

SpaceX
SpaceX CEO Elon Musk hints at new Falcon fairing reuse plan after Mr. Steven misses catch
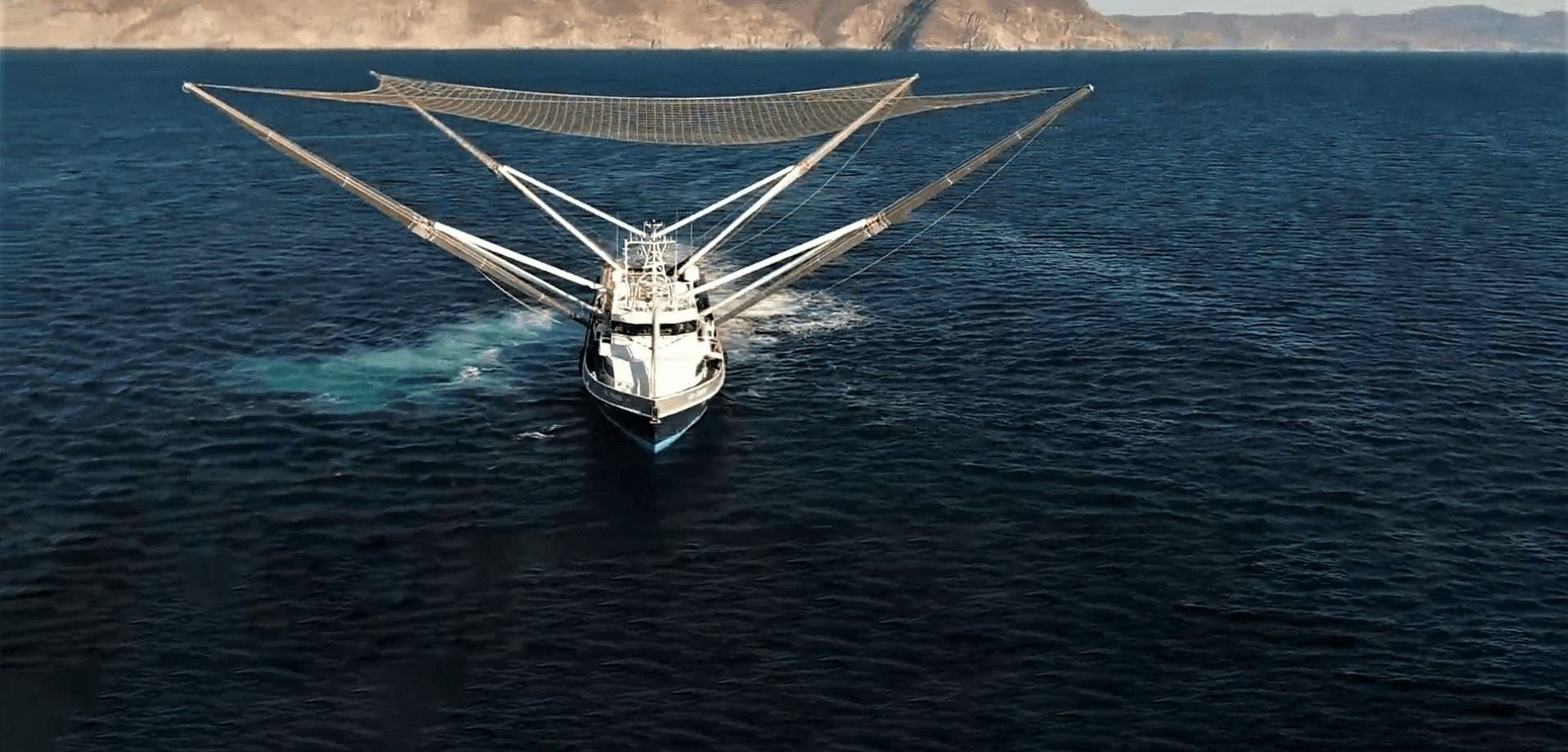
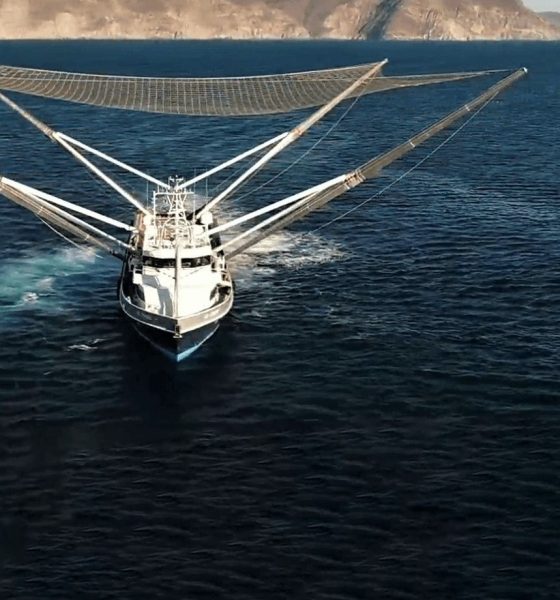
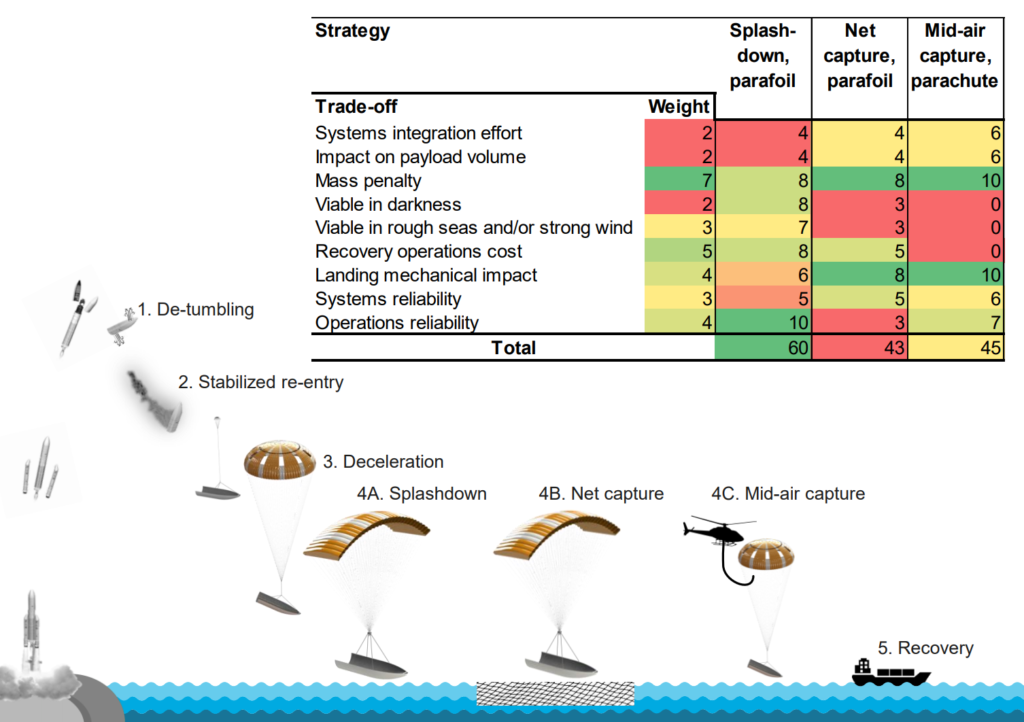
Ninety minutes after a flawless Falcon 9 launch, landing, and payload deployment, SpaceX CEO Elon Musk took to Twitter to provide an update on the status of Mr. Steven’s latest payload fairing catch attempt.
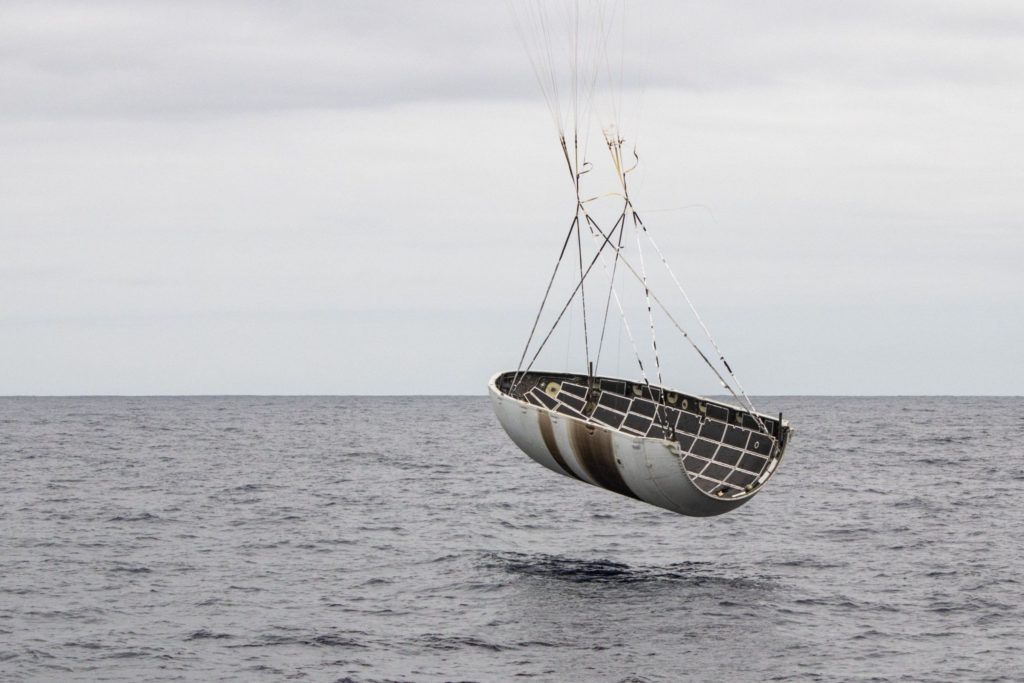
While sadly unsuccessful on the catch front, Musk noted that both fairing halves successfully performed gentle touchdowns on the ocean surface. Far more importantly, the CEO implied that – counter to past ocean surface recoveries – SpaceX fairing engineers and technicians would instead attempt to dry and clean these particular fairing halves well enough that they can be reused on a future launch.
Falcon fairing halves missed the net, but touched down softly in the water. Mr Steven is picking them up. Plan is to dry them out & launch again. Nothing wrong with a little swim.
— Elon Musk (@elonmusk) December 3, 2018
Intriguingly, this is almost a 180-degree shift in SpaceX’s long-publicized attitude towards fairing recovery, where the implication was that fairing halves would wind up being unreusable if they could not be prevented from landing directly on the ocean surface. To some extent, this was a reasonable argument – thanks to the highly sensitive satellites they enclose, payload fairings must be able to support an internal atmosphere equivalent to a reasonably high-performance clean room while still weighing next to nothing. Falcon 9’s fairing halves weigh approximately 800 kg apiece and are large enough to enclose an entire school bus with plenty of room to spare.
However, this narrative has not exactly been mirrored by prospective competitors, especially international technology manufacturer RUAG, which produces payload fairings and other composite assemblies for both ULA (United Launch Alliance) and Arianespace, SpaceX’s only serious commercial competitors. In a study released earlier this year, a RUAG-funded cost-benefit analysis concluded that the simplest, cheapest, and easiest route to fairing reuse would be simply finding ways to effectively waterproof and clean them after soft ocean landings.
- A RUAG study concluded that waterproofing and cleaning fairings was the best possible route to reuse. (RUAG)
- Close. (SpaceX)
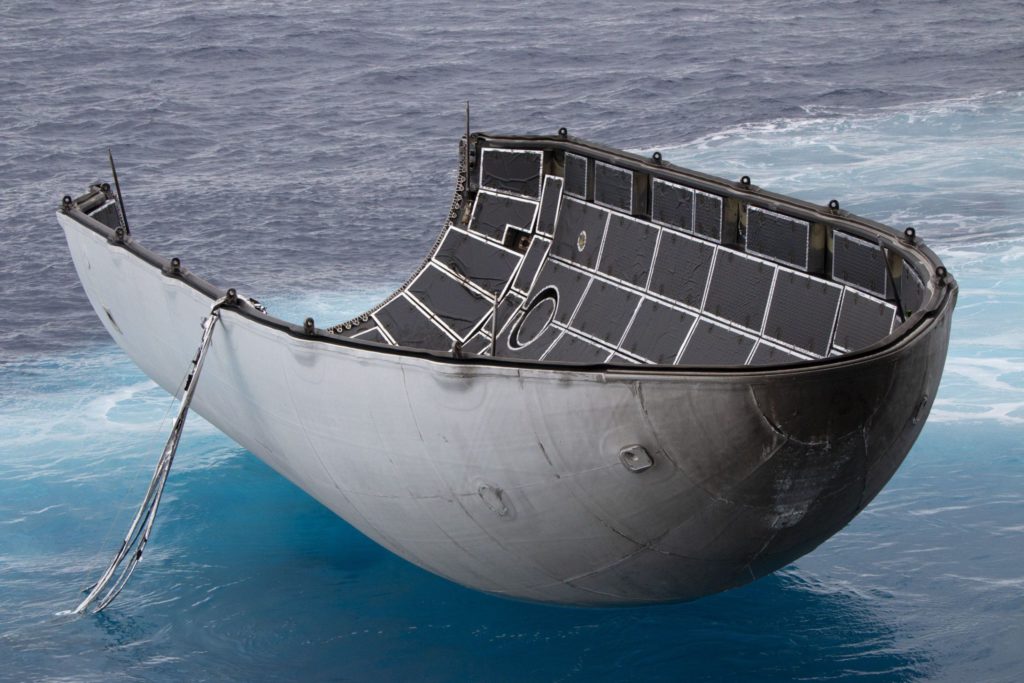
- Hans Koenigsmann was extremely excited about the condition of this particular fairing half, and included this photo in his IAC 2018 keynote. (SpaceX)
In a very literal sense, SpaceX has solved the hardest part of fairing recovery, essentially recovering fairing halves at all without catastrophic or irreparable structural damage in the process of reentering and landing. SpaceX already has a veritable fleet of soiled but wholly intact Falcon fairings, recovery by simply lifting them off the ocean surface after a gentle landing beneath each half’s guided parafoil. Much to its engineers’ chagrin, what SpaceX has yet to solve is the presumably extraordinarily challenging problem of guiding those parasailing fairings with extreme accuracy into Mr. Steven’s net, essentially the bullseye to end all bullseyes.
While it would be both extremely exciting to see Mr. Steven’s visually and technically fascinating net assembly be put to good use and equally disappointing to see his capabilities no longer be needed, Musk’s comment after today’s launch as nothing short of a complete change in his attitude towards fairing recovery, suggesting that SpaceX’s engineers have been working on waterproofing and thorough cleaning as a backup to Mr. Steven’s admittedly Rube Goldberg-esque fairing recovery mechanism.
Mr. Steven is stationed in the Pacific, as SpaceX will attempt to catch and recover the fairing this mission. pic.twitter.com/A7aBSJoFfc
— SpaceX (@SpaceX) December 3, 2018
Regardless of the avenue SpaceX takes, a reusable fairing is a still a reusable fairing, regardless of the gritty details of how that reusability is achieved. As Musk once rather hilariously noted, payload fairings are akin to a pallet of $5M plummeting through the air, a pallet that SpaceX would certainly like to recover. Perhaps, rather than catching that pallet of cash in a net, SpaceX can instead waterproof the bills and pick them up.
For prompt updates, on-the-ground perspectives, and unique glimpses of SpaceX’s rocket recovery fleet check out our brand new LaunchPad and LandingZone newsletters!

Elon Musk
FCC chair criticizes Amazon over opposition to SpaceX satellite plan
Carr made the remarks in a post on social media platform X.

U.S. Federal Communications Commission (FCC) Chairman Brendan Carr criticized Amazon after the company opposed SpaceX’s proposal to launch a large satellite constellation that could function as an orbital data center network.
Carr made the remarks in a post on social media platform X.
Amazon recently urged the FCC to reject SpaceX’s application to deploy a constellation of up to 1 million low Earth orbit satellites that could serve as artificial intelligence data centers in space.
The company described the proposal as a “lofty ambition rather than a real plan,” arguing that SpaceX had not provided sufficient details about how the system would operate.
Carr responded by pointing to Amazon’s own satellite deployment progress.
“Amazon should focus on the fact that it will fall roughly 1,000 satellites short of meeting its upcoming deployment milestone, rather than spending their time and resources filing petitions against companies that are putting thousands of satellites in orbit,” Carr wrote on X.
Amazon has declined to comment on the statement.
Amazon has been working to deploy its Project Kuiper satellite network, which is intended to compete with SpaceX’s Starlink service. The company has invested more than $10 billion in the program and has launched more than 200 satellites since April of last year.
Amazon has also asked the FCC for a 24-month extension, until July 2028, to meet a requirement to deploy roughly 1,600 satellites by July 2026, as noted in a CNBC report.
SpaceX’s Starlink network currently has nearly 10,000 satellites in orbit and serves roughly 10 million customers. The FCC has also authorized SpaceX to deploy 7,500 additional satellites as the company continues expanding its global satellite internet network.
Elon Musk
NASA watchdog says Starship development delays could affect Artemis timeline
The report noted that several technical milestones still need to be completed before Starship can serve as a crewed lunar lander.

A NASA watchdog report stated that continued development work on SpaceX’s Starship could affect the timeline for the agency’s planned Artemis moon missions. The report noted that several technical milestones still need to be completed before the spacecraft can serve as a crewed lunar lander.
The findings were detailed in a report from NASA’s Office of Inspector General, as noted in a report from Reuters.
NASA selected SpaceX’s Starship in 2021 to serve as the Human Landing System (HLS) for its Artemis lunar program. The vehicle is intended to transport astronauts from lunar orbit to the surface of the Moon and back as part of future Artemis missions.
According to the watchdog report, Starship’s development has experienced roughly two years of schedule delays compared to earlier expectations. Still, NASA is targeting 2028 for the first crewed lunar landing using the Starship lander.
One of the most significant technical milestones for Starship’s lunar missions is in-space refueling.
To support a crewed lunar landing, multiple Starship launches will be required to deliver propellant to orbit. Tanker versions of Starship will transfer fuel to a storage depot spacecraft, which will then refuel the lunar lander.
The report noted that this approach could require more than 10 Starship launches to fully refuel the spacecraft needed for a single lunar landing mission.
NASA officials indicated that demonstrating cryogenic propellant transfer in orbit remains one of the most important technical steps before Starship can be certified for lunar missions.
SpaceX has conducted 11 Starship test flights since 2023 as the company continues developing the fully reusable launch system. A 12th test flight, this time featuring Starship V3, is expected to be held in early April.
Elon Musk
SpaceX weighs Nasdaq listing as company explores early index entry: report
The company is reportedly seeking early inclusion in the Nasdaq-100 index.

Elon Musk’s SpaceX is reportedly leaning toward listing its shares on the Nasdaq for a potential initial public offering (IPO) that could become the largest in history.
As per a recent report, the company is reportedly seeking early inclusion in the Nasdaq-100 index. The update was reported by Reuters, citing people familiar with the matter.
According to the publication, SpaceX is considering Nasdaq as the venue for its eventual IPO, though the New York Stock Exchange is also competing for the listing. Neither exchange has reportedly been informed of a final decision.
Reuters has previously reported that SpaceX could pursue an IPO as early as June, though the company’s plans could still change.
One of the publication’s sources also suggested that SpaceX is targeting a valuation of about $1.75 trillion for its IPO. At that level, the company would rank among the largest publicly traded firms in the United States by market capitalization.
Nasdaq has proposed a rule change that could accelerate the inclusion of newly listed megacap companies into the Nasdaq-100 index.
Under the proposed “Fast Entry” rule, a newly listed company could qualify for the index in less than a month if its market capitalization ranks among the top 40 companies already included in the Nasdaq-100.
If SpaceX is successful in achieving its target valuation of $1.75 trillion, it would become the sixth-largest company by market value in the United States, at least based on recent share prices.
Newly listed companies typically have to wait up to a year before becoming eligible for major indexes such as the Nasdaq-100 or S&P 500.
Inclusion in a major index can significantly broaden a company’s shareholder base because many institutional investors purchase shares through index-tracking funds.
According to Reuters, Nasdaq’s proposed fast-track rule is partly intended to attract highly valued private companies such as SpaceX, OpenAI, and Anthropic to list on the exchange.




![Lucid Lunar robotaxi concept [Credit: Rendering by TESLARATI]](https://www.teslarati.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/03/lucid-lunar-robotaxi-concept-teslarati-rendering-80x80.jpg)





