SpaceX
DeepSpace: A critical juncture for SpaceX, Blue Origin, ULA, other players

This is a free preview of DeepSpace, Teslarati’s new member-only weekly newsletter. Each week, I’ll be taking a deep-dive into the most exciting developments in commercial space, from satellites and rockets to everything in between. Sign up for Teslarati’s newsletters here to receive a preview of our membership program.
A high-pressure competition between all four major US launch providers – SpaceX, ULA, Blue Origin, and Orbital ATK (now NGIS) – is about to head into its most critical stage, a period of 60 days allotted for interested parties to submit their completed proposals. According to the US Air Force (USAF), the final request for proposals (RFP) could come as early as March 29th, giving the four aforementioned companies until May 28th to complete their proposals.
All things considered, the growing pressure and some of the USAF’s strategy behind the program – known as Launch Service Procurement (LSP) Phase 2 – has raised significant questions that remain largely unanswered and lead to a few mild bouts of strife or unhappiness from contract competitors. Most notably, Blue Origin – having just won a USAF development contract worth $500M – has repeatedly requested that the USAF and Department of Defense (DoD) delay the RFP and contract awards until 2021, according to Space News’ Sandra Erwin. Meanwhile, a lack of clarification from the USAF means that it’s unclear whether the strategy behind launch contract awards (LSP) will end up contradicting or undermining a partially connected development program known as Launch Service Agreements (LSA) that saw the USAF award ~$2B to three providers (excluding SpaceX) between 2018 and 2024.
Battle of the Acronyms: LSP vs. LSA
- Recently rebranded by the US military as the National Security Space Launch (NSSL) program, LSP Phase 1 and 2 and LSA are the latest major procurement initiatives begun under the Evolved Expendable Launch Vehicle (EELV) program, spun up in the 1990s to provide a firmer foundation for the commercial launch of military spacecraft after the 1986 Shuttle Challenger disaster pushed most satellites off of the platform.
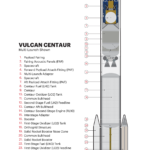
- Phase 2 of the EELV program has been ongoing for several years and will culminate with the procurement of 25+ launch contracts (LSP) from two providers no earlier than 2020. The USAF’s Launch Service Agreements are also a major strategic feature of Phase 2, nominally seeing the military branch contribute major funding to assist in the development of three separate launch vehicles (New Glenn, Vulcan, and Omega) with the intention of ultimately certifying those rockets for EELV (now NSSL) launches.
- LSA also saw the USAF award several tens of millions to SpaceX, Blue Origin, and Aerojet Rocketdyne to develop capabilities centered around advanced, new rocket engines (BE-4, AR-1, and Raptor), but the latest phase of LSA is valued at least several times higher than its earlier engine-specific awards.
-
- Oddly, the purpose of LSA was – at least on the cover – to effectively ensure that the Air Force had multiple (more than two) providers and thus preserve a healthy, competitive military launch market. A senior leader specifically stated that “the goal of [LSA] is to make sure [the US military has] a competitive industrial base.”
- Aside from an initial $181M awarded to Blue Origin, ULA, and Orbital ATK (now Northrop Grumman Innovation Systems, NGIS) in 2018 and 2019, the remaining funding – up to $320M for Blue Origin’s New Glenn, $610M for NGIS’ Omega, and $785M for ULA’s Vulcan – would be dispersed to each provider between 2020 and 2024.
- However, an odd and controversial bit of language behind the coming five-year launch services procurement (LSP) initiative would completely cut off funding to LSA awardees in the event that they fail to be awarded launches from the latest LSP.
- Additionally, the LSP awards are strictly meant – apparently very intentionally – to be distrubuted among two launch providers, despite a minimum at least four being able (SpaceX) or required (ULA, Blue, NGIS) to enter a bid.
- In other words, this guarantees that either one or two of the three LSA awardees would have the vast majority of their supposedly awarded development funding cut off after FY2020, four years early.
- Oddly, the purpose of LSA was – at least on the cover – to effectively ensure that the Air Force had multiple (more than two) providers and thus preserve a healthy, competitive military launch market. A senior leader specifically stated that “the goal of [LSA] is to make sure [the US military has] a competitive industrial base.”
- Despite continued protests from a number of stakeholders, the USAF has refused to budge from its decision to simultaneously A) create a duopoly, B) defeat the purpose of LSA awards, and C) mass-award ~25 launch contracts to two providers in 2020, anywhere from 12-24 months prior to the planned inaugural launches of all three LSA-funded rockets.
- Without cost-sharing development funds from the USAF and a chance of winning more than a handful of US military launch contracts between now and the late 2020s, it can be all but guaranteed that an LSA funding cutoff will either indefinitely pause or slow to a crawl a given provider’s development of their proposed launch vehicle.

A rocket and a hard place
- This sticky situation thus offers up a few potential ways that this badly-designed (or entirely dishonest) military launch development and procurement strategy will end up by the end of 2020. One way or another, the current strategy as it stands will end up providing two (or one, given that SpaceX will not receive LSA funding) companies with several years of development funding and at least five years of bountiful, guaranteed launch contracts.
- The four providers and two LSP slots available offer a set range of possible alternate realities, limited by political barriers that would, say, almost invariably prevent the USAF from severely harming ULA by cutting off the vast majority of the company’s only real source of income for 5+ years.
- ULA and SpaceX win: This maintains the status quo, wholly invalidating the point of using LSA funds to ensure “a competitive industrial base.” NGIS likely cancels/freezes all Omega development with no chance of competing in commercial markets. Blue Origin owner Jeff Bezos could significantly delay New Glenn’s readiness for military missions if he fails to invest an additional $500M in infrastructure. Likeliest result: a marginally competitive duopoly.
- ULA wins, SpaceX loses: Having just certified Falcon 9 – and nearly Falcon Heavy – for high-value military launches and awarded SpaceX a total of 10 launch contracts (9 yet to be completed), the USAF could effectively spit in SpaceX’s face and award ULA and Blue Origin or NGIS LSP’s 25+ launch contracts.
- It’s hard to exaggerate just how much of a slight this would be perceived as by SpaceX and its executives, CEO Elon Musk in particular. The USAF would be risking the creation of a major political enemy, one which has already demonstrated a willingness to take the federal government to court and win. The USAF/DoD would effectively be hedging their bets against an assumption that SpaceX’s nine present military launch contracts will sate the company and ensure that SpaceX indefinitely remains a certified EELV/NSSL provider.
- In this eventuality, either Blue Origin or NGIS would lose LSA funding and the prospect of almost any military launch contracts until the late 2020s. For NGIS, this would likely kill Omega.
- At the end of the day, it’s sadly conceivable that the USAF/DoD may end up awarding LSP contracts to ULA (effectively a politically-forced hand) and NGIS, the latter assuring Omega’s survival. The military would thus be assuming that the political fallout created with SpaceX and Blue Origin would not be enough to severely harm their relationships, while also assuming that their much stronger commercial prospects and independent funding sources would ensure that each provider remains certified and willing to compete for future NSSL/EELV launches.
Regardless of what happens, the contradictory ways the USAF/DoD have structured their LSA and LSP programs seems bizarrely intent on creating major headaches and potential problems where that could easily be avoided with extraordinarily simple changes, namely removing the inexplicable cap and allowing three or more companies to win some of the ~25 LSP launch contracts).
Mission Updates
- The second launch of Falcon Heavy – the rocket’s commercial debut – is still scheduled to occur as early as April 7th.
- After Falcon Heavy, Cargo Dragon’s CRS-17 resupply mission is firmly scheduled for April (April 25th), while the first dedicated Starlink launch is now NET May 2019.
Photo of the Week:

SpaceX CEO Elon Musk offered a glimpse of a 1650 Kelvin (2500ºF/1400ºC) test of Starship’s metallic heat shield, simulating mid-range temperatures such a shield’s windward side might experience during an orbital-velocity reentry.(c. Elon Musk/SpaceX)

Elon Musk
FCC chair criticizes Amazon over opposition to SpaceX satellite plan
Carr made the remarks in a post on social media platform X.

U.S. Federal Communications Commission (FCC) Chairman Brendan Carr criticized Amazon after the company opposed SpaceX’s proposal to launch a large satellite constellation that could function as an orbital data center network.
Carr made the remarks in a post on social media platform X.
Amazon recently urged the FCC to reject SpaceX’s application to deploy a constellation of up to 1 million low Earth orbit satellites that could serve as artificial intelligence data centers in space.
The company described the proposal as a “lofty ambition rather than a real plan,” arguing that SpaceX had not provided sufficient details about how the system would operate.
Carr responded by pointing to Amazon’s own satellite deployment progress.
“Amazon should focus on the fact that it will fall roughly 1,000 satellites short of meeting its upcoming deployment milestone, rather than spending their time and resources filing petitions against companies that are putting thousands of satellites in orbit,” Carr wrote on X.
Amazon has declined to comment on the statement.
Amazon has been working to deploy its Project Kuiper satellite network, which is intended to compete with SpaceX’s Starlink service. The company has invested more than $10 billion in the program and has launched more than 200 satellites since April of last year.
Amazon has also asked the FCC for a 24-month extension, until July 2028, to meet a requirement to deploy roughly 1,600 satellites by July 2026, as noted in a CNBC report.
SpaceX’s Starlink network currently has nearly 10,000 satellites in orbit and serves roughly 10 million customers. The FCC has also authorized SpaceX to deploy 7,500 additional satellites as the company continues expanding its global satellite internet network.
Elon Musk
NASA watchdog says Starship development delays could affect Artemis timeline
The report noted that several technical milestones still need to be completed before Starship can serve as a crewed lunar lander.

A NASA watchdog report stated that continued development work on SpaceX’s Starship could affect the timeline for the agency’s planned Artemis moon missions. The report noted that several technical milestones still need to be completed before the spacecraft can serve as a crewed lunar lander.
The findings were detailed in a report from NASA’s Office of Inspector General, as noted in a report from Reuters.
NASA selected SpaceX’s Starship in 2021 to serve as the Human Landing System (HLS) for its Artemis lunar program. The vehicle is intended to transport astronauts from lunar orbit to the surface of the Moon and back as part of future Artemis missions.
According to the watchdog report, Starship’s development has experienced roughly two years of schedule delays compared to earlier expectations. Still, NASA is targeting 2028 for the first crewed lunar landing using the Starship lander.
One of the most significant technical milestones for Starship’s lunar missions is in-space refueling.
To support a crewed lunar landing, multiple Starship launches will be required to deliver propellant to orbit. Tanker versions of Starship will transfer fuel to a storage depot spacecraft, which will then refuel the lunar lander.
The report noted that this approach could require more than 10 Starship launches to fully refuel the spacecraft needed for a single lunar landing mission.
NASA officials indicated that demonstrating cryogenic propellant transfer in orbit remains one of the most important technical steps before Starship can be certified for lunar missions.
SpaceX has conducted 11 Starship test flights since 2023 as the company continues developing the fully reusable launch system. A 12th test flight, this time featuring Starship V3, is expected to be held in early April.
Elon Musk
SpaceX weighs Nasdaq listing as company explores early index entry: report
The company is reportedly seeking early inclusion in the Nasdaq-100 index.

Elon Musk’s SpaceX is reportedly leaning toward listing its shares on the Nasdaq for a potential initial public offering (IPO) that could become the largest in history.
As per a recent report, the company is reportedly seeking early inclusion in the Nasdaq-100 index. The update was reported by Reuters, citing people familiar with the matter.
According to the publication, SpaceX is considering Nasdaq as the venue for its eventual IPO, though the New York Stock Exchange is also competing for the listing. Neither exchange has reportedly been informed of a final decision.
Reuters has previously reported that SpaceX could pursue an IPO as early as June, though the company’s plans could still change.
One of the publication’s sources also suggested that SpaceX is targeting a valuation of about $1.75 trillion for its IPO. At that level, the company would rank among the largest publicly traded firms in the United States by market capitalization.
Nasdaq has proposed a rule change that could accelerate the inclusion of newly listed megacap companies into the Nasdaq-100 index.
Under the proposed “Fast Entry” rule, a newly listed company could qualify for the index in less than a month if its market capitalization ranks among the top 40 companies already included in the Nasdaq-100.
If SpaceX is successful in achieving its target valuation of $1.75 trillion, it would become the sixth-largest company by market value in the United States, at least based on recent share prices.
Newly listed companies typically have to wait up to a year before becoming eligible for major indexes such as the Nasdaq-100 or S&P 500.
Inclusion in a major index can significantly broaden a company’s shareholder base because many institutional investors purchase shares through index-tracking funds.
According to Reuters, Nasdaq’s proposed fast-track rule is partly intended to attract highly valued private companies such as SpaceX, OpenAI, and Anthropic to list on the exchange.




![Lucid Lunar robotaxi concept [Credit: Rendering by TESLARATI]](https://www.teslarati.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/03/lucid-lunar-robotaxi-concept-teslarati-rendering-80x80.jpg)







