

News
Stoke Space to build SpaceX Raptor engine’s first real competitor
Seattle startup Stoke Space has revealed plans to develop an efficient rocket engine similar to the Raptors that power SpaceX’s Starship.
Formed in October 2019, Stoke Space secured its first significant round of funding – $9.1 million – less than three years ago. At that time, CEO and co-founder Andy Lapsa says that the startup had just five employees, no permanent workspace, and a “barren field” for a test site. Within 18 months, Stoke Space had turned that empty field into an impressive test facility, conducted numerous component tests, and assembled its first full-scale rocket engine – an exotic UFO-like device unlike any seen before.
It also raised another $65 million – enough funding to begin earnestly developing a potentially revolutionary rocket capable of launching more than 1.65 tons (~3600 lb) into orbit for less than half a million dollars. To realize that extremely ambitious goal, Stoke Space has taken the even more ambitious step of attempting to make the first rocket it develops fully reusable. Simultaneously, the company has incorporated several exotic technologies into that rocket, recently culminating in a surprise announcement that it will attempt to develop one of the most difficult types of engines to power that rocket’s booster stage.
The update that's rolling out to the fleet makes full use of the front and rear steering travel to minimize turning circle. In this case a reduction of 1.6 feet just over the air— Wes (@wmorrill3) April 16, 2024
Full-flow staged combustion
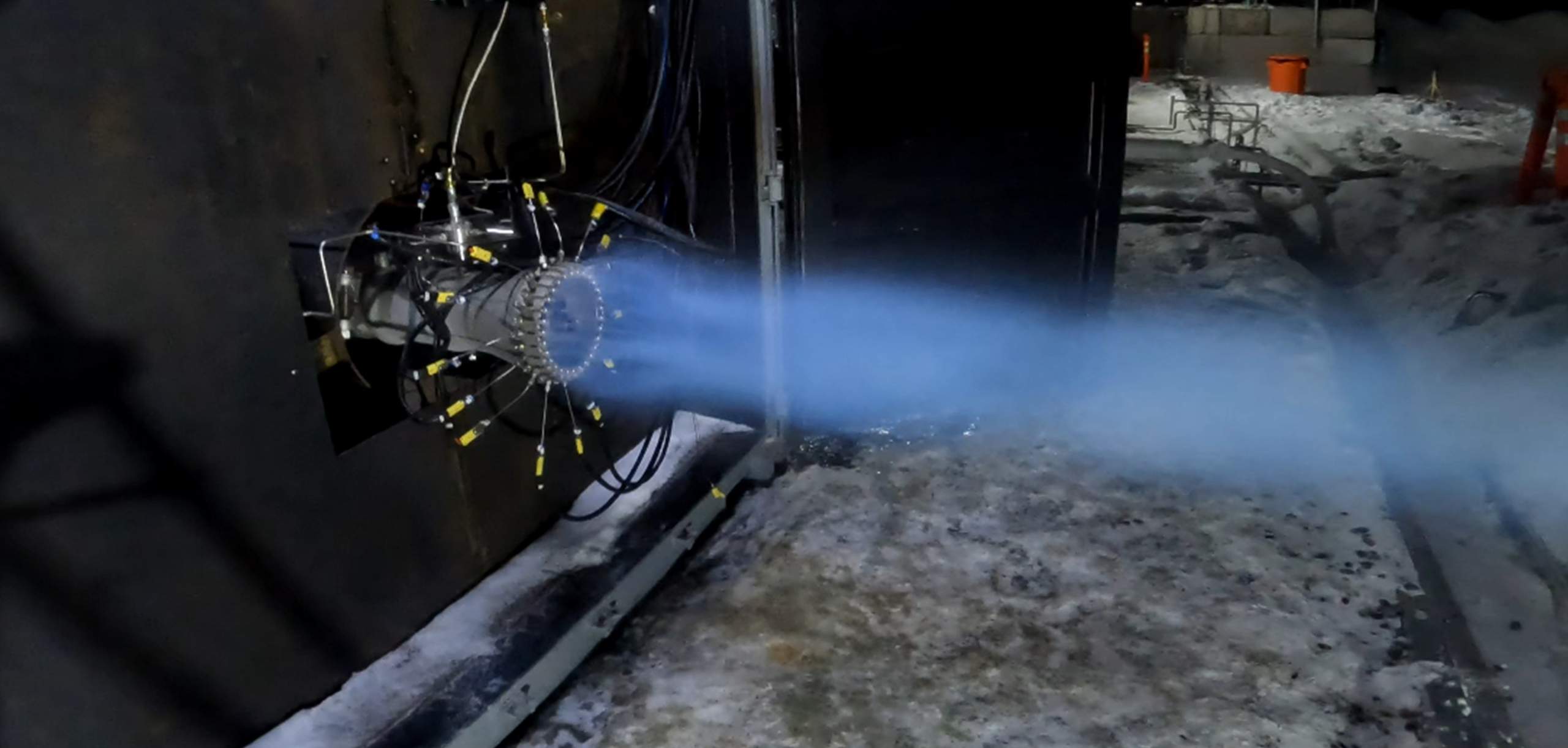
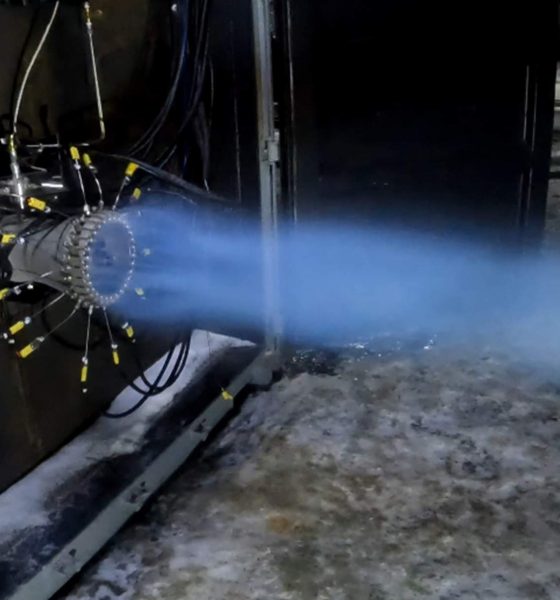
At the end of an extended interview and tour with YouTuber Tim Dodd (The Everyday Astronaut), CEO Andy Lapsa revealed that Stoke Space has decided to build a full-flow staged combustion (FFSC) engine for the first stage of its reusable rocket. FFSC is the most efficient type of combustion cycle available for a chemical bipropellant rocket engine, but it’s also the most difficult to develop.
A full-flow engine attempts to squeeze every possible ounce of performance out of the propellant it consumes. The most powerful and efficient chemical rocket engines must consume huge volumes of propellant in a short amount of time without destroying the launch vehicle they’re attached to. To create pressure and spin the pumps that are needed to feed that propellant into their main combustion chamber, engines often burn a small amount of propellant in a separate gas generator or preburner. Gas-generator engines vent that exhaust overboard, reducing efficiency but making for a much simpler design. Staged-combustion engines use preburners to create gas that pumps liquid propellant, and that exhaust gas is eventually injected into the main combustion chamber.
Full-flow staged combustion sets itself apart by having two separate pumps and preburners for oxidizer and fuel. Unlike simpler variants of staged combustion, FFSC engines turn all of their propellant into gas before injecting it into the combustion chamber. That hot gas increases the heat of combustion and the pressure inside the combustion chamber, ensuring that virtually all of the propellant that flows through the engine is combusted and turned into thrust as efficiently as possible. FFSC is exceptionally difficult because of the extra-high temperatures and pressures it requires, as well as the need for an oxygen-rich preburner and pump. In a high-pressure, hot-oxygen environment, virtually anything imaginable – including most metals – will spontaneously combust.
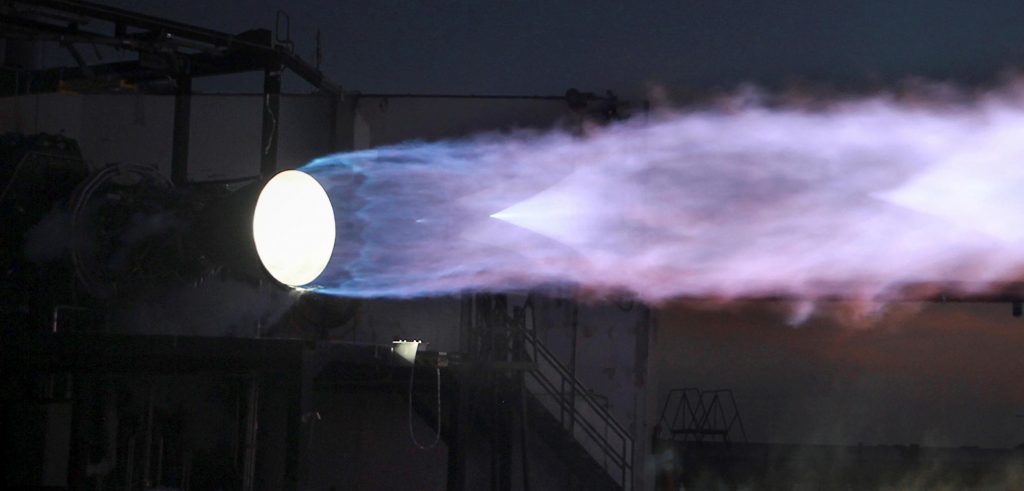
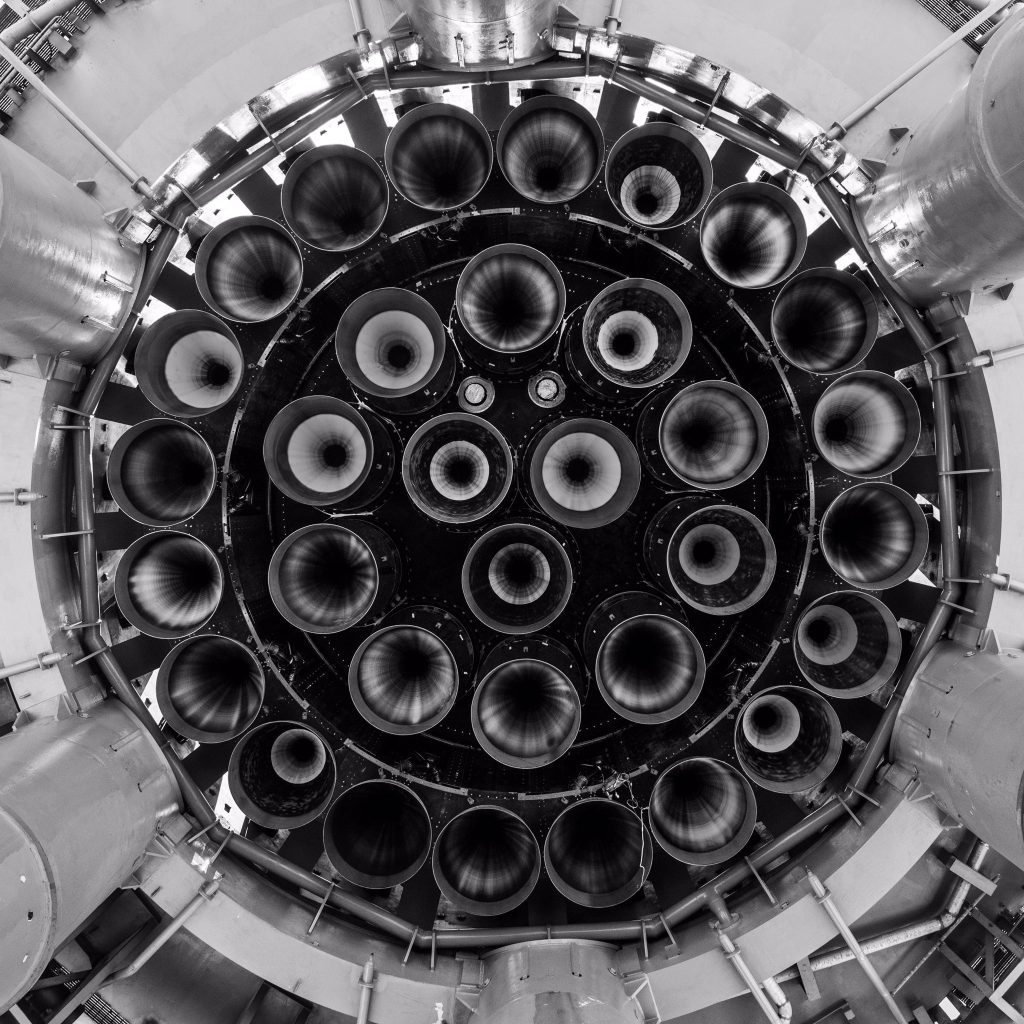






Only complex custom-designed alloys can survive those conditions. SpaceX’s Raptor, the only FFSC engine that has ever flown, is especially difficult because it’s meant to be highly reusable. To be successful, Raptor will have to survive those conditions dozens or even hundreds of times in a row with little to no maintenance in between.
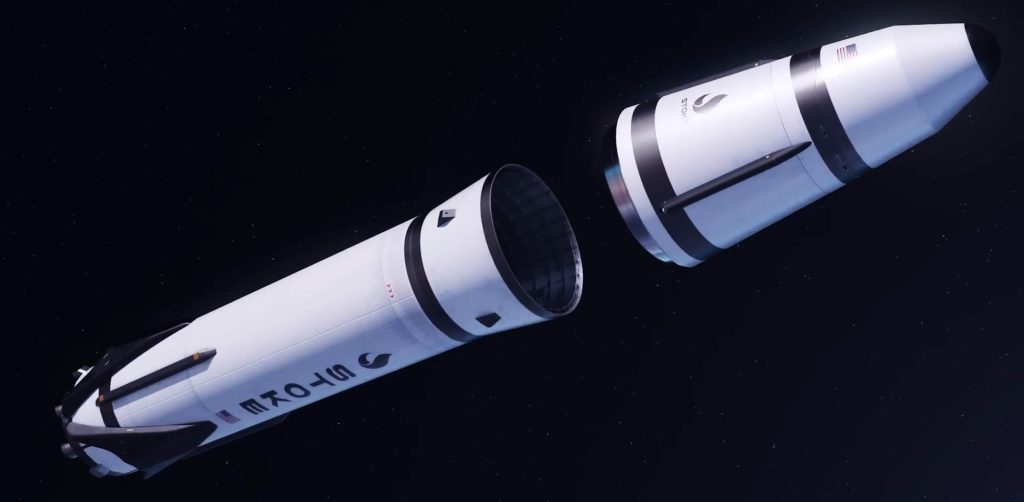
The first booster engine Stoke Space ever attempts to build will be a reusable full-flow staged combustion engine powered by liquid methane and liquid oxygen – essentially a smaller version of SpaceX’s Raptor. Stoke’s booster is otherwise familiar and features deployable landing legs like SpaceX’s Falcon boosters. Lapsa says it will likely also have grid fins.
Reusing the upper stage
In some ways, the upper stage of Stoke’s first rocket is even more ambitious. Powered by hydrogen and oxygen propellant, Stoke has designed a conical capsule-like upper stage with an integral fairing. The upper stage’s propulsion is exotic and unique. A large pump will feed propellant to up to 30 combustion chambers distributed around the rim of its heat shield. The exhaust coming from those 30 chambers will expand and partially push against the upper stage’s equally exotic metallic, liquid-cooled heat shield. That expansion against the heat shield improves the efficiency of the upper stage and means that its engine will technically be an aerospike.
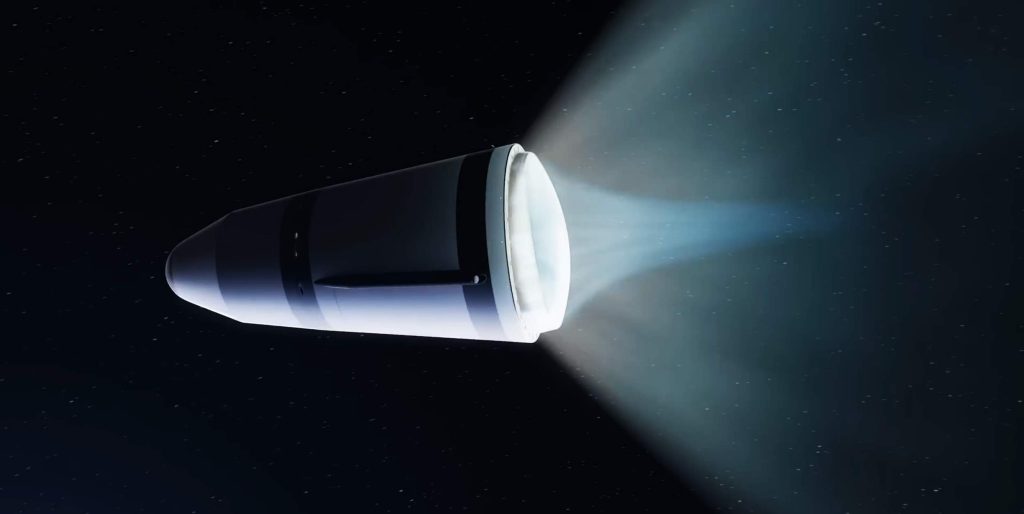
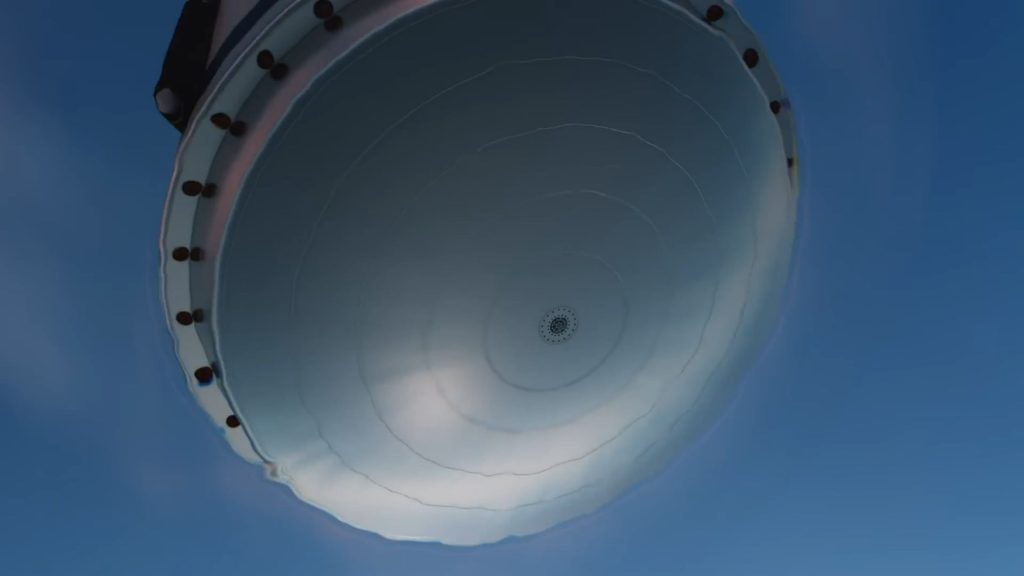
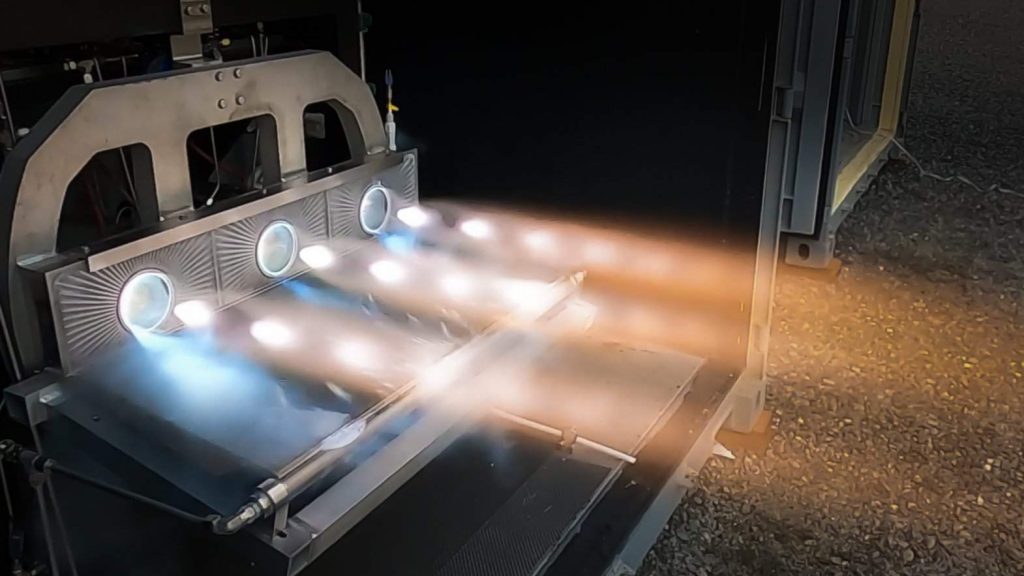
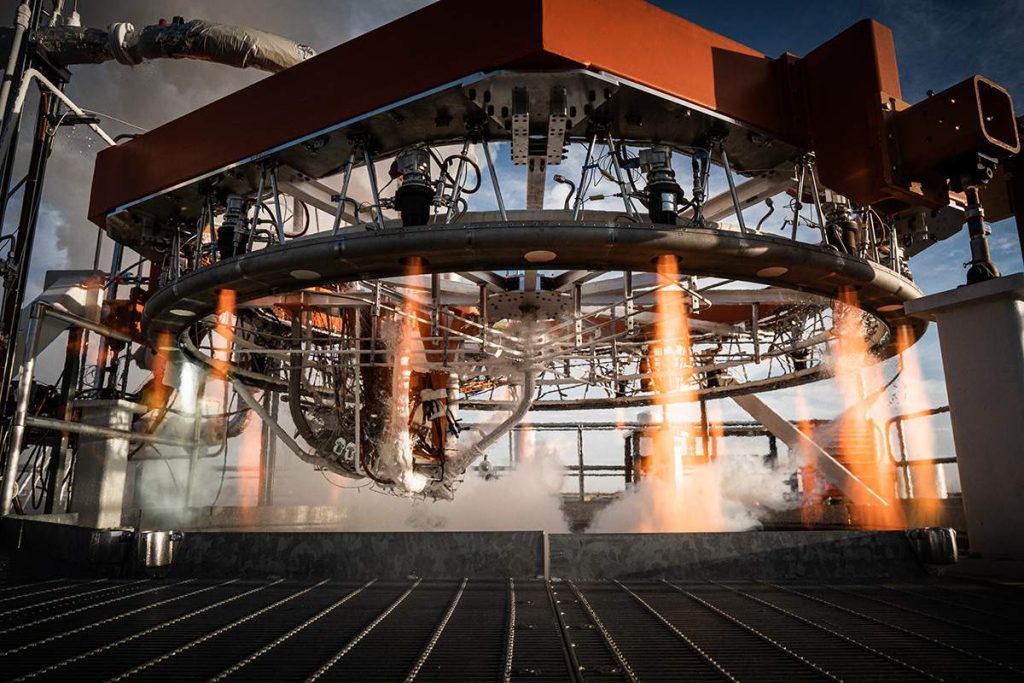
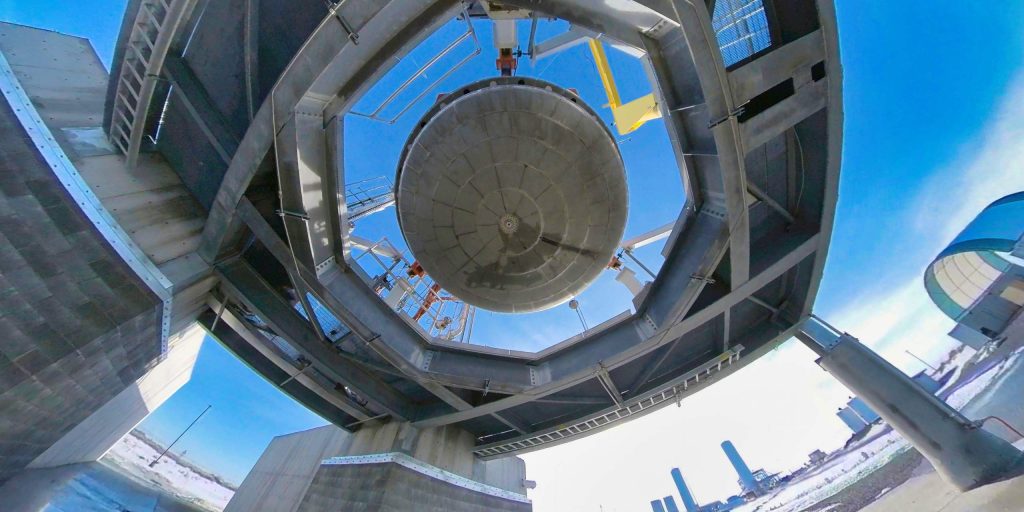
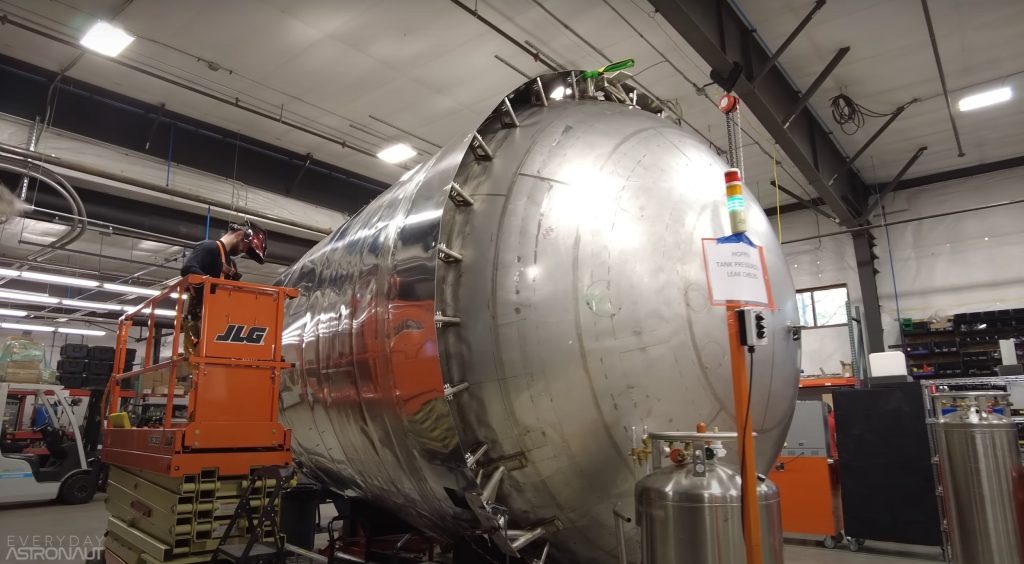

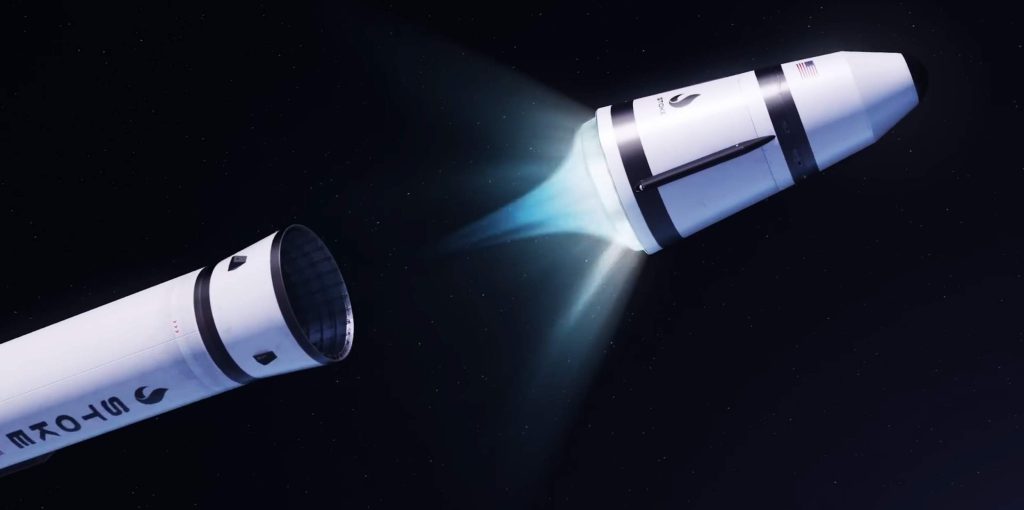






Stoke has already begun testing a full-scale version of the upper stage’s UFO-like rocket engine with 15 combustion chambers. Since testing began in the second half of 2022, Stoke has completed dozens of static fires. Everyday Astronaut’s tour also revealed that the startup has made significant progress fabricating and assembling its first full-scale upper stage prototype – tanks, nosecone, heat shield, engine, and all.
Reminiscent of SpaceX’s Grasshopper and Starhopper campaigns, Stoke plans to conduct hop tests with that prototype if it makes it through qualification testing. On February 7th, Stoke also revealed that it’s begun testing a crucial component of its full-flow booster engine. All told, Stoke Space is making progress at a remarkable pace and continues to tackle the hardest problems. The startup has also avoided widely publicizing any specific deadlines, instead choosing to let hardware and tangible results speak for themselves. Only time will tell if that approach pays off, but Stoke is off to an exceptionally impressive start in an industry full of impressive rocket startups.

News
Tesla dominates in the UK with Model Y and Model 3 leading the way

Tesla is dominating in the United Kingdom so far through 2025, and with about two weeks left in the year, the Model Y and Model 3 are leading the way.
The Model Y and Model 3 are the two best-selling electric vehicles in the United Kingdom, which is comprised of England, Scotland, Wales, and Northern Ireland, and it’s not particularly close.
According to data gathered by EU-EVs, the Model Y is sitting at 18,890 units for the year, while the Model 3 is slightly behind with 16,361 sales for the year so far.
The next best-selling EV is the Audi Q4 e-tron at 10,287 units, lagging significantly behind but ahead of other models like the BMW i4 and the Audi Q6 e-tron.
GOOD NEWS 🇬🇧 Tesla is absolutely crushing the UK electric vehicle market in 2025 💥
The numbers are in, and the dominance is clear. With an impressive amount of 42,270 vehicles delivered year-to-date, the brand now commands a solid 9.6% market share of the total auto market 🆒… pic.twitter.com/dkiGX9kzd0
— Ming (@tslaming) December 18, 2025
The Model Y has tasted significant success in the global market, but it has dominated in large markets like Europe and the United States.
For years, it’s been a car that has fit the bill of exactly what consumers need: a perfect combination of luxury, space, and sustainability.
Both vehicles are going to see decreases in sales compared to 2024; the Model Y was the best-selling car last year, but it sold 32,610 units in the UK. Meanwhile, the Model 3 had reached 17,272 units, which will keep it right on par with last year.
Tesla sold 50,090 units in the market last year, and it’s about 8,000 units shy of last year’s pace. It also had a stronger market share last year with 13.2 percent of the sales in the market. With two weeks left in 2025, Tesla has a 9.6 percent market share, leading Volkswagen with 8 percent.
The company likely felt some impact from CEO Elon Musk’s involvement with the Trump administration and, more specifically, his role with DOGE. However, it is worth mentioning that some months saw stronger consumer demand than others. For example, sales were up over 20 percent in February. A 14 percent increase followed this in June.
News
Tesla Insurance officially expands to new U.S. state
Tesla’s in-house Insurance program first launched back in late 2019, offering a new way to insure the vehicles that was potentially less expensive and could alleviate a lot of the issues people had with claims, as the company could assess and repair the damage itself.
Tesla Insurance has officially expanded to a new U.S. state, its thirteenth since its launch in 2019.
Tesla has confirmed that its in-house Insurance program has officially made its way to Florida, just two months after the company filed to update its Private Passenger Auto program in the state. It had tried to offer its insurance program to drivers in the state back in 2022, but its launch did not happen.
Instead, Tesla refiled the paperwork back in mid-October, which essentially was the move toward initiating the offering this month.
BREAKING: Tesla Insurance has just officially launched in Florida.
This is the first new state to receive @Tesla Insurance in more than 3 years. In total, Tesla insurance is now available in 13 U.S. states (map in thread below of all the states).
Tesla Insurance in Florida uses… pic.twitter.com/bDwh1IV6gD
— Sawyer Merritt (@SawyerMerritt) December 17, 2025
Tesla’s in-house Insurance program first launched back in late 2019, offering a new way to insure the vehicles that was potentially less expensive and could alleviate a lot of the issues people had with claims, as the company could assess and repair the damage itself.
It has expanded to new states since 2019, but Florida presents a particularly interesting challenge for Tesla, as the company’s entry into the state is particularly noteworthy given its unique insurance landscape, characterized by high premiums due to frequent natural disasters, dense traffic, and a no-fault system.
Annual average premiums for Florida drivers hover around $4,000 per year, well above the national average. Tesla’s insurance program could disrupt this, especially for EV enthusiasts. The state’s growing EV adoption, fueled by incentives and infrastructure development, aligns perfectly with Tesla’s ecosystem.
Moreover, there are more ways to have cars repaired, and features like comprehensive coverage for battery damage and roadside assistance tailored to EVs address those common painpoints that owners have.
However, there are some challenges that still remain. Florida’s susceptibility to hurricanes raises questions about how Tesla will handle claims during disasters.
Looking ahead, Tesla’s expansion of its insurance program signals the company’s ambition to continue vertically integrating its services, including coverage of its vehicles. Reducing dependency on third-party insurers only makes things simpler for the company’s automotive division, as well as for its customers.
News
Tesla Full Self-Driving gets sparkling review from South Korean politician
“Having already ridden in an unmanned robotaxi, the novelty wasn’t as strong for me, but it drives just as well as most people do. It already feels like a completed technology, which gives me a lot to think about.”
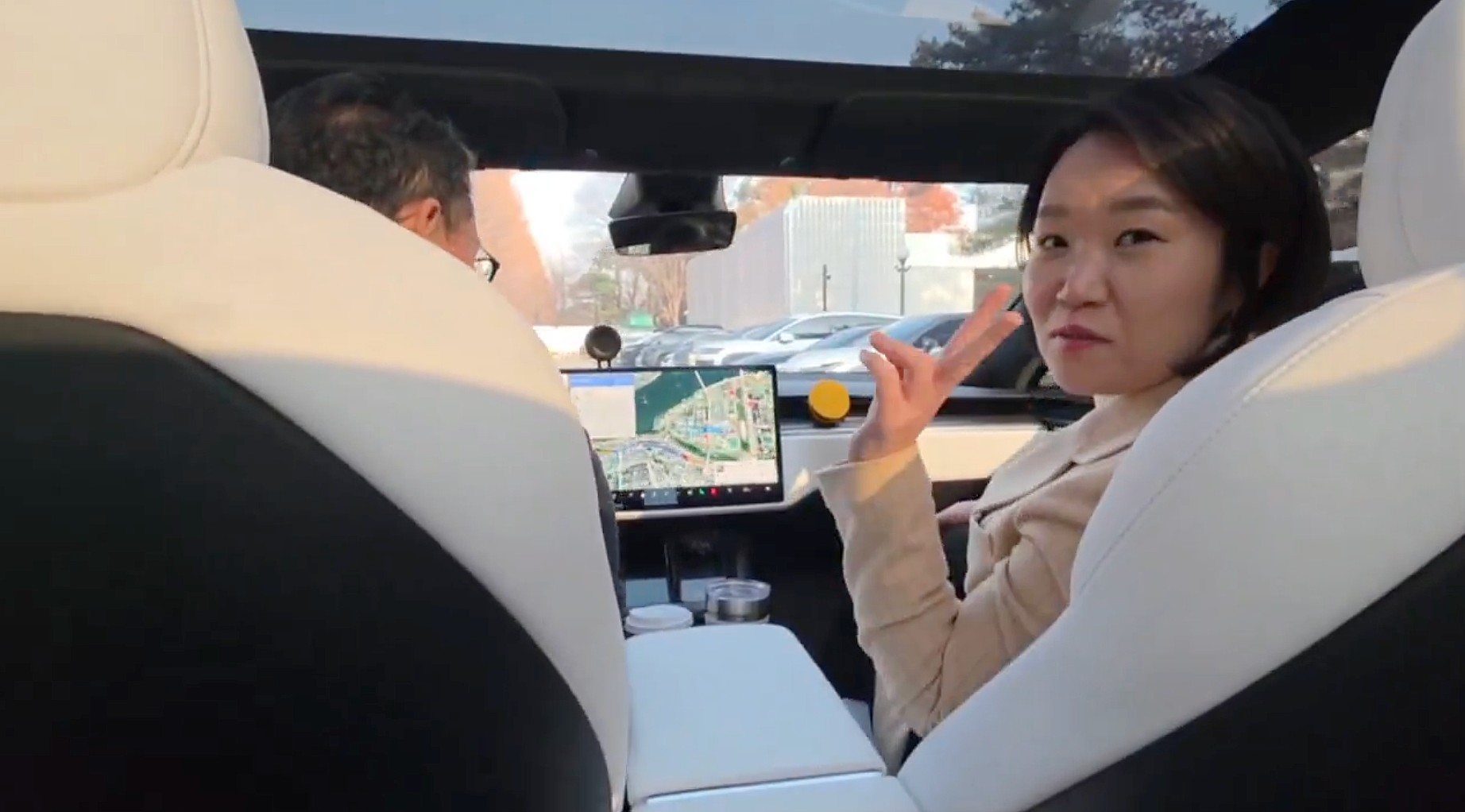

Tesla Full Self-Driving got its first sparkling review from South Korean politician Lee So-young, a member of the country’s National Assembly, earlier this week.
Lee is a member of the Strategy and Finance Committee in South Korea and is a proponent of sustainable technologies and their applications in both residential and commercial settings. For the first time, Lee was able to utilize Tesla’s Full Self-Driving technology as it launched in the country in late November.
Her thoughts on the suite were complimentary to the suite, stating that “it drives just as well as most people do,” and that “it already feels like a completed technology.”
드디어 오늘, 서울에서 테슬라 FSD 체험 했습니다.
JiDal Papa님의 모델S 협찬에 힘입어^^ 파파님 정말 감사합니다.
국회 -> 망원시장 -> 홍익대 -> 국회 복귀 코스였고요.
이미 무인 로보택시를 타봐서 그런지 신기함은
덜했지만, 웬만한 사람만큼 운전을 잘하네요.이미 완성된 기술이라고… pic.twitter.com/8pAidHBpRG
— 이소영 국회의원 (Soyoung Lee) (@im_soyounglee) December 17, 2025
Her translated post says:
“Finally, today I got to experience Tesla FSD in Seoul. Thanks to the Model S sponsored by JiDal Papa^^, I’m truly grateful to Papa. The route was from the National Assembly -> Mangwon Market -> Hongik University -> back to the National Assembly. Having already ridden in an unmanned robotaxi, the novelty wasn’t as strong for me, but it drives just as well as most people do. It already feels like a completed technology, which gives me a lot to think about. Once it actually spreads into widespread use, I feel like our daily lives are going to change a lot. Even I, with my license gathering dust in a drawer, don’t see much reason to learn to drive a manual anymore.”
Tesla Full Self-Driving officially landed in South Korea in late November, with the initial launch being one of Tesla’s most recent, v14.1.4.
It marked the seventh country in which Tesla was able to enable the driver assistance suite, following the United States, Puerto Rico, Canada, China, Mexico, Australia, and New Zealand.
It is important to see politicians and figures in power try new technologies, especially ones that are widely popular in other regions of the world and could potentially revolutionize how people travel globally.








