SpaceX
SpaceX goes all-in on steel Starship, scraps expensive carbon fiber BFR tooling
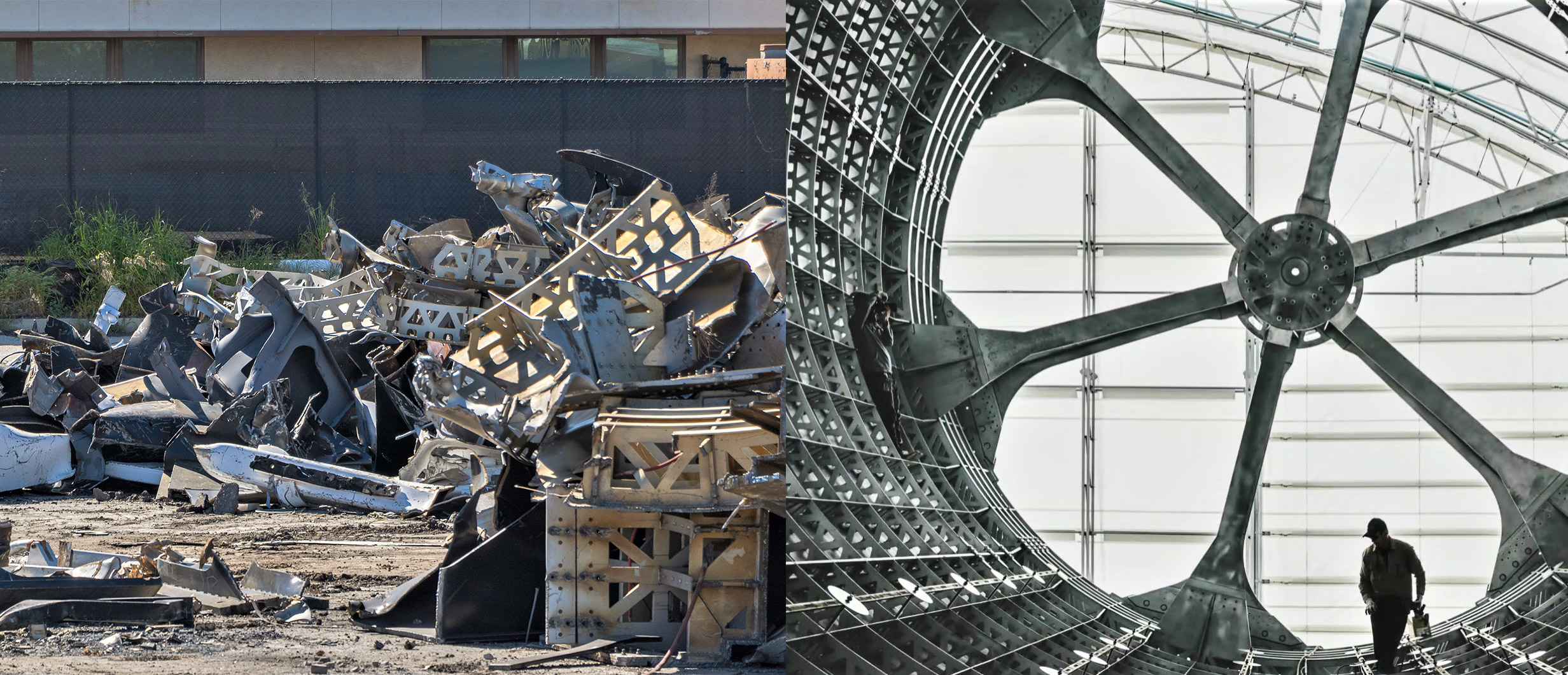
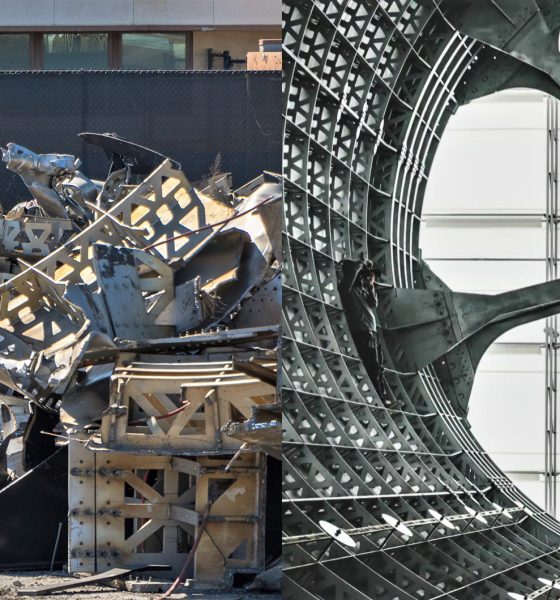
In a wholly unforeseen turn of events, SpaceX has taken the extraordinary step of permanently scrapping both its Port of Los Angeles-based BFR development tent and what seem to be the majority of what it contained, irreparably destroying custom-built tooling meant to support the fabrication of carbon composite BFR spaceships and boosters.
Likely worth anywhere from several to tens of millions of dollars (USD), SpaceX’s advanced BFR production tools were procured from industry-expert Ascent Aerospace sometime in 2017 before being officially delivered to the rocket company’s newly-erected Port of LA tent around April 2018. Situated at the port specifically due to logistical concerns about the high cost of transporting 9m/30ft-diameter objects from SpaceX’s main Hawthorne facilities to a barge for transport east, the company has decided to unequivocally destroy its aerospace-grade composite tooling less than 12 months after accepting delivery. Put simply, this is the best evidence yet that SpaceX – willing or not – has gone all-in on build Starship and Super Heavy out of stainless steel less than six months after CEO Elon Musk began to hint at the program’s utterly radical pivot.

From the very beginning of SpaceX and Elon Musk’s serious pursuit of an entirely reusable launch vehicle capable of transporting dozens of astronauts and passengers to and from Earth and Mars, the plan had been to build the vast majority of the rocket’s booster and spacecraft structures out of advanced carbon fiber composite materials. Above all else, this fundamental architecture was motivated largely by the significant performance gains a rocket could achieve by replacing traditional aluminum tanks and structures with carbon fiber.
For a rocket (and especially an orbital spaceship) meant to somehow make Earth-Mars transport both routine and at least minutely affordable, focusing primarily on the optimization of the mass of cargo delivered relative to the empty weight of the spaceship and booster made (and still does make) a great deal of sense. Assuming that the reusability of a system is roughly constant, the only conceivable way to further lower the cost of price per unit of cargo or passenger ticket would be to increase the usable cargo/passenger capacity for each individual launch, making an extremely light and high-performance rocket the low-hanging fruit target.


The centrality of carbon fiber composites remained with SpaceX’s Sept. 2017 iteration of BFR, downsized by 25% to a diameter of 9m (~30 ft). Around six months later, that commitment to composites was further solidified by the delivery of the first 9m-diameter carbon fiber tooling in March or April 2018. The tooling used to mold and
In the subsequent months of 2018, SpaceX’s BFR and composite R&D team spent tens of thousands of hours building out an ad-hoc advanced composites workshop inside a temporary tent in an industrial area, and ultimately managed to build a number of full-scale carbon fiber segments, including at least one large tank barrel section and the beginnings of a tank dome. In September 2018, that progress was partially revealed alongside the announcement that Japanese billionaire Yasuka Maezawa had purchased the first crewed lunar launch of BFR for several hundred million dollars, set to occur no earlier than 2023.
Two months after indicating that the first BFR “airframe/tank barrel section” would be built out of a “new carbon fiber material”, Musk provided the very first teaser for a “counterintuitive” development that would later be identified as the CEO’s decision to wholly replace BFR’s proposed used of composites with stainless steel and an advanced metallic heat shield. Still more than a little controversial and hard to follow almost half a year later, the feeling at the time was that SpaceX’s eccentric leader had decided to throw away more than 24 months of composite BFR design and development work for an almost entirely unproven alternative approach.
For better or for worse, it appears that SpaceX (or maybe just Musk) has quite literally trashed the most concrete demonstration of a prior commitment to advanced carbon fiber composites, scrapping the vast majority of its composite tooling and perhaps even the prototype BFR segments built in 2018.


It remains to be seen whether the now-permanent decision to pursue a stainless steel design in place of carbon fiber was a very expensive mistake, a stroke of genius, or something in between, However, the undeniably brisk progress made with the BFR’s steel variant in last four or so months bodes well – at a minimum – for Musk’s optimism that this radical change will ultimately result in an operational vehicle far sooner (and presumably cheaper) than the composites route.
Generally speaking, it seems safe to – on the face of it – agree with Musk’s argument that steel should ultimately lend itself far more easily to reusability thanks to its high tolerance for extreme temperatures. Unlike Falcon 9’s aluminum structures (and even the most exotic, advanced carbon fiber composites), certain varieties of stainless steel can weather heating approaching that experienced during orbital reentry with minimal erosion or damage to its mechanical properties. As Musk puts it, the Super Heavy booster’s suborbital trajectory could require almost no heat shielding – and perhaps even paint – at all.
Only time will tell whether the inevitably harsher realities of real-life engineering are so kind. In the meantime, SpaceX is perhaps just hours away from the first attempted static-fire test of a Raptor installed on something approaching flight-hardware, in this case a full-scale Starship hop test prototype.
Check out Teslarati’s Marketplace! We offer Tesla accessories, including for the Tesla Cybertruck and Tesla Model 3.

Elon Musk
FCC chair criticizes Amazon over opposition to SpaceX satellite plan
Carr made the remarks in a post on social media platform X.

U.S. Federal Communications Commission (FCC) Chairman Brendan Carr criticized Amazon after the company opposed SpaceX’s proposal to launch a large satellite constellation that could function as an orbital data center network.
Carr made the remarks in a post on social media platform X.
Amazon recently urged the FCC to reject SpaceX’s application to deploy a constellation of up to 1 million low Earth orbit satellites that could serve as artificial intelligence data centers in space.
The company described the proposal as a “lofty ambition rather than a real plan,” arguing that SpaceX had not provided sufficient details about how the system would operate.
Carr responded by pointing to Amazon’s own satellite deployment progress.
“Amazon should focus on the fact that it will fall roughly 1,000 satellites short of meeting its upcoming deployment milestone, rather than spending their time and resources filing petitions against companies that are putting thousands of satellites in orbit,” Carr wrote on X.
Amazon has declined to comment on the statement.
Amazon has been working to deploy its Project Kuiper satellite network, which is intended to compete with SpaceX’s Starlink service. The company has invested more than $10 billion in the program and has launched more than 200 satellites since April of last year.
Amazon has also asked the FCC for a 24-month extension, until July 2028, to meet a requirement to deploy roughly 1,600 satellites by July 2026, as noted in a CNBC report.
SpaceX’s Starlink network currently has nearly 10,000 satellites in orbit and serves roughly 10 million customers. The FCC has also authorized SpaceX to deploy 7,500 additional satellites as the company continues expanding its global satellite internet network.
Elon Musk
NASA watchdog says Starship development delays could affect Artemis timeline
The report noted that several technical milestones still need to be completed before Starship can serve as a crewed lunar lander.

A NASA watchdog report stated that continued development work on SpaceX’s Starship could affect the timeline for the agency’s planned Artemis moon missions. The report noted that several technical milestones still need to be completed before the spacecraft can serve as a crewed lunar lander.
The findings were detailed in a report from NASA’s Office of Inspector General, as noted in a report from Reuters.
NASA selected SpaceX’s Starship in 2021 to serve as the Human Landing System (HLS) for its Artemis lunar program. The vehicle is intended to transport astronauts from lunar orbit to the surface of the Moon and back as part of future Artemis missions.
According to the watchdog report, Starship’s development has experienced roughly two years of schedule delays compared to earlier expectations. Still, NASA is targeting 2028 for the first crewed lunar landing using the Starship lander.
One of the most significant technical milestones for Starship’s lunar missions is in-space refueling.
To support a crewed lunar landing, multiple Starship launches will be required to deliver propellant to orbit. Tanker versions of Starship will transfer fuel to a storage depot spacecraft, which will then refuel the lunar lander.
The report noted that this approach could require more than 10 Starship launches to fully refuel the spacecraft needed for a single lunar landing mission.
NASA officials indicated that demonstrating cryogenic propellant transfer in orbit remains one of the most important technical steps before Starship can be certified for lunar missions.
SpaceX has conducted 11 Starship test flights since 2023 as the company continues developing the fully reusable launch system. A 12th test flight, this time featuring Starship V3, is expected to be held in early April.
Elon Musk
SpaceX weighs Nasdaq listing as company explores early index entry: report
The company is reportedly seeking early inclusion in the Nasdaq-100 index.

Elon Musk’s SpaceX is reportedly leaning toward listing its shares on the Nasdaq for a potential initial public offering (IPO) that could become the largest in history.
As per a recent report, the company is reportedly seeking early inclusion in the Nasdaq-100 index. The update was reported by Reuters, citing people familiar with the matter.
According to the publication, SpaceX is considering Nasdaq as the venue for its eventual IPO, though the New York Stock Exchange is also competing for the listing. Neither exchange has reportedly been informed of a final decision.
Reuters has previously reported that SpaceX could pursue an IPO as early as June, though the company’s plans could still change.
One of the publication’s sources also suggested that SpaceX is targeting a valuation of about $1.75 trillion for its IPO. At that level, the company would rank among the largest publicly traded firms in the United States by market capitalization.
Nasdaq has proposed a rule change that could accelerate the inclusion of newly listed megacap companies into the Nasdaq-100 index.
Under the proposed “Fast Entry” rule, a newly listed company could qualify for the index in less than a month if its market capitalization ranks among the top 40 companies already included in the Nasdaq-100.
If SpaceX is successful in achieving its target valuation of $1.75 trillion, it would become the sixth-largest company by market value in the United States, at least based on recent share prices.
Newly listed companies typically have to wait up to a year before becoming eligible for major indexes such as the Nasdaq-100 or S&P 500.
Inclusion in a major index can significantly broaden a company’s shareholder base because many institutional investors purchase shares through index-tracking funds.
According to Reuters, Nasdaq’s proposed fast-track rule is partly intended to attract highly valued private companies such as SpaceX, OpenAI, and Anthropic to list on the exchange.


![Lucid Lunar robotaxi concept [Credit: Rendering by TESLARATI]](https://www.teslarati.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/03/lucid-lunar-robotaxi-concept-teslarati-rendering-80x80.jpg)





