News
Exxon Mobil kicked off from S&P 500’s Top 10 list for the first time in 90 years
Texas-based oil giant Exxon Mobil Corp. has long been a mainstay in the S&P 500’s Top 10 list, but its tenure as one of Wall Street’s biggest companies is starting to show some cracks. As indicated by month-end company weightings recently published by the S&P Dow Jones Indices, Exxon has been kicked off the S&P 500’s Top 10 list, the first time since the index was conceived 90 years ago.
Visa Inc. has replaced Exxon Mobil as the 10th-largest member of the S&P 500 by weighting on August 1. Two weeks later, American multinational consumer goods corporation Procter & Gamble also overtook the Texas-based oil veteran. Exxon Mobil currently stands as the 12th largest company in the S&P 500, a far cry from its 1st-place ranking in 2009.
Tom Sanzillo, director of the Institute for Energy Economics and Financial Analysis, noted in a statement to Bloomberg that the oil sector is currently facing challenges, particularly as several regions across the globe seem intent on moving away from fossil fuels. “The oil sector has gone from being the leader of the world economy to a laggard,” he said.
In what could only be described as a sign of the changing times, six out of ten companies in the S&P 500’s Top 10 list are connected to the tech sector. Among these are Microsoft, Apple, and Alphabet, all of which are currently engaged in active programs aimed at embracing sustainability. Apple, for example, uses recycled metals for its premium devices like the MacBook Air and Mac mini, while Microsoft has pledged to cut its carbon emissions by 75% by 2030.
In a segment on CNBC during a particularly volatile time for oil stocks last year, Paul Sankey of Mizuho Securities described a phenomenon known as the “Tesla Effect” that is starting to make its way to the oil industry. “Essentially, the big issue is the so-called ‘Tesla Effect,’ the general ‘End of the Oil Age’ theme that is a problem for these (oil) stocks. The Tesla Effect is the overall concept that (while) the 20th century was driven by oil, the 21st century will be driven by electricity. There’s a 30-year transition, and we’re somewhere probably 10 years into that transition. Ultimately, (the) terminal value of oil has been severely affected by the potential for us to change behavior,” the analyst said.
Exxon’s departure from the S&P 500’s Top 10 list did not happen overnight. While the oil giant was the index’s largest company in 2009, it has seen a steady decline over the past years. Ten years ago, Exxon’s weight in the S&P 500 was a considerable 5%. Today, it is a more far more humble 1%, according to data aggregated by Bloomberg.
Also aggravating Exxon Mobil’s exit from the S&P 500’s Top 10 list is the volatility of oil and gas prices, as well as notable price slumps, and overarching concerns about oil demand. These factors have made the energy sector in the S&P 500 one of the worst performers in recent months. This year alone, the S&P 500’s energy sector is being outperformed by other sectors in the index such as real estate, communications, and consumer staples, among others.

News
Tesla hiring for Commercial Charging role hints at Semi push in Europe
The job opening was highlighted by David Forer, Senior Project Developer for Charging at Tesla, on LinkedIn.
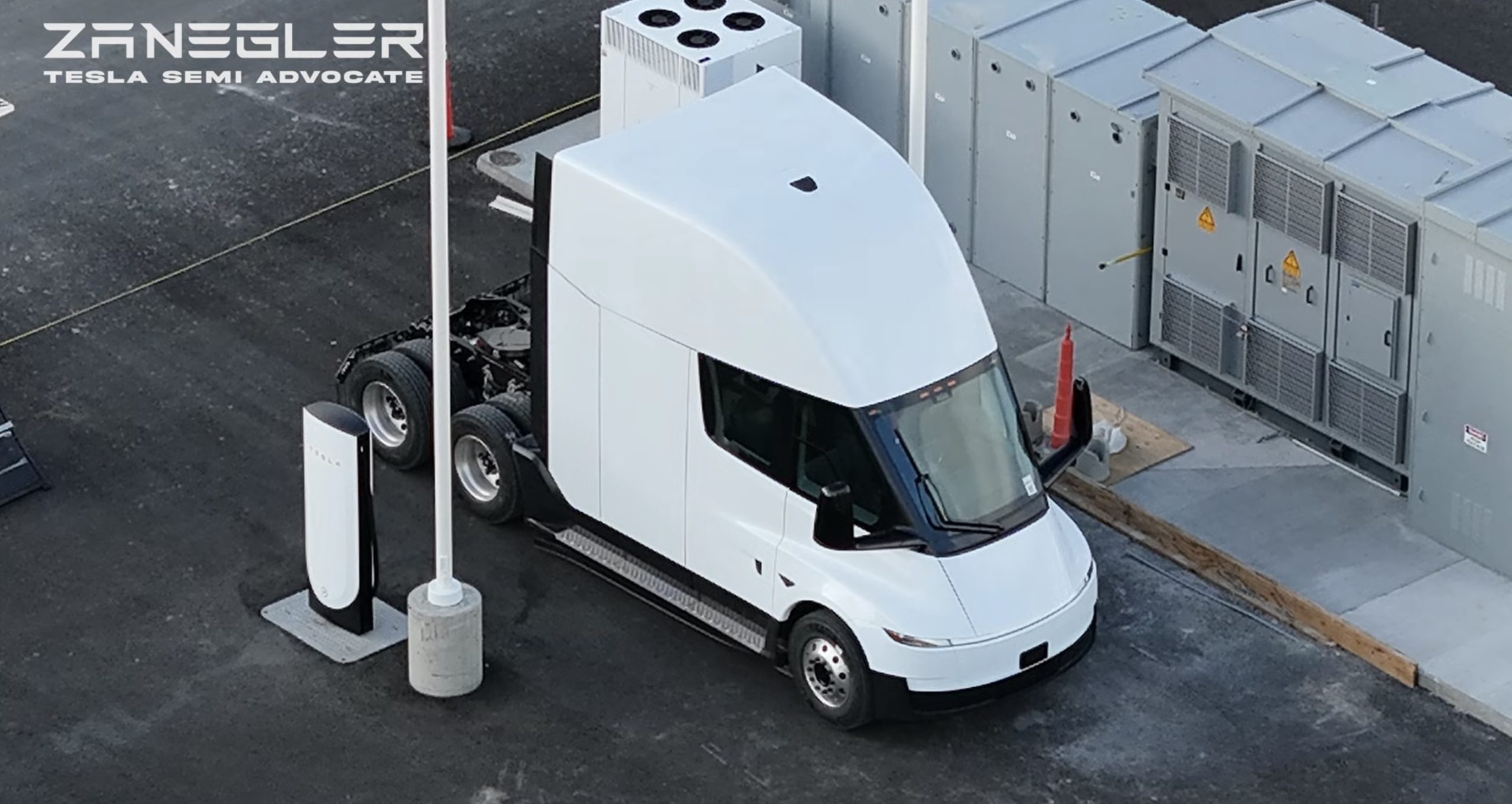

Tesla appears to be expanding its Commercial Charging efforts in Central Europe. The job opening was highlighted by David Forer, Senior Project Developer for Charging at Tesla, on LinkedIn.
In a post on LinkedIn, Forer stated that Tesla is looking for a “high-energy executer to own Commercial Charging Sales in Central Europe.” He added that the role will involve closing commercial deals across Tesla’s “entire product range (Supercharging & Megacharging).”
The job listing specifies that the hire will lead the sale of Tesla’s high-power charging products, including Supercharger and Heavy Duty Charging, to major partners such as charge point operators, real estate owners, and retail companies. The role requires fluency in German and English and is based onsite in Munich.
Tesla already operates more than 75,000 Superchargers globally, though the Semi’s Megacharger network is still in its early stages. The inclusion of Heavy Duty Charging in the job description is notable, then, as it aligns with Tesla’s Megacharger infrastructure, which is designed to support the Tesla Semi.
Tesla CEO Elon Musk recently confirmed that the Tesla Semi is moving into high-volume production this 2026. In a post on X, Musk noted that “Tesla Semi starts high volume production this year.”
Aerial footage of the Tesla Semi Factory near Giga Nevada also shows that the facility looks nearly complete, with work now underway inside the facility.
Tesla has also refreshed the Semi lineup on its official website, listing two variants: Standard and Long Range. The Standard trim offers up to 325 miles of range with an energy consumption rating of 1.7 kWh per mile, while the Long Range version provides up to 500 miles.
Both variants support fast charging and can recover up to 60% of range in 30 minutes using compatible infrastructure such as the Megacharger Network.
The presence of Heavy Duty Charging in a Central Europe-focused sales role could indicate that Tesla is preparing charging infrastructure ahead of wider Semi deployment in the region. While Tesla has not formally announced a European launch timeline for the Semi, the vehicle, particularly its range, makes it an ideal fit for the area.
Elon Musk
Tesla Full Self-Driving set to get an awesome new feature, Elon Musk says
Tesla Full Self-Driving is set to get an awesome new feature in the near future, CEO Elon Musk confirmed on X.
Full Self-Driving is the company’s semi-autonomous driving program, which is among the best available to the general public. It still relies on the driver to ultimately remain in control and pay attention, but it truly does make traveling less stressful and easier.
However, Tesla still continuously refines the software through Over-the-Air updates, which are meant to resolve shortcomings in the performance of the FSD suite. Generally, Tesla does a great job of this, but some updates are definitely regressions, at least with some of the features.
Tesla Cybertruck owner credits FSD for saving life after freeway medical emergency
Tesla and Musk are always trying to improve the suite’s performance by fixing features that are presently available, but they also try to add new things that would be beneficial to owners. One of those things, which is coming soon, is giving the driver the ability to prompt FSD with voice demands.
For example, asking the car to park close to the front door of your destination, or further away in an empty portion of the parking lot, would be an extremely beneficial feature. Adjusting navigation is possible through Grok integration, but it is not always effective.
Musk confirmed that voice prompts for FSD would be possible:
Coming
— Elon Musk (@elonmusk) February 21, 2026
Tesla Full Self-Driving is a really great thing, but it definitely has its shortcomings. Navigation is among the biggest complaints that owners have, and it is easily my biggest frustration with using it. Some of the routes it chooses to take are truly mind-boggling.
Another thing it has had issues with is being situated in the correct lane at confusing intersections or even managing to properly navigate through local traffic signs. For example, in Pennsylvania, there are a lot of stop signs with “Except Right Turn” signs directly under.
This gives those turning right at a stop sign the opportunity to travel through it. FSD has had issues with this on several occasions.
Parking preferences would be highly beneficial and something that could be resolved with this voice prompt program. Grocery stores are full of carts not taken back by customers, and many people choose to park far away. Advising FSD of this preference would be a great advantage to owners.
Cybertruck
Elon Musk clarifies Tesla Cybertruck ’10 day’ comment, fans respond
Some are arguing that the decision to confirm a price hike in ten days is sort of counterproductive, especially considering it is based on demand. Giving consumers a timeline of just ten days to make a big purchase like a pickup truck for $60,000, and basically stating the price will go up, will only push people to make a reservation.

Elon Musk has clarified what he meant by his comment on X yesterday that seemed to indicate that Tesla would either do away with the new All-Wheel-Drive configuration of the Cybertruck or adjust the price.
The response was cryptic as nobody truly knew what Musk’s plans were for the newest Tesla Cybertruck trim level. We now have that answer, and fans of the company are responding in a polarizing fashion.
On Thursday night, Tesla launched the Cybertruck All-Wheel-Drive, priced competitively at $59,990. It was a vast improvement from the Rear-Wheel-Drive configuration Tesla launched last year at a similar price point, which was eventually cancelled just a few months later due to low demand.
Tesla launches new Cybertruck trim with more features than ever for a low price
However, Musk said early on Friday, “just for 10 days,” the truck would either be available or priced at $59,990. We can now confirm Tesla will adjust the price based on more recent comments from the CEO.
Musk said the price will fluctuate, but it “depends on how much demand we see at this price level.”
Depends on how much demand we see at this price level
— Elon Musk (@elonmusk) February 20, 2026
Some are defending the decision, stating that it is simply logical to see how the Cybertruck sells at this price and adjust accordingly.
Case 1: You don’t like it -> don’t buy it
Case 2 (me): You like it, it’s fits your situation and needs -> you buy it.
Case 3: Complain endlessly for no reason, you weren’t going to get one anyway, but you want people to know you’re mad, for some reason.
Silly netizens.— Ryan Scanlan 👥 (@Xenius) February 21, 2026
Others, not so much.
Alright I’m obviously not the one successful enough to be calling the shots at Tesla and worth almost a trillion dollars
But people were excited about the awesome Cybertruck news and then it got taken away, that’s why people are annoyed. The wording felt more like a threat.… pic.twitter.com/NWVNklcXoJ— Dirty Tesla (@DirtyTesLa) February 21, 2026
No but fr wtf you doing dude???????
— Greggertruck (@greggertruck) February 20, 2026
It’s how it was communicated.
If it had been stated clearly on the website for everyone to see, everyone would be fine.
— KiTT_2020 (@kitt_2020) February 20, 2026
Some are arguing that the decision to confirm a price hike in ten days is sort of counterproductive, especially considering it is based on demand. Giving consumers a timeline of just ten days to make a big purchase like a pickup truck for $60,000, and basically stating the price will go up, will only push people to make a reservation.
Demand will look strong because people want to lock in this price. The price will inevitably go up, and demand for the trim will likely fall a bit because of the increased cost.
Many are arguing Musk should have kept this detail internal, but transparency is a good policy to have. It is a polarizing move to confirm a price increase in just a week-and-a-half, but the community is obviously split on how to feel.