Installation of large-scale energy storage systems is expected to continue increasing in the U.S. throughout 2024, as championed by only a handful of states thus far.
According to data from the Energy Information Administration (EIA) shared on Tuesday, U.S. energy storage system deployment is expected to nearly double in 2024, with battery capacity forecasted to grow by 89 percent. As of November 2023, two U.S. states have installed substantially more energy storage systems than others, making up the vast majority of battery capacity available.
The data shows that California leads energy storage availability by a wide margin, with just over 7.3 GW (7,302 MW) of battery capacity installed. Texas follows in second with nearly 3.2 GW (3,167 MW) installed, while Arizona, Florida, and Massachusetts are next in the lineup.
You can see the full top 10 list for U.S. states with the most battery capacity installed below, courtesy of the EIA.
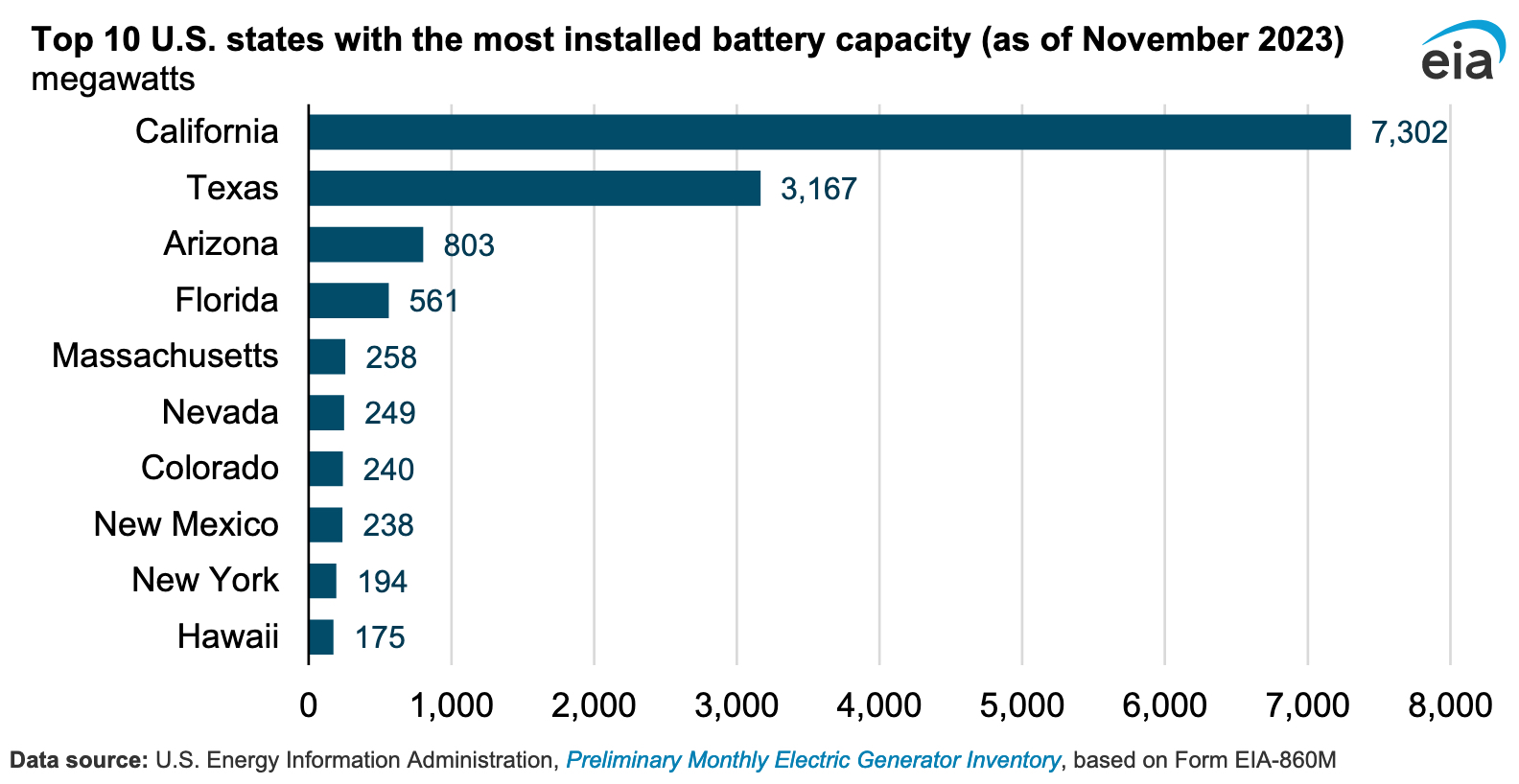
Credit: Energy Information Administration
The data takes into account planned storage system projects for the next two years, and the agency says developers are aiming to expand U.S. storage capacity by 30 GW by the end of 2024. As the EIA also notes, U.S. battery storage capacity has been increasing since 2021, and if the aforementioned goal is achieved, the country will have more energy storage than petroleum liquids, geothermal, wood and wood waste, or landfill gas by the end of this year.
There are over 300 utility-scale battery storage projects planned to be brought online by 2025, with roughly half of them being in Texas. Currently, the largest operating battery energy storage system (BESS) is a project operated by Vistra in Moss Landing, California, which has 750 MW of capacity and is located not far from Tesla’s 182.5 MW Megapack site in the same city.
Four out of five of the largest BESS installations set to take place in 2024 or 2025 are in Texas, as listed below:
- Lunis Creek BESS SLF (Texas, 621 MW)
- Clear Fork Creek BESS SLF (Texas, 600 MW)
- Hecate Energy Ramsey Storage (Texas, 500 MW)
- Bellefield Solar and Energy Storage Farm (California, 500 MW)
- Dogwood Creek Solar and BESS (Texas, 443 MW)
As for the recent increases in storage capacity, the agency says that quickly increasing wind and solar generation fleets in California and Texas have increased the need for growth in the battery storage sector. With energy storage projects, utility operators are able to store power during times of low electricity demand and then deploy stored energy during times of peak demand.
Credit: Energy Information Administration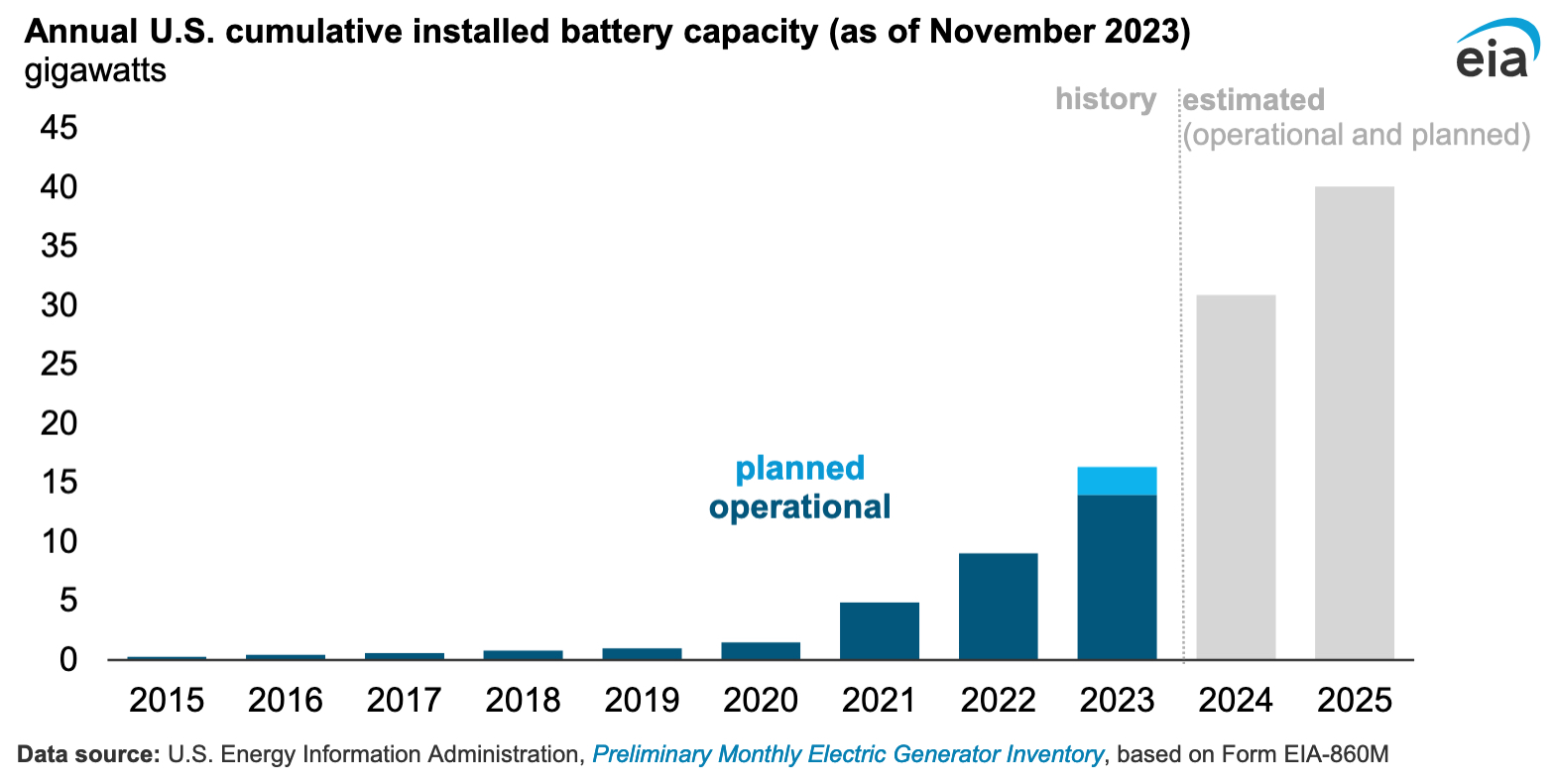
The news comes just a few days after Tesla Megapacks went live on the island of Oahu in Hawaii, enabling a 185 MW project that has helped the island move away from the use of coal. The project isn’t represented in the EIA’s dataset, since that data only accounts for installations through last November.
In addition to its grid-scale Megapacks, Tesla also offers smaller, residential-level Powerpacks to create what it calls Virtual Power Plants (VPPs), essentially forming giant, distributed batteries that customers can use to sell energy back to the grid in times of peak demand. Currently, Tesla has pilots for these programs in states including California, Texas and Massachusetts, along with the U.S. territory of Puerto Rico.
Tesla Powerwall owner earns $574 by participating in California’s VPP program
What are your thoughts? Let me know at zach@teslarati.com, find me on X at @zacharyvisconti, or send your tips to us at tips@teslarati.com.

Elon Musk
xAI’s Grok approved for Pentagon classified systems: report
Under the agreement, Grok can be deployed in systems handling classified intelligence analysis, weapons development, and battlefield operations.

Elon Musk’s xAI has signed an agreement with the United States Department of Defense (DoD) to allow Grok to be used in classified military systems.
Previously, Anthropic’s Claude had been the only AI system approved for the most sensitive military work, but a dispute over usage safeguards has reportedly prompted the Pentagon to broaden its options, as noted in a report from Axios.
Under the agreement, Grok can be deployed in systems handling classified intelligence analysis, weapons development, and battlefield operations.
The publication reported that xAI agreed to the Pentagon’s requirement that its technology be usable for “all lawful purposes,” a standard Anthropic has reportedly resisted due to alleged ethical restrictions tied to mass surveillance and autonomous weapons use.
Defense Secretary Pete Hegseth is scheduled to meet with Anthropic CEO Dario Amodei in what sources expect to be a tense meeting, with the publication hinting that the Pentagon could designate Anthropic a “supply chain risk” if the company does not lift its safeguards.
Axios stated that replacing Claude fully might be technically challenging even if xAI or other alternative AI systems take its place. That being said, other AI systems are already in use by the DoD.
Grok already operates in the Pentagon’s unclassified systems alongside Google’s Gemini and OpenAI’s ChatGPT. Google is reportedly close to an agreement that will result in Gemini being used for classified use, while OpenAI’s progress toward classified deployment is described as slower but still feasible.
The publication noted that the Pentagon continues talks with several AI companies as it prepares for potential changes in classified AI sourcing.
Elon Musk
Elon Musk denies Starlink’s price cuts are due to Amazon Kuiper
“This has nothing to do with Kuiper, we’re just trying to make Starlink more affordable to a broader audience,” Musk wrote in a post on X.

Elon Musk has pushed back on claims that Starlink’s recent price reductions are tied to Amazon’s Kuiper project.
In a post on X, Musk responded directly to a report suggesting that Starlink was cutting prices and offering free hardware to partners ahead of a planned IPO and increased competition from Kuiper.
“This has nothing to do with Kuiper, we’re just trying to make Starlink more affordable to a broader audience,” Musk wrote in a post on X. “The lower the cost, the more Starlink can be used by people who don’t have much money, especially in the developing world.”
The speculation originated from a post summarizing a report from The Information, which ran with the headline “SpaceX’s Starlink Makes Land Grab as Amazon Threat Looms.” The report stated that SpaceX is aggressively cutting prices and giving free hardware to distribution partners, which was interpreted as a reaction to Amazon’s Kuiper’s upcoming rollout and possible IPO.
In a way, Musk’s comments could be quite accurate considering Starlink’s current scale. The constellation currently has more than 9,700 satellites in operation today, making it by far the largest satellite broadband network in operation. It has also managed to grow its user base to 10 million active customers across more than 150 countries worldwide.
Amazon’s Kuiper, by comparison, has launched approximately 211 satellites to date, as per data from SatelliteMap.Space, some of which were launched by SpaceX’s Falcon 9 rocket. Starlink surpassed that number in early January 2020, during the early buildout of its first-generation network.
Lower pricing also aligns with Starlink’s broader expansion strategy. SpaceX continues to deploy satellites at a rapid pace using Falcon 9, and future launches aboard Starship are expected to significantly accelerate the constellation’s growth. A larger network improves capacity and global coverage, which can support a broader customer base.
In that context, price reductions can be viewed as a way to match expanding supply with growing demand. Musk’s companies have historically used aggressive pricing strategies to drive adoption at scale, particularly when vertical integration allows costs to decline over time.
News
Tesla Giga Berlin makes a statement of solidarity amid IG Metall conflict
The display comes as tensions between Tesla and IG Metall continue to escalate.

Tesla Giga Berlin is sending a strong message of solidarity amid its ongoing legal dispute with German union IG Metall.
In a post on social media platform X, Giga Berlin plant manager André Thierig shared an image of the facility’s lobby covered with a large banner that reads: “Progress. Innovation. Success.” He added that the slogan reflects what the facility has stood for since Day One.
“Our lobby at Giga Berlin covered in a huge banner these days. Progress. Innovation. Success – this is what we stand for since we started production in 2022 and how we will go into our future!” Thierig wrote in his post on X.
The display comes as tensions between Tesla and IG Metall continue to escalate.
The dispute began after Tesla accused a union representative of secretly recording a works council meeting at Giga Berlin. Tesla stated that it filed a criminal complaint after the alleged incident. Police later confirmed they had seized a computer belonging to an IG Metall member as part of their investigation.
“What has happened today at Giga Berlin is truly beyond words! An external union representative from IG Metall attended a works council meeting. For unknown reasons he recorded the internal meeting and was caught in action! We obviously called police and filed a criminal complaint!” Thierig wrote on X at the time.
IG Metall denied the accusation and characterized Tesla’s move as an election tactic ahead of upcoming works council elections. The union subsequently filed a defamation complaint against Thierig. Authorities later confirmed that an investigation had been opened in connection with the matter.
Giga Berlin began production in 2022 and has since become one of Tesla’s key European manufacturing hubs, producing the Model Y, the company’s best-selling vehicle. The facility has expanded capacity over the past years despite environmental protests, labor disputes, and regulatory scrutiny.










