
Investor's Corner
HyperLoop Test Track Coming To California
HyperLoop Transportation Technologies has purchased land in central California to build HyperLoop test track to see if the this nutty idea actually works.
HyperLoop Transportation Technologies has struck a deal to buy enough land near Interstate 5 in central California to build a 5 mile long HyperLoop test track, reports Navigant Research. It will cost about $100,000,000 and serve as a “proof of concept” facility for the HyperLoop idea proposed by Elon Musk in 2013. The money to pay for it is expected to come from an IPO later this year, with construction beginning in 2016.
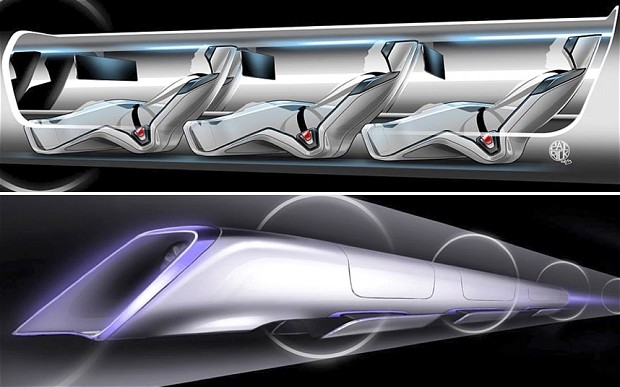
If you’re not familiar with the HyperLoop, think of it as one of those pneumatic tubes that connect drivers and tellers at drive-thru banks, only hundreds of miles long and big enough to carry people. Musk thinks such a system could whisk passengers from LA to San Francisco in about 35 minutes at speeds up to 800 mph.
If that seems a little fantastic to you, remember this is the man who thought it was possible to build a rocket ship for a fraction of what it costs other companies — and then did it. Today, his SpaceX company has years of business worth billions of dollars booked, while those others are crying for customers. Saying “It can’t be done,” to Musk is like telling Congress to stop spending your money.
For all his genius, not even Elon Musk can overturn the laws of physics. All transportation devices have to deal with friction losses and wind resistance. As speeds increase, so does friction, but the real enemy of high speed travel is wind resistance. Aerodynamic loads increase with the square of speed. That’s why it takes 4 times as much power to punch a hole in the air at 100 mph than it does at 50 mph.
The HyperLoop doesn’t repeal the laws of physics; it finds new ways to minimize their effects. It’s one of those “Don’t raise the bridge, lower the river,” kind of things and it’s brilliant. Let’s start with wind resistance. The HyperLoop will consist of a steel tube hundreds of miles long that has a partial vacuum inside. Less air means less wind resistance. Less wind resistance means higher speeds with less power.
Part two of the plan eliminates all the wheels, axles and motors that cause friction in regular vehicles. Instead, the transportation modules inside the HyperLoop tube will “float” on a thin layer of air, slashing friction to nearly zero. Instead of motors, the train will be propelled by electrically powered linear accelerators installed along its entire length. Once again, the idea is brilliant. But will it work?
Musk says passengers in his HyperLoop will be whisked along in complete comfort. But skeptics point out that they will be sealed inside windowless pods during the journey. Those who suffer from claustrophobia shouldn’t buy a ticket. There will be no beverage service, no restrooms and no possibility of moving around during the journey. Furthermore, they will be bombarded by the sound of what little air is left inside the tube rushing by at near supersonic speeds.
While Musk assumes the ride will be serenely smooth, in reality the alignment of the tube will have to be virtually perfect over its entire length for that to happen. Hello? We are talking about California here, a state known for its frequent seismic activity. Then there are considerations like how to keep the HyperLink tube sealed against air leaks and safe from vandalism.
The test track is designed to answer all those questions and win over the doubters. If the idea is validated, Musk says a Hyperloop along the heavily traveled I 5 corridor could be built for about $8 billion. Contrast that with the $64 billion the Amtrak high speed rail line scheduled to begin construction soon is supposed to cost. When was the last time a government project came in on time and under budget? Of course, Musk’s numbers don’t include the costs of developing his idea and making it a reality.
Elon Musk’s greatest gift is spinning wondrous tales about what could be and convincing people to invest today in his promise of tomorrow. Then he uses the funds raised to make tomorrow happen. So far, more people have made money investing in Musk and his dreams than have lost it. When the HyperLoop Transportation Technologies IPO takes place, will you be on the phone to your broker, placing a “buy” order? Or do you think the HyperLoop is mostly hype and hyperbole?
The problem with predicting the future is the future is so stubbornly unpredictable.

Investor's Corner
Tesla gets tip of the hat from major Wall Street firm on self-driving prowess
“Tesla is at the forefront of autonomous driving, supported by a camera-only approach that is technically harder but much cheaper than the multi-sensor systems widely used in the industry. This strategy should allow Tesla to scale more profitably compared to Robotaxi competitors, helped by a growing data engine from its existing fleet,” BoA wrote.

Tesla received a tip of the hat from major Wall Street firm Bank of America on Wednesday, as it reinitiated coverage on Tesla shares with a bullish stance that comes with a ‘Buy’ rating and a $460 price target.
In a new note that marks a sharp reversal from its neutral position earlier in 2025, the bank declared Tesla’s Full Self-Driving (FSD) technology the “leading consumer autonomy solution.”
Analysts highlighted Tesla’s camera-only architecture, known as Tesla Vision, as a strategic masterstroke. While technically more challenging than the multi-sensor setups favored by rivals, the vision-based approach is dramatically cheaper to produce and maintain.
This cost edge, combined with Tesla’s rapidly expanding real-world data engine, positions the company to scale robotaxis far more profitably than competitors, BofA argues in the new note:
“Tesla is at the forefront of autonomous driving, supported by a camera-only approach that is technically harder but much cheaper than the multi-sensor systems widely used in the industry. This strategy should allow Tesla to scale more profitably compared to Robotaxi competitors, helped by a growing data engine from its existing fleet.”
The bank now attributes roughly 52% of Tesla’s total valuation to its Robotaxi ambitions. It also flagged meaningful upside from the Optimus humanoid robot program and the fast-growing energy storage business, suggesting the auto segment’s recent headwinds, including expired incentives, are being eclipsed by these higher-margin opportunities.
Tesla’s own data underscores exactly why Wall Street is waking up to FSD’s potential. According to Tesla’s official safety reporting page, the FSD Supervised fleet has now surpassed 8.4 billion cumulative miles driven.
Tesla FSD (Supervised) fleet passes 8.4 billion cumulative miles
That total ballooned from just 6 million miles in 2021 to 80 million in 2022, 670 million in 2023, 2.25 billion in 2024, and a staggering 4.25 billion in 2025 alone. In the first 50 days of 2026, owners added another 1 billion miles — averaging more than 20 million miles per day.
This avalanche of real-world, camera-captured footage, much of it on complex city streets, gives Tesla an unmatched training dataset. Every mile feeds its neural networks, accelerating improvement cycles that lidar-dependent rivals simply cannot match at scale.
Tesla owners themselves will tell you the suite gets better with every release, bringing new features and improvements to its self-driving project.
The $460 target implies roughly 15 percent upside from recent trading levels around $400. While regulatory and safety hurdles remain, BofA’s endorsement signals growing institutional conviction that Tesla’s data advantage is not hype; it’s a tangible moat already delivering billions of miles of proof.
Elon Musk
SpaceX IPO could push Elon Musk’s net worth past $1 trillion: Polymarket
The estimates were shared by the official Polymarket Money account on social media platform X.

Recent projections have outlined how a potential $1.75 trillion SpaceX IPO could generate historic returns for early investors. The projections suggest the offering would not only become the largest IPO in history but could also result in unprecedented windfalls for some of the company’s key investors.
The estimates were shared by the official Polymarket Money account on social media platform X.
As noted in a Polymarket Money analysis, Elon Musk invested $100 million into SpaceX in 2002 and currently owns approximately 42% of the company. At a $1.75 trillion valuation following SpaceX’s potential $1.75 trillion IPO, that stake would be worth roughly $735 billion.
Such a figure would dramatically expand Musk’s net worth. When combined with his holdings in Tesla Inc. and other ventures, a public debut at that level could position him as the world’s first trillionaire, depending on market conditions at the time of listing.
The Bloomberg Billionaires Index currently lists Elon Musk with a net worth of $666 billion, though a notable portion of this is tied to his TSLA stock. Tesla currently holds a market cap of $1.51 trillion, and Elon Musk’s currently holds about 13% to 15% of the company’s outstanding common stock.
Founders Fund, co-founded by Peter Thiel, invested $20 million in SpaceX in 2008. Polymarket Money estimates the firm owns between 1.5% and 3% of the private space company. At a $1.75 trillion valuation, that range would translate to approximately $26.25 billion to $52.5 billion in value.
That return would represent one of the most significant venture capital outcomes in modern Silicon Valley history, with a growth of 131,150% to 262,400%.
Alphabet Inc., Google’s parent company, invested $900 million into SpaceX in 2015 and is estimated to hold between 6% and 7% of the private space firm. At the projected IPO valuation, that stake could be worth between $105 billion and $122.5 billion. That’s a growth of 11,566% to 14,455%.
Other major backers highlighted in the post include Fidelity Investments, Baillie Gifford, Valor Equity Partners, Bank of America, and Andreessen Horowitz, each potentially sitting on multibillion-dollar gains.
Elon Musk
Elon Musk hints Tesla investors will be rewarded heavily
“Hold onto your Tesla stock. It’s going to be worth a lot, I think. That’s my bet,” Musk said.

Elon Musk recently hinted that he believes Tesla investors will be rewarded heavily if they continue to hold onto their shares, and he reiterated that in a new interview that the company released on its social accounts this week.
Musk is one of the most successful CEOs in the modern era and has mammothed competitors on the Forbes Net Worth List over the past year as his holdings in his various companies have continued to swell.
Tesla investors, especially those who have been holding shares for several years, have also felt substantial gains in their portfolios. Over the past five years, the stock is up over 78 percent. Since February 2019, nearly seven years ago to the day, the stock is up over 1,800 percent.
Musk said in the interview:
“Hold onto your Tesla stock. It’s going to be worth a lot, I think. That’s my bet.”
Elon Musk in new interview: “Hold on to your $TSLA stock. It’s going to be worth a lot, I think. That’s my bet.” pic.twitter.com/cucirBuhq0
— Sawyer Merritt (@SawyerMerritt) February 26, 2026
It’s no secret Musk has been extremely bullish on his own companies, but Tesla in particular, because it is publicly traded.
However, the company has so many amazing projects that have an opportunity to revolutionize their respective industries. There is certainly a path to major growth on Wall Street for Tesla through its various future projects, including Optimus, Cybercab, Semi, and Unsupervised FSD.
- Optimus (Tesla’s humanoid robot): Musk has discussed its potential for tasks like childcare, walking dogs, or assisting elderly parents, positioning it as a massive long-term driver of company value.
- Cybercab (Tesla’s robotaxi/autonomous ride-hailing vehicle): a fully autonomous vehicle geared specifically for Tesla’s ride-sharing ambitions.
- Semi (Tesla’s electric truck, with mentions of expansion, like in Europe): brings Tesla into the commercial logistics sector.
- Unsupervised FSD (Full Self-Driving software achieving full autonomy without human supervision): turns every Tesla owner’s vehicle into a fully-autonomous vehicle upon release
These projects specifically are some of the highest-growth pillars Tesla has ever attempted to develop, especially in Musk’s eyes, as he has said Optimus will be the best-selling product of all-time.
Many analysts agree, but the bullish ones, like Cathie Wood of ARK Invest, are perhaps the one who believes Tesla has incredible potential on Wall Street, predicting a $2,600 price target for 2030, but this is not even including Optimus.
She told Bloomberg last March that she believes that the project will present a potential additive if Tesla can scale faster than anticipated.









