Space
Europe postpones Mars mission over ExoMars rover issue and Coronavirus
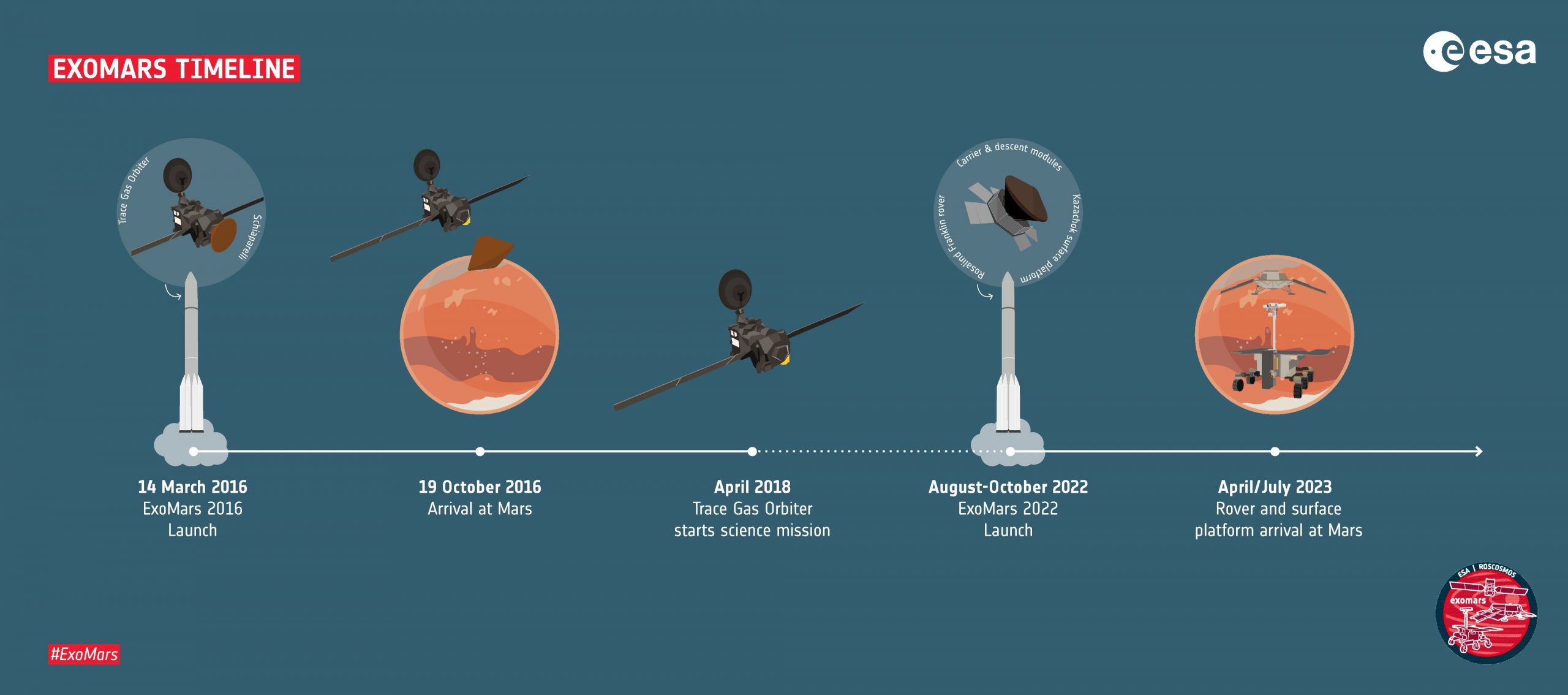
The European Space Agency (ESA) announced that its ExoMars rover would not fly this year. The mission, a collaboration with the Russian Space Agency (Roscosmos), was set to launch this summer. However, the launch has been postponed to 2022 due to technical issues and the logistical impact due to the global Conoavirus outbreak.
“This is a very tough decision, but it’s, I’m sure, the right one,” ESA Director General Jan Wörner said during a news conference at ESA’s headquarters in Paris after consulting with the head of Roscosmos, Dmitry Rogozin. “The parties had to recognise that the final phase of ExoMars activities are compromised by the general aggravation of the epidemiological situation in European countries.”
“We agreed together it’s better to go for success than just to go for launch at this time,” Wörner said. “Although we are close to launch readiness, we cannot cut corners. Launching this year would mean sacrificing remaining essential tests.”
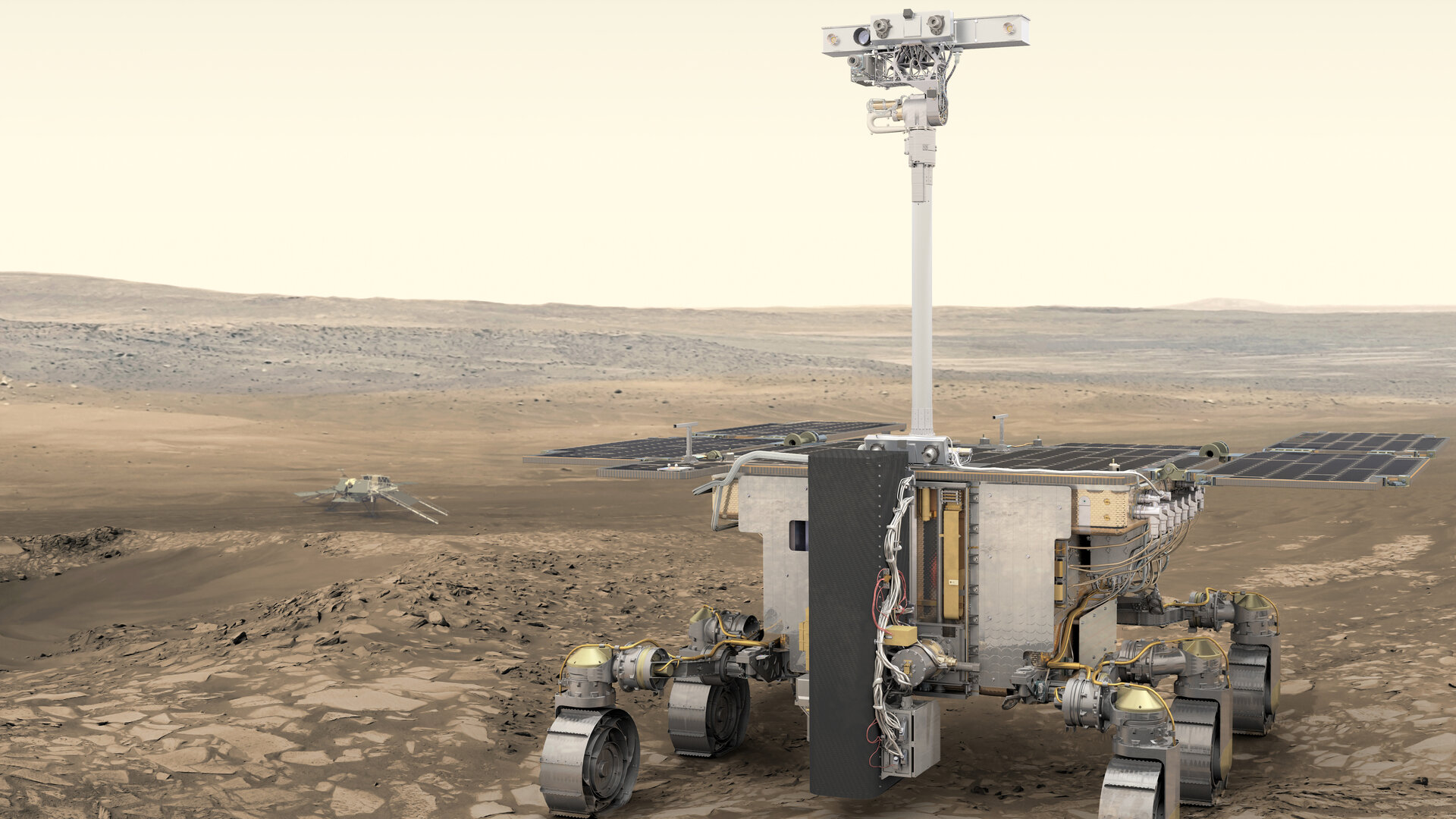
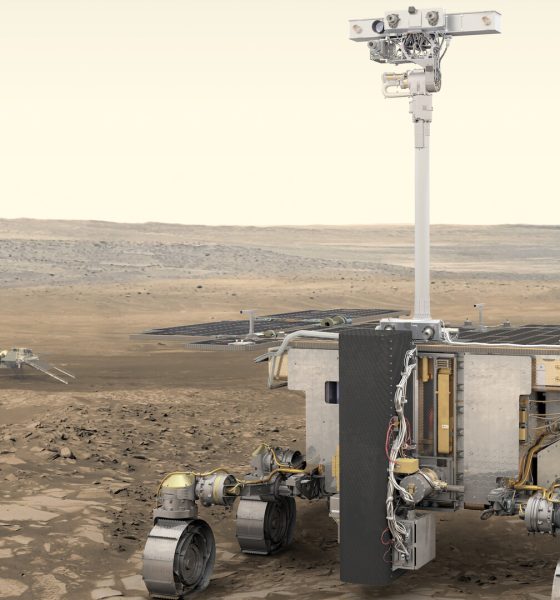
The ExoMars rover is Europe’s first Mars rover. Named after Rosalind Franklin, a British pioneer of DNA science, the robotic explorer will search for signs of life on the red planet’s surface. Wörner said the agency needs more time to troubleshoot issues with the spacecraft’s parachute system as well as precise electronics, so the delay is necessary.
Also, the recent coronavirus outbreak that’s spreading around the globe isn’t helping. So instead of rushing, the team is taking the next two years to conduct extensive testing and make sure they get it right.
“We have made a difficult but well-weighed decision to postpone the launch to 2022,” Rogozin said in a statement. “I am confident that the steps that we and our European colleagues are taking to ensure mission success will be justified and will unquestionably bring solely positive results for the mission implementation.”
The ExoMars rover is a follow-on to ESA’s ExoMars Orbiter mission, which reached the red planet in 2016. That mission consisted of two parts: the Trace Gas Orbiter (TGO) and the Schiaparelli lander, a technology demonstrator. Unfortunately, the Schiaparelli crash-landed during its descent to the Martian surface.
Landing a spacecraft on Mars is hard. The planet’s atmosphere is thinner than what we see on Earth, and as such its takes a combination of sophisticated tools, including heat shields, retrorockets, and even giant, inflatable airbags, to safely touch down on the surface.
If anyone of those techniques fails, the spacecraft will crash, which is what happened with Schiaparelli.
Despite being around for decades, parachutes are still pretty tricky, especially using them on another planet. ESA engineers have made many adjustments to the parachute system, but keep seeing the same result: they rip as soon as they deploy. Test, after test, the chutes failed. Engineers have tried reinforcing them with Teflon to make them slide out of their bags easier, but no luck.
ESA even tried to seek advice from NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, which has built every single rover on Mars and, unfortunately needs more time to collaborate on parachute design. Because there’s only a limited window of launch opportunity, ESA officials decided to make the tough call to postpone until the next Mars window opens in 2022.
Appreciate @esa and @roscosmos for making the tough decision to postpone @ESA_ExoMars to 2022. Launching & safely landing a spacecraft on Mars are extremely demanding and require many technologies & systems to function perfectly. Your work is inspiring everyone to do hard things. https://t.co/ttPzDyQJWa
— Thomas Zurbuchen (@Dr_ThomasZ) March 12, 2020
The rover and its launcher, a Russian Proton rocket, are ready to go. The agency has more parachute tests in the works, including high-altitude drops.
Additionally, Wörner said the team discovered issues with the descent module’s electronic equipment, which are essential to the mission’s success. This piece of equipment controls functions like spacecraft power, propulsion, and even parachute control. It will take some time for the bugs to be fixed.
“Due to the troubleshooting of these anomalies at system level, the final version of the flight software has been delayed, and there is not enough time to fully test it before a 2020 launch and gain the confidence we need,” Wörner said.
You can technically launch to Mars anytime, but space agencies around the world choose specific windows that open every two years. During this time, Mars and Earth are in line, so that it takes less time and uses less fuel. In 2022, that window is open from August to October.
Once it reaches the Martian surface, the rover will study an ancient lake bed. It will scour the red planet’s surface in search of biosignatures, or signs of life.

Elon Musk
SpaceX reportedly discussing merger with xAI ahead of blockbuster IPO

In a groundbreaking new report from Reuters, SpaceX is reportedly discussing merger possibilities with xAI ahead of the space exploration company’s plans to IPO later this year, in what would be a blockbuster move.
The outlet said it would combine rockets and Starlink satellites, as well as the X social media platform and AI project Grok under one roof. The report cites “a person briefed on the matter and two recent company filings seen by Reuters.”
Musk, nor SpaceX or xAI, have commented on the report, so, as of now, it is unconfirmed.
With that being said, the proposed merger would bring shares of xAI in exchange for shares of SpaceX. Both companies were registered in Nevada to expedite the transaction, according to the report.
On January 21, both entities were registered in Nevada. The report continues:
“One of them, a limited liability company, lists SpaceX and Bret Johnsen, the company’s chief financial officer, as managing members, while the other lists Johnsen as the company’s only officer, the filings show.”
The source also stated that some xAI executives could be given the option to receive cash in lieu of SpaceX stock. No agreement has been reached, nothing has been signed, and the timing and structure, as well as other important details, have not been finalized.
SpaceX is valued at $800 billion and is the most valuable privately held company, while xAI is valued at $230 billion as of November. SpaceX could be going public later this year, as Musk has said as recently as December that the company would offer its stock publicly.
The plans could help move along plans for large-scale data centers in space, something Musk has discussed on several occasions over the past few months.
At the World Economic Forum last week, Musk said:
“It’s a no-brainer for building solar-powered AI data centers in space, because as I mentioned, it’s also very cold in space. The net effect is that the lowest cost place to put AI will be space and that will be true within two to three years, three at the latest.”
He also said on X that “the most important thing in the next 3-4 years is data centers in space.”
If the report is true and the two companies end up coming together, it would not be the first time Musk’s companies have ended up coming together. He used Tesla stock to purchase SolarCity back in 2016. Last year, X became part of xAI in a share swap.
Elon Musk
Tesla CEO Elon Musk trolls budget airline after it refuses Starlink on its planes
“I really want to put a Ryan in charge of Ryan Air. It is your destiny,” Musk said.

Tesla CEO Elon Musk trolled budget airline Ryanair on his social media platform X this week following the company’s refusal to adopt Starlink internet on its planes.
Earlier this week, it was reported that Ryanair did not plan to install Starlink internet services on its planes due to its budgetary nature and short flight spans, which are commonly only an hour or so in total duration.
Initially, Musk said installing Starlink on the company’s planes would not impact cost or aerodynamics, but Ryanair responded on its X account, which is comical in nature, by stating that a propaganda it would not fall for was “Wi-Fi on planes.”
Musk responded by asking, “How much would it cost to buy you?” Then followed up with the idea of buying the company and replacing the CEO with someone named Ryan:
I really want to put a Ryan in charge of Ryan Air. It is your destiny.
— Elon Musk (@elonmusk) January 19, 2026
Polymarket now states that there is an 8 percent chance that Musk will purchase Ryanair, which would cost Musk roughly $36 billion, based on recent financial data of the public company.
Although the banter has certainly crossed a line, it does not seem as if there is any true reason to believe Musk would purchase the airline. More than anything, it seems like an exercise of who will go further.
Starlink passes 9 million active customers just weeks after hitting 8 million
However, it is worth noting that if something is important enough, Musk will get involved. He bought Twitter a few years ago and then turned it into X, but that issue was much larger than simple banter with a company that does not want to utilize one of the CEO’s products.
The insufferable, special needs chimp currently running Ryan Air is an accountant. Has no idea how airplanes even fly.
— Elon Musk (@elonmusk) January 20, 2026
In a poll posted yesterday by Musk, asking whether he should buy Ryanair and “restore Ryan as their rightful ruler.” 76.5 percent of respondents said he should, but others believe that the whole idea is just playful dialogue for now.
But it is not ideal to count Musk out, especially if things continue to move in the direction they have been.
News
SpaceX shades airline for seeking contract with Amazon’s Starlink rival

SpaceX employees, including its CEO Elon Musk, shaded American Airlines on social media this past weekend due to the company’s reported talks with Amazon’s Starlink rival, Leo.
Starlink has been adopted by several airlines, including United Airlines, Qatar Airways, Hawaiian Airlines, WestJet, Air France, airBaltic, and others. It has gained notoriety as an extremely solid, dependable, and reliable option for airline travel, as traditional options frequently cause users to lose connection to the internet.
Many airlines have made the switch, while others continue to mull the options available to them. American Airlines is one of them.
A report from Bloomberg indicates the airline is thinking of going with a Starlink rival owned by Amazon, called Leo. It was previously referred to as Project Kuiper.
American CEO Robert Isom said (via Bloomberg):
“While there’s Starlink, there are other low-Earth-orbit satellite opportunities that we can look at. We’re making sure that American is going to have what our customers need.”
Isom also said American has been in touch with Amazon about installing Leo on its aircraft, but he would not reveal the status of any discussions with the company.
The report caught the attention of Michael Nicolls, the Vice President of Starlink Engineering at SpaceX, who said:
“Only fly on airlines with good connectivity… and only one source of good connectivity at the moment…”
CEO Elon Musk replied to Nicolls by stating that American Airlines risks losing “a lot of customers if their connectivity solution fails.”
American Airlines will lose a lot of customers if their connectivity solution fails
— Elon Musk (@elonmusk) December 14, 2025
There are over 8,000 Starlink satellites in orbit currently, offering internet coverage in over 150 countries and territories globally. SpaceX expands its array of satellites nearly every week with launches from California and Florida, aiming to offer internet access to everyone across the globe.
Currently, the company is focusing on expanding into new markets, such as Africa and Asia.








