher nickel content limited the impact of cobalt on batteries, possibly removing the need to use it at all. Nickel is more widely available across the globe, which keeps its cost down and mitigates the socioeconomic impacts often associated with resource mining operations. Overall, the discussion between Mitchell and Kempaiah indicated that Tesla can probably go cobalt-free soon, making it less vulnerable to the cobalt industry.
Finally, Tesla takes great care to educate its customers about proper battery maintenance, especially with regard to the negative impact of bad charging habits. Specifically, keeping an electric car battery charged at 100% for long periods degrades the battery very quickly, while keeping charging states within an optimal range will give it a long life. Tesla makes it a point to communicate to customers the importance of battery health on their overall ownership experience and value of their purchase.
When asked for his opinion by Mitchell, Kempaiah attributed the lack of education by other brands as a disconnect between engineering teams and marketing teams. While battery “best practices” are provided to EV customers by all manufacturers, the importance of communicating the true impact of bad charging habits may not be emphasized enough to be included as prominently as it should.
In summary, Tesla is constantly developing the technology in its vehicles, and its particular attention to its batteries looks to have given the company a significant advantage over its competitors. Perhaps other automakers will take a few tips from Tesla in the future, even if it’s as limited as improving communications with customers.
Watch Sean Mitchell’s full interview with Ravindra Kempaiah below:

News
Tesla Robotaxi ride-hailing without a Safety Monitor proves to be difficult

Tesla Robotaxi ride-hailing without a Safety Monitor is proving to be a difficult task, according to some riders who made the journey to Austin to attempt to ride in one of its vehicles that has zero supervision.
Last week, Tesla officially removed Safety Monitors from some — not all — of its Robotaxi vehicles in Austin, Texas, answering skeptics who said the vehicles still needed supervision to operate safely and efficiently.
BREAKING: Tesla launches public Robotaxi rides in Austin with no Safety Monitor
Tesla aimed to remove Safety Monitors before the end of 2025, and it did, but only to company employees. It made the move last week to open the rides to the public, just a couple of weeks late to its original goal, but the accomplishment was impressive, nonetheless.
However, the small number of Robotaxis that are operating without Safety Monitors has proven difficult to hail for a ride. David Moss, who has gained notoriety recently as the person who has traveled over 10,000 miles in his Tesla on Full Self-Driving v14 without any interventions, made it to Austin last week.
He has tried to get a ride in a Safety Monitor-less Robotaxi for the better part of four days, and after 38 attempts, he still has yet to grab one:
Wow just wow!
It’s 8:30PM, 29° out ice storm hailing & Tesla Robotaxi service has turned back on!
Waymo is offline & vast majority of humans are home in the storm
Ride 38 was still supervised but by far most impressive yet pic.twitter.com/1aUnJkcYm8
— David Moss (@DavidMoss) January 25, 2026
Tesla said last week that it was rolling out a controlled test of the Safety Monitor-less Robotaxis. Ashok Elluswamy, who heads the AI program at Tesla, confirmed that the company was “starting with a few unsupervised vehicles mixed in with the broader Robotaxi fleet with Safety Monitors,” and that “the ratio will increase over time.”
This is a good strategy that prioritizes safety and keeps the company’s controlled rollout at the forefront of the Robotaxi rollout.
However, it will be interesting to see how quickly the company can scale these completely monitor-less rides. It has proven to be extremely difficult to get one, but that is understandable considering only a handful of the cars in the entire Austin fleet are operating with no supervision within the vehicle.
News
Tesla gives its biggest hint that Full Self-Driving in Europe is imminent

Tesla has given its biggest hint that Full Self-Driving in Europe is imminent, as a new feature seems to show that the company is preparing for frequent border crossings.
Tesla owner and influencer BLKMDL3, also known as Zack, recently took his Tesla to the border of California and Mexico at Tijuana, and at the international crossing, Full Self-Driving showed an interesting message: “Upcoming country border — FSD (Supervised) will become unavailable.”
FSD now shows a new message when approaching an international border crossing.
Stayed engaged the whole way as we crossed the border and worked great in Mexico! pic.twitter.com/bDzyLnyq0g
— Zack (@BLKMDL3) January 26, 2026
Due to regulatory approvals, once a Tesla operating on Full Self-Driving enters a new country, it is required to comply with the laws and regulations that are applicable to that territory. Even if legal, it seems Tesla will shut off FSD temporarily, confirming it is in a location where operation is approved.
This is something that will be extremely important in Europe, as crossing borders there is like crossing states in the U.S.; it’s pretty frequent compared to life in America, Canada, and Mexico.
Tesla has been working to get FSD approved in Europe for several years, and it has been getting close to being able to offer it to owners on the continent. However, it is still working through a lot of the red tape that is necessary for European regulators to approve use of the system on their continent.
This feature seems to be one that would be extremely useful in Europe, considering the fact that crossing borders into other countries is much more frequent than here in the U.S., and would cater to an area where approvals would differ.
Tesla has been testing FSD in Spain, France, England, and other European countries, and plans to continue expanding this effort. European owners have been fighting for a very long time to utilize the functionality, but the red tape has been the biggest bottleneck in the process.
Tesla Europe builds momentum with expanding FSD demos and regional launches
Tesla operates Full Self-Driving in the United States, China, Canada, Mexico, Puerto Rico, Australia, New Zealand, and South Korea.
Elon Musk
SpaceX Starship V3 gets launch date update from Elon Musk
The first flight of Starship Version 3 and its new Raptor V3 engines could happen as early as March.
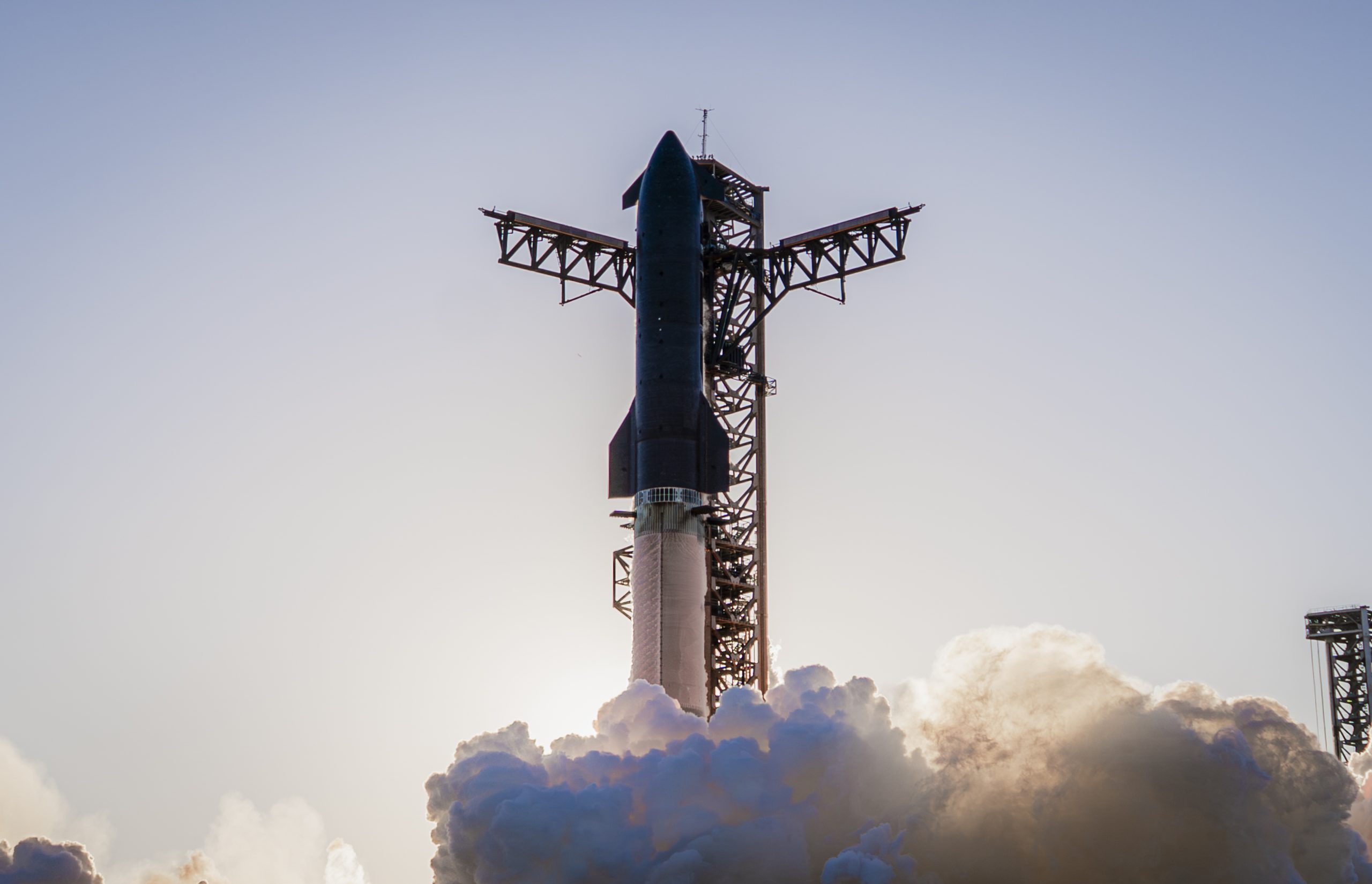

Elon Musk has announced that SpaceX’s next Starship launch, Flight 12, is expected in about six weeks. This suggests that the first flight of Starship Version 3 and its new Raptor V3 engines could happen as early as March.
In a post on X, Elon Musk stated that the next Starship launch is in six weeks. He accompanied his announcement with a photo that seemed to have been taken when Starship’s upper stage was just about to separate from the Super Heavy Booster. Musk did not state whether SpaceX will attempt to catch the Super Heavy Booster during the upcoming flight.
The upcoming flight will mark the debut of Starship V3. The upgraded design includes the new Raptor V3 engine, which is expected to have nearly twice the thrust of the original Raptor 1, at a fraction of the cost and with significantly reduced weight. The Starship V3 platform is also expected to be optimized for manufacturability.
The Starship V3 Flight 12 launch timeline comes as SpaceX pursues an aggressive development cadence for the fully reusable launch system. Previous iterations of Starship have racked up a mixed but notable string of test flights, including multiple integrated flight tests in 2025.
Interestingly enough, SpaceX has teased an aggressive timeframe for Starship V3’s first flight. Way back in late November, SpaceX noted on X that it will be aiming to launch Starship V3’s maiden flight in the first quarter of 2026. This was despite setbacks like a structural anomaly on the first V3 booster during ground testing.
“Starship’s twelfth flight test remains targeted for the first quarter of 2026,” the company wrote in its post on X.








