
News
NASA lab confirms DNA sugar can be made in space, adding evidence that ‘life’ could be all over the universe
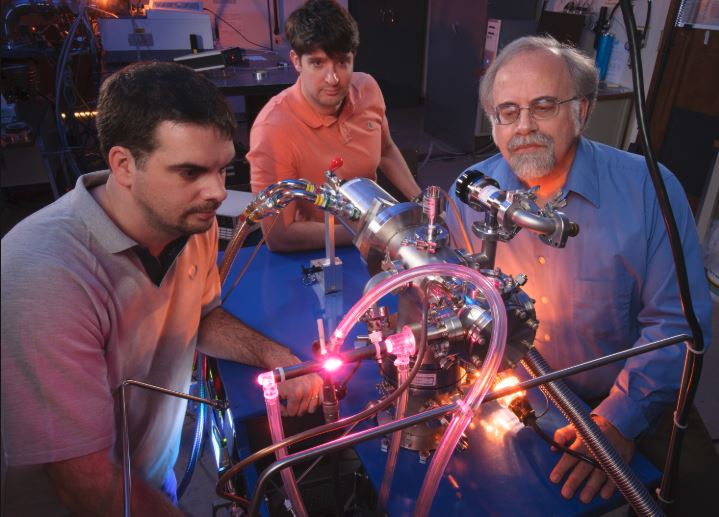
NASA researchers at the Ames’ Astrophysics and Astrochemistry Lab in Mountain View, California have provided the first experimental evidence demonstrating that the sugar in DNA – 2-deoxyribose – can be formed in interstellar space. In their study published on December 18, 2018 in the journal Nature Communications, Michel Nuevo, George Cooper, and Scott Sandford combined organic compounds, water vapor, and light – all elements present in interstellar space – inside a vacuum chamber mimicking the cosmic environment and observed the results. Along with the DNA sugar, a variety of other sugar derivatives were found to have been created. This discovery is more evidence that the chemical building blocks of life could be common all over the universe, seeding other planets as they did Earth in the ancient past.
One of the biggest questions science is constantly pursuing is whether we are alone in the universe, a research endeavor that takes many paths. Astrophysicist Carl Sagan is famously quoted often, saying, “The nitrogen in our DNA, the calcium in our teeth, the iron in our blood, the carbon in our apple pies were made in the interiors of collapsing stars. We are made of star stuff.” It meant that the universe is filled with the building blocks of life, thus the pursuit to find out how those building blocks combine to actually form life is an endeavor with the farthest reaching implications. Scott Sandford, one of the study’s researchers, added to this in reference to his own team’s experiment, saying, “The universe is an organic chemist. It has big beakers and lots of time – and the result is a lot of organic material, some of which is useful to life.”
To make their discovery, the Ames team cooled an aluminum substance to near absolute zero inside a vacuum chamber (since space is a vacuum), and added a mixture of water vapor and methanol gas before exposing it to ultraviolet light and heat, fully mimicking the interstellar environment. The space between stars is filled with dust and gases and is constantly subjected to light particles bombarding in from every radiation-emitting source around it. The experiment was designed to help answer the question of whether the space environment itself can make the compounds essential to life rather than just the single-elemental building blocks. Another team of researchers in France previously discovered the creation of ribose – the sugar in RNA, a possible precursor to DNA – in an experiment similar to the current study, setting the stage for the team’s further findings.

A growing number of organic compounds have been found on meteorites over the years including carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and sulphur. Despite the actively changing geography of Earth complicating the discovery of remnants from its very early days, scientists have been able to find and study things like carbonaceous chondrites, meteorites originating from asteroids as old as our solar system. This research has made it possible to analyze how planets have formed and evolved over billions of years. Combining this type of research along with other work demonstrating that meteorites in general contain the building blocks of life and travel throughout the galaxies of the universe, the expanding number of exoplanets being found could imply even more significant possibilities.
Exoplanets, i.e., planets that orbit stars other than our own, are being discovered on a regular basis as data from prior and current observatory and telescope missions is reviewed. Over the last 20 years since “planet hunting” really got started, over 3800 exoplanets have been confirmed with around 2900 more awaiting confirmation. By observing the amount of light a distant star dims over period of time, scientists can determine whether there is a planet orbiting it, its size, distance from its star, and the colors missing in the planets’ atmosphere light spectrum which tell what chemicals are present, such as oxygen, carbon dioxide, nitrogen, and so forth. After analyzing all of these things, it can be predicted whether an exoplanet may be Earth-like and whether it’s in what’s called the “Goldilocks Zone”, or position where life as we know it might have the right conditions to evolve.
That may seem like a lot of conditions to meet, but it’s estimated that around 20-50 percent of the stars in our night sky may have small, rocky planets in their stars’ habitable zones. As more is learned about planet formation, that number may be revised up or down. Thus far, one planetary system has been studied extensively that has planets somewhat similar to Earth: TRAPPIST-1. It’s comprised of an ultra-cool dwarf star with 7 rocky worlds orbiting it, all of them potentially having water, some more than Earth. Considering the growing evidence that the seeds for life to evolve are prominently distributed and created throughout space with the number of potentially Earth-like planets being discovered, we may have some exciting news from the interstellar world in the near future.

Elon Musk
SpaceX officially acquires xAI, merging rockets with AI expertise

SpaceX has officially acquired xAI, merging rockets with AI expertise in what is the first move to bring Elon Musk’s companies under one umbrella.
On February 2, SpaceX officially announced the acquisition of xAI, uniting two powerhouse companies under a single entity, creating what the space exploration company called in a blog post “one of the most ambitious, vertically integrated innovation engines on (and off) Earth.”
🚨 BREAKING: Elon Musk has posted a new blog on SpaceX’s website confirming the acquisition of xAI pic.twitter.com/TFgeHGMpXc
— TESLARATI (@Teslarati) February 2, 2026
The deal will integrate xAI’s advanced AI capabilities, including the Grok chatbot and massive training infrastructure, with SpaceX’s rocket technology, Starlink satellite network, and ambitious space exploration goals.
The acquisition comes at a pivotal moment: xAI is valued at around $230 billion as of late 2025, and has been racing to scale AI compute amid global competition from companies like OpenAI, Google, and Meta. Meanwhile, SpaceX, which was recently valued at $800 billion, is facing escalating costs for its multiplanetary ambitions.
By combining forces, the merged entity gains a unified approach to tackle one of AI’s biggest bottlenecks: the enormous energy and infrastructure demands of next-gen models.
Musk wrote in a blog post on SpaceX’s website that:
“In the long term, space-based AI is obviously the only way to scale. To harness even a millionth of our Sun’s energy would require over a million times more energy than our civilization currently uses! The only logical solution therefore is to transport these resource-intensive efforts to a location with vast power and space. I mean, space is called “space” for a reason.”
Musk details the need for orbital data centers, stating that his estimate is that “within 2 to 3 years, the lowest cost way to generate AI compute will be in space.
This cost-efficiency alone will enable innovative companies to forge ahead in training their AI models and processing data at unprecedented speeds and scales, accelerating breakthroughs in our understanding of physics and invention of technologies to benefit humanity.”
SpaceX recently filed for approval from the FCC to launch up to one million solar-powered satellites configured as high-bandwidth, optically linked compute platforms.
These facilities would harness near-constant sunlight with minimal maintenance, delivering what the company projects as transformative efficiency.
Musk has long argued that space offers the ultimate solution for power-hungry AI projects. But that’s not all the merger will take care of.
Additionally, it positions the company to fund broader goals. Revenue from the Starlink expansion, potential SpaceX IPO, and AI-driven applications could accelerate the development of lunar bases, as Musk believes multiplanetary life will be crucial to saving civilization.
Critics question the feasibility of massive constellations amid orbital debris concerns and regulatory hurdles. Yet, proponents see it as a bold step toward a multiplanetary computing infrastructure that extends human civilization beyond Earth.
News
Tesla Model Y Performance Review: The Best Trim of the Best Vehicle?
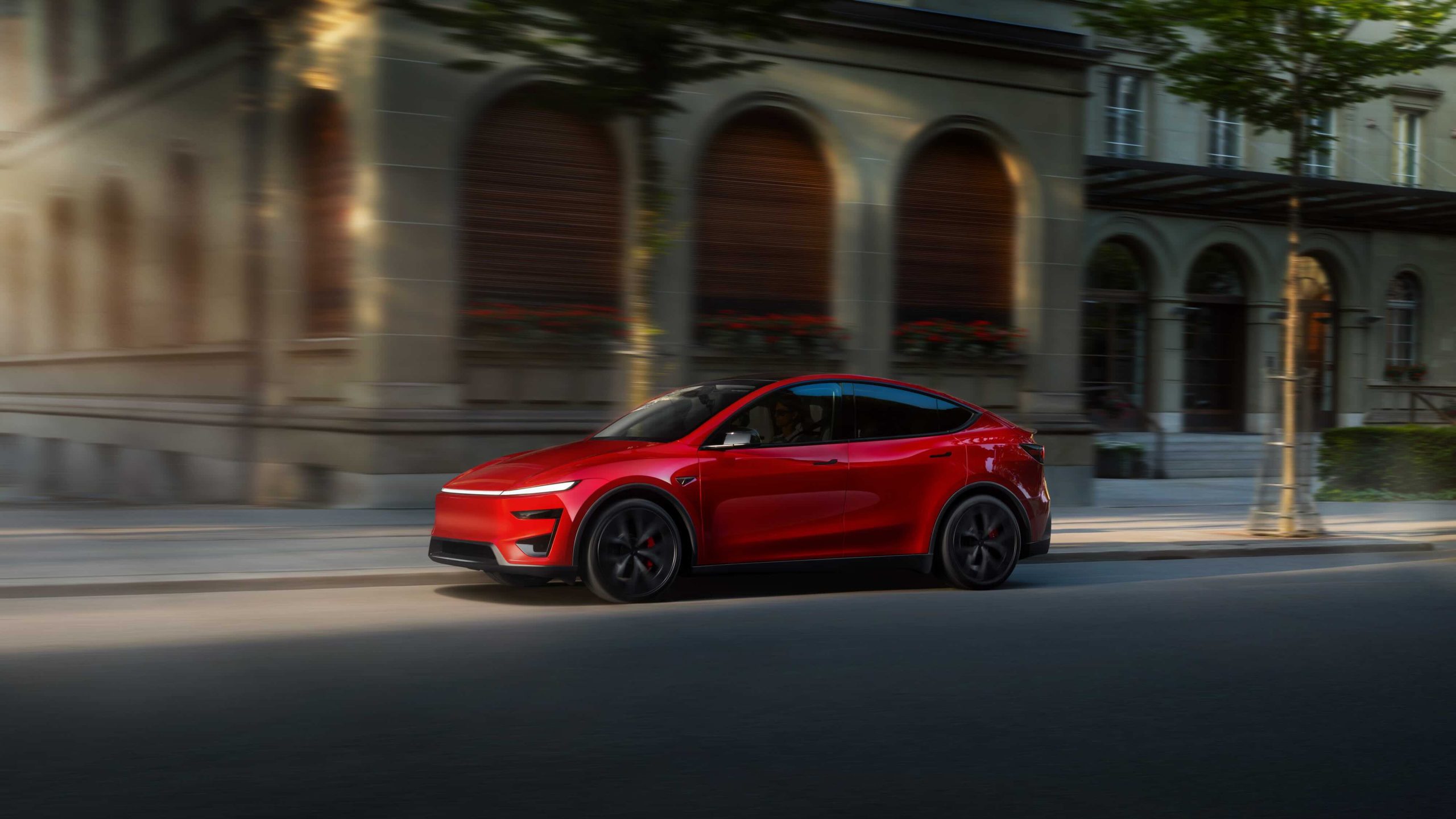

The Tesla Model Y Performance was in my hands for seven days after the company reached out and got me a brand new unit. As a Premium All-Wheel-Drive owner, I was really interested to see if the Performance trim was worth the $11,000 difference, and what I learned might be a surprise.
The only “performance” version of any Tesla vehicle I’ve had the opportunity to have several days with was the Cyberbeast back in June, and a few days with that made me want a Cybertruck more than I already did. It had white-knuckle speed, and as someone who truly loves to drive a larger vehicle, it fit the bill for everything I wanted out of an electric pickup.
We picked up the Tesla Model Y Performance yesterday!
We have a whole SEVEN days with it and we want to do anything you’d like us to (within reason) with it!
Let us know below 👇 what you’re interested in knowing pic.twitter.com/BRG9nOSwGW
— TESLARATI (@Teslarati) January 20, 2026
With that past experience, I was truly excited to try the new Model Y Performance, especially considering I own a Model Y already, and after six months of ownership, it has truly won me over as the best car I’ve ever owned. Although my 2008 Ford Escape Hybrid is a close second, mostly due to nostalgia and it being my “dream car” as a kid in high school at the time, the Model Y is unequivocally better, obviously. It’s hard to shake the feelings of your first “nice” car; I think we could all relate to that in a way.
First charge in the Tesla Model Y Performance!
This is a v2 Supercharger, so not quite as fast as what we’d like, but it will do for now. pic.twitter.com/Akyb2BLMcS
— TESLARATI (@Teslarati) January 21, 2026
Before I even picked up the Model Y Performance, I was expecting a handful of things: better performance, better handling, more comfortable seats, and a thirst for spirited driving on the windy backroads of Southern Pennsylvania. Admittedly, a snowstorm disrupted a lot of my testing, but I was still able to have some fun in the car.
With that being said, my thoughts are sure to potentially ruffle some feathers.
First Impressions of the Tesla Model Y Performance
I picked up the Model Y Performance on January 19 and had it for one week. The Ultra Red paint with the White interior option was a great look, and it was fun to have a car with that look, considering my Model Y is Black on Black.
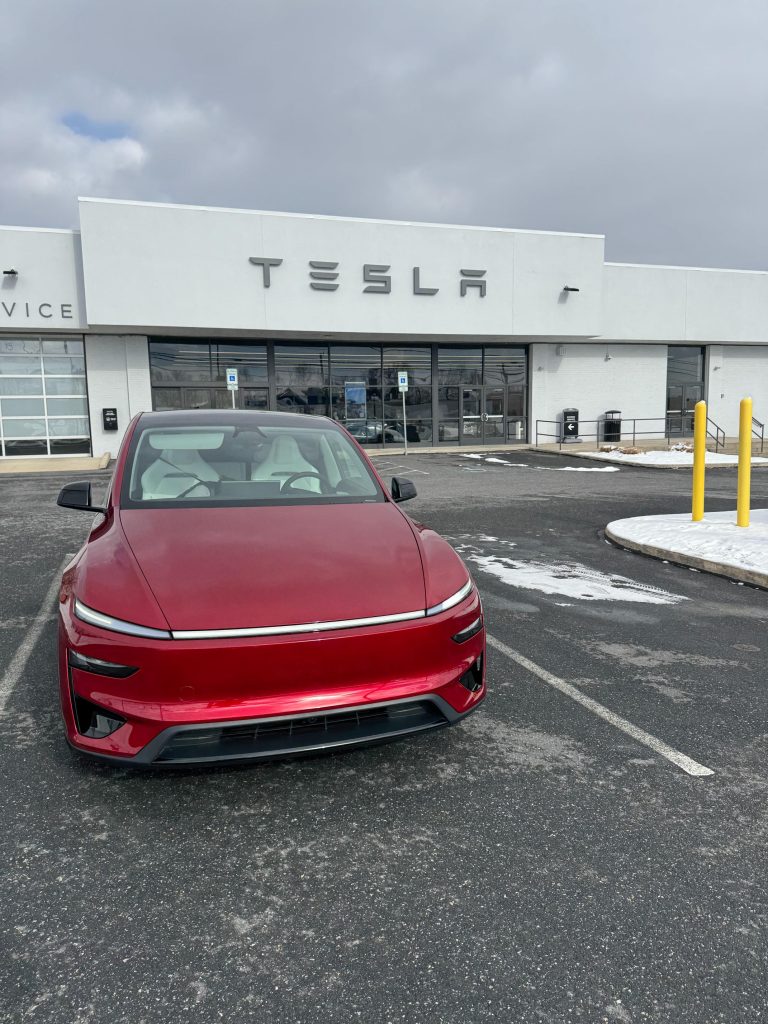

One thing that is really interesting and somewhat surprising is that Tesla hasn’t adjusted the fact that the Ultra Red is a different shade than the Performance brake calipers. Additionally, the rear light bar, which signals braking, is a different shade of red than the car and the brake calipers.
This was something that the Tesla Showroom employees pointed out to me, and, just like they said, I’ll never be able to not see it.
Interior Quality
The first thing I noticed was the Performance seats, which are geared to hug you a tad more and keep you intact during spirited drives. They were, without a doubt, more comfortable than the seats in my Premium AWD.
Interestingly, when I gave this opinion on X, some Performance owners said that the seats were less comfortable and, on longer drives, I’d feel it. My Fiancè and I drove about 120 miles in the car that weekend, and we had no complaints. They were supremely comfortable, and we both really enjoyed them, almost to the point that we’d rather have those seats than the ones in the Premium AWD.
🚨 Tesla Model Y Performance White Interior is 🔥
This seriously might be the best Tesla out there pic.twitter.com/BnSe1GJqqi
— TESLARATI (@Teslarati) January 22, 2026
Additionally, the center screen is slightly larger, but not to the extent that I had really noticed any true difference. In the new Model Y for 2026, the screen is the same size as the one in the Performance trim at 16 inches.
It was previously 15.4 inches.
Some other changes include Performance pedals that are made of what appears to be a stainless steel alloy and Carbon Fiber accents on the doors and dash. Other than that, there are no significant differences; it’s very similar to the other Premium trims of the Model Y. The big difference from an interior standpoint is simply the front seats.
Exterior Differences
Tesla used a lot of different techniques to help improve performance and aerodynamics, including a carbon fiber spoiler and rear diffuser, both of which help with air displacement and improve handling, range, and overall performance.
These additions are clean and give the car a sporty look, perfectly catered to the aesthetic Tesla was obviously going for with the car. I’ve already mentioned the brake calipers, which are an awesome touch, but the offsetting tones of red between them and the paint are a bit displeasing to the eye. I hope this is something that is resolved, but it isn’t completely necessary, nor a priority.
The Nitty Gritty – Ride Quality and Performance
With all the changes from an aesthetic standpoint, including the ones that are geared toward improving performance, the real indicator of whether this trim is worth the extra $11,000 is simple: Is it faster and more fun to drive than the Premium All-Wheel-Drive?
I’m going to break that down here:
Speed and Acceleration
There is a slightly noticeable difference in acceleration, as the 4.6-second 0-60 MPH on the AWD is 1.3 seconds slower than the 3.3-second rate on the Performance. Although that sounds like a decent difference, the big change I noticed was the sound. In the Performance, you can really hear those motors hum, which was a nice touch and really interesting and fun to experience.
It was definitely quicker than my AWD, but I think I really expected to be thrown back into my seat like I was with the Cyberbeast, which features a 2.6-second 0-60 MPH acceleration rate. That was truly a massive difference that anyone can really feel. The 1.3-second difference between the AWD and Performance was, in a way, underwhelming.
I was not disappointed with it, but I really hoped to feel that same rush of adrenaline I had with the Cyberbeast. I think I’m just so used to the acceleration at this point that it does not “wow” me any longer. At the time of the Cyberbeast Demo Drive, I was still driving a gas car.
The Performance, like the AWD, is very capable. It’s great for merging on the highway and getting into a tight window when traffic is heavier. It’s great for taking some quicker drives, and it’s a lot of fun to take out on the road. By no means am I disappointed with it, but I will say maybe my expectations were a tad too high.
Handling
This is where I will say I was sort of disappointed, because I have heard from many people that the suspension is better in the Model Y Performance compared to the All-Wheel-Drive.
I didn’t really feel like it was “better,” but the same, which is still an absolutely amazing ride experience. My AWD is great for tight turns at increased speeds, where I felt the difference was in the seats, as those Performance ones truly did seem to “hug” me more and keep me more stable.
The Performance trim features adaptive suspension, lower/stiffer springs, and larger wheels, all of which are meant to improve handling. I’m not sure if it is simply because I didn’t get to push it as much as I wanted to due to weather, but I felt like the feel of the ride was really similar to my AWD. I had no complaints.
Overall Thoughts
The Model Y Performance is definitely a sportier look than the AWD and Standard models, and it definitely has its advantages. I think that it’s a really great car, but I did not feel an incredible number of differences from the AWD.
🚨 ONE WEEK with the Tesla Model Y Performance: Review and Initial Thoughts
We didn’t get to have as much fun as we wanted in the MYP due to the snow storm, but we were able to give some initial thoughts on the car with the little bit of reasonable weather we had pic.twitter.com/C75WQMNHKO
— TESLARATI (@Teslarati) January 27, 2026
There was a lot to love: the seats, the look, the acceleration. The latter is something that is definitely great if you plan to take your car to a track, but for public roads, it’s not something that is a substantial “need.” When I pushed it on a road local to me and posted a video of it, the commenters were sure to tell me I was going too fast.
I want to be clear that I have zero complaints about the Model Y Performance, and if it were to have come out ahead of me getting my AWD, I probably would have entertained the idea if I could have made the numbers work.
The Model Y, from Standard to Premium, is a great car in every sense of the word. The ride quality is great, the build quality is excellent, and the interior and exterior features, as a whole, make it the best car in the world (to me).
Elon Musk
Elon Musk explains why Tesla’s 4680 battery breakthrough is a big deal
Tesla confirmed in its Q4 and FY 2025 update letter that it is now producing 4680 cells whose anode and cathode were produced during the dry electrode process.

Tesla’s breakthroughs with its 4680 battery cell program mark a significant milestone for the electric vehicle maker. This was, at least, as per Elon Musk in a recent post on social media platform X.
Tesla confirmed in its Q4 and FY 2025 update letter that it is now producing 4680 cells whose anode and cathode were produced during the dry electrode process.
Why dry-electrode matters
In a post on X, Elon Musk stated that making the dry-electrode process work at scale was “incredibly difficult,” calling it a major achievement for Tesla’s engineering, production, and supply chain teams, as well as its partner suppliers. He also shared his praise for the Tesla team for overcoming such a difficult task.
“Making the dry electrode process work at scale, which is a major breakthrough in lithium battery production technology, was incredibly difficult. Congratulations to the @Tesla engineering, production and supply chain teams and our strategic partner suppliers for this excellent achievement!” Musk wrote in his post.
Tesla’s official X account expanded on Musk’s remarks, stating that dry-electrode manufacturing “cuts cost, energy use & factory complexity while dramatically increasing scalability.” Bonne Eggleston, Tesla’s Vice President of 4680 batteries, also stated that “Getting dry electrode technology to scale is just the beginning.”
Tesla’s 4680 battery program
Tesla first introduced the dry-electrode concept at Battery Day in 2020, positioning it as a way to eliminate solvent-based electrode drying, shrink factory footprints, and lower capital expenditures. While Tesla has produced 4680 cells for some time, the dry cathode portion of the process proved far more difficult to industrialize than expected.
Together with its confirmation that it is producing 4680 cells in Austin with both electrodes manufactured using the dry process, Tesla has also stated that it has begun producing Model Y vehicles with 4680 battery packs. As per Tesla, this strategy was adopted as a safety layer against trade barriers and tariff risks.
“We have begun to produce battery packs for certain Model Ys with our 4680 cells, unlocking an additional vector of supply to help navigate increasingly complex supply chain challenges caused by trade barriers and tariff risks,” Tesla wrote in its Q4 and FY 2025 update letter.








