

News
SpaceX’s surprise Falcon 9 drone ship landing explained ahead of Cargo Dragon launch
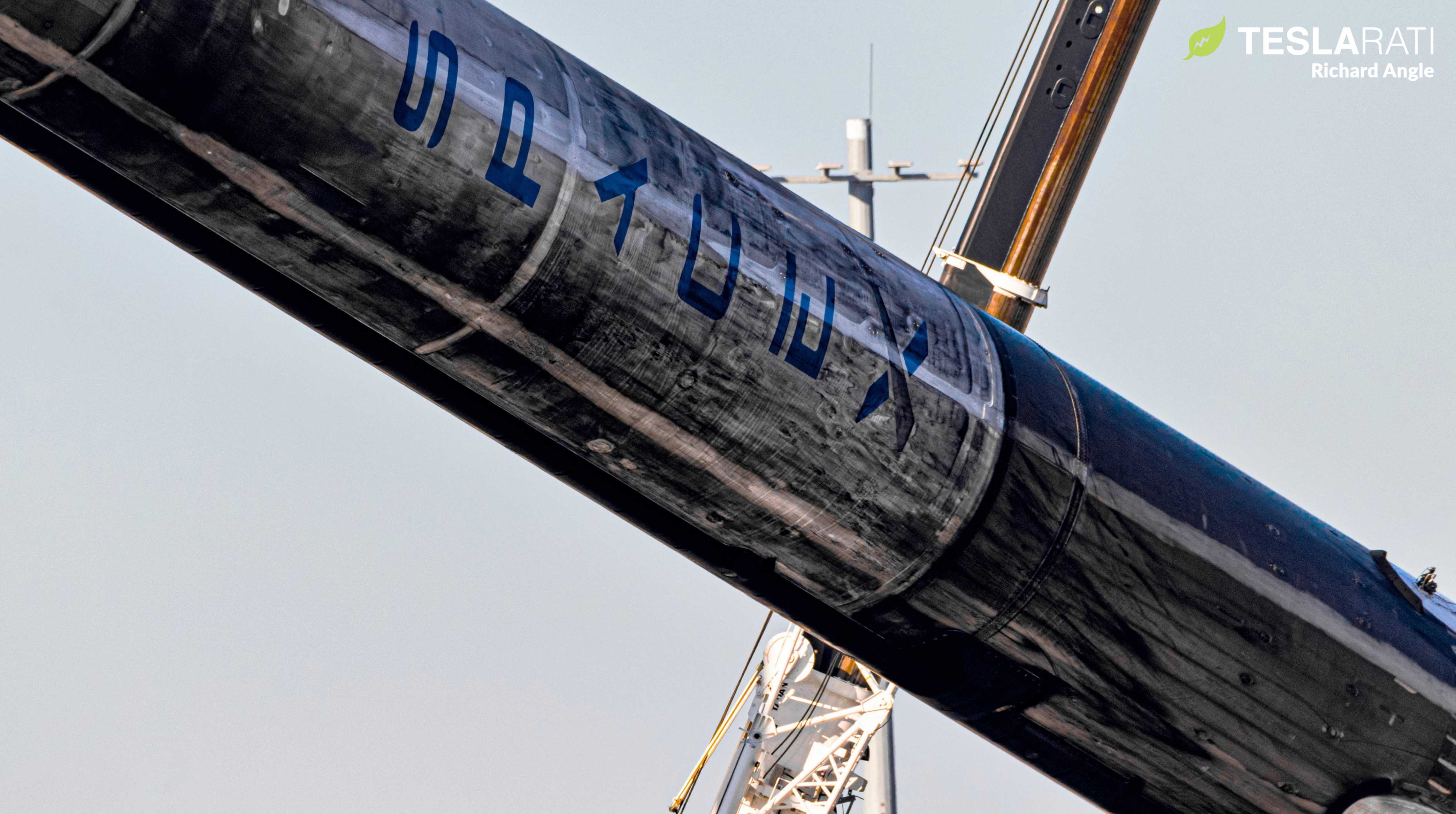
Speaking in a press briefing prior to NASA’s next Cargo Dragon launch, a SpaceX official shed some light on a surprise Falcon 9 drone ship landing planned for Wednesday, revealing the circumstances behind the unique decision.
A few days ago, it became clear that SpaceX and NASA and decided to perform a drone ship booster landing attempt after Cargo Dragon’s CRS-19 launch, an unusual trajectory compared to the more typical return-to-launch-site (RTLS) Landing Zone recoveries. Teslarati discussed this quandary earlier today.
“As it turns out, this Falcon 9 landing is a bit of mystery: it’s unclear why exactly SpaceX has decided to land the booster at sea instead of the usual Landing Zone recoveries that have followed most recent Cargo Dragon launches. Typically, the low insertion orbit (~200 km x ~390 km) and relatively low mass of Cargo Dragon (less than 10 tons or 22,000 lb) means that Falcon 9 has (literally) tons of propellant left over, giving it the margins needed to flip around, cancel out a huge amount of horizontal velocity, and boost 100+ km (62+ mi) back to shore.
Instead, new Falcon 9 booster B1058 is scheduled to land aboard drone ship OCISLY some 350 km (220 mi) downrange, an unusual distance. For reference, SpaceX’s May 2019 CRS-17 mission is the only time Falcon 9 has landed at sea after a CRS launch since CRS-8, the rocket’s first successful drone ship recovery. That scenario was forced because LZ-1/2 had coincidently been showered in Crew Dragon debris after C201 exploded during testing. Even then, OCISLY was stationed just 20 or so kilometers offshore, meaning that Falcon 9 B1056 still performed a routine Return To Launch Site (RTLS) landing in spirit.”
Teslarati.com — December 3rd

According to Jessica Jensen, SpaceX’s director of Dragon mission management, the actual reason behind Falcon 9 B1058’s surprise drone ship landing is relatively simple and was more or less one of the possibilities posed earlier today at Teslarati.
“[It’s] also possible that CRS-19 will follow in the footsteps of CRS-18, which sported a prototype Falcon 9 upper stage designed to push the enveloped of its orbital longevity. Falcon 9 B1056 still managed to land at LZ-1 after CRS-18, but a more ambitious follow-on test could potentially require much more propellant, accounting for the drone ship’s position further downrange “
Much as predicted, SpaceX is essentially going to perform an even more ambitious coast test, requiring significantly larger propellant margins that took away from Falcon 9’s own landing propellant budget. For whatever reason, the gray coating covering the CRS-18 upper stage’s RP-1 (refined kerosene) tank is not present on Falcon 9. Based on a picture taken of the horizontal rocket by a NASA Social CRS-19 attendee, CRS-19’s upper stage looks no different than any other.
Jensen says that the coast test will be performed for unspecified “other” customers, presumably referring to the US Air Force (USAF) and other commercial customers interested in direct-to-geostationary (GEO) launch services. Direct GEO launches require rocket upper stages to perform extremely long coasts in orbit, all while fighting the hostile vacuum environment’s temperature swings and radiation belts and attempting to prevent cryogenic propellant from boiling off or freezing solid. In simple terms, it’s incredibly difficult to build a reliable, high-performance upper stage capable of remaining fully functional after 6-12+ hours in orbit.
Although SpaceX said that the test was for “other” customers, that may well have been a cryptic way to avoid indicating that one such customer might be NASA itself. NASA is in the midst of a political battle for the Europa Clipper spacecraft’s launch contract, which is currently legally obligated to launch on NASA’s SLS rocket. Said rocket will likely cost on the order of >$2 billion per launch, meaning that simply using Falcon Heavy or Delta IV Heavy could save no less than ~$1.5 billion. Incredibly, that means that simply using a commercial launch vehicle could save NASA enough money to fund an entire Curiosity-sized Mars rover or even a majority of the cost of building a dedicated Europa lander. Such a launch would demand every ounce of Falcon Heavy’s performance, including a very long orbital coast.
Regardless of the prospective beneficiaries of SpaceX’s planned Falcon 9 upper stage test, CRS-19 is scheduled to launch no earlier than 12:51 pm EST (16:51 UTC), December 4th. High upper-level winds may delay the mission 24 hours to December 5th but for now, it remains on track for Wednesday.
Check out Teslarati’s Marketplace! We offer Tesla accessories, including for the Tesla Cybertruck and Tesla Model 3.
News
SpaceX’s Crew-11 mission targets July 31 launch amid tight ISS schedule
The flight will lift off from Launch Complex 39A at Kennedy Space Center in Florida.
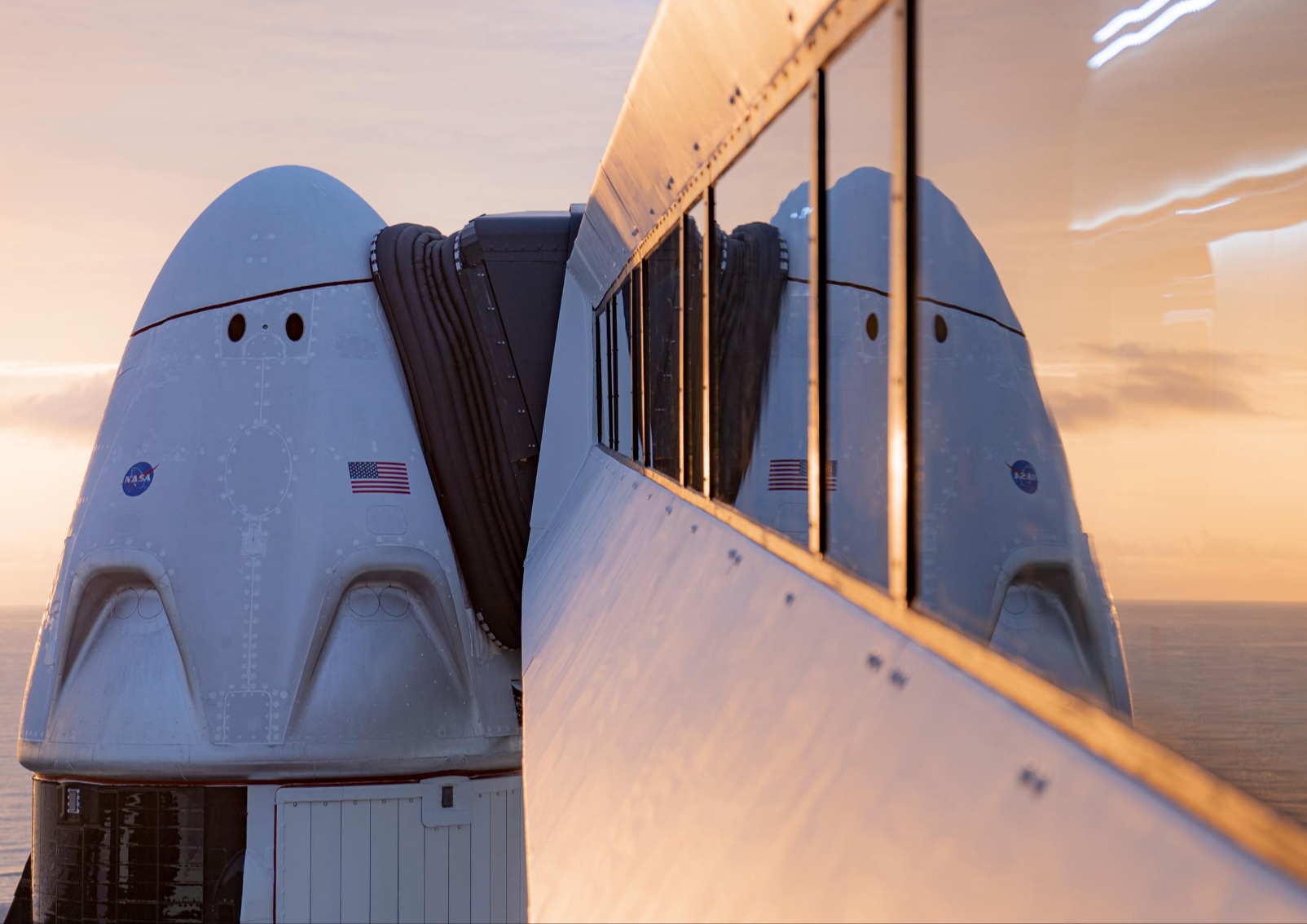

NASA and SpaceX are targeting July 31 for the launch of Crew-11, the next crewed mission to the International Space Station (ISS). The flight will lift off from Launch Complex 39A at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, using the Crew Dragon Endeavour and a Falcon 9 booster.
Crew Dragon Endeavour returns
Crew-11 will be the sixth flight for Endeavour, making it SpaceX’s most experienced crew vehicle to date. According to SpaceX’s director of Dragon mission management, Sarah Walker, Endeavour has already carried 18 astronauts representing eight countries since its first mission with NASA’s Bob Behnken and Doug Hurley in 2020, as noted in an MSN report.
“This Dragon spacecraft has successfully flown 18 crew members representing eight countries to space already, starting with (NASA astronauts) Bob (Behnken) and Doug (Hurley) in 2020, when it returned human spaceflight capabilities to the United States for the first time since the shuttle retired in July of 2011,” Walker said.
For this mission, Endeavour will debut SpaceX’s upgraded drogue 3.1 parachutes, designed to further enhance reentry safety. The parachutes are part of SpaceX’s ongoing improvements to its human-rated spacecraft, and Crew-11 will serve as their first operational test.
The Falcon 9 booster supporting this launch is core B1094, which has launched in two previous Starlink missions, as well as the private Ax-4 mission on June 25, as noted in a Space.com report.
The four-members of Crew-11 are NASA astronauts Zena Cardman and Mike Fincke, as well as Japan’s Kimiya Yui and Russia’s Oleg Platonov.
Tight launch timing
Crew-11 is slated to arrive at the ISS just as NASA coordinates a sequence of missions, including the departure of Crew-10 and the arrival of SpaceX’s CRS-33 mission. NASA’s Bill Spetch emphasized the need for careful planning amid limited launch resources, noting the importance of maintaining station altitude and resupply cadence.
“Providing multiple methods for us to maintain the station altitude is critically important as we continue to operate and get the most use out of our limited launch resources that we do have. We’re really looking forward to demonstrating that capability with (CRS-33) showing up after we get through the Crew-11 and Crew-10 handover,” Spetch stated.
Lifestyle
EV fans urge Tesla to acquire Unplugged Performance for edge in fleet and security industry
Unplugged Performance has built a name for itself by producing performance upgrades for Tesla vehicles.
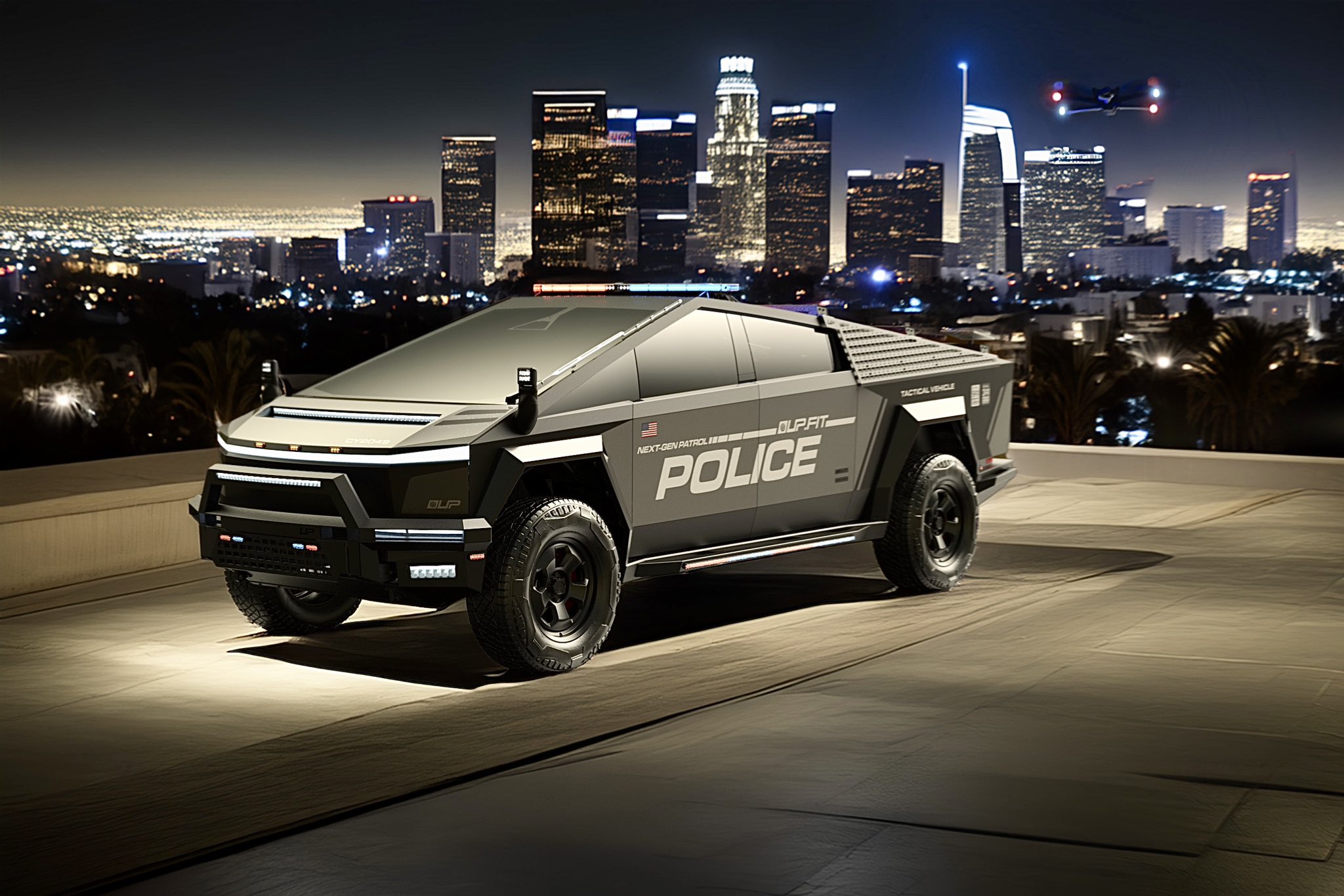

A growing number of Tesla enthusiasts and longtime community voices are calling on the electric vehicle maker to acquire Unplugged Performance, a California-based aftermarket company best known for tuning Tesla vehicles and developing specialized government fleet solutions under its UP.FIT division.
The idea was once considered a niche proposal among EV fans, but it is now gaining serious attention not just as a performance play but as a strategic move to deepen Tesla’s roots in the fleet and security industry.
A strategic fit
Unplugged Performance has built a name for itself by producing performance upgrades for Tesla vehicles, from track-optimized components to visual and aerodynamic upgrades. But in recent years, its UP.FIT division has pivoted toward a more functional future by outfitting Tesla vehicles like Model Ys for police, military, and government use.
That work has sparked growing calls for closer collaboration with Tesla, especially as the EV maker increasingly leans into autonomy, AI, and fleet services as core components of its next chapter.
“I posted this four years ago, but I think it’s more true now than ever,” wrote Whole Mars Catalog, a well-known Tesla investor and FSD Beta tester, on X. “Tesla should buy Unplugged. But not just as a Performance division. What they are doing with UP.FIT unlocks large government and commercial fleet purchases that can improve utilization.”
Tesla fans such as shareholder Sawyer Merritt echoed the sentiment, calling Unplugged a “great fit within Tesla.” adding, “They are literally located directly next to Tesla’s design studio in Hawthorne.”
Enabling the next wave
Supporters of the idea noted that integrating Unplugged into Tesla’s corporate structure could help accelerate the adoption of autonomous technologies in government sectors. With UP.FIT patrol cars already in use across some U.S. police departments, Tesla fans envisioned a future where self-driving Teslas could potentially revolutionize law enforcement, search-and-rescue, and public service logistics.
“Just imagine how autonomous patrol cars could transform policing and bring us into a safer future,” the veteran FSD tester wrote.
The benefits could also extend to Tesla’s existing consumer base. “They also have some incredible products in the works that I think will appeal to many ordinary Tesla drivers — not just those looking for performance or mods. Stuff that’s so good it should have come straight from the design studio next door,” Whole Mars Catalog noted.
Unplugged Performance, founded in 2013, shares not just a product vision with Tesla, but also geography. Its Hawthorne headquarters sits directly adjacent to Tesla’s design studio, and the two companies have maintained a close working relationship over the years. The aftermarket firm has long positioned itself as a “mission-aligned” partner to Tesla.
In response to the recent calls for acquisition, Unplugged Performance acknowledged the support from the community. “Our very existence is to support the Tesla mission with @UpfitTesla and @UnpluggedTesla,” Unplugged CEO Ben Schaffer posted on X. “We love working with Tesla and are grateful for the community’s support since 2013!”
News
Tesla debuts hands-free Grok AI with update 2025.26: What you need to know
All new Tesla vehicles delivered on or after July 12, 2025, will include Grok AI out of the box

Tesla has begun rolling out Grok, an in-car conversational AI assistant developed by xAI, to eligible vehicles starting July 12. The feature marks the most direct integration yet between Elon Musk’s artificial intelligence startup and Tesla’s consumer product lineup, offering drivers hands-free access to a chat-style companion while on the road.
Grok comes pre-installed on new vehicles
According to Tesla’s FAQ page for the feature, all new vehicles delivered on or after July 12, 2025, will include Grok AI out of the box. Owners of older vehicles may gain access through an over-the-air update, provided their vehicle meets a few hardware and software requirements.
Specifically, Grok is currently only supported on Tesla models equipped with an AMD infotainment processor and running vehicle software version 2025.26 and higher. Compatible models include the Model S, Model 3, Model X, Model Y, and Cybertruck. A Premium Connectivity subscription or active Wi-Fi connection is also required.
Tesla notes that additional vehicle compatibility may arrive in future software updates.
Grok’s features and limitations for now
Drivers can engage with Grok using the App Launcher or by pressing and holding the voice command button on the steering wheel. Grok is designed to answer questions and hold conversations using natural language, offering responses tailored to its chosen personality—ranging from “Storyteller” to the more eccentric “Unhinged.”
For fun, Tesla posted a demonstration of Grok likely running on “Unhinged” talking about what it would do to Optimus when they are on a date, much to the shock of the humanoid robot’s official social media account.
It should be noted, however, that Grok cannot currently issue commands to the vehicle itself, at least for now. Traditional voice commands for tasks like climate control, navigation, or media remain separate from Grok as of writing.
The feature is being released in Beta and does not require a Grok account or xAI subscription to activate, although that policy may change over time.
Grok privacy and in-car experience
Tesla emphasizes that interactions with Grok are securely processed by xAI and not linked to a user’s Tesla account or vehicle. Conversations remain anonymous unless a user signs into Grok separately to sync their history across devices.
Tesla has also begun promoting Grok directly on its official vehicle webpages, showcasing the feature as part of its in-car experience, further highlighting the company’s increasing focus on AI and infotainment features on its all-electric vehicles.
-

 Elon Musk2 weeks ago
Elon Musk2 weeks agoTesla investors will be shocked by Jim Cramer’s latest assessment
-

 Elon Musk3 days ago
Elon Musk3 days agoxAI launches Grok 4 with new $300/month SuperGrok Heavy subscription
-

 Elon Musk5 days ago
Elon Musk5 days agoElon Musk confirms Grok 4 launch on July 9 with livestream event
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoTesla Model 3 ranks as the safest new car in Europe for 2025, per Euro NCAP tests
-

 Elon Musk1 week ago
Elon Musk1 week agoxAI’s Memphis data center receives air permit despite community criticism
-

 News2 weeks ago
News2 weeks agoXiaomi CEO congratulates Tesla on first FSD delivery: “We have to continue learning!”
-

 Elon Musk2 weeks ago
Elon Musk2 weeks agoTesla scrambles after Musk sidekick exit, CEO takes over sales
-

 News2 weeks ago
News2 weeks agoTesla sees explosive sales growth in UK, Spain, and Netherlands in June


















