News
Mars could have a Leap Day like Earth but way more complicated
February 29, “leap day”, is an oddity on the calendar that occurs every four years in an attempt to sync up the Gregorian calendar (the calendar most of the world uses to keep time) with Earth’s rotation around the sun.
One calendar year on Earth is 365 days long; however, the Earth actually takes 365.2422 days to lap the sun. That puts the planet roughly a quarter of a day behind at the end of each year.
To maintain consistency and ensure the seasons line up each year, an extra day was added to the already short month of February — a modification that happens every four years. But even this doesn’t fully solve the problem; additional tweaks are needed.
For instance, if a year is divisible by 100, there’s no extra day — unless the year is divisible by 400. That means that 1700, 1800 and 1900 did not have a leap day, but 2000 did. This adjustment ensures that Earth is as close as possible to the same point in its orbit in consecutive calendar years and keeps our seasons inline.
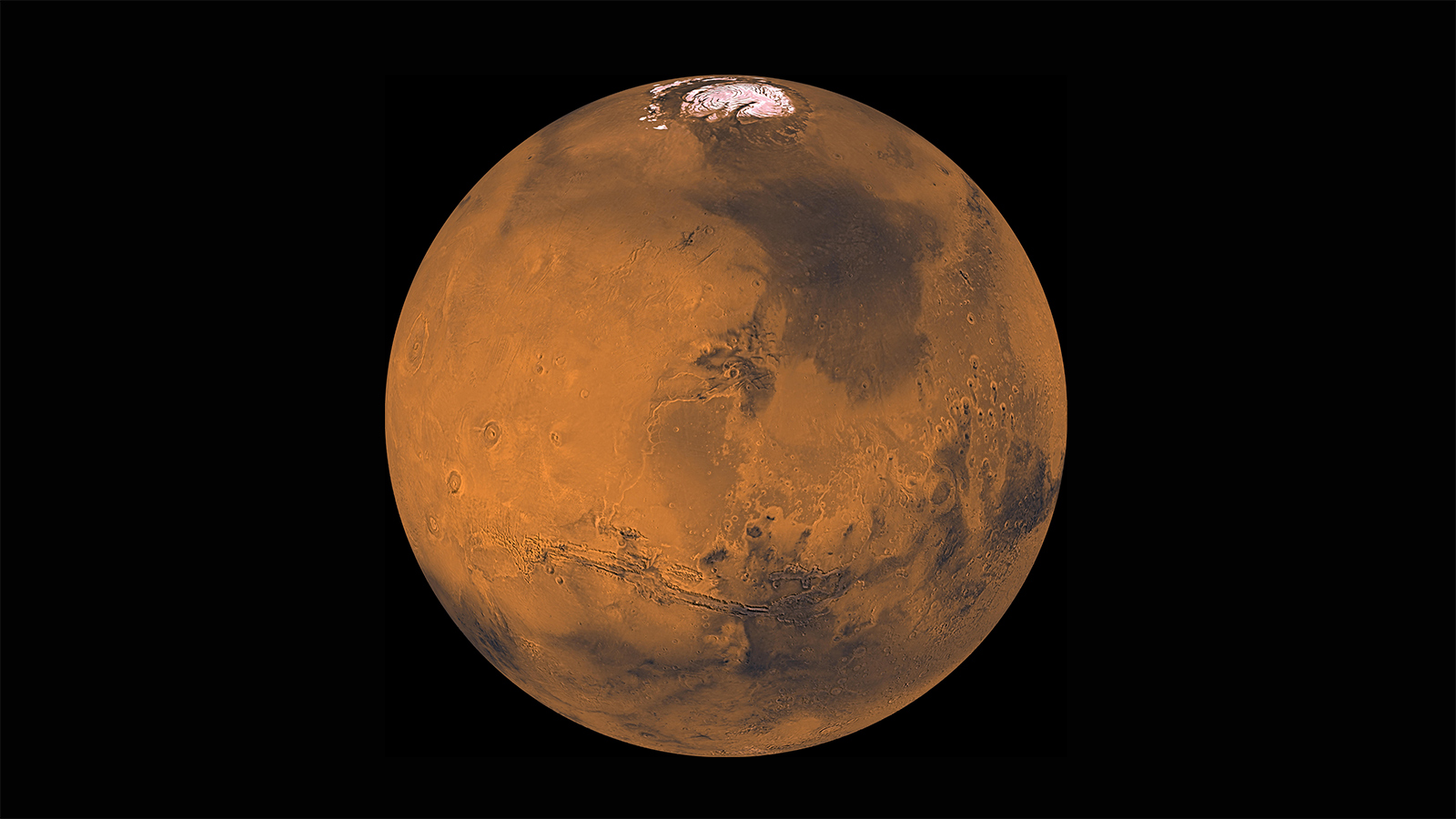
Unsurprisingly, Earth is not the only planet that needs leap days. The phenomenon could occur on other planets in our solar system as well as those around other stars. That’s because you can’t fit an exact number of spins into one trip around the sun for any planet. There’s usually going to be something left over. Leap days on other worlds, such as Mars, could be more complicated than those here on Earth.
One year on Mars lasts for approximately 668.6 Martian days. (A Martian day is called a sols and equals 24 hours, 39 minutes, and 35.244 seconds.) Future inhabitants might decide that a year on the red planet will be described as 668 days. How do we adjust?
Over the decades, many different ideas for the Martian calendar have been proposed. The most popular one, called the Darian calendar, was created in 1985 by Tomas Gangale.
According to Gangale, the Martian calendar would feature 24 months, each named for the Latin and Sanskrit words for the constellation of the zodiac, like Sagittarius and Dhanus, and so forth. The first five months in each quarter would have 28 Martian days (or sols), with the sixth having only 27. Even-numbered years would total 668 days and odd-numbered years would have 669. The exception to that rule: even-numbered years that were divisible by 10.

Another option was proposed by Michael Allison, a retired NASA scientist. In his version, the Martian calendar would have 668-days divided into 22 months, each totaling 30 or 31 days, similar in fashion to Earth. To make sure the seasons lined up, all years divisible by five will have three leap days, bringing the total to 671.
So which of these calendars do scientists use to keep track of time on Mars? Currently, none.
Instead, they use two systems to keep track of time: one counts the number of Martian days since the start of a mission, and the other keeps track of where Mars was in its orbit at that time.
Right now scientists don’t care if the seasons line up perfectly with the calendar, but that may change when you add humans into the mix. NASA and other space agencies around the world have their sights set on Mars. Once humans land on the red planet and spend significant time there, we are going to need a common calendar to keep track of seasons.

News
Tesla preps to build its most massive Supercharger yet: 400+ V4 stalls
The project will be an expansion of the current Eddie World Supercharger in Yermo, California, and will take place in several stages.
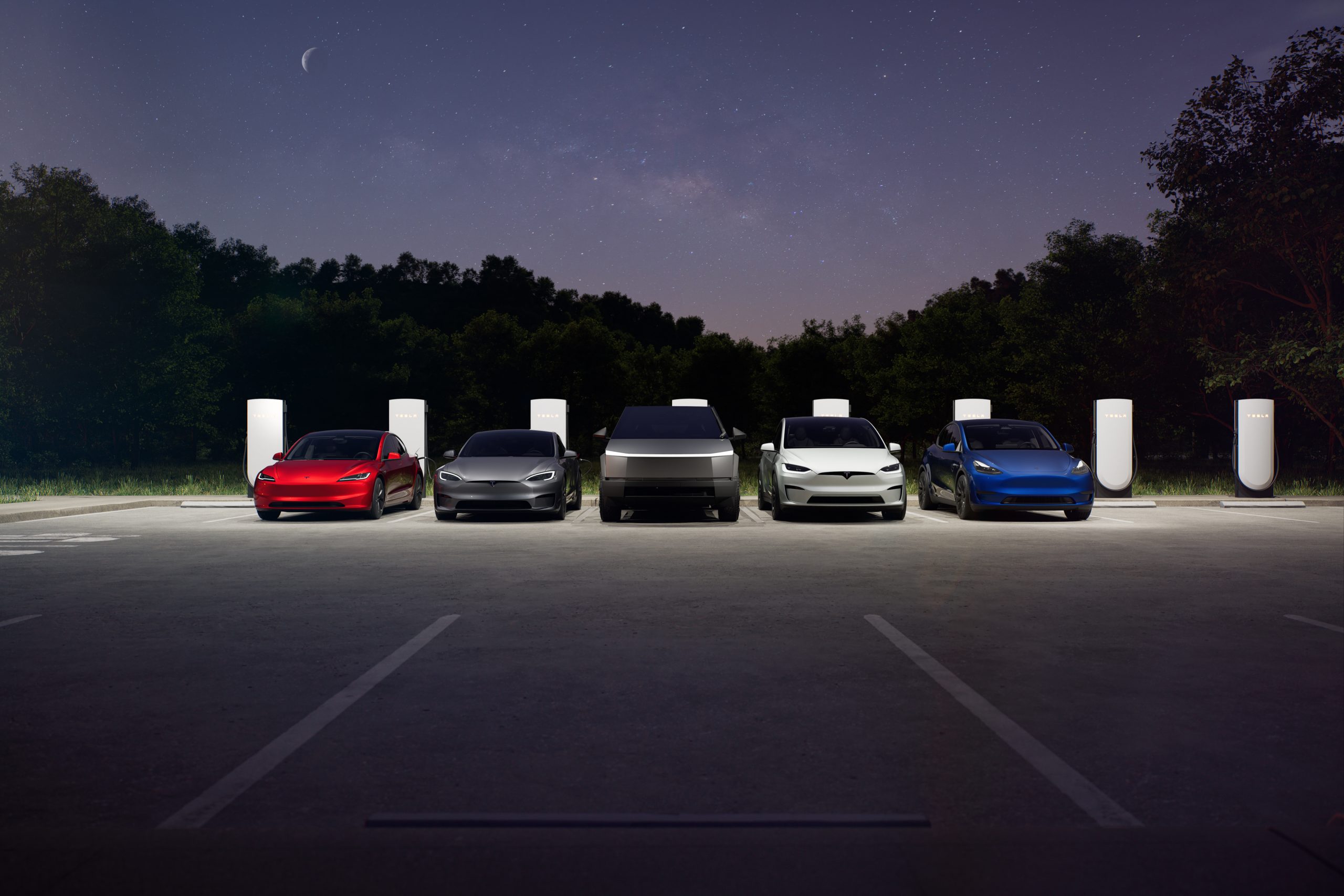

Tesla is preparing to build its most massive Supercharger yet, as it recently submitted plans for an over 400-stall Supercharging station in California, which would dwarf its massive 168-stall location in Lost Hills, California.
The project will be an expansion of the current Eddie World Supercharger in Yermo, California, and will take place in several stages.
The expansion, adjacent to the existing Eddie World Supercharger, which is currently comprised of 22 older V2 and V3 stalls limited to 150 kW, unfolds across six phases.
Construction on Phase 1 begins later this year with 72 V4 stalls. Subsequent stages will progressively add hundreds more, culminating in over 400 next-generation chargers. Site plans label expansive parking arrays across Phases 1–5 along Calico Boulevard, with Phase 6 design still to be determined.
Tesla is planning an absolutely massive Supercharger expansion in Yermo, California!!
Over the course of 6 phases, Tesla is set to add over 400 V4 stalls in a commercial development known as Eddie World 2.
The first phase, which should begin construction sometime this year,… pic.twitter.com/ks5Y5dE8lR
— MarcoRP (@MarcoRPi1) March 6, 2026
The project was first flagged by MarcoRP, a notable Tesla Supercharger watcher.
Strategically located midway on I-15 between Los Angeles and Las Vegas, the station targets heavy EV traffic on this high-demand corridor.
The surrounding 20-mile stretch already hosts over 200 high-power stalls (including 40 at 250 kW, 120 at 325 kW, and more), plus 96 in nearby Baker—yet bottlenecks persist during peak travel.
In scale, it eclipses all existing Tesla Superchargers. The current record holder, the solar- and Megapack-powered “Project Oasis” in Lost Hills, California, offers 164 stalls. Barstow’s former leader had 120. Eddie World 2 will be more than double that size, cementing Tesla’s dominance in ultra-high-capacity charging.
Tesla finishes its biggest Supercharger ever with 168 stalls
Development blends charging with convenience. Architectural drawings show integrated retail: a 10,100 square foot Cracker Barrel, a 4,300 square foot McDonald’s, a 3,800 square foot convenience store, additional restaurants, drive-thrus, outdoor dining, and lease space.
EV-centric features include pull-through bays for Cybertrucks and trailers, ensuring accessibility for larger vehicles and future Semi trucks.
News
Tesla makes latest move to remove Model S and Model X from its lineup
Tesla’s latest decisive step toward phasing out its flagship sedan and SUV was quietly removing the Model S and Model X from its U.S. referral program earlier this week.

Tesla has made its latest move that indicates the Model S and Model X are being removed from the company’s lineup, an action that was confirmed by the company earlier this quarter, that the two flagship vehicles would no longer be produced.
Tesla has ultimately started phasing out the Model S and Model X in several ways, as it recently indicated it had sold out of a paint color for the two vehicles.
Now, the company is making even more moves that show its plans for the two vehicles are being eliminated slowly but surely.
Tesla’s latest decisive step toward phasing out its flagship sedan and SUV was quietly removing the Model S and Model X from its U.S. referral program earlier this week.
The change eliminates the $1,000 referral discount previously available to new buyers of these vehicles. Existing Tesla owners purchasing a new Model S or Model X will now only receive a halved loyalty discount of $500, down from $1,000.
The updates extend beyond the two flagship vehicles. New Cybertruck buyers using a referral code on Premium AWD or Cyberbeast configurations will no longer get $1,000 off. Instead, both referrer and buyer receive three months of Full Self-Driving (Supervised).
The loyalty discount for Cybertruck purchases, excluding the new Dual Motor AWD trim level, has also been cut to $500.
NEWS: Tesla has removed the Model S and Model X from the referral program.
New owners also no longer get a $1,000 referral discount on a new Cybertruck Premium AWD or Cyberbeast. Instead, you now get 3 months of FSD (Supervised).
Additionally, Tesla has reduced the loyalty… pic.twitter.com/IgIY8Hi2WJ
— Sawyer Merritt (@SawyerMerritt) March 6, 2026
These adjustments apply only in the United States, and reflect Tesla’s broader strategy to optimize margins while boosting adoption of its autonomous driving software.
The timing is no coincidence. Tesla confirmed earlier this year that Model S and Model X production will end in the second quarter of 2026, roughly June, as the company reallocates factory capacity toward its Optimus humanoid robot and next-generation vehicles.
With annual sales of the low-volume flagships already declining (just 53,900 units in 2025), incentives are no longer needed to drive demand. Production is winding down, and Tesla expects strong remaining interest without subsidies.
Industry observers see this as the clearest sign yet of an “end-of-life” phase for the vehicles that once defined Tesla’s luxury segment. Community reactions on X range from nostalgia, “Rest in power S and X”, to frustration among long-time owners who feel perks are eroding just as the models approach discontinuation.
Some buyers are rushing orders to lock in final discounts before they vanish entirely.
Doug DeMuro names Tesla Model S the Most Important Car of the last 30 years
For Tesla, the move prioritizes efficiency: fewer discounts on outgoing models, a stronger push for FSD subscriptions, and a focus on high-margin Cybertruck trims amid surging orders.
Loyalists still have a narrow window to purchase a refreshed Plaid or Long Range model with remaining incentives, but the message is clear: Tesla’s lineup is evolving, and the era of the original flagships is drawing to a close.
News
Tesla Australia confirms six-seat Model Y L launch in 2026
Compared with the standard five-seat Model Y, the Model Y L features a longer body and extended wheelbase to accommodate an additional row of seating.
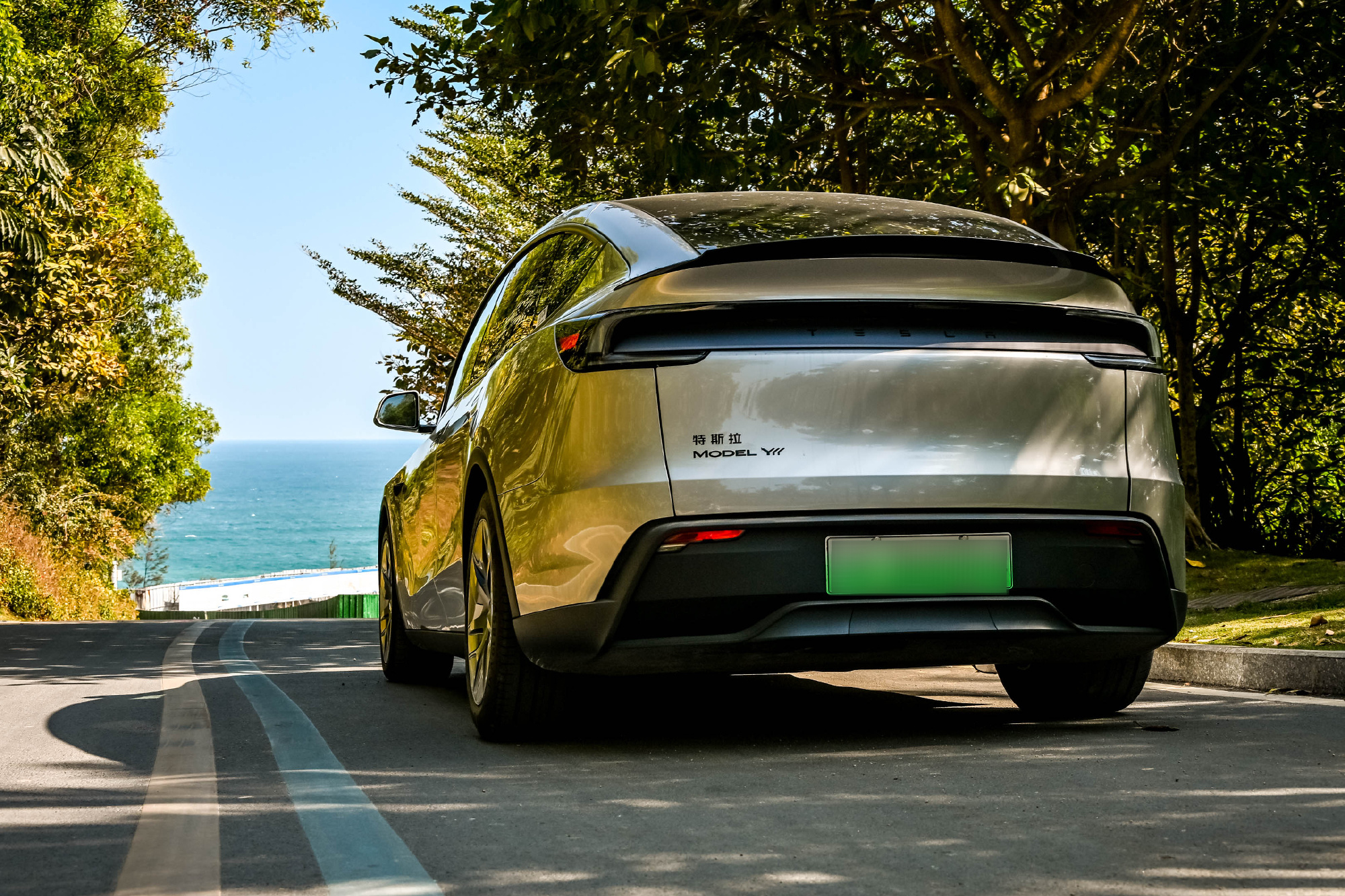

Tesla has confirmed that the larger six-seat Model Y L will launch in Australia and New Zealand in 2026.
The confirmation was shared by techAU through a media release from Tesla Australia and New Zealand.
The Model Y L expands the Model Y lineup by offering additional seating capacity for customers seeking a larger electric SUV. Compared with the standard five-seat Model Y, the Model Y L features a longer body and extended wheelbase to accommodate an additional row of seating.
The Model Y L is already being produced at Tesla’s Gigafactory Shanghai for the Chinese market, though the vehicle will be manufactured in right-hand-drive configuration for markets such as Australia and New Zealand.
Tesla Australia and New Zealand confirmed the vehicle will feature seating for six passengers.
“As shown in pictures from its launch in China, Model Y L will have a new seating configuration providing room for 6 occupants,” Tesla Australia and New Zealand said in comments shared with techAU.
Instead of a traditional seven-seat arrangement, the Model Y L uses a 2-2-2 layout. The middle row features two individual seats, allowing easier access to the third row while providing additional space for passengers.
Tesla Australia and New Zealand also confirmed that the Model Y L will be covered by the company’s updated warranty structure beginning in 2026.
“As with all new Tesla Vehicles from the start of 2026, the Model Y L will come with a 5-year unlimited km vehicle warranty and 8 years for the battery,” the company said.
The updated policy increases Tesla’s vehicle warranty from the previous four-year or 80,000-kilometer coverage.
Battery and drive unit warranties remain unchanged depending on the variant. Rear-wheel-drive models carry an eight-year or 160,000-kilometer warranty, while Long Range and Performance variants are covered for eight years or 192,000 kilometers.
Tesla has not yet announced official pricing or range figures for the Model Y L in Australia.








