News
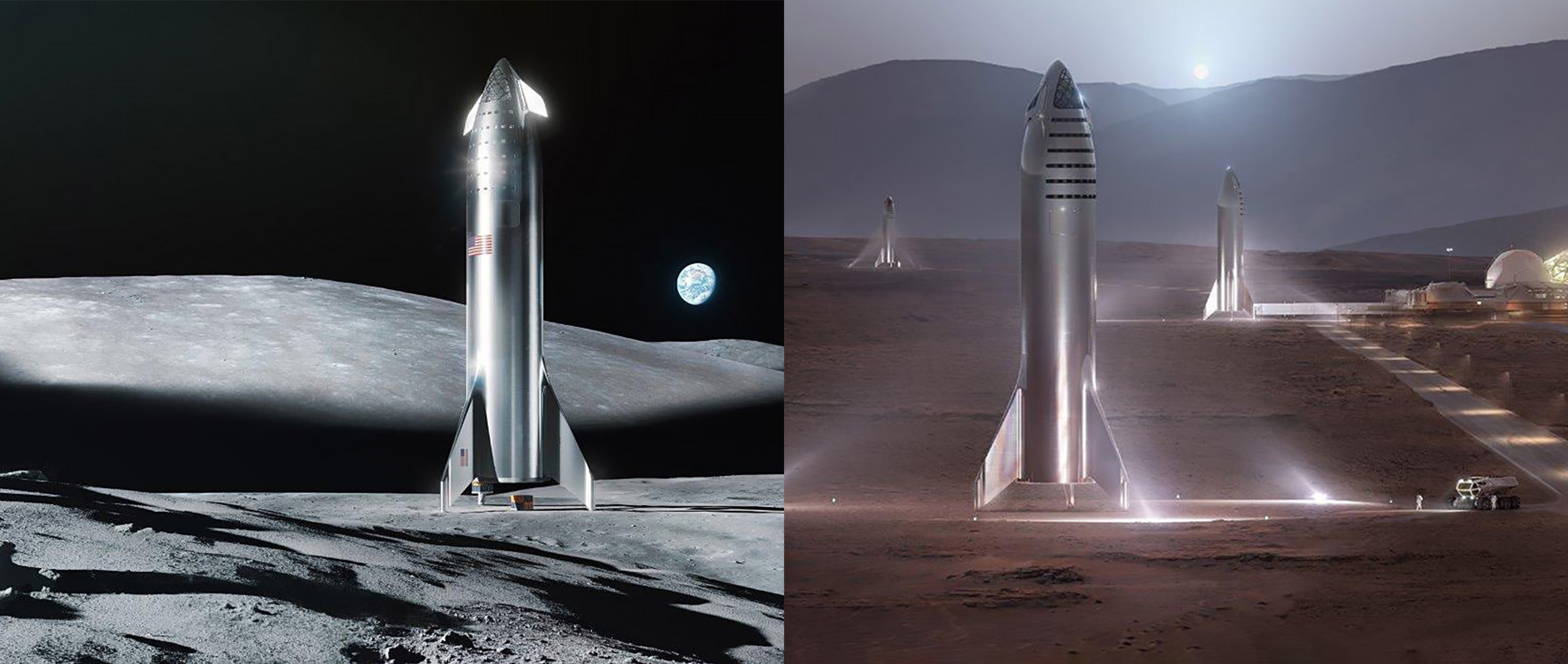
SpaceX’s Elon Musk says landing Starship on the Moon could be easier than convincing NASA
Speaking in an interview with TIME Magazine’s Jeffrey Kluger, SpaceX CEO Elon Musk telegraphed some clear, latent frustration with US space agency NASA, indicating that quite literally building Starship and landing it on the Moon could be easier than convincing NASA that the company is serious.
Although minor progress has been made in the last six or so months, NASA headquarters – for the most part – still effectively operates as if SpaceX’s next-generation launch vehicle plans do not exist, all while the agency is seriously considering other similarly unproven rockets with years of development remaining. In light of this frustrating inconsistency, Musk has taken to publicly acknowledging that developing, building, and launching Starship completely internally may be an easier (and faster) fight to win than attempting to convince NASA to assist in Starship development or even just be willing to use it as a launch option.
NASA assistance or support could come in any number of forms, ranging from a cost-sharing development contract, a developmental launch contract like the US Air Force’s STP-2 Falcon Heavy mission, or something as basic as publicly expressing support for the SpaceX program and a willingness to launch NASA payloads on it down the road. For now, the closest SpaceX has gotten to public NASA interest in and acknowledgment of Starship is an official Starship render posted by the Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC).
In a sign of just how unengaged NASA is, the closest SpaceX’s Starship/Super Heavy vehicle has gotten to an acknowledgment from NASA headquarters is quite literally having an outdated BFR render subtly included in a few slideshows and documents published less than two months ago (late May 2019).
Ironically, despite the fact that Starship – first and foremost – is designed to be a giant, human-rated reusable spacecraft nominally capable of carrying dozens of astronauts into space and back, the US military appears to have been far more receptive to Starship. This is despite the fact that a BFR-heavy bid may have cost SpaceX a development contract last year. Even with the challenges such an ambitious vehicle poses, the US Department of Defense is still interested in at least discussing potential use-cases and providing input that might influence SpaceX’s final design.
Speaking in September 2018, CEO Elon Musk indicated SpaceX’s BFR (now Starship/Super Heavy) program was likely to cost ~$5B – no less than $2B and no more than $10B. However, this answer – provided off the cuff as a response to a reporter’s question – was almost certainly directed at BFR prior to a radical move from carbon composite structures and tanks to stainless steel. Since then, Musk has made some radical claims about the potential of an efficient, stainless-steel rocket, indicating that it could actually cost less to build than Falcon 9 – a far smaller rocket with a fraction of the performance.
In other words, if the potentially low cost of the vehicle itself also translates to a low development cost, SpaceX could quite feasibly develop Starship/Super Heavy from scratch with nothing more than traditional investment rounds. In the first half of 2019 alone, SpaceX has raised more than $1B in funding through three separate rounds, all of which have been described by Musk and other executives as “oversubscribed” – the demand for SpaceX equity far outstrips supply.
“If it were to take longer to convince NASA and the authorities that we can do it versus just doing it, then [SpaceX] might just do it [ourselves]. It may literally be easier to just land Starship on the moon than try to convince NASA that we can.”
— Elon Musk, July 12th, 2019, via TIME Magazine
As such, unless NASA’s attitude undergoes rapid changes, SpaceX may simply leave the agency behind when it comes to space exploration beyond low Earth orbit. In the event that quite literally developing, building, and launching a giant, stainless steel rocket and spaceship is faster, more efficient, and less disruptive than trying to convince NASA to get its foot in the door, SpaceX might have to forge its own path. If SpaceX can raise enough funding to develop its next-generation rocket independently, what comes next is anyone’s guess.
Ultimately, Musk believes that SpaceX can make that Starship Moon landing happen as few as two years from now, with the first crewed landing potentially coming as few as one or two years after that. All told, this ambitious timeline would see SpaceX land humans on the Moon – perhaps entirely commercially – as early as 2022 or 2023.
Check out Teslarati’s Marketplace! We offer Tesla accessories, including for the Tesla Cybertruck and Tesla Model 3.

Elon Musk
Starbase after dark: Musk’s latest photo captures a Spaceport on the brink of history
SpaceX’s Starbase city in Boca Chica, Texas is rapidly transforming the southern tip of the Lone Star State into one of the most ambitious launch complexes in history.
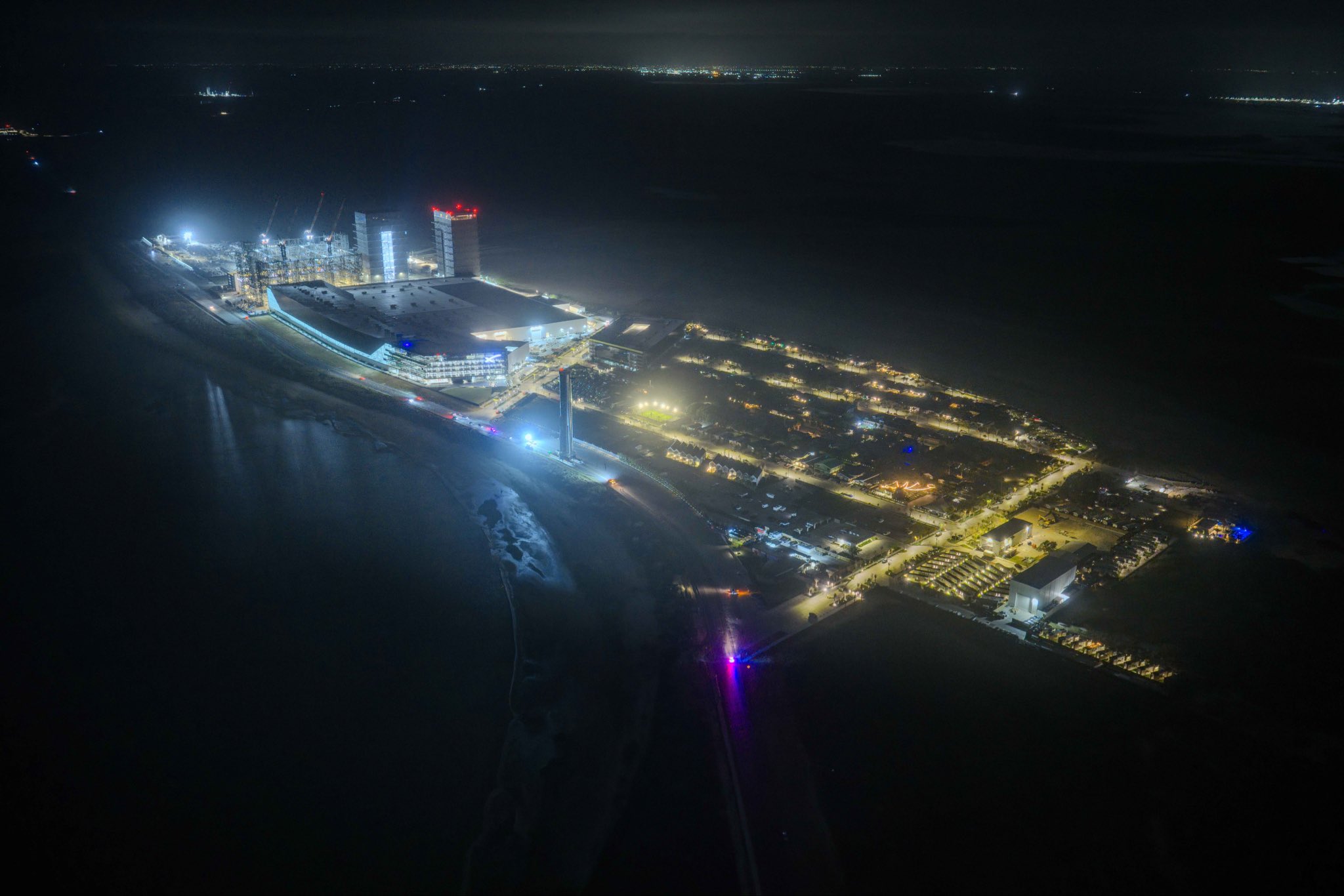

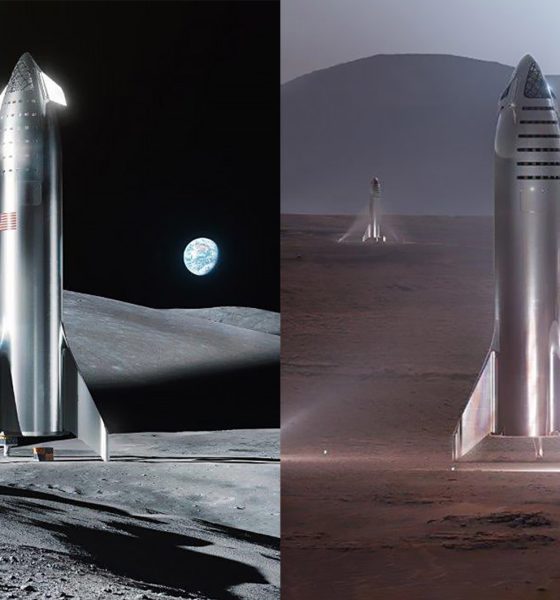
A striking nighttime photograph of SpaceX’s Starbase facility in Boca Chica, Texas, shared recently by Elon Musk on X, offers a dramatic glimpse of an operation that is rapidly transforming the southern tip of the Lone Star State into one of the most ambitious launch complexes in history.
The most immediately visible change in the photo is the presence of two fully erected Starship launch towers dominating the coastal skyline. The second orbital launch pad, known as Pad B, now features its fully erected tower, OLIT-3, which stands approximately 474 feet tall and incorporates an integrated water-cooled flame trench designed to minimize damage and reduce turnaround time between launches. The dual-tower silhouette against the night sky signals a decisive shift from experimental testing facility to high-cadence launch operations.
Grok Image concept of Elon Musk’s latest Starbase photo via X
Back at Starbase, Pad 2 is approaching hardware completion, with upgraded chopstick arms, a new chilldown vent system, and all 20 hold-down arms now fitted with protective doors to shield them from the intense exhaust of up to 33 Raptor 3 engines, according to a deeper dive by NASASpaceFlight.
SpaceX has also received approval to nearly double the footprint of the Starbase launch site, with groundwork already underway to add LNG liquefaction plants, expanded propellant storage, and additional ground support infrastructure.
The photo also carries a milestone civic dimension. Starbase officially became a Texas city in May 2025 after a community vote, with SpaceX employees elected as mayor and commissioners of the newly incorporated municipality. That legal status streamlines launch approvals and gives SpaceX direct control over local infrastructure decisions.
The FAA has approved an increase in launches from Starbase in Texas from five to twenty-five per year, clearing the runway for the kind of flight frequency needed to fulfill Starship’s ultimate mission of ferrying cargo and crew to the Moon, servicing the Department of Defense, deploying next-generation Starlink satellites, and eventually establishing Elon Musk’s long sought after goal of a self-sustaining human presence on Mars.
Seen from above in the dark, Starbase looks less like a test site and more like a spaceport.
News
Tesla loses Director who designed one of the company’s best features
Thomas Dmytryk, who has spent over 11 years with Tesla and helped to develop Over-the-Air updates and the company’s vehicles’ ability to utilize them to improve, has decided to leave.

Tesla has lost the director who designed one of the company’s best features: Over-the-Air updates.
Thomas Dmytryk, who has spent over 11 years with Tesla and helped to develop Over-the-Air updates and the company’s vehicles’ ability to utilize them to improve, has decided to leave. In a lengthy statement on LinkedIn, Dmytryk said that he’s “closing the book.” He had nothing but good things to say:
“After 11 incredible years at Tesla, I’m closing the book. It’s been the ride of a lifetime: always on the news, innovating relentlessly, constantly pushing the limits. Tesla is THE place for talented, passionate people. I feel insanely lucky to have been part in that culture for so long.”
It appears the intense lifestyle of developing and creating intensively for so long might have caught up to Dmytryk, who did not give his definitive plans for the future, and it appears he may be taking some time off before jumping into a new venture:
“The future? Extremely bright. Ambitions intact, just getting started as a transformative company that could elevate billions of lives. So why leave now?! Human life’s always been my North Star, right now I need to be with mines. I’ve always admired Tesla’s top leadership and vision. But what I’ve always found incredible is the tenacity, brilliance and devotion of people on the front line. YOU make Tesla unstoppable. I wish you all the best and of course EPIC wins.”
The move was first reported by NotaTeslaApp.
Over-the-Air updates are among Tesla’s best features. They are used to improve the Full Self-Driving suite, add features, remedy recalls, and more. Many vehicles have the ability to receive OTA updates, as I did in a Ford Bronco previous to my Model Y. However, Tesla does them better than anyone else: they’re seamless, effective, and frequent. Your car always improves.
The move is a blow to Tesla, of course, considering Dmytryk’s massive contribution to the company and extremely long tenure spent, but not something that is overwhelmingly detrimental. Tesla deals with a lot of extremely intelligent people, some of whom are the best in their field, so they are sure to find a suitable replacement.
However, it’s no secret that the company has been losing some of its top talent, some of whom were in executive roles. Some have left to take on new projects, and others have not revealed their career plans.
It seems at least some of those employees are simply deciding to walk away and try new things after working so hard for so long. According to Dmytryk’s LinkedIn, he also played a large part in Musk’s acquisition of X, as he stated he “worked at Twitter/X ~45/week while working at the same pace for Tesla.”
That averages a 13-hour day, seven days a week, or 18 hours for the normal five-day work week.
News
Tesla’s most wanted Model Y heads to new region with no sign of U.S. entry
Unlike the standard Model Y, the “L” stretches the wheelbase by roughly 150 mm and the overall length by about 177 mm to 4,976 mm. The result is a genuine 2-2-2 seating layout that gives six adults proper legroom and cargo space — a true family hauler without the cramped third-row compromises of many three-row SUVs.

Tesla’s most wanted Model Y configuration is heading to a new region, and although U.S. fans and owners have requested the vehicle since its release last year, it appears the company has no plans to bring it to the market.
According to fresh regulatory filings, the six-seat Model Y L is coming to South Korea with signs indicating an imminent launch. The extended-wheelbase configuration, already a hit in China, just cleared energy-efficiency certification from the Korea Energy Agency, paving the way for deliveries as early as the first half of 2026.
The vehicle is already built at Tesla’s Giga Shanghai facility in China, making it an ideal candidate for the Asian market, as well as the European one, as the factory has been known as a bit of an export hub in the past.
$TSLA
BREAKING: The official launch of Tesla Model Y L in S.Korea seems to be quite imminent.Additional credentials related to Model YL were released today.
✅ Battery Manufacturer: LG Energy Solutions
✅ Number of passengers: 6 people
✅ Total battery capacity: 97.25 kWh… pic.twitter.com/hmy64XYi80— Tsla Chan (@Tslachan) March 6, 2026
It seems like Tesla was prepping for this release anyway, as the timing was no accident. A camouflaged Model Y L prototype was spotted testing on Korean highways the same day the certification dropped. Tesla has already secured similar approvals for Australia and New Zealand, with both markets expecting the larger Model Y in 2026.
Unlike the standard Model Y, the “L” stretches the wheelbase by roughly 150 mm and the overall length by about 177 mm to 4,976 mm. The result is a genuine 2-2-2 seating layout that gives six adults proper legroom and cargo space — a true family hauler without the cramped third-row compromises of many three-row SUVs.
South Korean filings list it as an all-wheel-drive imported electric passenger vehicle with a 97.25 kWh total battery capacity supplied by LG Energy Solution. Local tests show an impressive 543 km (337 miles) combined range at room temperature and 454 km (282 miles) in colder conditions, easing one of the biggest concerns for Korean EV buyers.
Tesla Model Y lineup expansion signals an uncomfortable reality for consumers
But for U.S. fans, things are not looking good for a launch in the market.
CEO Elon Musk has been blunt. The six-seater “wouldn’t arrive in the U.S. until late 2026, if ever,” he said, pointing to the company’s heavy bet on unsupervised Full Self-Driving and robotaxi platforms like the Cybercab. With the Model X slated for discontinuation, many families hoped the stretched Model Y would slide into the lineup as an affordable three-row bridge. So far, that hope remains unfulfilled.
For now, South Korean drivers will be among the first buyers outside China to enjoy the spacious, efficient Model Y L. Tesla continues its global rollout strategy, tailoring vehicles to regional tastes while North American customers keep refreshing their apps and crossing their fingers.
The Model Y L proves the appetite for practical, family-sized electric SUVs is stronger than ever. Hopefully, Tesla will listen to its fans and bring the vehicle to the U.S. where it would likely sell well.








