
SpaceX
SpaceX fully installs Super Heavy booster’s ‘aerocovers’
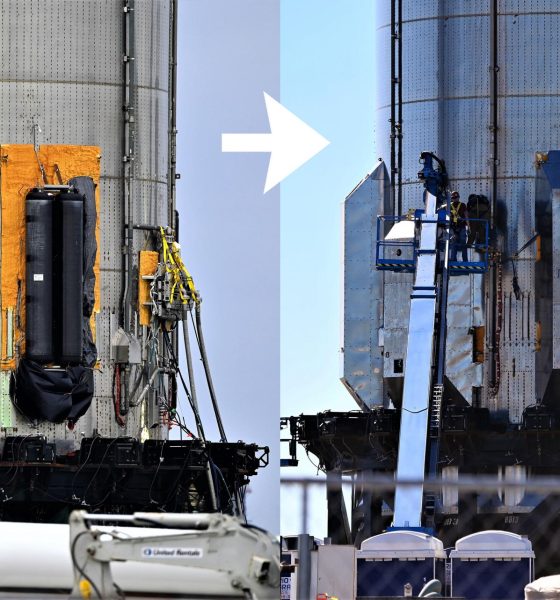
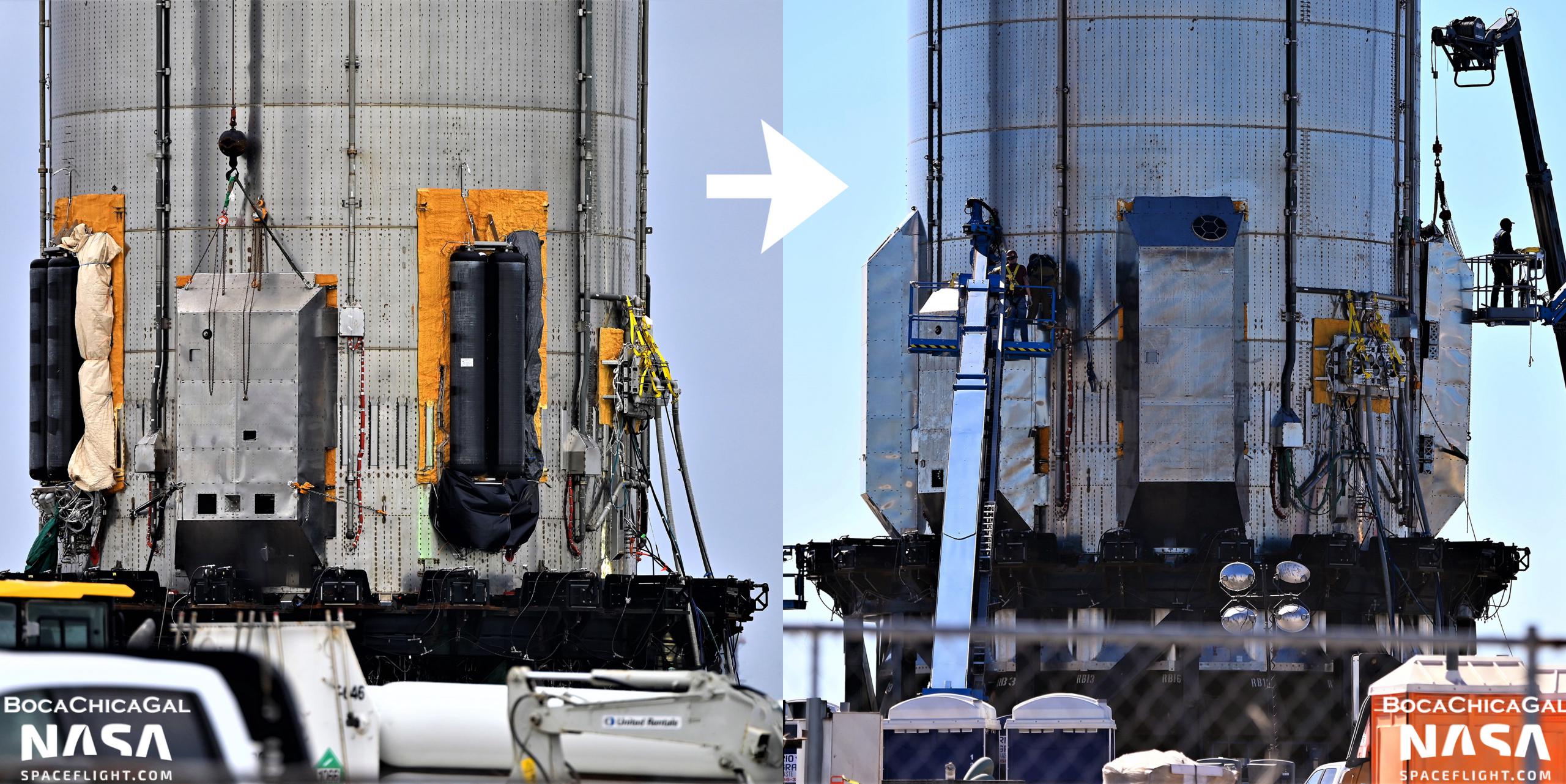
For the first time, SpaceX has more or less installed a full set of ‘aerocovers’ on a Super Heavy booster prototype.
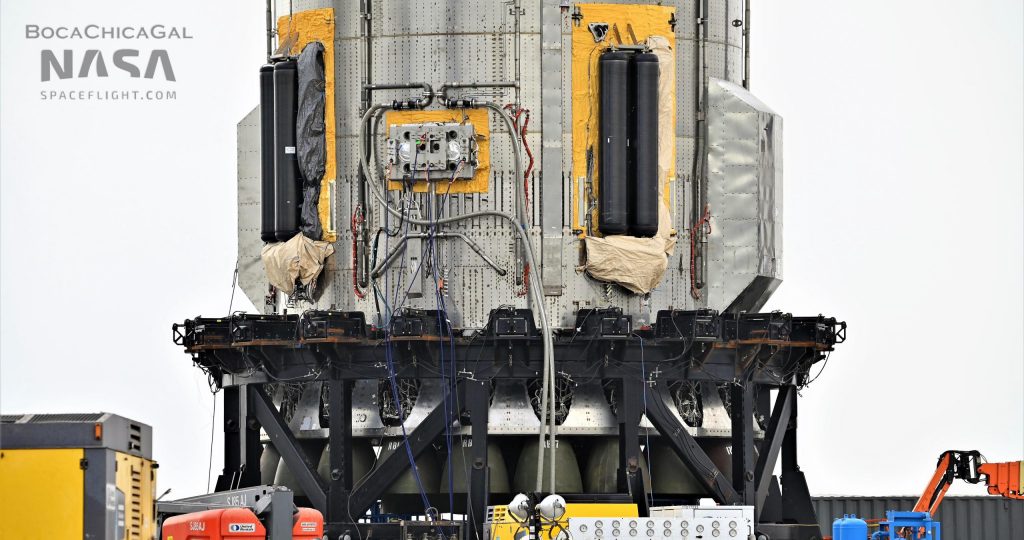
Designed to protect the booster from both itself and Earth’s atmosphere during ground testing, liftoff, ascent, and reentry, Super Heavy’s the structures amount to thin, steel shells mounted on metal box frames. The most obvious aerocovers slot over the top of six racks of equipment installed on the outside of Super Heavy’s aft end, giving the booster a sort of utility belt of hydraulic systems, pressure vessels, avionics, and heat exchangers. Unsurprisingly, those racks are festooned with electronics, composites, and thousands of feet of wiring and thin plumbing – none of which are particularly suited to sit a few dozen feet from the fury of 29-33 Raptor engines or near the leading edge of a hypersonic reentry vehicle.
Aside from the steel they’re mounted on, it’s likely that every system located on Super Heavy’s ‘utility built’ would begin malfunctioning or be destroyed outright if directly exposed to just a few seconds of the hypersonic buffeting and heating Starship boosters will experience during reentry. Unlike Falcon boosters, which almost always use reentry burns to slow down and create a sort of heat shield with their own exhaust, SpaceX is theoretically designing Super Heavy to survive the full force of reentry without an extra burn to cushion the blow.
To survive reentry and still land in good enough condition to enable anything close to same-day reusability, which is SpaceX’s goal, every ounce of at-risk equipment installed on Super Heavy’s exterior will likely need to be carefully shielded. In theory, that’s the purpose of the aerocovers SpaceX has only just begun to fully install – let alone test – on Super Heavy B4.
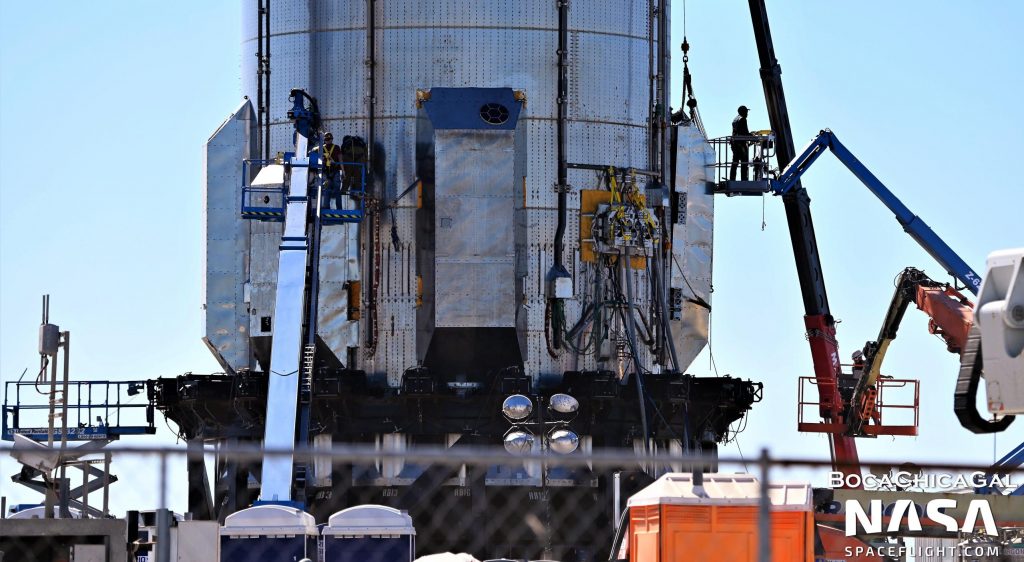


Before Booster 4’s most recent installation on the orbital launch mount, SpaceX did install covers over a pair of hydraulic and heat exchanger racks but left all four composite overwrapped pressure vessel (COPV) racks and an umbilical port uncovered. After B4 was removed from the launch mount for the third time on December 30th, both covers were uninstalled. On January 14th, 2022, though, SpaceX rapidly installed all six covers for the first time and began sealing each cover’s exposed corners. On January 17th, SpaceX even installed aerodynamic surfaces around Booster 4’s protruding umbilical port, smoothing out any hypothetical airflow around the device.
Prior to main aerocover installation, SpaceX also added at least half a dozen small boxes seemingly designed to protect a number of thin metal probes that pierce through Super Heavy’s tanks and skin and are connected to avionics boxes. Additionally, while less visible, teams also worked to finish Super Heavy B4’s Raptor heat shielding with a large number of similar sheet steel covers and panels. Without official photos from SpaceX or another lift onto the launch mount, it’s impossible to know if Booster 4’s Raptor heat shield is fully closed out, but the shielding that runs around its circumference appears to be finished.
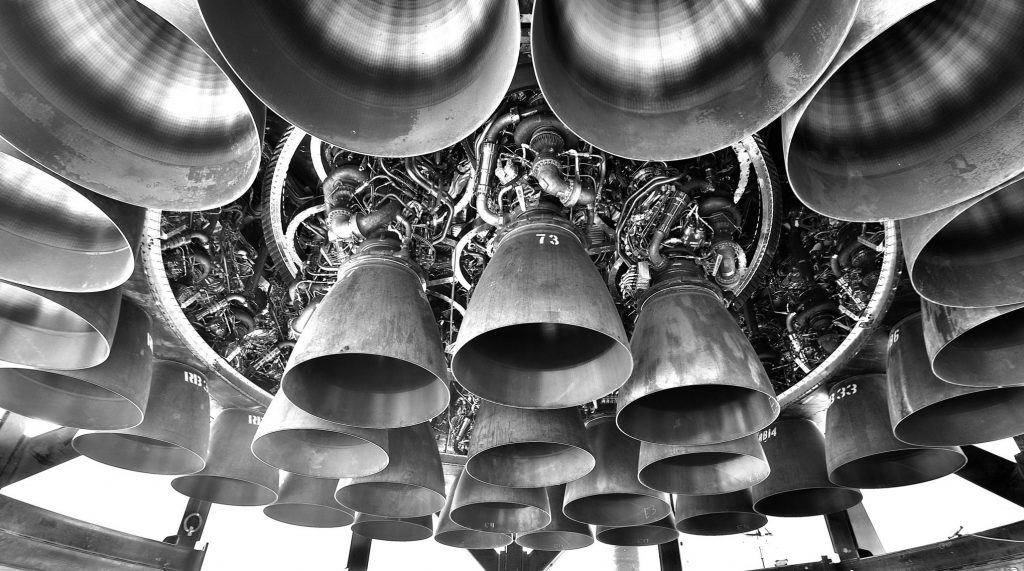
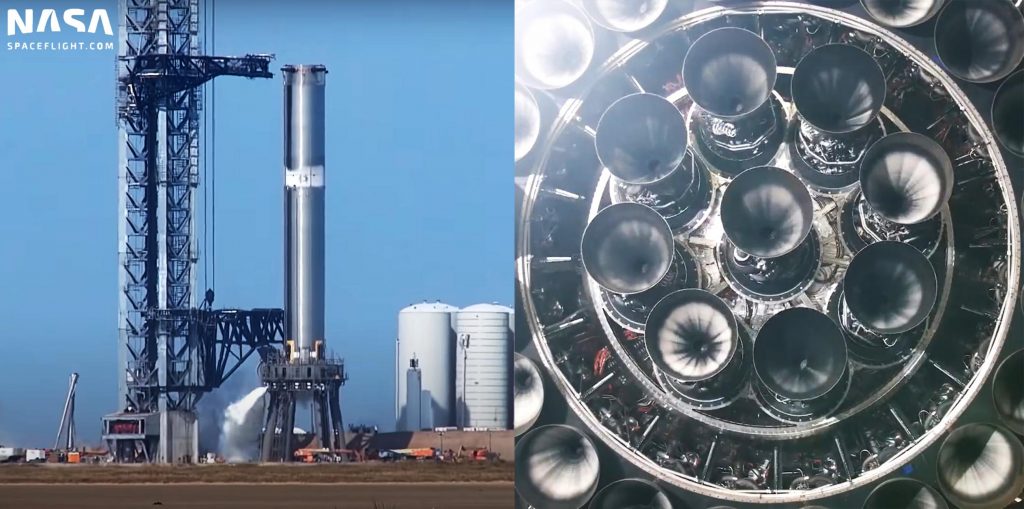

As it stands, Super Heavy B4 is likely just a few parts shy of true completion and is about as ready as it’ll ever be for static fire testing. More likely than not, those aerocovers and Raptor heat shields are essential for Super Heavy B4 to be able to perform more than one test at a time without immediately requiring major repairs. Unlike Starship, which has mostly tested three engines at once and only performed a few six-engine static fires, Super Heavy B4 may eventually test all 29 Raptor engines simultaneously.
When almost 30 engines are involved, even nominal preburner testing will likely produce a massive fireball that could engulf Super Heavy’s aft (if not the entire booster) with flames. For static fire testing, Raptors typically produce a smaller and briefer (but still substantial) fireball during shutdown, creating another potential source of damage to any sensitive hardware located anywhere on or in Booster 4’s thrust section. As such, Super Heavy aerocovers may be just as important for surviving static fires as they’ll be for surviving launches and landings.
It’s unclear if or when Super Heavy B4 will return to the orbital launch mount for wet dress rehearsal and static fire testing. SpaceX has ambiguous test windows scheduled from 10am to 10pm on January 18th, 19th, and 20th.

Elon Musk
NASA watchdog says Starship development delays could affect Artemis timeline
The report noted that several technical milestones still need to be completed before Starship can serve as a crewed lunar lander.

A NASA watchdog report stated that continued development work on SpaceX’s Starship could affect the timeline for the agency’s planned Artemis moon missions. The report noted that several technical milestones still need to be completed before the spacecraft can serve as a crewed lunar lander.
The findings were detailed in a report from NASA’s Office of Inspector General, as noted in a report from Reuters.
NASA selected SpaceX’s Starship in 2021 to serve as the Human Landing System (HLS) for its Artemis lunar program. The vehicle is intended to transport astronauts from lunar orbit to the surface of the Moon and back as part of future Artemis missions.
According to the watchdog report, Starship’s development has experienced roughly two years of schedule delays compared to earlier expectations. Still, NASA is targeting 2028 for the first crewed lunar landing using the Starship lander.
One of the most significant technical milestones for Starship’s lunar missions is in-space refueling.
To support a crewed lunar landing, multiple Starship launches will be required to deliver propellant to orbit. Tanker versions of Starship will transfer fuel to a storage depot spacecraft, which will then refuel the lunar lander.
The report noted that this approach could require more than 10 Starship launches to fully refuel the spacecraft needed for a single lunar landing mission.
NASA officials indicated that demonstrating cryogenic propellant transfer in orbit remains one of the most important technical steps before Starship can be certified for lunar missions.
SpaceX has conducted 11 Starship test flights since 2023 as the company continues developing the fully reusable launch system. A 12th test flight, this time featuring Starship V3, is expected to be held in early April.
Elon Musk
SpaceX weighs Nasdaq listing as company explores early index entry: report
The company is reportedly seeking early inclusion in the Nasdaq-100 index.

Elon Musk’s SpaceX is reportedly leaning toward listing its shares on the Nasdaq for a potential initial public offering (IPO) that could become the largest in history.
As per a recent report, the company is reportedly seeking early inclusion in the Nasdaq-100 index. The update was reported by Reuters, citing people familiar with the matter.
According to the publication, SpaceX is considering Nasdaq as the venue for its eventual IPO, though the New York Stock Exchange is also competing for the listing. Neither exchange has reportedly been informed of a final decision.
Reuters has previously reported that SpaceX could pursue an IPO as early as June, though the company’s plans could still change.
One of the publication’s sources also suggested that SpaceX is targeting a valuation of about $1.75 trillion for its IPO. At that level, the company would rank among the largest publicly traded firms in the United States by market capitalization.
Nasdaq has proposed a rule change that could accelerate the inclusion of newly listed megacap companies into the Nasdaq-100 index.
Under the proposed “Fast Entry” rule, a newly listed company could qualify for the index in less than a month if its market capitalization ranks among the top 40 companies already included in the Nasdaq-100.
If SpaceX is successful in achieving its target valuation of $1.75 trillion, it would become the sixth-largest company by market value in the United States, at least based on recent share prices.
Newly listed companies typically have to wait up to a year before becoming eligible for major indexes such as the Nasdaq-100 or S&P 500.
Inclusion in a major index can significantly broaden a company’s shareholder base because many institutional investors purchase shares through index-tracking funds.
According to Reuters, Nasdaq’s proposed fast-track rule is partly intended to attract highly valued private companies such as SpaceX, OpenAI, and Anthropic to list on the exchange.
Elon Musk
Starbase after dark: Musk’s latest photo captures a Spaceport on the brink of history
SpaceX’s Starbase city in Boca Chica, Texas is rapidly transforming the southern tip of the Lone Star State into one of the most ambitious launch complexes in history.
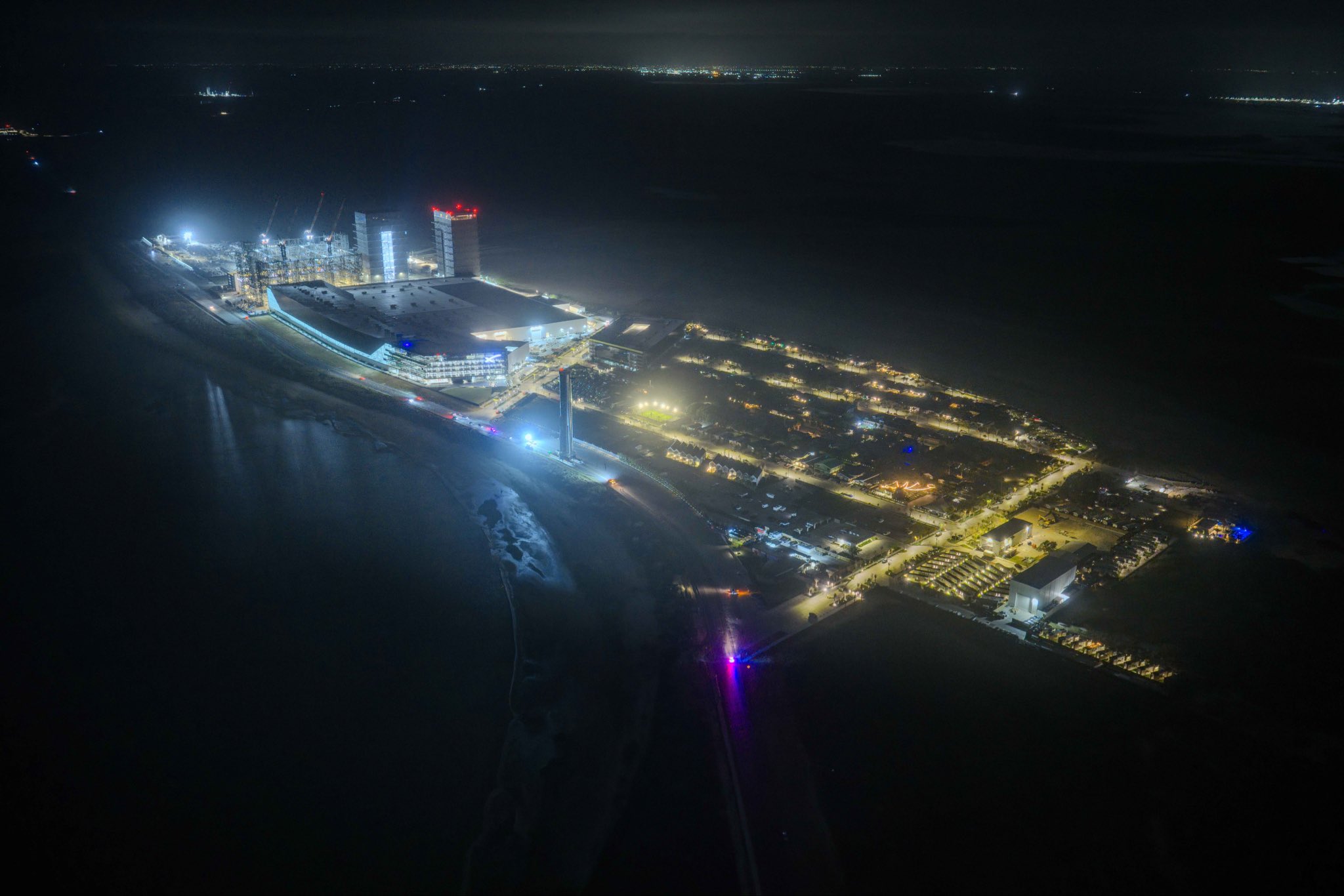

A striking nighttime photograph of SpaceX’s Starbase facility in Boca Chica, Texas, shared recently by Elon Musk on X, offers a dramatic glimpse of an operation that is rapidly transforming the southern tip of the Lone Star State into one of the most ambitious launch complexes in history.
The most immediately visible change in the photo is the presence of two fully erected Starship launch towers dominating the coastal skyline. The second orbital launch pad, known as Pad B, now features its fully erected tower, OLIT-3, which stands approximately 474 feet tall and incorporates an integrated water-cooled flame trench designed to minimize damage and reduce turnaround time between launches. The dual-tower silhouette against the night sky signals a decisive shift from experimental testing facility to high-cadence launch operations.
Grok Image concept of Elon Musk’s latest Starbase photo via X
Back at Starbase, Pad 2 is approaching hardware completion, with upgraded chopstick arms, a new chilldown vent system, and all 20 hold-down arms now fitted with protective doors to shield them from the intense exhaust of up to 33 Raptor 3 engines, according to a deeper dive by NASASpaceFlight.
SpaceX has also received approval to nearly double the footprint of the Starbase launch site, with groundwork already underway to add LNG liquefaction plants, expanded propellant storage, and additional ground support infrastructure.
The photo also carries a milestone civic dimension. Starbase officially became a Texas city in May 2025 after a community vote, with SpaceX employees elected as mayor and commissioners of the newly incorporated municipality. That legal status streamlines launch approvals and gives SpaceX direct control over local infrastructure decisions.
The FAA has approved an increase in launches from Starbase in Texas from five to twenty-five per year, clearing the runway for the kind of flight frequency needed to fulfill Starship’s ultimate mission of ferrying cargo and crew to the Moon, servicing the Department of Defense, deploying next-generation Starlink satellites, and eventually establishing Elon Musk’s long sought after goal of a self-sustaining human presence on Mars.
Seen from above in the dark, Starbase looks less like a test site and more like a spaceport.








