SpaceX
SpaceX’s Starship engine breaks Russian rocketry record held for two decades
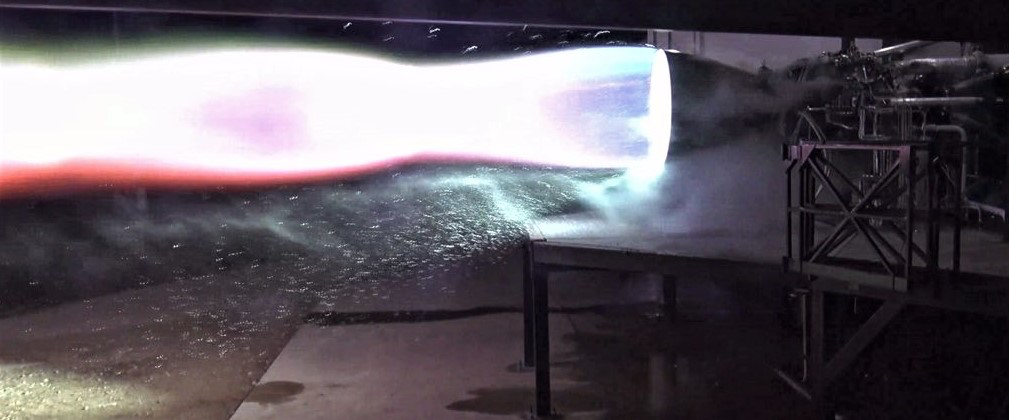
SpaceX CEO Elon Musk says the company’s Raptor engine, meant to power Starship and Super Heavy, has surpassed a rocketry record held by Russian scientists and engineers for more than two decades.
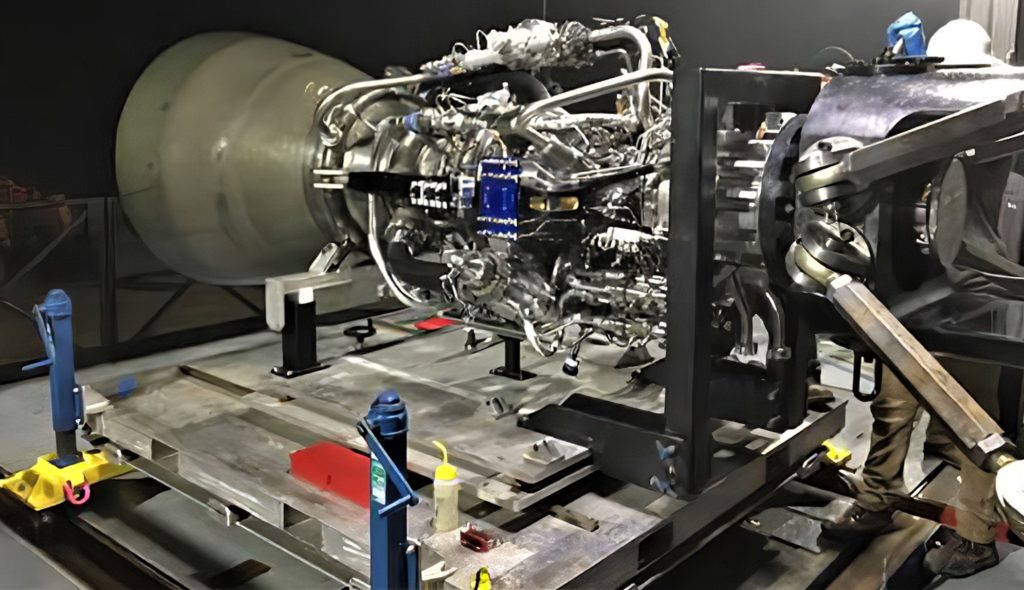
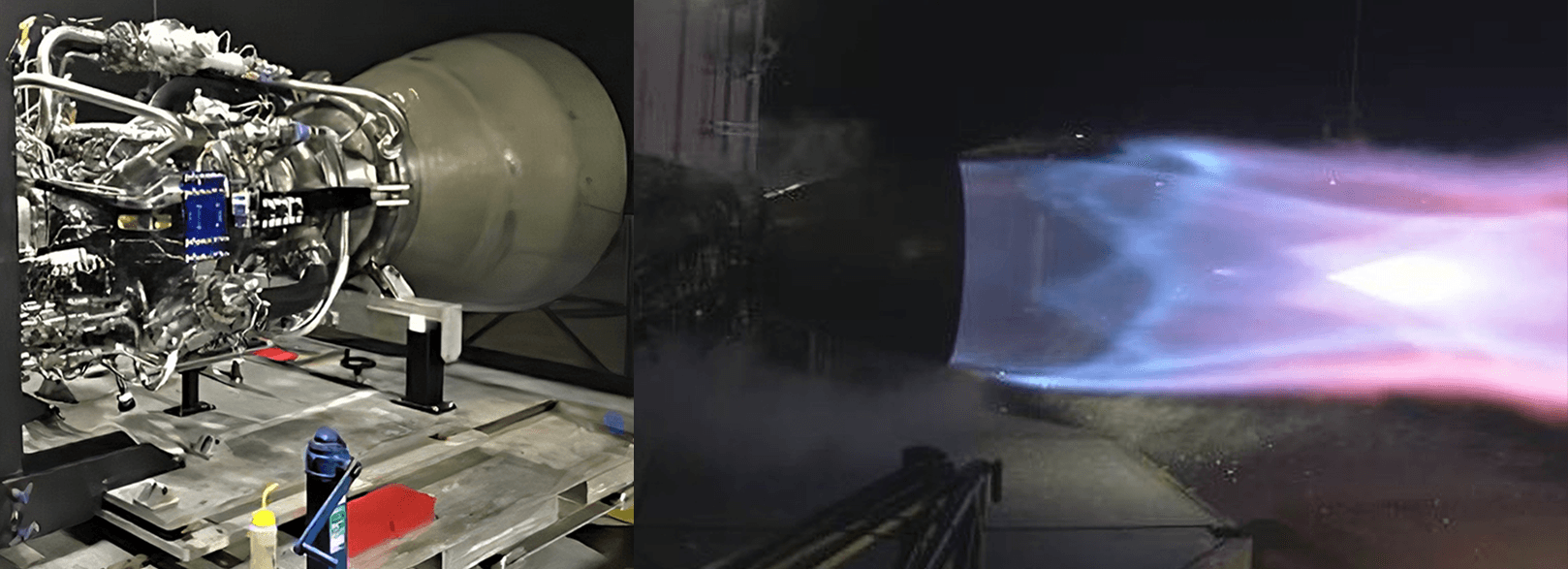
Known as combustion chamber pressure, Raptor has reportedly surpassed a modern Russian engine known as the RD-180, reaching forces equivalent to one Tesla Model 3 balanced on every square inch of Raptor’s combustion chamber, the hardware directly adjacent to a rocket engine’s bell-shaped nozzle.
Raptor reached 268.9 bar today, exceeding prior record held by the awesome Russian RD-180. Great work by @SpaceX engine/test team! pic.twitter.com/yPrvO0JhyY
— Elon Musk (@elonmusk) February 11, 2019
First and foremost, it’s far too early to actually crown Raptor as the new official record-holder for combustion chamber pressure. RD-180 has been reliably flying on ULA’s Atlas V rocket with chamber pressures as high ~257.5 bar (3735 psi) since the year 2000, while Raptor has been performing subscale integrated testing for roughly two years and full-scale integrated testing for less than seven days. As such, the fact that full-scale Raptor has achieved ~269 bar (3900 psi) is an almost unbelievably impressive achievement but probably shouldn’t be used to jump to any conclusions just yet.
Thanks to the 10-20% performance boost supercool liquid methane and oxygen will bring Raptor, currently stuck using propellant just barely cold enough to remain liquid, the engine performing tests could already be made to reach its design specification of 300+ bar (4350+ psi), although Musk cautioned that he wasn’t sure Raptor would be able to survive that power in its current iteration. Nevertheless, 250 bar is apparently more than enough to operate Starship and its Super Heavy booster during most regimes of flight, although maximum thrust (and thus max chamber pressures) is probably desirable for the first minute or so after launch when gravity losses are most significant.
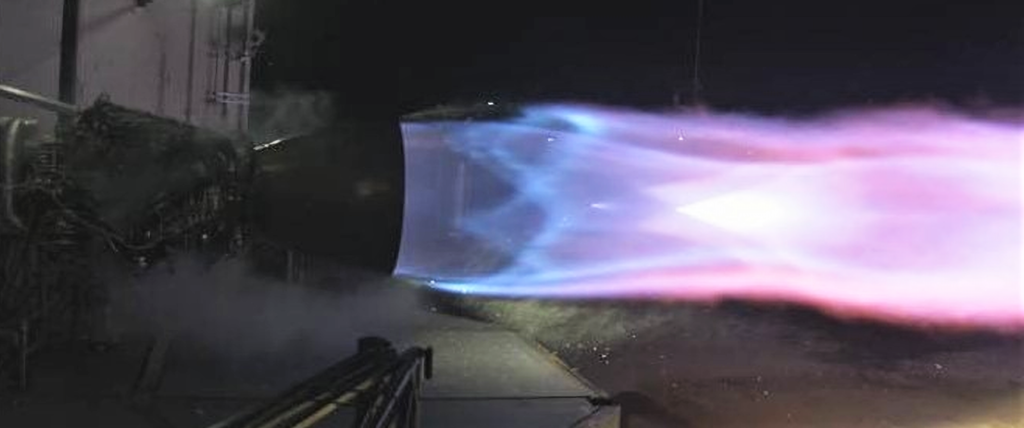
- CEO Elon Musk revealed the first official photos of SpaceX’s finalized Raptor engine, set to support Starship hop tests and early BFR launches. (SpaceX)
- The first finalized Raptor engine (SN01) completed a successful static fire debut on the evening of February 3rd. (SpaceX)
- SpaceX has now tested Raptor successfully at more than twice the thrust of Merlin 1D, the engine that powers Falcon 9. (SpaceX)
- Eventually, three Raptors will be installed on the first full-scale Starship prototype, currently being assembled in South Texas. (NASASpaceflight – bocachicagal.
Ultimately, the sheer speed of SpaceX’s full-scale Raptor test program is easily the most impressive and encouraging aspect of the brand new engine design. While SpaceX does tend towards testing to destruction over putting on kid-gloves around flight or development hardware, it’s safe to say that even SpaceX would avoid frivolously destroying the first full-scale Raptor after just a few dozen seconds of integrated hot-fire testing, indicating that no major red flags have cropped up since the company’s propulsion team began testing on February 3rd. In fact, Musk estimated that six separate static-fires have been performed with Raptor in the seven days since its first ignition.
I think 6 where we lit main chamber & several with only preburners
— Elon Musk (@elonmusk) February 11, 2019
As of 2017, Raptor’s McGregor, Texas test cell was fundamentally capped at test durations under 100 seconds, making comparisons difficult. Still, the best possible recent point of comparison to Raptor’s test program can be found in NASA’s series of tests of Space Shuttle engines in preparation for the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, an expendable launch vehicle being built by Boeing, Aerojet-Rocketdyne, NGIS (formerly Orbital-ATK), and others with NASA funds. Known as RS-25 under the SLS Program, the Space Shuttle engines being test-fired by NASA have already performed multiple full-duration missions to orbit and back on the four Space Shuttle orbiters built. After half a decade in storage, they are being re-tested (effectively acceptance testing) to ensure that they are ready to be expended on SLS launches.
In the first round of 2015 tests, NASA’s Stennis Space Center test stage supported six RS-25 static-fires total, ranging from two weeks to almost five months between tests. RS-25 testing has remained on a similar schedule in 2016-2018, averaging 4-6 tests annually with no fewer than two weeks between static-fires. Given that the vast majority of those ex-Space Shuttle Main Engine tests tend to last hundreds of seconds, it’s not a perfect comparison, but it offers at least a general idea of just how incredible it is to see a groundbreaking engine like Raptor test-fired almost daily just days after it was installed on a test stand for the first time.
— Elon Musk (@elonmusk) February 4, 2019
Check out Teslarati’s newsletters for prompt updates, on-the-ground perspectives, and unique glimpses of SpaceX’s rocket launch and recovery processes!

Elon Musk
Elon Musk shares insights on SpaceX and Tesla’s potential scale
In a pair of recent posts on X, Musk argued that both companies operate in domains where growth is not linear, but exponential.

Elon Musk outlined why he believes Tesla and SpaceX ultimately dwarf their competitors, pointing to autonomy, robotics, and space-based energy as forces that fundamentally reshape economic scale.
In a pair of recent posts on X, Musk argued that both companies operate in domains where growth is not linear, but exponential.
Space-based energy
In a response to a user on X who observed that SpaceX has a larger valuation than all six US defense companies combined, Musk explained that space-based industries will eventually surpass the total economic value of Earth. He noted that space allows humanity to harness roughly 100,000 times more energy than Earth currently uses, while still consuming less than a millionth of the Sun’s total energy output.
That level of available energy should enable the emergence and development of industries that are simply not possible within Earth’s physical and environmental constraints. Continuous solar exposure in space, as per Musk’s comment, removes limitations imposed by atmosphere, weather, and land availability.
Autonomy and robots
In a follow-up post, Elon Musk explaned that “due to autonomy, Tesla is worth more than the rest of the auto industry.” Musk added that this assessment does not yet account for Optimus, Tesla’s humanoid robot. As per the CEO, once Optimus reaches scaled production, it could increase Earth’s gross domestic product by an order of magnitude, ultimately paving the way for sustainable abundance.
Even before the advent of Optimus, however, Tesla’s autonomous driving system already gives vehicles the option to become revenue-generating assets through services like the Tesla Robotaxi network. Tesla’s autonomous efforts seem to be on the verge of paying off, as services like the Robotaxi network have already been launched in its initial stages in Austin and the Bay Area.
Elon Musk
Tesla CEO Elon Musk trolls budget airline after it refuses Starlink on its planes
“I really want to put a Ryan in charge of Ryan Air. It is your destiny,” Musk said.

Tesla CEO Elon Musk trolled budget airline Ryanair on his social media platform X this week following the company’s refusal to adopt Starlink internet on its planes.
Earlier this week, it was reported that Ryanair did not plan to install Starlink internet services on its planes due to its budgetary nature and short flight spans, which are commonly only an hour or so in total duration.
Initially, Musk said installing Starlink on the company’s planes would not impact cost or aerodynamics, but Ryanair responded on its X account, which is comical in nature, by stating that a propaganda it would not fall for was “Wi-Fi on planes.”
Musk responded by asking, “How much would it cost to buy you?” Then followed up with the idea of buying the company and replacing the CEO with someone named Ryan:
I really want to put a Ryan in charge of Ryan Air. It is your destiny.
— Elon Musk (@elonmusk) January 19, 2026
Polymarket now states that there is an 8 percent chance that Musk will purchase Ryanair, which would cost Musk roughly $36 billion, based on recent financial data of the public company.
Although the banter has certainly crossed a line, it does not seem as if there is any true reason to believe Musk would purchase the airline. More than anything, it seems like an exercise of who will go further.
Starlink passes 9 million active customers just weeks after hitting 8 million
However, it is worth noting that if something is important enough, Musk will get involved. He bought Twitter a few years ago and then turned it into X, but that issue was much larger than simple banter with a company that does not want to utilize one of the CEO’s products.
The insufferable, special needs chimp currently running Ryan Air is an accountant. Has no idea how airplanes even fly.
— Elon Musk (@elonmusk) January 20, 2026
In a poll posted yesterday by Musk, asking whether he should buy Ryanair and “restore Ryan as their rightful ruler.” 76.5 percent of respondents said he should, but others believe that the whole idea is just playful dialogue for now.
But it is not ideal to count Musk out, especially if things continue to move in the direction they have been.
Elon Musk
Lufthansa Group to equip Starlink on its 850-aircraft fleet
Under the collaboration, Lufthansa Group will install Starlink technology on both its existing fleet and all newly delivered aircraft, as noted by the group in a press release.

Lufthansa Group has announced a partnership with Starlink that will bring high-speed internet connectivity to every aircraft across all its carriers.
This means that aircraft across the group’s brands, from Lufthansa, SWISS, and Austrian Airlines to Brussels Airlines, would be able to enjoy high-speed internet access using the industry-leading satellite internet solution.
Starlink in-flight internet
Under the collaboration, Lufthansa Group will install Starlink technology on both its existing fleet and all newly delivered aircraft, as noted by the group in a press release.
Starlink’s low-Earth orbit satellites are expected to provide significantly higher bandwidth and lower latency than traditional in-flight Wi-Fi, which should enable streaming, online work, and other data-intensive applications for passengers during flights.
Starlink-powered internet is expected to be available on the first commercial flights as early as the second half of 2026. The rollout will continue through the decade, with the entire Lufthansa Group fleet scheduled to be fully equipped with Starlink by 2029. Once complete, no other European airline group will operate more Starlink-connected aircraft.
Free high-speed access
As part of the initiative, Lufthansa Group will offer the new high-speed internet free of charge to all status customers and Travel ID users, regardless of cabin class. Chief Commercial Officer Dieter Vranckx shared his expectations for the program.
“In our anniversary year, in which we are celebrating Lufthansa’s 100th birthday, we have decided to introduce a new high-speed internet solution from Starlink for all our airlines. The Lufthansa Group is taking the next step and setting an essential milestone for the premium travel experience of our customers.
“Connectivity on board plays an important role today, and with Starlink, we are not only investing in the best product on the market, but also in the satisfaction of our passengers,” Vranckx said.