

News
First living tissue 3D printed in space aboard International Space Station
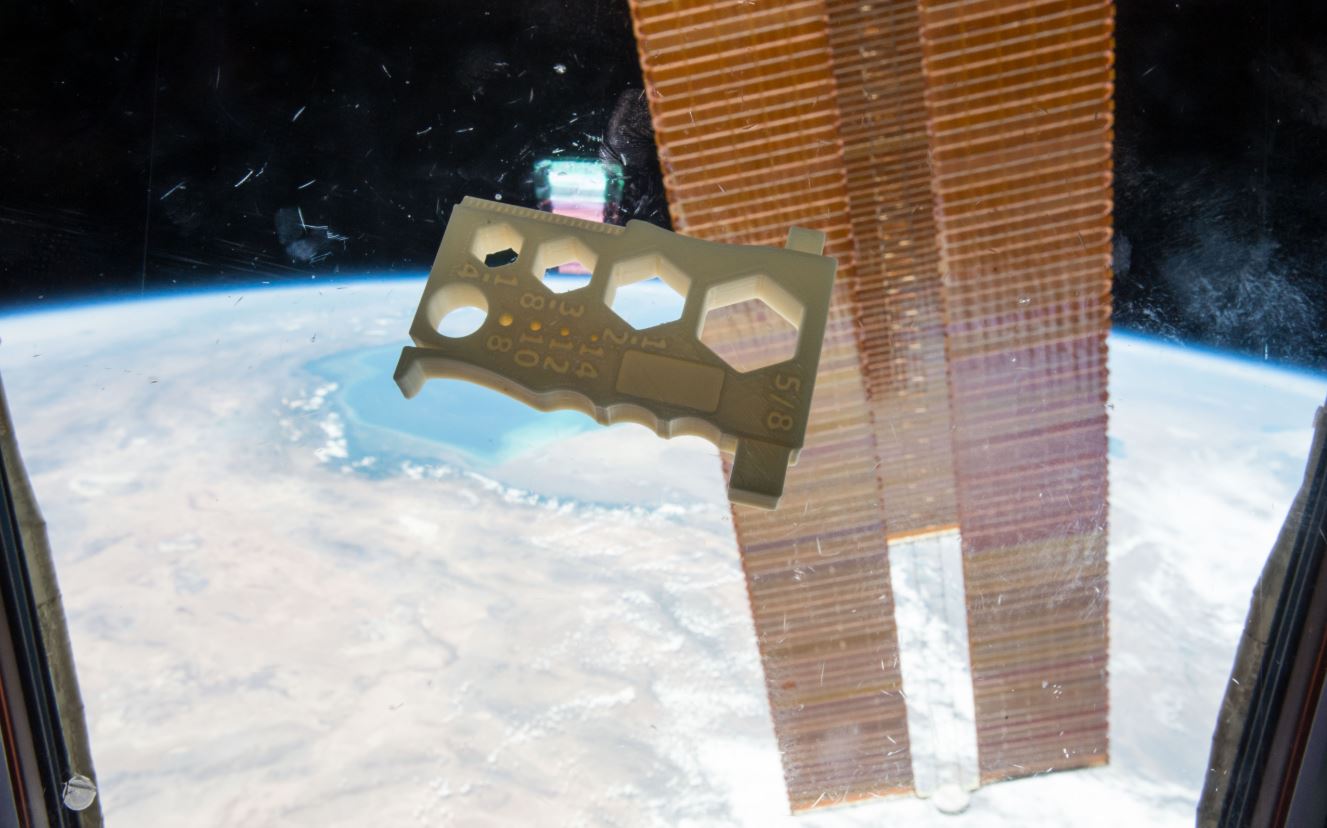
Using the “Organaut”, a 3D bioprinter designed for microgravity, Russia has become the first country to print living tissue in space. After a December 3rd cargo delivery to the International Space Station (ISS), cosmonaut Oleg Kononenko completed an experiment with the machine in the Russian sector of the station, successfully producing human cartilage tissue and a rodent thyroid gland. The Organaut was designed via a collaboration with the printer’s maker, 3D Bioprinting Solutions, and Russia’s national space agency, Roscosmos. The United States also has its own bioprinting mission scheduled for the first half of 2019, joining in the march to develop biological solutions for problems that space is well suited to solve.
A 3D bioprinter operates by creating one layer at a time of specified tissue or stem cell material arranged as needed to grow and form as biologically programmed to do. As summarized by Aryeh Batt, the CEO of Precise Bio, a company dedicated to 3D printed bioproducts for human eyes, “Essentially, the biology does the work, but you have to put them in the correct environment to make it happen.” In the case of Organaut, an internal robotic mechanism drips living cell fabric layers from an automatic syringe. When living tissue is bioprinted under Earth’s gravity, the artificial cells grow in a flatter structure than their natural state in the human body. In microgravity, however, they form a shape closer to their normal dimensions.
Along with demonstrating the growth advantages of microgravity, Organaut’s tissue samples will provide the ability to study the effect of radiation on the body. “We will look at how the constructs came together, and how they behaved,” confirmed Usef Hesuani, head of laboratory projects and a managing partner of 3D Bioprinting Solutions in a recent press conference. The original Organaut printer was aboard the Soyuz MS-10 spacecraft which experienced an launch failure on October 11, 2018, forcing the U.S. and Russian crew to make an emergency landing. A second one was quickly put together for the subsequent mission.
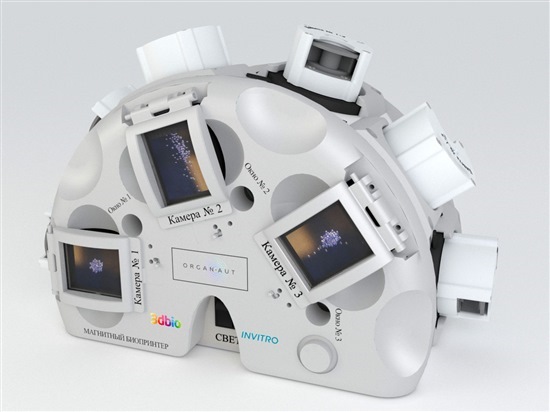
The parent company of 3D Bioprinting Solutions is INVITRO, the largest private medical company in Russia. Founded in 1995 by Aleksandr Ostrovsky, it has 8 laboratories and over 1000 medical offices in eastern Europe, but is primarily based in Skolkovo, a high technology business area in Moscow. Bioprinting Solutions made headlines in 2015 when it printed and transplanted a functioning mouse thyroid gland. The experiment performed aboard the ISS with Organaut was a modified version of their prior work.
Unlike NASA, Roscosmos does not generally partner with private companies for its research endeavors. In an effort to inspire Russian students to enter STEM fields within their country, the agency sought to spotlight the developing bioprinting industry by using the Organaut. The successful partnership with 3D Bioprinting Solutions has now motivated the agency to continue partnering with private companies in the future. The company itself also sees advantages to collaborations of its own with other Skolkova-area manufacturers. “We have companies that are making satellite platforms…it is possible to conduct a similar experiment amid microgravity on small spacecraft [like satellites]…smaller and cheaper,” noted Ivan Kosenkov, 3D Bioprinting Solutions’ project manager.
Organaut’s printed tissues were returned to Earth with the Soyuz MS-09 spacecraft on December 20th, and the results of the experiment are expected to be published at the end of January 2019. In February, NASA plans to send a bioprinter capable of producing beating heart tissue to the ISS. Named the 3D BioFabrication Facility (BFF), the machine was developed through a partnership with two companies well-established in 3D printing and on-orbit hardware, nScrypt and Techshot. Since the thickness of heart tissue is difficult to build under gravity without structural assistance that could impede functionality, the companies developed the BFF with the hypothesis that microgravity would overcome this limitation. Thus far, the concept has been proven during parabolic flight tests, i.e., aboard the “Vomit Comet” airplane that performs multiple parabolic maneuvers in an airliner to create 20-30 seconds of weightlessness each.
News
Tesla begins Robotaxi certification push in Arizona: report
Tesla seems serious about expanding its Robotaxi service to several states in the coming months.

Tesla has initiated discussions with Arizona transportation regulators to certify its driverless Robotaxi service in the state, as per a recent report from Bloomberg News. The move follows Tesla’s launch of its Robotaxi pilot program in Austin, Texas, as well as CEO Elon Musk’s recent comments about the service’s expansion in the Bay Area.
The Arizona Department of Transportation confirmed to Bloomberg that Tesla has reached out to begin the certification process for autonomous ride-sharing operations in the state. While details remain limited, the outreach suggests that Tesla is serious about expanding its driverless Robotaxi service to several territories in the coming months.
The Arizona development comes as Tesla prepares to expand its service area in Austin this weekend, as per CEO Elon Musk in a post on X. Musk also stated that Tesla is targeting the San Francisco Bay Area as its next major market, with a potential launch “in a month or two,” pending regulatory approvals.
Tesla first launched its autonomous ride-hailing program on June 22 in Austin with a small fleet of Model Y vehicles, accompanied by a Tesla employee in the passenger seat to monitor safety. While still classified as a test, Musk has said the program will expand to about 1,000 vehicles in the coming months. Tesla will later upgrade its Robotaxi fleet with the Cyercab, a two-seater that is designed without a steering wheel.
Sightings of Cybercab castings around the Giga Texas complex suggests that Tesla may be ramping the initial trial production of the self-driving two-seater. Tesla, for its part, has noted in the past that volume production of the Cybercab is expected to start sometime next year.
In California, Tesla has already applied for a transportation charter-party carrier permit from the state’s Public Utilities Commission. The company is reportedly taking a phased approach to operating in California, with the Robotaxi service starting with pre-arranged rides for employees in vehicles with safety drivers.
News
Tesla sets November 6 date for 2025 Annual Shareholder Meeting
The automaker announced the date on Thursday in a Form 8-K.

Tesla has scheduled its 2025 annual shareholder meeting for November 6, addressing investor concerns that the company was nearing a legal deadline to hold the event.
The automaker announced the date on Thursday in a Form 8-K submitted to the United States Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC). The company also listed a new proposal submission deadline of July 31 for items to be included in the proxy statement.
Tesla’s announcement followed calls from a group of 27 shareholders, including the leaders of large public pension funds, which urged Tesla’s board to formally set the meeting date, as noted in a report from The Wall Street Journal.
The group noted that under Texas law, where Tesla is now incorporated, companies must hold annual meetings within 13 months of the last one if requested by shareholders. Tesla’s previous annual shareholder meeting was held on June 13, 2024, which placed the July 13 deadline in focus.
Tesla originally stated in its 2024 annual report that it would file its proxy statement by the end of April. However, an amended filing on April 30 indicated that the Board of Directors had not yet finalized a meeting date, at least at the time.
The April filing also confirmed that Tesla’s board had formed a special committee to evaluate certain matters related to CEO Elon Musk’s compensation plan. Musk’s CEO performance award remains at the center of a lengthy legal dispute in Delaware, Tesla’s former state of incorporation.
Due to the aftermath of Musk’s legal dispute about his compensation plan in Delaware, he has not been paid for his work at Tesla for several years. Musk, for his part, has noted that he is more concerned about his voting stake in Tesla than his actual salary.
At last year’s annual meeting, TSLA shareholders voted to reapprove Elon Musk’s compensation plan and ratified Tesla’s decision to relocate its legal domicile from Delaware to Texas.
Elon Musk
Grok coming to Tesla vehicles next week “at the latest:” Elon Musk
Grok’s rollout to Tesla vehicles is expected to begin next week at the latest.

Elon Musk announced on Thursday that Grok, the large language model developed by his startup xAI, will soon be available in Tesla vehicles. Grok’s rollout to Tesla vehicles is expected to begin next week at the latest, further deepening the ties between the two Elon Musk-led companies.
Tesla–xAI synergy
Musk confirmed the news on X shortly after livestreaming the release of Grok 4, xAI’s latest large language model. “Grok is coming to Tesla vehicles very soon. Next week at the latest,” Musk wrote in a post on social media platform X.
During the livestream, Musk and several members of the xAI team highlighted several upgrades to Grok 4’s voice capabilities and performance metrics, positioning the LLM as competitive with top-tier models from OpenAI and Google.
The in-vehicle integration of Grok marks a new chapter in Tesla’s AI development. While Tesla has long relied on in-house systems for autonomous driving and energy optimization, Grok’s integration would introduce conversational AI directly into its vehicles’ user experience. This integration could potentially improve customer interaction inside Tesla vehicles.
xAI and Tesla’s collaborative footprint
Grok’s upcoming rollout to Tesla vehicles adds to a growing business relationship between Tesla and xAI. Earlier this year, Tesla disclosed that it generated $198.3 million in revenue from commercial, consulting, and support agreements with xAI, as noted in a report from Bloomberg News. A large portion of that amount, however, came from the sale of Megapack energy storage systems to the artificial intelligence startup.
In July 2023, Musk polled X users about whether Tesla should invest $5 billion in xAI. While no formal investment has been made so far, 68% of poll participants voted yes, and Musk has since stated that the idea would be discussed with Tesla’s board.
-

 Elon Musk1 week ago
Elon Musk1 week agoTesla investors will be shocked by Jim Cramer’s latest assessment
-

 Elon Musk19 hours ago
Elon Musk19 hours agoxAI launches Grok 4 with new $300/month SuperGrok Heavy subscription
-

 Elon Musk3 days ago
Elon Musk3 days agoElon Musk confirms Grok 4 launch on July 9 with livestream event
-

 News7 days ago
News7 days agoTesla Model 3 ranks as the safest new car in Europe for 2025, per Euro NCAP tests
-

 Elon Musk2 weeks ago
Elon Musk2 weeks agoA Tesla just delivered itself to a customer autonomously, Elon Musk confirms
-

 Elon Musk1 week ago
Elon Musk1 week agoxAI’s Memphis data center receives air permit despite community criticism
-

 Elon Musk2 weeks ago
Elon Musk2 weeks agoTesla’s Omead Afshar, known as Elon Musk’s right-hand man, leaves company: reports
-

 News2 weeks ago
News2 weeks agoXiaomi CEO congratulates Tesla on first FSD delivery: “We have to continue learning!”

















