

News
SpaceX Falcon Heavy beats out ULA Vulcan rocket for NASA Moon rover launch
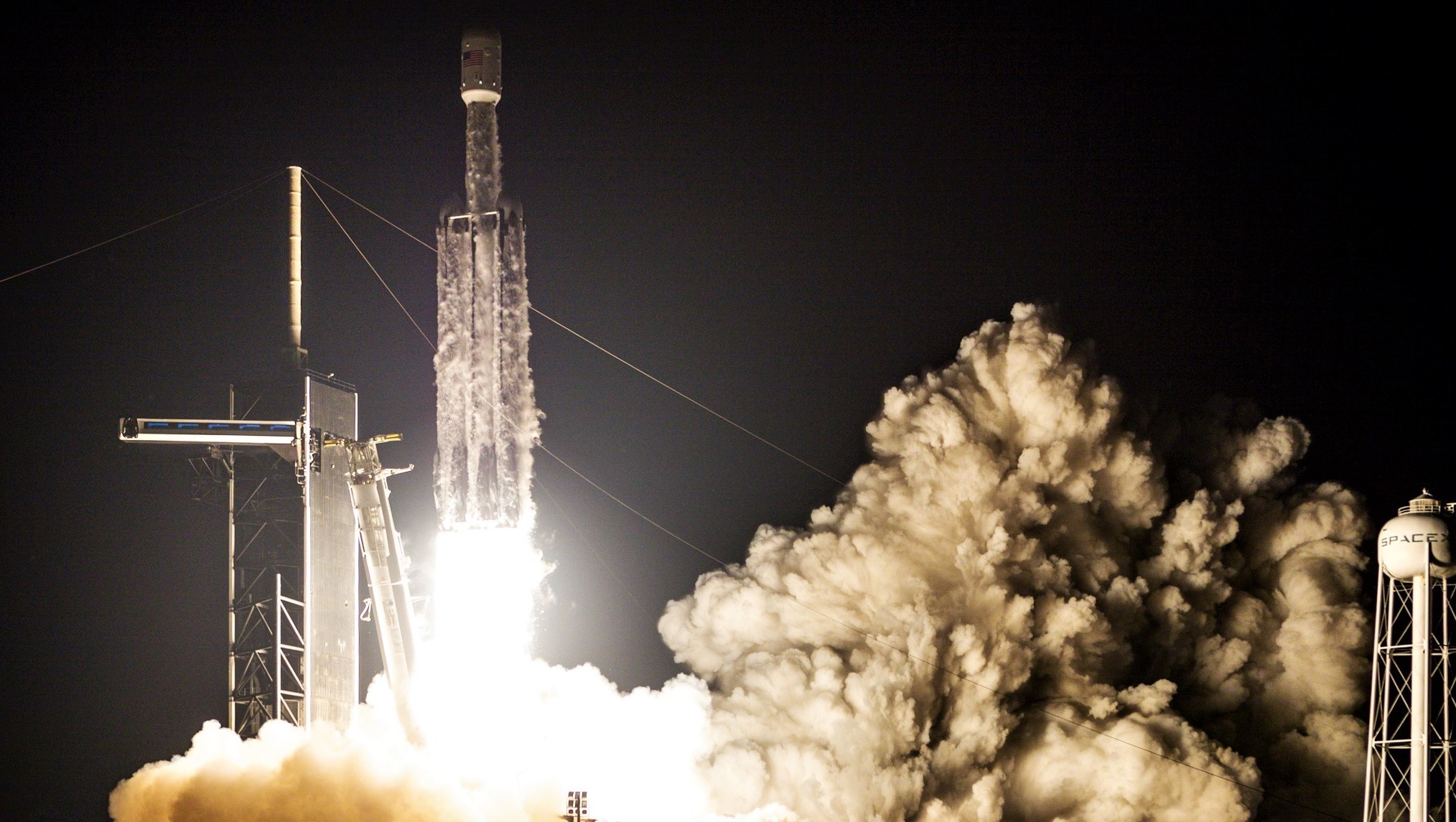
SpaceX’s Falcon Heavy rocket appears to have edged out competitor United Launch Alliance’s (ULA) next-generation Vulcan Centaur launch vehicle to send a NASA rover and commercial lander to the Moon in 2023.
Back in August 2019, not long after NASA first began announcing significant contracts under its Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) program, startup Astrobotic announced that it contracted with ULA to launch its first small “Peregrine” lander and a dozen or so attached NASA payloads to the Moon in 2021. Rather than the extremely expensive but operational Atlas V rocket, the startup instead chose to manifest Peregrine on the first launch of Vulcan Centaur, a new ULA rocket meant to replace both Atlas V and Delta IV Heavy.
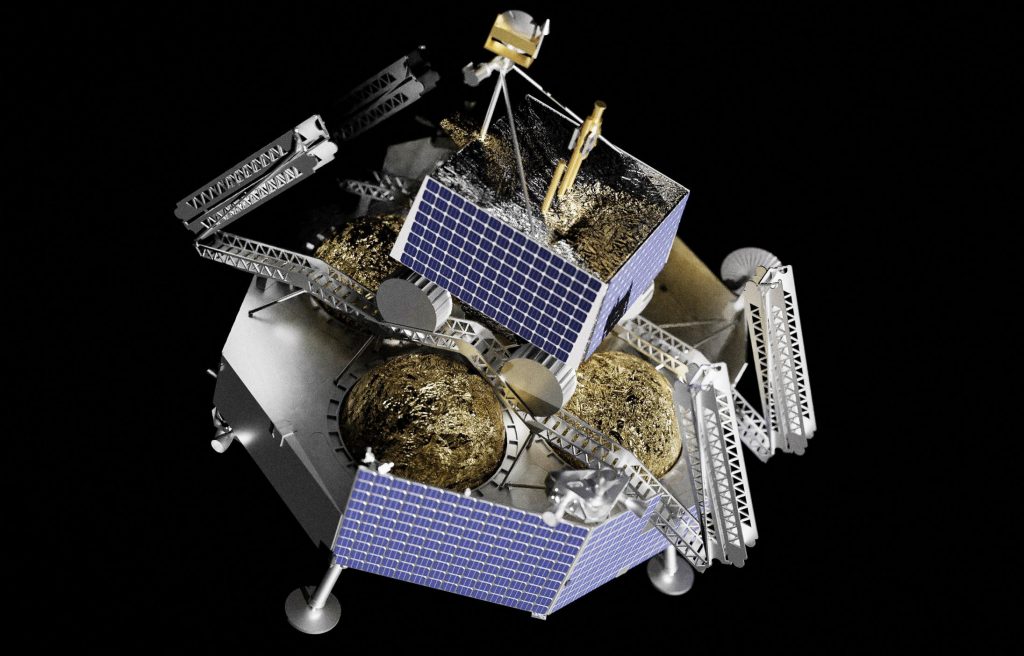
Less than two years later, Astrobotic has decided to purchase a dedicated launch from SpaceX – not ULA – for even larger “Griffin” lander that aims to deliver NASA’s ice-prospecting VIPER rover to the Moon and kick off the exploration of permanently-shadowed craters at its south pole.

Back in August 2019, Astrobotic’s announcement stated that “it selected United Launch Alliance’s (ULA) Vulcan Centaur rocket in a [highly competitive commercial process].” It later became clear that the Peregrine lander – while still scheduled to be sent directly to the Moon on a trans-lunar injection (TLI) trajectory – would not be the only payload on the mission. None of Vulcan Flight 1’s other payloads are known, but the presence of other paying customers helps explain how Vulcan beat SpaceX for the contract.
More importantly, companies willing to risk their payload(s) on new rockets have historically been enticed to overlook some of that first-flight risk with major discounts. In other words, in the often unlikely event that a company manages to sell a commercial rocket’s first launch, it’s incredibly unlikely that the same rocket will ever sell that cheaply again.

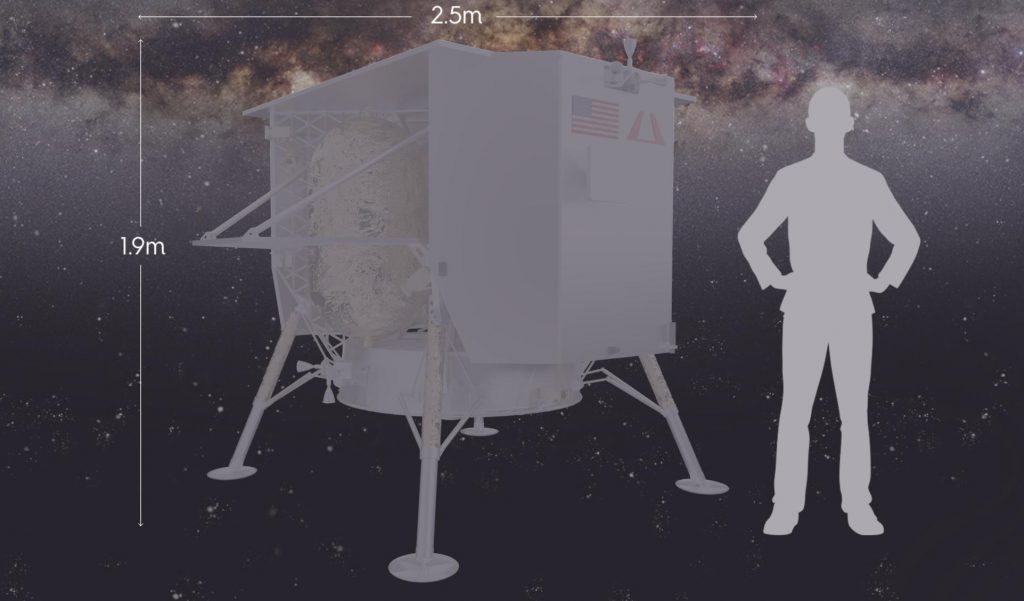

That appears to be exactly the case for ULA’s Vulcan Centaur rocket, which secured a lunar lander contract for its launch debut only to lose a similar lunar lander launch contract from the same company – well within the range of Vulcan’s claimed capabilities – less than two years later. If SpaceX’s relatively expensive Falcon Heavy managed to beat early Vulcan launch pricing, there is virtually no chance whatsoever that Vulcan Centaur will ever be able to commercially compete with Falcon 9.
In fact, back in 2015 when Astrobotic began making noise about its plans to build commercial Moon landers, the larger Griffin was expected to weigh some 2220 kg (~4900 lb) fully-fueled and – when combined with SpaceX’s Falcon 9 workhorse – be able to land payloads as large as 270 kg (~600 lb) on the Moon. It’s unclear if that figure assumed an expendable Falcon 9 launch or if it was using numbers from the rocket’s most powerful variant, which was still a few years away at the time.
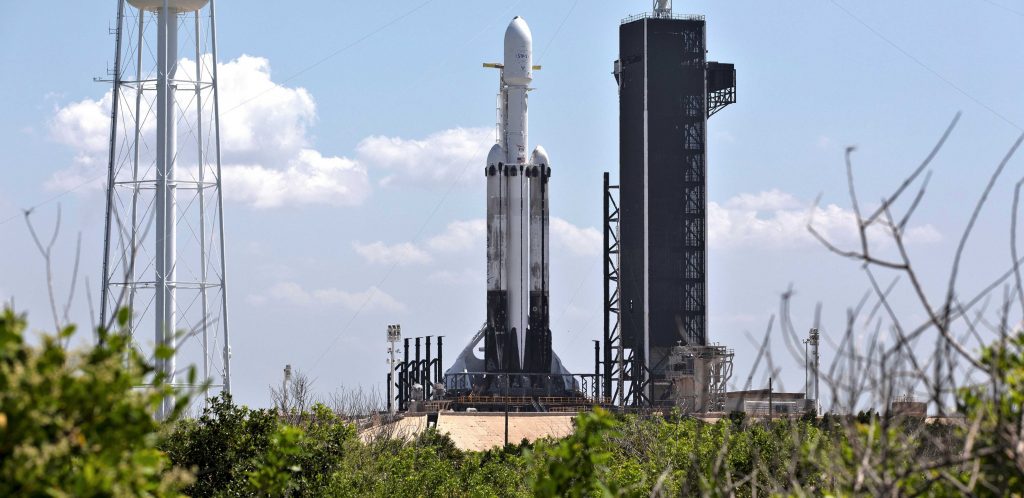
Either way, NASA’s VIPER lander – expected to have a launch mass of ~430 kg (~950 lb) – is a bit too heavy for a single-stick Falcon 9 flight to TLI. It’s also reasonable to assume that Griffin’s dry and fueled mass has grown substantially after more than half a decade of design maturation and the first Peregrine lander reaching the hardware production and assembly phase. While Falcon 9 narrowly falls short of the performance needed for Griffin/VIPER, a fully recoverable Falcon Heavy is capable of launching more than 6.5 metric tons to TLI, offering a safety margin of almost 100%.
Astrobotic says it has purchased a dedicated Falcon Heavy launch for Griffin-1 and VIPER, but it would be far from surprising to see one or multiple secondary payloads find their way onto a mission with multiple tons of extra capacity. Presumably assuming that its Q4 2021 or early 2022 Peregrine Moon landing debut is successful, Astrobotic and SpaceX aim to land Griffin-1 and NASA’s VIPER rover on the Moon as early as “late 2023.”

Elon Musk
Brazil Supreme Court orders Elon Musk and X investigation closed
The decision was issued by Supreme Court Justice Alexandre de Moraes following a recommendation from Brazil’s Prosecutor-General Paulo Gonet.

Brazil’s Supreme Federal Court has ordered the closure of an investigation involving Elon Musk and social media platform X. The inquiry had been pending for about two years and examined whether the platform was used to coordinate attacks against members of the judiciary.
The decision was issued by Supreme Court Justice Alexandre de Moraes following a recommendation from Brazil’s Prosecutor-General Paulo Gonet.
According to a report from Agencia Brasil, the investigation conducted by the Federal Police did not find evidence that X deliberately attempted to attack the judiciary or circumvent court orders.
Prosecutor-General Paulo Gonet concluded that the irregularities identified during the probe did not indicate fraudulent intent.
Justice Moraes accepted the prosecutor’s recommendation and ruled that the investigation should be closed. Under the ruling, the case will remain closed unless new evidence emerges.
The inquiry stemmed from concerns that content on X may have enabled online attacks against Supreme Court justices or violated rulings requiring the suspension of certain accounts under investigation.
Justice Moraes had previously taken several enforcement actions related to the platform during the broader dispute involving social media regulation in Brazil.
These included ordering a nationwide block of the platform, freezing Starlink accounts, and imposing fines on X totaling about $5.2 million. Authorities also froze financial assets linked to X and SpaceX through Starlink to collect unpaid penalties and seized roughly $3.3 million from the companies’ accounts.
Moraes also imposed daily fines of up to R$5 million, about $920,000, for alleged evasion of the X ban and established penalties of R$50,000 per day for VPN users who attempted to bypass the restriction.
Brazil remains an important market for X, with roughly 17 million users, making it one of the platform’s larger user bases globally.
The country is also a major market for Starlink, SpaceX’s satellite internet service, which has surpassed one million subscribers in Brazil.
Elon Musk
FCC chair criticizes Amazon over opposition to SpaceX satellite plan
Carr made the remarks in a post on social media platform X.

U.S. Federal Communications Commission (FCC) Chairman Brendan Carr criticized Amazon after the company opposed SpaceX’s proposal to launch a large satellite constellation that could function as an orbital data center network.
Carr made the remarks in a post on social media platform X.
Amazon recently urged the FCC to reject SpaceX’s application to deploy a constellation of up to 1 million low Earth orbit satellites that could serve as artificial intelligence data centers in space.
The company described the proposal as a “lofty ambition rather than a real plan,” arguing that SpaceX had not provided sufficient details about how the system would operate.
Carr responded by pointing to Amazon’s own satellite deployment progress.
“Amazon should focus on the fact that it will fall roughly 1,000 satellites short of meeting its upcoming deployment milestone, rather than spending their time and resources filing petitions against companies that are putting thousands of satellites in orbit,” Carr wrote on X.
Amazon has declined to comment on the statement.
Amazon has been working to deploy its Project Kuiper satellite network, which is intended to compete with SpaceX’s Starlink service. The company has invested more than $10 billion in the program and has launched more than 200 satellites since April of last year.
Amazon has also asked the FCC for a 24-month extension, until July 2028, to meet a requirement to deploy roughly 1,600 satellites by July 2026, as noted in a CNBC report.
SpaceX’s Starlink network currently has nearly 10,000 satellites in orbit and serves roughly 10 million customers. The FCC has also authorized SpaceX to deploy 7,500 additional satellites as the company continues expanding its global satellite internet network.
Energy
Tesla Energy gains UK license to sell electricity to homes and businesses
The license was granted to Tesla Energy Ventures Ltd. by UK energy regulator Ofgem after a seven-month review process.

Tesla Energy has received a license to supply electricity in the United Kingdom, opening the door for the company to serve homes and businesses in the country.
The license was granted to Tesla Energy Ventures Ltd. by UK energy regulator Ofgem after a seven-month review process.
According to Ofgem, the license took effect at 6 p.m. local time on Wednesday and applies to Great Britain.
The approval allows Tesla’s energy business to sell electricity directly to customers in the region, as noted in a Bloomberg News report.
Tesla has already expanded similar services in the United States. In Texas, the company offers electricity plans that allow Tesla owners to charge their vehicles at a lower cost while also feeding excess electricity back into the grid.
Tesla already has a sizable presence in the UK market. According to price comparison website U-switch, there are more than 250,000 Tesla electric vehicles in the country and thousands of Tesla home energy storage systems.
Ofgem also noted that Tesla Motors Ltd., a separate entity incorporated in England and Wales, received an electricity generation license in June 2020.
The new UK license arrives as Tesla continues expanding its global energy business.
Last year, Tesla Energy retained the top position in the global battery energy storage system (BESS) integrator market for the second consecutive year. According to Wood Mackenzie’s latest rankings, Tesla held about 15% of global market share in 2024.
The company also maintained a dominant position in North America, where it captured roughly 39% market share in the region.
At the same time, competition in the energy storage sector is increasing. Chinese companies such as Sungrow have been expanding their presence globally, particularly in Europe.








