News
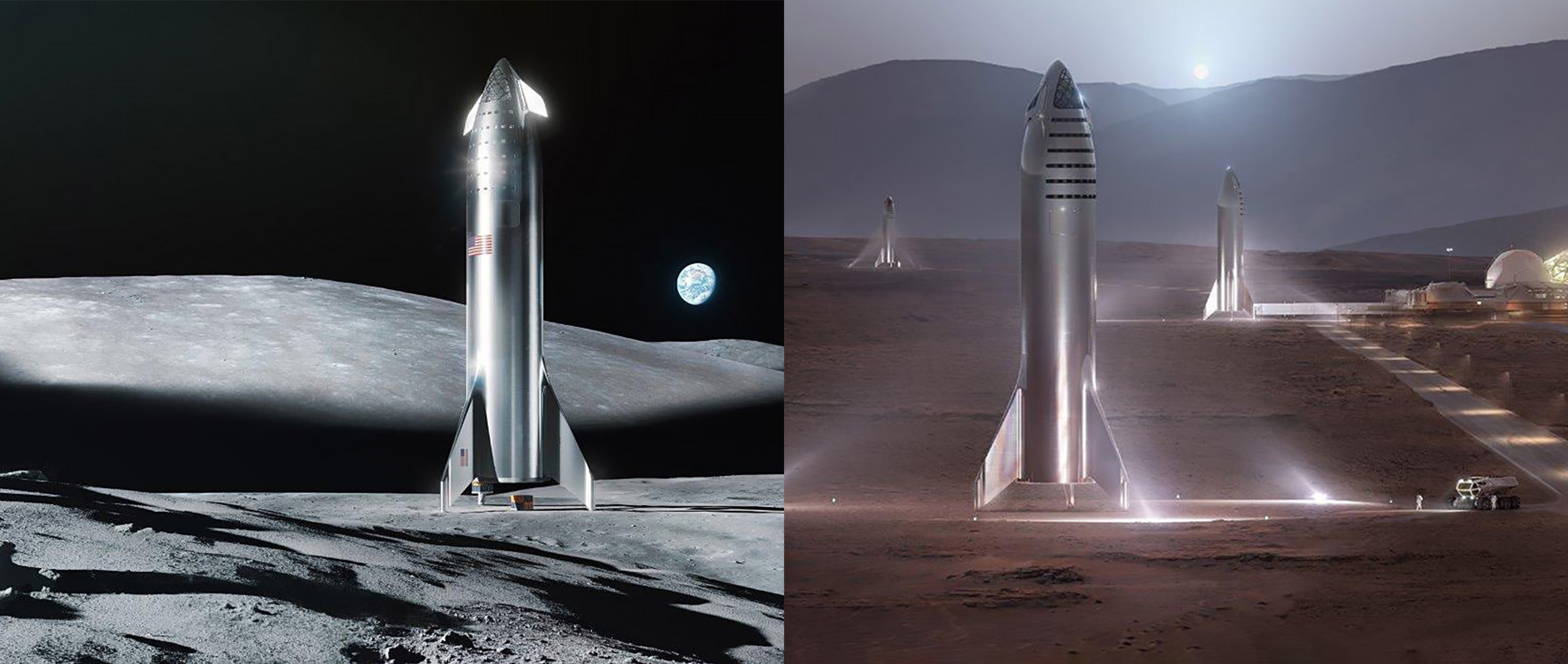
SpaceX’s Elon Musk says landing Starship on the Moon could be easier than convincing NASA
Speaking in an interview with TIME Magazine’s Jeffrey Kluger, SpaceX CEO Elon Musk telegraphed some clear, latent frustration with US space agency NASA, indicating that quite literally building Starship and landing it on the Moon could be easier than convincing NASA that the company is serious.
Although minor progress has been made in the last six or so months, NASA headquarters – for the most part – still effectively operates as if SpaceX’s next-generation launch vehicle plans do not exist, all while the agency is seriously considering other similarly unproven rockets with years of development remaining. In light of this frustrating inconsistency, Musk has taken to publicly acknowledging that developing, building, and launching Starship completely internally may be an easier (and faster) fight to win than attempting to convince NASA to assist in Starship development or even just be willing to use it as a launch option.
NASA assistance or support could come in any number of forms, ranging from a cost-sharing development contract, a developmental launch contract like the US Air Force’s STP-2 Falcon Heavy mission, or something as basic as publicly expressing support for the SpaceX program and a willingness to launch NASA payloads on it down the road. For now, the closest SpaceX has gotten to public NASA interest in and acknowledgment of Starship is an official Starship render posted by the Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC).
In a sign of just how unengaged NASA is, the closest SpaceX’s Starship/Super Heavy vehicle has gotten to an acknowledgment from NASA headquarters is quite literally having an outdated BFR render subtly included in a few slideshows and documents published less than two months ago (late May 2019).
Ironically, despite the fact that Starship – first and foremost – is designed to be a giant, human-rated reusable spacecraft nominally capable of carrying dozens of astronauts into space and back, the US military appears to have been far more receptive to Starship. This is despite the fact that a BFR-heavy bid may have cost SpaceX a development contract last year. Even with the challenges such an ambitious vehicle poses, the US Department of Defense is still interested in at least discussing potential use-cases and providing input that might influence SpaceX’s final design.
Speaking in September 2018, CEO Elon Musk indicated SpaceX’s BFR (now Starship/Super Heavy) program was likely to cost ~$5B – no less than $2B and no more than $10B. However, this answer – provided off the cuff as a response to a reporter’s question – was almost certainly directed at BFR prior to a radical move from carbon composite structures and tanks to stainless steel. Since then, Musk has made some radical claims about the potential of an efficient, stainless-steel rocket, indicating that it could actually cost less to build than Falcon 9 – a far smaller rocket with a fraction of the performance.
In other words, if the potentially low cost of the vehicle itself also translates to a low development cost, SpaceX could quite feasibly develop Starship/Super Heavy from scratch with nothing more than traditional investment rounds. In the first half of 2019 alone, SpaceX has raised more than $1B in funding through three separate rounds, all of which have been described by Musk and other executives as “oversubscribed” – the demand for SpaceX equity far outstrips supply.
“If it were to take longer to convince NASA and the authorities that we can do it versus just doing it, then [SpaceX] might just do it [ourselves]. It may literally be easier to just land Starship on the moon than try to convince NASA that we can.”
— Elon Musk, July 12th, 2019, via TIME Magazine
As such, unless NASA’s attitude undergoes rapid changes, SpaceX may simply leave the agency behind when it comes to space exploration beyond low Earth orbit. In the event that quite literally developing, building, and launching a giant, stainless steel rocket and spaceship is faster, more efficient, and less disruptive than trying to convince NASA to get its foot in the door, SpaceX might have to forge its own path. If SpaceX can raise enough funding to develop its next-generation rocket independently, what comes next is anyone’s guess.
Ultimately, Musk believes that SpaceX can make that Starship Moon landing happen as few as two years from now, with the first crewed landing potentially coming as few as one or two years after that. All told, this ambitious timeline would see SpaceX land humans on the Moon – perhaps entirely commercially – as early as 2022 or 2023.
Check out Teslarati’s Marketplace! We offer Tesla accessories, including for the Tesla Cybertruck and Tesla Model 3.

Elon Musk
Musk bankers looking to trim xAI debt after SpaceX merger: report
xAI has built up $18 billion in debt over the past few years, with some of this being attributed to the purchase of social media platform Twitter (now X) and the creation of the AI development company. A new financing deal would help trim some of the financial burden that is currently present ahead of the plan to take SpaceX public sometime this year.

Elon Musk’s bankers are looking to trim the debt that xAI has taken on over the past few years, following the company’s merger with SpaceX, a new report from Bloomberg says.
xAI has built up $18 billion in debt over the past few years, with some of this being attributed to the purchase of social media platform Twitter (now X) and the creation of the AI development company. Bankers are trying to create some kind of financing plan that would trim “some of the heavy interest costs” that come with the debt.
The financing deal would help trim some of the financial burden that is currently present ahead of the plan to take SpaceX public sometime this year. Musk has essentially confirmed that SpaceX would be heading toward an IPO last month.
The report indicates that Morgan Stanley is expected to take the leading role in any financing plan, citing people familiar with the matter. Morgan Stanley, along with Goldman Sachs, Bank of America, and JPMorgan Chase & Co., are all expected to be in the lineup of banks leading SpaceX’s potential IPO.
Since Musk acquired X, he has also had what Bloomberg says is a “mixed track record with debt markets.” Since purchasing X a few years ago with a $12.5 billion financing package, X pays “tens of millions in interest payments every month.”
That debt is held by Bank of America, Barclays, Mitsubishi, UFJ Financial, BNP Paribas SA, Mizuho, and Société Générale SA.
X merged with xAI last March, which brought the valuation to $45 billion, including the debt.
SpaceX announced the merger with xAI earlier this month, a major move in Musk’s plan to alleviate Earth of necessary data centers and replace them with orbital options that will be lower cost:
“In the long term, space-based AI is obviously the only way to scale. To harness even a millionth of our Sun’s energy would require over a million times more energy than our civilization currently uses! The only logical solution, therefore, is to transport these resource-intensive efforts to a location with vast power and space. I mean, space is called “space” for a reason.”
The merger has many advantages, but one of the most crucial is that it positions the now-merged companies to fund broader goals, fueled by revenue from the Starlink expansion, potential IPO, and AI-driven applications that could accelerate the development of lunar bases.
News
Tesla pushes Full Self-Driving outright purchasing option back in one market
Tesla announced last month that it would eliminate the ability to purchase the Full Self-Driving software outright, instead opting for a subscription-only program, which will require users to pay monthly.

Tesla has pushed the opportunity to purchase the Full Self-Driving suite outright in one market: Australia.
The date remains February 14 in North America, but Tesla has pushed the date back to March 31, 2026, in Australia.
NEWS: Tesla is ending the option to buy FSD as a one-time outright purchase in Australia on March 31, 2026.
It still ends on Feb 14th in North America. https://t.co/qZBOztExVT pic.twitter.com/wmKRZPTf3r
— Sawyer Merritt (@SawyerMerritt) February 13, 2026
Tesla announced last month that it would eliminate the ability to purchase the Full Self-Driving software outright, instead opting for a subscription-only program, which will require users to pay monthly.
If you have already purchased the suite outright, you will not be required to subscribe once again, but once the outright purchase option is gone, drivers will be required to pay the monthly fee.
The reason for the adjustment is likely due to the short period of time the Full Self-Driving suite has been available in the country. In North America, it has been available for years.
Tesla hits major milestone with Full Self-Driving subscriptions
However, Tesla just launched it just last year in Australia.
Full Self-Driving is currently available in seven countries: the United States, Canada, China, Mexico, Australia, New Zealand, and South Korea.
The company has worked extensively for the past few years to launch the suite in Europe. It has not made it quite yet, but Tesla hopes to get it launched by the end of this year.
In North America, Tesla is only giving customers one more day to buy the suite outright before they will be committed to the subscription-based option for good.
The price is expected to go up as the capabilities improve, but there are no indications as to when Tesla will be doing that, nor what type of offering it plans to roll out for owners.
Elon Musk
Starlink terminals smuggled into Iran amid protest crackdown: report
Roughly 6,000 units were delivered following January’s unrest.

The United States quietly moved thousands of Starlink terminals into Iran after authorities imposed internet shutdowns as part of its crackdown on protests, as per information shared by U.S. officials to The Wall Street Journal.
Roughly 6,000 units were delivered following January’s unrest, marking the first known instance of Washington directly supplying the satellite systems inside the country.
Iran’s government significantly restricted online access as demonstrations spread across the country earlier this year. In response, the U.S. purchased nearly 7,000 Starlink terminals in recent months, with most acquisitions occurring in January. Officials stated that funding was reallocated from other internet access initiatives to support the satellite deployment.
President Donald Trump was aware of the effort, though it remains unclear whether he personally authorized it. The White House has not issued a comment about the matter publicly.
Possession of a Starlink terminal is illegal under Iranian law and can result in significant prison time. Despite this, the WSJ estimated that tens of thousands of residents still rely on the satellite service to bypass state controls. Authorities have reportedly conducted inspections of private homes and rooftops to locate unauthorized equipment.
Earlier this year, Trump and Elon Musk discussed maintaining Starlink access for Iranians during the unrest. Tehran has repeatedly accused Washington of encouraging dissent, though U.S. officials have mostly denied the allegations.
The decision to prioritize Starlink sparked internal debate within U.S. agencies. Some officials argued that shifting resources away from Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) could weaken broader internet access efforts. VPNs had previously played a major role in keeping Iranians connected during earlier protest waves, though VPNs are not effective when the actual internet gets cut.
According to State Department figures, about 30 million Iranians used U.S.-funded VPN services during demonstrations in 2022. During a near-total blackout in June 2025, roughly one-fifth of users were still able to access limited connectivity through VPN tools.
Critics have argued that satellite access without VPN protection may expose users to geolocation risks. After funds were redirected to acquire Starlink equipment, support reportedly lapsed for two of five VPN providers operating in Iran.
A State Department official has stated that the U.S. continues to back multiple technologies, including VPNs alongside Starlink, to sustain people’s internet access amidst the government’s shutdowns.








