News
SpaceX sets Dragon reuse record, debuts drone ship on first launch in two months
Update #2: After a 24-hour weather delay, conditions were far more favorable on August 29th, allowing a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket to lift off for the first time in almost two months and send a cargo-filled Dragon spacecraft on its way to the International Space Station (ISS).
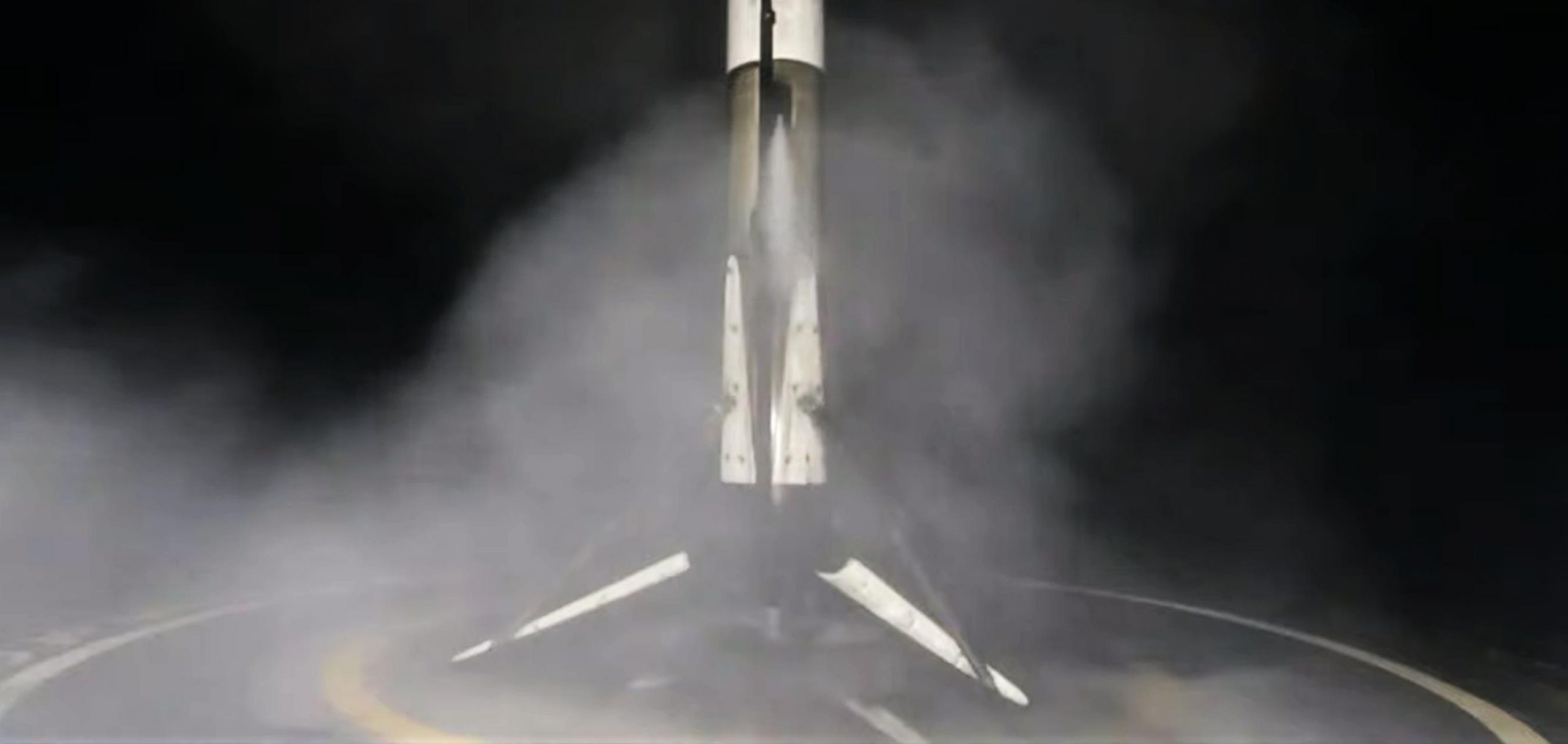
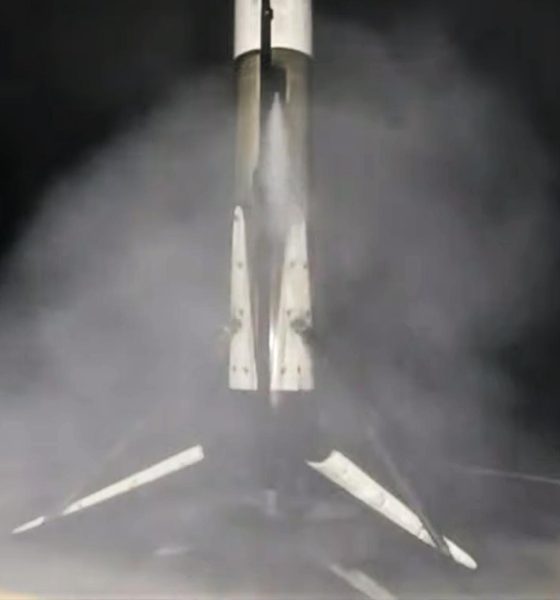
Aside from marking the end of SpaceX’s longest launch hiatus in two years, CRS-23’s successful liftoff also means that the company has smashed the world record for fastest orbital space capsule reuse. As part of Cargo Dragon 2’s first reuse ever, SpaceX launched Dragon C208 just seven and a half months (227d) after its first orbital reentry and splashdown, handily beating the previous record of 328 days. Additionally, flying for the fourth time, Falcon 9 booster B1064 became the first rocket to land on brand new SpaceX drone ship A Shortfall of Gravitas (ASOG) after sending Dragon C208 on its way to the ISS.
Getting a nice view of CRS-23's trunk as it separates, confirming no trunk cargo on this flight. pic.twitter.com/ZeJjviKqFE— Jonathan McDowell (@planet4589) August 29, 2021
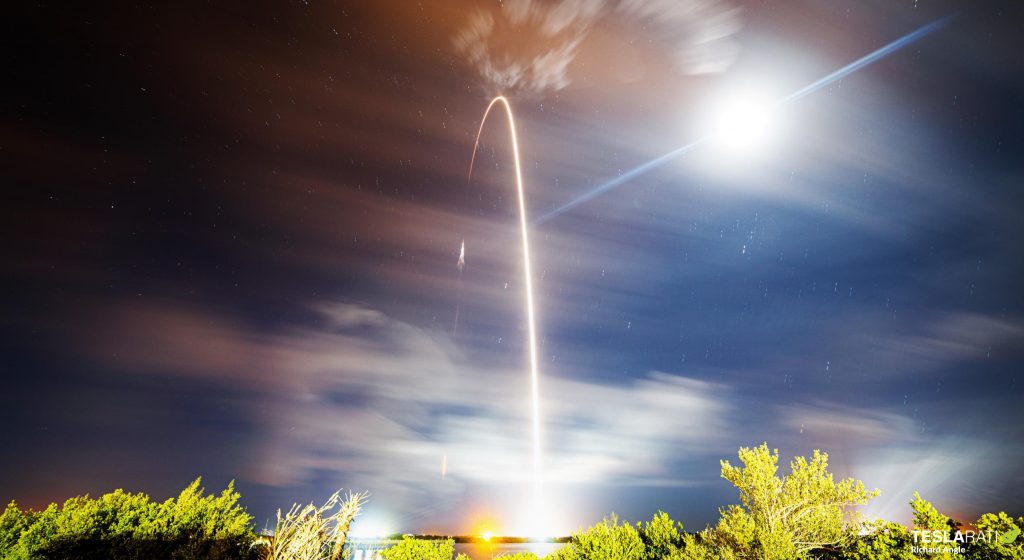

Update: Although the weather forecast has worsened, SpaceX remains on track to attempt its first launch in eight weeks – a mission that will also smash one of the company’s orbital spacecraft reusability records.
While mostly mundane, a system preceding Tropical Storm Ida is producing conditions less than optimal for rocket launches, raising the risk of in-flight lightning strikes and the chances of Falcon 9 and Dragon flying through clouds containing precipitation (rain/ice/etc). Ultimately, that means that there’s just a 40% chance (down from 50% in the last few days) that weather conditions will be favorable for SpaceX to launch CRS-23. Regardless, barring a surprise announcement in the next few hours, it appears that there’s enough of a chance that SpaceX and NASA will still make an attempt.
If all goes according to plan, a flight-proven Falcon 9 rocket will send an upgraded Cargo Dragon on the way to orbit for the second time in seven months – almost twice as fast a turnaround as SpaceX’s ~340-day record for orbital spacecraft reuse. Tune in below around 3:20am EDT (07:20 UTC) to catch the hopeful launch live.
For the first time in more than nine weeks, SpaceX has completed a routine Falcon 9 preflight test known as a static fire and verified that the rocket is ready to launch later this week.
Save for at least one booster qualification test completed at SpaceX’s McGregor, Texas development facilities, Falcon 9’s August 25th static fire is the first since June 22nd. The upgraded Cargo Dragon space station resupply mission the rocket will support will also be SpaceX’s first launch since June 30th – the company’s longest hiatus between launches since a three-month pause that began two years ago.
Now, just a few days before that drought is expected to end, a SpaceX executive has partially explained why the company hasn’t launched a single Falcon rocket in ~60 days after completing a record 20 orbital launches in the first half of 2021.
Speaking at the 2021 Space Symposium on August 24th, SpaceX President and COO Gwynne Shotwell revealed that the company had chosen to pause Starlink missions (representing the vast majority of its 2021 launches) and focus on preparing a new generation of satellites for flight. Believed to be called Starlink V1.5, those new satellites represent a relatively small design change save for one crucial addition: multiple lasers.
All the way back in mid-2018, SpaceX launched its very first pair of Starlink prototype satellites – spacecraft that largely functioned as expected and provided a wealth of data but were almost nothing like the Starlink V0.9 and V1.0 spacecraft SpaceX would eventually start launching in 2019. Nevertheless, they did carry sets of small lasers generally known as optical intersatellite links or OISLs for short. Not radically dissimilar to the hundreds of thousands of miles of fiber optic cables that make up the backbone of the internet, lasers operating in the vacuum of space can effectively mirror the extraordinary bandwidth and performance offered by fiber connections – but wirelessly.
Instead of carefully insulated cables filled with tiny threads of glass, which really just serve as a controlled environment for light-based communications, OISLs enable a similar feat by replacing cables with extraordinarily precise mechanisms capable of aiming lasers with sub-millimeter precision from dozens or hundreds of miles away. As a result, laser interlinks are fairly complex and expensive devices – not something currently economical to install on thousands of satellites mainly focused on affordability.
SpaceX, of course, has wanted to install unprecedentedly affordable laser interlinks on thousands of Starlink satellites for as long as the constellation has been publicly discussed. If realized, it would create an extraordinary orbital mesh network that would allow Starlink to self-route a large portion of user communications without the need for a colossal network of tens of thousands of ground stations covering every inch of Earth – land, sea, ice, and all. A Starlink constellation with near-universal laser interlinks could also potentially allow the constellation to not only match – but beat by a large margin – the latency of best-case terrestrial fiber-optic connections.
After effectively completing Starlink’s first ‘shell’ of satellites earlier this year, SpaceX shifted its focus to preparing for polar Starlink launches from both its west and east coast facilities. While the first shell lacked interlinks entirely, SpaceX appears to have decided that all polar Starlink satellites will be launched with its own custom-built space lasers, even if that means delaying Starlink launches until those lasers are ready for action. Due to the fact that the vast majority of SpaceX’s launches as of late have been its own Starlink missions, the company’s Falcon rockets simply haven’t had anything to launch.
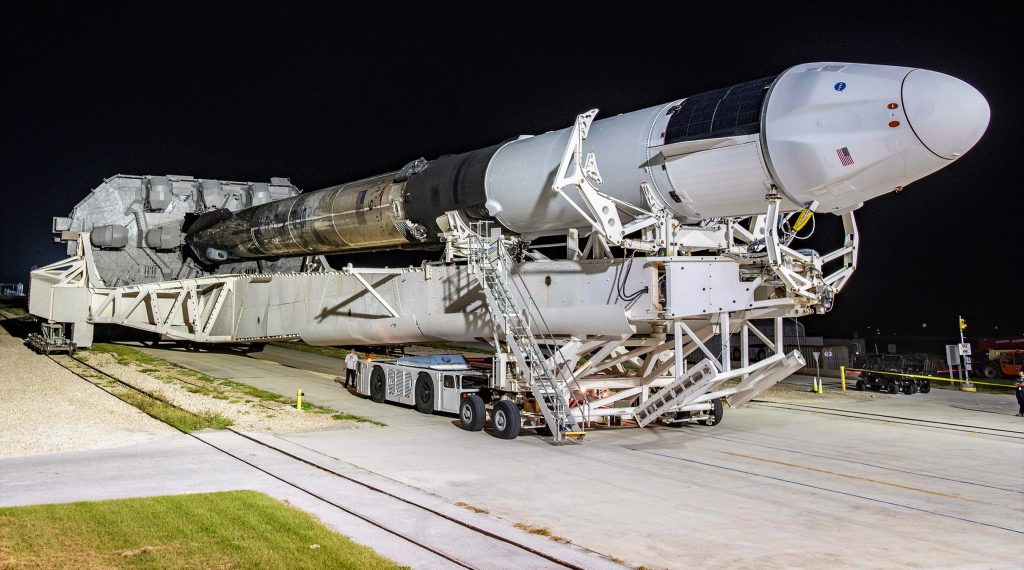
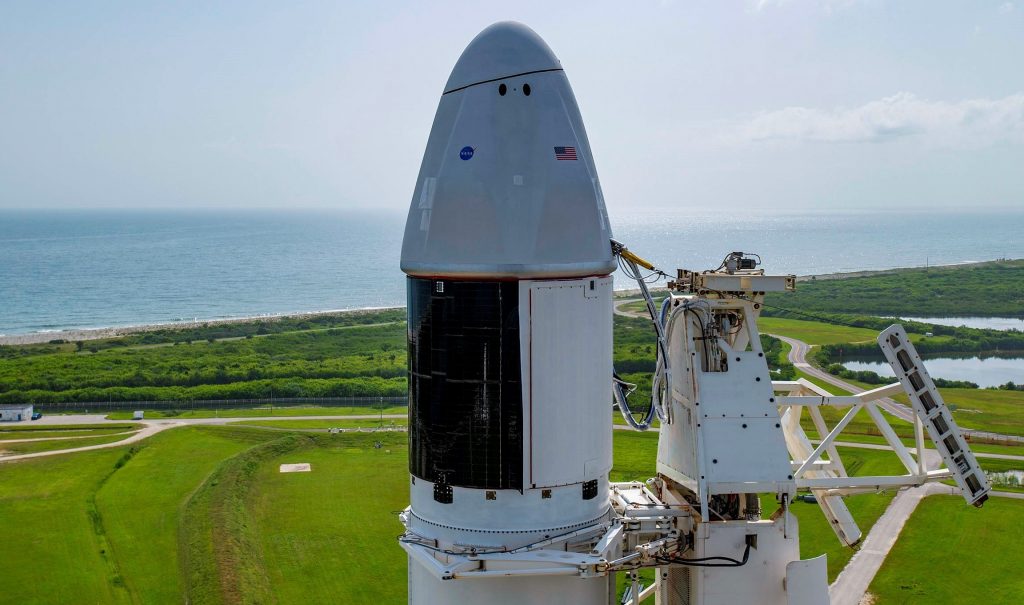


That should change on August 28th, when a thrice-flown Falcon 9 booster launches a refurbished spacecraft on its second orbital space station resupply – a first for SpaceX’s upgraded Cargo Dragon 2 vehicle. A Shortfall of Gravitas (ASOG), SpaceX’s newest drone ship, will also be supporting its first Falcon landing ever as part of CRS-23, hopefully recovering Falcon 9 booster B1064 for a fifth launch later this year.
Tune in around 3:20am (07:20 UTC) on Saturday, August 28th to watch SpaceX’s first launch in two months live.

Elon Musk
Tesla Full Self-Driving set to get an awesome new feature, Elon Musk says
Tesla Full Self-Driving is set to get an awesome new feature in the near future, CEO Elon Musk confirmed on X.
Full Self-Driving is the company’s semi-autonomous driving program, which is among the best available to the general public. It still relies on the driver to ultimately remain in control and pay attention, but it truly does make traveling less stressful and easier.
However, Tesla still continuously refines the software through Over-the-Air updates, which are meant to resolve shortcomings in the performance of the FSD suite. Generally, Tesla does a great job of this, but some updates are definitely regressions, at least with some of the features.
Tesla Cybertruck owner credits FSD for saving life after freeway medical emergency
Tesla and Musk are always trying to improve the suite’s performance by fixing features that are presently available, but they also try to add new things that would be beneficial to owners. One of those things, which is coming soon, is giving the driver the ability to prompt FSD with voice demands.
For example, asking the car to park close to the front door of your destination, or further away in an empty portion of the parking lot, would be an extremely beneficial feature. Adjusting navigation is possible through Grok integration, but it is not always effective.
Musk confirmed that voice prompts for FSD would be possible:
Coming
— Elon Musk (@elonmusk) February 21, 2026
Tesla Full Self-Driving is a really great thing, but it definitely has its shortcomings. Navigation is among the biggest complaints that owners have, and it is easily my biggest frustration with using it. Some of the routes it chooses to take are truly mind-boggling.
Another thing it has had issues with is being situated in the correct lane at confusing intersections or even managing to properly navigate through local traffic signs. For example, in Pennsylvania, there are a lot of stop signs with “Except Right Turn” signs directly under.
This gives those turning right at a stop sign the opportunity to travel through it. FSD has had issues with this on several occasions.
Parking preferences would be highly beneficial and something that could be resolved with this voice prompt program. Grocery stores are full of carts not taken back by customers, and many people choose to park far away. Advising FSD of this preference would be a great advantage to owners.
Cybertruck
Elon Musk clarifies Tesla Cybertruck ’10 day’ comment, fans respond
Some are arguing that the decision to confirm a price hike in ten days is sort of counterproductive, especially considering it is based on demand. Giving consumers a timeline of just ten days to make a big purchase like a pickup truck for $60,000, and basically stating the price will go up, will only push people to make a reservation.

Elon Musk has clarified what he meant by his comment on X yesterday that seemed to indicate that Tesla would either do away with the new All-Wheel-Drive configuration of the Cybertruck or adjust the price.
The response was cryptic as nobody truly knew what Musk’s plans were for the newest Tesla Cybertruck trim level. We now have that answer, and fans of the company are responding in a polarizing fashion.
On Thursday night, Tesla launched the Cybertruck All-Wheel-Drive, priced competitively at $59,990. It was a vast improvement from the Rear-Wheel-Drive configuration Tesla launched last year at a similar price point, which was eventually cancelled just a few months later due to low demand.
Tesla launches new Cybertruck trim with more features than ever for a low price
However, Musk said early on Friday, “just for 10 days,” the truck would either be available or priced at $59,990. We can now confirm Tesla will adjust the price based on more recent comments from the CEO.
Musk said the price will fluctuate, but it “depends on how much demand we see at this price level.”
Depends on how much demand we see at this price level
— Elon Musk (@elonmusk) February 20, 2026
Some are defending the decision, stating that it is simply logical to see how the Cybertruck sells at this price and adjust accordingly.
Case 1: You don’t like it -> don’t buy it
Case 2 (me): You like it, it’s fits your situation and needs -> you buy it.
Case 3: Complain endlessly for no reason, you weren’t going to get one anyway, but you want people to know you’re mad, for some reason.
Silly netizens.— Ryan Scanlan 👥 (@Xenius) February 21, 2026
Others, not so much.
Alright I’m obviously not the one successful enough to be calling the shots at Tesla and worth almost a trillion dollars
But people were excited about the awesome Cybertruck news and then it got taken away, that’s why people are annoyed. The wording felt more like a threat.… pic.twitter.com/NWVNklcXoJ— Dirty Tesla (@DirtyTesLa) February 21, 2026
No but fr wtf you doing dude???????
— Greggertruck (@greggertruck) February 20, 2026
It’s how it was communicated.
If it had been stated clearly on the website for everyone to see, everyone would be fine.
— KiTT_2020 (@kitt_2020) February 20, 2026
Some are arguing that the decision to confirm a price hike in ten days is sort of counterproductive, especially considering it is based on demand. Giving consumers a timeline of just ten days to make a big purchase like a pickup truck for $60,000, and basically stating the price will go up, will only push people to make a reservation.
Demand will look strong because people want to lock in this price. The price will inevitably go up, and demand for the trim will likely fall a bit because of the increased cost.
Many are arguing Musk should have kept this detail internal, but transparency is a good policy to have. It is a polarizing move to confirm a price increase in just a week-and-a-half, but the community is obviously split on how to feel.
Cybertruck
Tesla Cybertruck’s newest trim will undergo massive change in ten days, Musk says
It appears as if the new All-Wheel-Drive trim of Cybertruck won’t be around for too long, however. Elon Musk revealed this morning that it will be around “only for the next 10 days.”

Tesla’s new Cybertruck trim has already gotten the axe from CEO Elon Musk, who said the All-Wheel-Drive configuration of the all-electric pickup will only be available “for the next ten days.”
Musk could mean the price, which is $59,990, or the availability of the trim altogether.
Last night, Tesla launched the All-Wheel-Drive configuration of the Cybertruck, a pickup that comes in at less than $60,000 and features a competitive range and features that are not far off from the offerings of the premium trim.
Tesla launches new Cybertruck trim with more features than ever for a low price
It was a nice surprise from Tesla, considering that last year, it offered a Rear-Wheel-Drive trim of the Cybertruck that only lasted a few months. It had extremely underwhelming demand because it was only $10,000 cheaper than the next trim level up, and it was missing a significant number of premium features.
Simply put, it was not worth the money. Tesla killed the RWD Cybertruck just a few months after offering it.
With the news that Tesla was offering this All-Wheel-Drive configuration of the Cybertruck, many fans and consumers were encouraged. The Cybertruck has been an underwhelming seller, and this seemed to be a lot of truck for the price when looking at its features:
- Dual Motor AWD w/ est. 325 mi of range
- Powered tonneau cover
- Bed outlets (2x 120V + 1x 240V) & Powershare capability
- Coil springs w/ adaptive damping
- Heated first-row seats w/ textile material that is easy to clean
- Steer-by-wire & Four Wheel Steering
- 6’ x 4’ composite bed
- Towing capacity of up to 7,500 lbs
- Powered frunk
It appears as if this trim of Cybertruck won’t be around for too long, however. Musk revealed this morning that it will be around “only for the next 10 days.”
Only for the next 10 days https://t.co/82JnvZQGh2
— Elon Musk (@elonmusk) February 20, 2026
Musk could mean the price of the truck and not necessarily the ability to order it. However, most are taking it as a cancellation.
If it is, in fact, a short-term availability decision, it is baffling, especially as Tesla fans and analysts claim that metrics like quarterly deliveries are no longer important. This seems like a way to boost sales short-term, and if so many people are encouraged about this offering, why would it be kept around for such a short period of time?
Some are even considering the potential that Tesla axes the Cybertruck program as a whole. Although Musk said during the recent Q4 Earnings Call that Cybertruck would still be produced, the end of the Model S and Model X programs indicates Tesla might be prepared to do away with any low-volume vehicles that do not contribute to the company’s future visions of autonomy.
The decision to axe the car just ten days after making it available seems like a true head-scratcher.